Microflora on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Microbiota are the range of
Microbiota are the range of
 All plants and animals, from simple life forms to humans, live in close association with microbial organisms. Several advances have driven the perception of microbiomes, including:
* the ability to perform genomic and gene expression analyses of single cells and of entire microbial communities in the disciplines of
All plants and animals, from simple life forms to humans, live in close association with microbial organisms. Several advances have driven the perception of microbiomes, including:
* the ability to perform genomic and gene expression analyses of single cells and of entire microbial communities in the disciplines of
 Microbiota are the range of
Microbiota are the range of microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s that may be commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit f ...
, mutualistic, or pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
found in and on all multicellular organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
s, including plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s. Microbiota include bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
, protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
s, fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, and virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis
In biology, homeostasis (British English, British also homoeostasis; ) is the state of steady internal physics, physical and chemistry, chemical conditions maintained by organism, living systems. This is the condition of optimal functioning fo ...
of their host.
The term ''microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably wel ...
'' describes either the collective genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
s of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources an ...
or else the microbes themselves.
The microbiome and host emerged during evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
as a synergistic
Synergy is an interaction or cooperation giving rise to a whole that is greater than the simple sum of its parts (i.e., a non-linear addition of force, energy, or effect). The term ''synergy'' comes from the Attic Greek word συνεργία ' f ...
unit from epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in ...
and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product (short-chain fatty acid
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) are fatty acids of two to six carbon atoms. The SCFAs' lower limit is interpreted differently, either with one, two, three or four carbon atoms. Derived from intestine, intestinal microbe, microbial fermentation of ...
), acetate
An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base (e.g. alkaline, earthy, metallic, nonmetallic, or radical base). "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion (specifically, the negatively charged ion called ...
.
Introduction
 All plants and animals, from simple life forms to humans, live in close association with microbial organisms. Several advances have driven the perception of microbiomes, including:
* the ability to perform genomic and gene expression analyses of single cells and of entire microbial communities in the disciplines of
All plants and animals, from simple life forms to humans, live in close association with microbial organisms. Several advances have driven the perception of microbiomes, including:
* the ability to perform genomic and gene expression analyses of single cells and of entire microbial communities in the disciplines of metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of all genetics, genetic material from all organisms in a particular environment, providing insights into their composition, diversity, and functional potential. Metagenomics has allowed researchers to profile the mic ...
and metatranscriptomics
* databases accessible to researchers across multiple disciplines
* methods of mathematical analysis suitable for complex data sets
Biologists have come to appreciate that microbes make up an important part of an organism's phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
, far beyond the occasional symbiotic case study.
Types of microbe-host relationships
Commensalism
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit fr ...
, a concept developed by Pierre-Joseph van Beneden (1809–1894), a Belgian professor at the University of Louvain during the nineteenth century is central to the microbiome, where microbiota colonize a host in a non-harmful coexistence. The relationship with their host is called mutualistic when organisms perform tasks that are known to be useful for the host, parasitic, when disadvantageous to the host. Other authors define a situation as mutualistic where both benefit, and commensal, where the unaffected host benefits the symbiont. A nutrient exchange may be bidirectional or unidirectional, may be context dependent and may occur in diverse ways. Microbiota that are expected to be present, and that under normal circumstances do not cause disease, are deemed ''normal flora'' or ''normal microbiota''; normal flora can not only be harmless, but can be protective of the host.
Acquisition and change
The initial acquisition of microbiota in animals from mammalians to marinesponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and a ...
s is at birth, and may even occur through the germ cell line. In plants, the colonizing process can be initiated below ground in the root zone, around the germinating seed, the spermosphere, or originate from the above ground parts, the phyllosphere and the flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
zone or anthosphere. The stability of the rhizosphere microbiota over generations depends upon the plant type but even more on the soil composition, i.e. living and non living environment. Clinically, new microbiota can be acquired through fecal microbiota transplant to treat infections such as chronic ''C. difficile'' infection.
Microbiota by host

Humans
The human microbiota includesbacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
, archaea
Archaea ( ) is a Domain (biology), domain of organisms. Traditionally, Archaea only included its Prokaryote, prokaryotic members, but this has since been found to be paraphyletic, as eukaryotes are known to have evolved from archaea. Even thou ...
and viruses. Micro-animal
Microfauna ( and ) are microscopic animals and organisms that exhibit animal-like qualities and have body sizes that are usually <0.1 mm. Microfauna are represented in the animal kingdom (e.g. s which live on the human body are excluded. The
FAQ: Human Microbiome
January 2014Judah L. Rosner for Microbe Magazine, Feb 2014
Ten Times More Microbial Cells than Body Cells in Humans?
/ref>Alison Abbott for Nature News. Jan 8 201
Scientists bust myth that our bodies have more bacteria than human cells
/ref> In fact, these are so small that there are around 100 trillion microbiota on the human body, around 39 trillion by revised estimates, with only 0.2 kg of total mass in a "reference" 70 kg human body. The Human Microbiome Project sequenced the genome of the human microbiota, focusing particularly on the microbiota that normally inhabit the skin, mouth, nose, digestive tract, and vagina. It reached a milestone in 2012 when it published initial results.
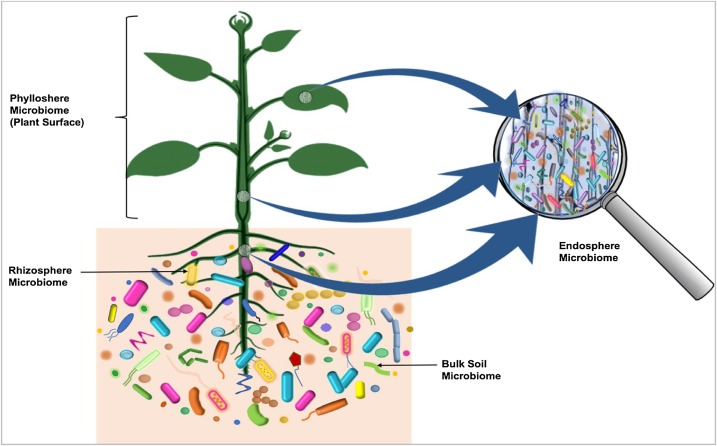
 The plant microbiome was recently discovered to originate from the seed. Microorganism which are transmitted via seed migrate into the developing seedling in a specific route in which certain community move to the leaves and others to the roots. In the diagram on the right, microbiota colonizing the
The plant microbiome was recently discovered to originate from the seed. Microorganism which are transmitted via seed migrate into the developing seedling in a specific route in which certain community move to the leaves and others to the roots. In the diagram on the right, microbiota colonizing the  Plants are attractive hosts for microorganisms since they provide a variety of nutrients. Microorganisms on plants can be
Plants are attractive hosts for microorganisms since they provide a variety of nutrients. Microorganisms on plants can be
 Organisms evolve within ecosystems so that the change of one organism affects the change of others. The
Organisms evolve within ecosystems so that the change of one organism affects the change of others. The
human microbiome
The human microbiome is the aggregate of all microbiota that reside on or within human tissues and biofluids along with the corresponding List of human anatomical features, anatomical sites in which they reside, including the human gastrointes ...
refers to their collective genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
s.
Humans are colonized by many microorganisms; the traditional estimate was that humans live with ten times more non-human cells than human cells; more recent estimates have lowered this to 3:1 and even to about 1:1 by number (1:350 by mass).American Academy of MicrobiologFAQ: Human Microbiome
January 2014Judah L. Rosner for Microbe Magazine, Feb 2014
Ten Times More Microbial Cells than Body Cells in Humans?
/ref>Alison Abbott for Nature News. Jan 8 201
Scientists bust myth that our bodies have more bacteria than human cells
/ref> In fact, these are so small that there are around 100 trillion microbiota on the human body, around 39 trillion by revised estimates, with only 0.2 kg of total mass in a "reference" 70 kg human body. The Human Microbiome Project sequenced the genome of the human microbiota, focusing particularly on the microbiota that normally inhabit the skin, mouth, nose, digestive tract, and vagina. It reached a milestone in 2012 when it published initial results.
Non-human animals
* Amphibians have microbiota on their skin. Some species are able to carry a fungus named ''Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'', which in others can cause a deadly infection Chytridiomycosis depending on their microbiome, resisting pathogen colonization or inhibiting their growth with antimicrobial skin peptides. *Newborn marsupials are born with histologically immature immune tissues and unable to mount their own specific immune defence. They are therefore heavily reliant on their mother's immune system and the milk for their protection. Most marsupials have pouches, and their own microbiota changes throughout the reproductive stages: oestrus, birth/oestrus, and post-oestrus. Some pouch and skin secretions have had antimicrobial peptides identified, that presumably support the young at this vulnerable time. * In mammals, herbivores such as cattle depend on theirrumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants. The rumen and the reticulum make up the reticulorumen in ruminant animals. The diverse microbial communities in the rumen allows it to serve as the primary si ...
microbiome to convert cellulose into proteins, short chain fatty acids, and gases. Culture methods cannot provide information on all microorganisms present. Comparative metagenomic studies yielded the surprising result that individual cattle possess markedly different community structures, predicted phenotype, and metabolic potentials, even though they were fed identical diets, were housed together, and were apparently functionally identical in their utilization of plant cell wall resources.
* Mice
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
have become the most studied mammalian regarding their microbiomes. The gut microbiota have been studied in relation to allergic airway disease, obesity, gastrointestinal diseases and diabetes. Perinatal shifting of microbiota through low dose antibiotics can have long-lasting effects on future susceptibility to allergic airway disease. The frequency of certain subsets of microbes has been linked to disease severity. The presence of specific microbes early in postnatal life, instruct future immune responses. In gnotobiotic mice certain gut bacteria were found to transmit a particular phenotype to recipient germ-free mice, that promoted accumulation of colonic regulatory T cells, and strains that modulated mouse adiposity and cecal metabolite concentrations. This combinatorial approach enables a systems-level understanding of microbial contributions to human biology. But also other mucoide tissues as lung and vagina have been studied in relation to diseases such as asthma, allergy and vaginosis.
* Insects have their own microbiomes. For example, leaf-cutter ants form huge underground colonies harvesting hundreds of kilograms of leaves each year and are unable to digest the cellulose in the leaves directly. They maintain fungus gardens as the colony's primary food source. While the fungus itself does not digest cellulose, a microbial community containing a diversity of bacteria is doing so. Analysis of the microbial population's genome revealed many genes with a role in cellulose digestion. This microbiome's predicted carbohydrate-degrading enzyme profile is similar to that of the bovine rumen, but the species composition
Relative species abundance is a component of biodiversity and is a measure of how common or rare a species is relative to other species in a defined location or community.Hubbell, S. P. 2001. ''The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeog ...
is almost entirely different. Gut microbiota of the fruit fly can affect the way its gut looks, by impacting epithelial renewal rate, cellular spacing, and the composition of different cell types in the epithelium. When the moth Spodoptera exigua is infected with baculovirus
''Baculoviridae'' is a family of viruses. Arthropods, among the most studied being Lepidoptera, Hymenoptera and Diptera, serve as natural hosts. Currently, 85 species are placed in this family, assigned to four genera.
Baculoviruses are known ...
immune-related genes are downregulated and the amount of its gut microbiota increases. In the dipteran intestine, enteroendocrine cells sense the gut microbiota-derived metabolites and coordinate antibacterial, mechanical, and metabolic branches of the host intestinal innate immune response to the commensal microbiota.
*Fish have their own microbiomes, including the short-lived species Nothobranchius furzeri (turquoise killifish). Transferring the gut microbiota from young killfish into middle-aged killifish significantly extends the lifespans of the middle-aged killfish.
Plants
 The plant microbiome was recently discovered to originate from the seed. Microorganism which are transmitted via seed migrate into the developing seedling in a specific route in which certain community move to the leaves and others to the roots. In the diagram on the right, microbiota colonizing the
The plant microbiome was recently discovered to originate from the seed. Microorganism which are transmitted via seed migrate into the developing seedling in a specific route in which certain community move to the leaves and others to the roots. In the diagram on the right, microbiota colonizing the rhizosphere
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or Substrate (biology), substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Pore space in soil, Soil pores in the rhizosphere can ...
, entering the roots and colonizing the next tuber generation via the stolon
In biology, a stolon ( from Latin ''wikt:stolo, stolō'', genitive ''stolōnis'' – "branch"), also known as a runner, is a horizontal connection between parts of an organism. It may be part of the organism, or of its skeleton. Typically, animal ...
s, are visualized with a red color. Bacteria present in the mother tuber
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure that plants use as storage organs for nutrients, derived from stems or roots. Tubers help plants perennate (survive winter or dry months), provide energy and nutrients, and are a means of asexual reproduc ...
, passing through the stolons and migrating into the plant as well as into the next generation of tubers are shown in blue.
* The soil is the main reservoir for bacteria that colonize potato tubers
* Bacteria are recruited from the soil more or less independent of the potato variety
* Bacteria might colonize the tubers predominantly from the inside of plants via the stolon
* The bacterial microbiota of potato tubers consists of bacteria transmitted from one tuber generation to the next and bacteria recruited from the soil colonize potato plants via the root.
 Plants are attractive hosts for microorganisms since they provide a variety of nutrients. Microorganisms on plants can be
Plants are attractive hosts for microorganisms since they provide a variety of nutrients. Microorganisms on plants can be epiphyte
An epiphyte is a plant or plant-like organism that grows on the surface of another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphyt ...
s (found on the plants) or endophyte
An endophyte is an endosymbiont, often a bacterium or fungus, that lives within a plant for at least part of its life cycle without causing apparent disease. Endophytes are ubiquitous and have been found in all species of plants studied to date; ...
s (found inside plant tissue). Oomycetes and fungi
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
have, through convergent evolution, developed similar morphology and occupy similar ecological niches. They develop hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one o ...
, threadlike structures that penetrate the host cell. In mutualistic situations the plant often exchanges hexose sugars for inorganic phosphate from the fungal symbiont. It is speculated that such very ancient associations have aided plants when they first colonized land. Plant-growth promoting bacteria (PGPB) provide the plant with essential services such as nitrogen fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen ...
, solubilization of minerals such as phosphorus, synthesis of plant hormones
Plant hormones (or phytohormones) are signal molecules, produced within plants, that occur in extremely low concentrations. Plant hormones control all aspects of plant growth and development, including embryogenesis, the regulation of Organ (anat ...
, direct enhancement of mineral uptake, and protection from pathogens. PGPBs may protect plants from pathogens by competing with the pathogen for an ecological niche or a substrate, producing inhibitory allelochemicals, or inducing systemic resistance in host plants to the pathogen
Research
The symbiotic relationship between a host and its microbiota is under laboratory research for how it may shape theimmune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
of mammals. In many animals, the immune system and microbiota may engage in "cross-talk" by exchanging chemical signals, which may enable the microbiota to influence immune reactivity and targeting. Bacteria can be transferred from mother to child through direct contact and after birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
. As the infant microbiome is established, commensal bacteria quickly populate the gut, prompting a range of immune responses and "programming" the immune system with long-lasting effects. The bacteria are able to stimulate lymphoid tissue associated with the gut mucosa, which enables the tissue to produce antibodies for pathogens that may enter the gut.
The human microbiome may play a role in the activation of toll-like receptors
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane protein, single-spanning receptor (biochemistry), receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages ...
in the intestines, a type of pattern recognition receptor host cells use to recognize dangers and repair damage. Pathogens can influence this coexistence leading to immune dysregulation including and susceptibility to diseases, mechanisms of inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
, immune tolerance
Immune tolerance, also known as immunological tolerance or immunotolerance, refers to the immune system's state of unresponsiveness to substances or tissues that would otherwise trigger an immune response. It arises from prior exposure to a specif ...
, and autoimmune diseases
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated that ...
.
Co-evolution of microbiota
 Organisms evolve within ecosystems so that the change of one organism affects the change of others. The
Organisms evolve within ecosystems so that the change of one organism affects the change of others. The hologenome theory of evolution
The hologenome theory of evolution recasts the individual animal or plant (and other multicellular organisms) as a community or a " holobiont" – the host plus all of its symbiotic microbes. Consequently, the collective genomes of the holobiont ...
proposes that an object of natural selection is not the individual organism, but the organism together with its associated organisms, including its microbial communities.
Coral reefs. The hologenome theory originated in studies on coral reefs. Coral reefs are the largest structures created by living organisms, and contain abundant and highly complex microbial communities. Over the past several decades, major declines in coral populations have occurred. Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
, water pollution and over-fishing are three stress factors that have been described as leading to disease susceptibility. Over twenty different coral diseases have been described, but of these, only a handful have had their causative agents isolated and characterized. Coral bleaching
Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to loss of Symbiosis, symbiotic algae and Photosynthesis, photosynthetic pigments. This loss of pigment can be caused by various stressors, such as changes in water temperature, light, ...
is the most serious of these diseases. In the Mediterranean Sea, the bleaching of '' Oculina patagonica'' was first described in 1994 and shortly determined to be due to infection by Vibrio shiloi. From 1994 to 2002, bacterial bleaching of ''O. patagonica'' occurred every summer in the eastern Mediterranean. Surprisingly, however, after 2003, ''O. patagonica'' in the eastern Mediterranean has been resistant to ''V. shiloi'' infection, although other diseases still cause bleaching. The surprise stems from the knowledge that corals are long lived, with lifespans on the order of decades, and do not have adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system (AIS), also known as the acquired immune system, or specific immune system is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized cells, organs, and processes that eliminate pathogens specifically. The ac ...
s. Their innate immune system
The innate immune system or nonspecific immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies in vertebrates (the other being the adaptive immune system). The innate immune system is an alternate defense strategy and is the dominant immune s ...
s do not produce antibodies, and they should seemingly not be able to respond to new challenges except over evolutionary time scales.
The puzzle of how corals managed to acquire resistance to a specific pathogen led to a 2007 proposal, that a dynamic relationship exists between corals and their symbiotic microbial communities. It is thought that by altering its composition, the holobiont can adapt to changing environmental conditions far more rapidly than by genetic mutation and selection alone. Extrapolating this hypothesis to other organisms, including higher plants and animals, led to the proposal of the hologenome theory of evolution.
the hologenome theory was still being debated.
A major criticism has been the claim that ''V. shiloi'' was misidentified as the causative agent of coral bleaching, and that its presence in bleached ''O. patagonica'' was simply that of opportunistic colonization. If this is true, the basic observation leading to the theory would be invalid. The theory has gained significant popularity as a way of explaining rapid changes in adaptation that cannot otherwise be explained by traditional mechanisms of natural selection. Within the hologenome theory, the holobiont has not only become the principal unit of natural selection but also the result of other step of integration that it is also observed at the cell (symbiogenesis
Symbiogenesis (endosymbiotic theory, or serial endosymbiotic theory) is the leading evolutionary theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic organisms. The theory holds that mitochondria, plastids such as chloroplasts, and possibl ...
, endosymbiosis
An endosymbiont or endobiont is an organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism. Typically the two organisms are in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship. Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria (called rhizobia), whi ...
) and genomic levels.
Research methods
Targeted amplicon sequencing
Targeted amplicon sequencing relies on having some expectations about the composition of the community that is being studied. In target amplicon sequencing a phylogenetically informative marker is targeted for sequencing. Such a marker should be present in ideally all the expected organisms. It should also evolve in such a way that it is conserved enough that primers can target genes from a wide range of organisms while evolving quickly enough to allow for finer resolution at the taxonomic level. A common marker for human microbiome studies is the gene for bacterial16S rRNA
16S ribosomal RNA (or 16Svedberg, S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome (SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure.
The genes coding for it are referred to as ...
(''i.e.'' "16S rDNA", the sequence of DNA which encodes the ribosomal RNA molecule). Since ribosomes are present in all living organisms, using 16S rDNA allows for DNA to be amplified from many more organisms than if another marker were used. The 16S rRNA gene contains both slowly evolving regions and 9 fast evolving regions, also known as hypervariable regions (HVRs); the former can be used to design broad primers while the latter allow for finer taxonomic distinction. However, species-level resolution is not typically possible using the 16S rDNA. Primer selection is an important step, as anything that cannot be targeted by the primer will not be amplified and thus will not be detected, moreover different sets of primers can be selected to amplify different HVRs in the gene, or pairs of them. The appropriate choice of which HVRs to amplify has to be made according to the taxonomic groups of interest, as different target regions has been shown to influence taxonomical classification.
Targeted studies of eukaryotic and viral communities are limited and subject to the challenge of excluding host DNA from amplification and the reduced eukaryotic and viral biomass in the human microbiome.
After the amplicons are sequenced, molecular phylogenetic
Molecular phylogenetics () is the branch of phylogeny that analyzes genetic, hereditary molecular differences, predominantly in DNA sequences, to gain information on an organism's evolutionary relationships. From these analyses, it is possible to ...
methods are used to infer the composition of the microbial community. This can be done through clustering methodologies, by clustering the amplicons into operational taxonomic unit
An operational taxonomic unit (OTU) is an operational definition used to classify groups of closely related individuals. The term was originally introduced in 1963 by Robert R. Sokal and Peter H. A. Sneath in the context of numerical taxonomy, wh ...
s (OTUs); or alternatively with denoising methodologies, identifying amplicon sequence variants (ASVs).
Phylogenetic relationships are then inferred between the sequences. Due to the complexity of the data, distance measures such as UniFrac distances are usually defined between microbiome samples, and downstream multivariate methods are carried out on the distance matrices. An important point is that the scale of data is extensive, and further approaches must be taken to identify patterns from the available information. Tools used to analyze the data include VAMPS, QIIME, mothur and DADA2 or UNOISE3 for denoising.
Metagenomic sequencing
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of all genetics, genetic material from all organisms in a particular environment, providing insights into their composition, diversity, and functional potential. Metagenomics has allowed researchers to profile the mic ...
is also used extensively for studying microbial communities. In metagenomic sequencing, DNA is recovered directly from environmental samples in an untargeted manner with the goal of obtaining an unbiased sample from all genes of all members of the community. Recent studies use shotgun Sanger sequencing
Sanger sequencing is a method of DNA sequencing that involves electrophoresis and is based on the random incorporation of chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides by DNA polymerase during in vitro DNA replication. After first being developed by Fred ...
or pyrosequencing
Pyrosequencing is a method of DNA sequencing (determining the order of nucleotides in DNA) based on the "sequencing by synthesis" principle, in which the sequencing is performed by detecting the nucleotide incorporated by a DNA polymerase. Pyrosequ ...
to recover the sequences of the reads. The reads can then be assembled into contigs. To determine the phylogenetic identity of a sequence, it is compared to available full genome sequences using methods such as BLAST. One drawback of this approach is that many members of microbial communities do not have a representative sequenced genome, but this applies to 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing as well and is a fundamental problem. With shotgun sequencing, it can be resolved by having a high coverage (50–100x) of the unknown genome, effectively doing a de novo genome assembly. As soon as there is a complete genome of an unknown organism available it can be compared phylogenetically and the organism put into its place in the tree of life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythology, mythological, religion, religious, and philosophy, philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The ...
, by creating new taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
. An emerging approach is to combine shotgun sequencing with proximity-ligation data ( Hi-C) to assemble complete microbial genomes without culturing.
Despite the fact that metagenomics is limited by the availability of reference sequences, one significant advantage of metagenomics over targeted amplicon sequencing is that metagenomics data can elucidate the functional potential of the community DNA. Targeted gene surveys cannot do this as they only reveal the phylogenetic relationship between the same gene from different organisms. Functional analysis is done by comparing the recovered sequences to databases of metagenomic annotations such as KEGG
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) is a collection of databases dealing with genomes, biological pathways, diseases, drugs, and chemical substances. KEGG is utilized for bioinformatics research and education, including data analysis ...
. The metabolic pathways that these genes are involved in can then be predicted with tools such as MG-RAST, CAMERA and IMG/M.
RNA and protein-based approaches
Metatranscriptomics studies have been performed to study the gene expression of microbial communities through methods such as the pyrosequencing of extracted RNA. Structure based studies have also identified non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) such as ribozymes from microbiota. Metaproteomics is an approach that studies the proteins expressed by microbiota, giving insight into its functional potential.Projects
The Human Microbiome Project launched in 2008 was a United StatesNational Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in 1887 and is part of the United States Department of Health and Human Service ...
initiative to identify and characterize microorganisms found in both healthy and diseased humans. The five-year project, best characterized as a feasibility study with a budget of $115 million, tested how changes in the human microbiome are associated with human health or disease.
The Earth Microbiome Project (EMP) is an initiative to collect natural samples and analyze the microbial community around the globe. Microbes are highly abundant, diverse and have an important role in the ecological system. Yet , it was estimated that the total global environmental DNA sequencing effort had produced less than 1 percent of the total DNA found in a liter of seawater or a gram of soil, and the specific interactions between microbes are largely unknown. The EMP aims to process as many as 200,000 samples in different biomes, generating a complete database of microbes on earth to characterize environments and ecosystems by microbial composition and interaction. Using these data, new ecological and evolutionary theories can be proposed and tested.
Gut microbiota and type 2 diabetes
The gut microbiota are very important for the host health because they play role in degradation of non-digestible polysaccharides (fermentation of resistant starch, oligosaccharides, inulin) strengthening gut integrity or shaping the intestinal epithelium, harvesting energy, protecting against pathogens, and regulating host immunity. Several studies showed that the gut bacterial composition in diabetic patients became altered with increased levels of ''Lactobacillus gasseri'', ''Streptococcus mutans'' and Clostridiales members, with decrease in butyrate-producing bacteria such as ''Roseburia intestinalis'' and ''Faecalibacterium prausnitzii.'' This alteration is due to many factors such as antibiotic abuse, diet, and age''.'' The decrease in butyrate production is associated with defects in intestinal permeability, which could lead to endotoxemia, which is the increased level of circulating Lipopolysaccharides from gram negative bacterial cells wall. It is found that endotoxemia has association with development of insulin resistance. In addition that butyrate production affects serotonin level. Elevated serotonin level has contribution in obesity, which is known to be a risk factor for development of diabetes.Gut microbiota and cancer
The human gut microbial composition is modulated by dietary bile acids. There appears to be a metabolic link between cancer associated gut microbes and a fat- and meat rich diet. In rodents, elevated levels ofbile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver in peroxisomes. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile ...
s produced by the gut microbiota in response to a high fat diet are associated with an increased the risk of colorectal cancer. The secondary bile acid deoxycholic acid, produced from the primary bile acid cholic acid by the gut microbiota, is elevated in the colonic contents of humans in response to a high fat diet. In populations that have a high incidence of colorectal cancer fecal concentrations of bile acids, particularly deoxycholic acid produced by the action of gut microbiota, are higher.
Gut microbiota development and antibiotics
The colonization of the human gut microbiota may start already before birth. There are multiple factors in the environment that affects the development of the microbiota with birthmode being one of the most impactful. Another factor that has been observed to cause huge changes in the gut microbiota, particularly in children, is the use of antibiotics, associating with health issues such as higher BMI, and further an increased risk towards metabolic diseases such as obesity. In infants it was observed that amoxicillin and macrolides cause significant shifts in the gut microbiota characterized by a change in the bacterial classes Bifidobacteria, Enterobacteria and Clostridia. A single course of antibiotics in adults causes changes in both the bacterial and fungal microbiota, with even more persistent changes in the fungal communities.Seelbinder, B., Chen, J., Brunke, S., Vazquez-Uribe, R., Santhaman, R., Meyer, A. C., ... & Panagiotou, G. (2020). Antibiotics create a shift from mutualism to competition in human gut communities with a longer-lasting impact on fungi than bacteria. Microbiome, 8(1), 1-20 The bacteria and fungi live together in the gut and there is most likely a competition for nutrient sources present. Seelbinder ''et al''. found that commensal bacteria in the gut regulate the growth and pathogenicity of ''Candida albicans'' by their metabolites, particularly by propionate, acetic acid and 5-dodecenoate. ''Candida'' has previously been associated with IBD and further it has been observed to be increased in non-responders to a biological drug, infliximab, given to IBD patients with severe IBD. Propionate and acetic acid are both short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that have been observed to be beneficial to gut microbiota health. When antibiotics affect the growth of bacteria in the gut, there might be an overgrowth of certain fungi, which might be pathogenic when not regulated.Privacy issues
Microbial DNA inhabiting a person's human body can uniquely identify the person. A person's privacy may be compromised if the person anonymously donated microbe DNA data. Their medical condition and identity could be revealed.See also
*Anagenesis
Anagenesis is the gradual evolution of a species that continues to exist as an interbreeding population. This contrasts with cladogenesis, which occurs when branching or splitting occurs, leading to two or more lineages and resulting in separate ...
* Biome
A biome () is a distinct geographical region with specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It consists of a biological community that has formed in response to its physical environment and regional climate. In 1935, Tansley added the ...
* Human virome
* List of bacterial vaginosis microbiota
Bacterial vaginosis is caused by an imbalance of the naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina. The normally predominant species of ''Lactobacilli'' are markedly reduced. This is the list of organisms that are found in the vagina that are asso ...
* Marine microbiota
* Microbiota of the lower reproductive tract of women
* Phytobiome
* Probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the microbiota in the gut. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria– host interactions ...
* Psychobiotic
* Skin flora
Skin flora, also called skin microbiota, refers to microbiota (community (ecology), communities of microorganisms) that reside on the skin, typically human skin.
Many of them are bacterium, bacteria of which there are around 1,000 species upon hu ...
* Vaginal flora
Vaginal flora, vaginal microbiota or vaginal microbiome are the microorganisms that colonize the vagina. They were discovered by the German gynecologist Albert Döderlein in 1892 and are part of the overall human flora.
The amount and type of ba ...
* Vaginal microbiota in pregnancy
References
{{Portal bar, Biology, Medicine Microbiology Bacteriology Bacteria Microbiomes