Methanol Dehydrogenase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 In
In enzymology
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
, a methanol dehydrogenase (MDH) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
: CH3OH CH2O + 2 electrons + 2H+
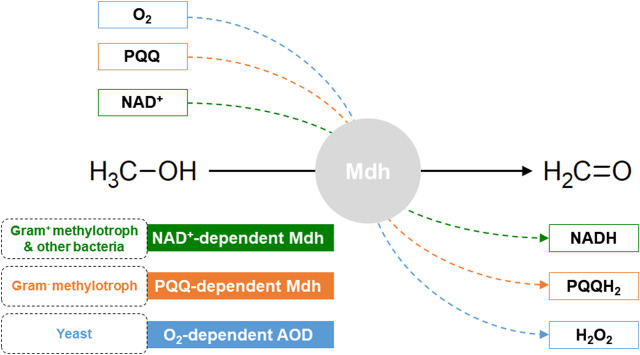
How the electrons are captured and transported depends upon the kind of methanol dehydrogenase. There are three main types of MDHs: NAD+-dependent MDH, pyrrolo-quinoline quinone dependent MDH, and oxygen-dependent alcohol oxidase.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually ut ...
s, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name
A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature.
A semisystematic name or semitrivi ...
of this enzyme class is methanol:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in methane metabolism
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
.
Classes of Methanol Dehydrogenase

NAD+ Dependent MDH
A common electron acceptor in biological systems is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+); some enzymes use a related molecule called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+). An NAD+-dependent methanol dehydrogenase() was first reported in aGram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
The Gram stain is ...
methylotroph
Methylotrophs are a diverse group of microorganisms that can use reduced one-carbon compounds, such as methanol or methane, as the carbon source for their growth; and multi-carbon compounds that contain no carbon-carbon bonds, such as dimethyl eth ...
and is an enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
that catalyzes
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
the chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
:
: CH3OH + NAD+ CH2O + NADH + H+
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ...
and NAD+, whereas its 3 products
Product may refer to:
Business
* Product (business), an item that can be offered to a market to satisfy the desire or need of a customer.
* Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution
...
are formaldehyde (CH2O), NADH
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an ade ...
, and H+. This can be performed under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
NAD+ -dependent MDHs are found in thermophilic, Gram positive methylotrophs, but can also been obtained from some non-methylotrophic bacteria. NAD+-dependent MDHs have so far been found in ''Bacillus
''Bacillus'', from Latin "bacillus", meaning "little staff, wand", is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum ''Bacillota'', with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-sh ...
'' sp., ''Lysinibacillus
''Lysinibacillus'' is a genus of bacteria from the family of Bacillaceae. Members of this genus, in contrast to the type species of the genus ''Bacillus'', contains peptidoglycan with lysine, aspartic acid, alanine and glutamic acid.
Phylogeny ...
'' sp.,and ''Cupriavidus
''Cupriavidus'' is a genus of bacteria that includes the former genus ''Wautersia''. They are characterized as Gram-negative, motile, rod-shaped organisms with oxidative metabolism. They possess peritrichous flagella, are obligate aerobic organi ...
'' sp.
PQQ-Dependent MDH
For Gram-negative bacteria, methanol oxidation occurs in theperiplasm
The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the ''periplasmic space'' in Gram-negative (more accurately "diderm") bacteria. Using cryo-electron micros ...
ic space, facilitated by PQQ-dependent MDH. PQQ-dependent MDHs contain a PQQ prosthetic group, which has the role of capturing electrons from methanol oxidation and passing them to the cytochrome
Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central iron (Fe) atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in the electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its ...
.
MxaFI and XoxF are the genes that encode for PQQ-dependent MDHs. In MxaFI-type MDH, calcium (Ca2+) is encoded as the cofactor for PQQ-dependent methylotrophy. XoxF-type MDHs use lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises at least the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–70, from lanthanum through ytterbium. In the periodic table, they fill the 4f orbitals. Lutetium (el ...
s (Ln3+) as cofactors and are highly selective towards early lanthanides (typically La-Nd). Sm3+, Eu3+, and Gd3+ can support some XoxF-type organisms, but less effectively. Pm3+ and Tb-Lu have shown no evidence of utilization so far.
Many methylotrophs encode both MxaFI and XoxF, but those that encode only one will encode exclusively for XoxF.
O2-Dependent Alcohol Oxidase
Oxygen-dependent alcohol oxidase (AOX) can be obtained from eukaryotic methylotrophs in theperoxisome
A peroxisome () is a membrane-bound organelle, a type of microbody, found in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. Peroxisomes are oxidative organelles. Frequently, molecular oxygen serves as a co-substrate, from which hydrogen perox ...
of yeasts. Formaldehyde and hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscosity, viscous than Properties of water, water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usua ...
(H2O2) are formed through the oxidation of methanol. Dihydroxyacetone synthase (DAS) and catalase
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting ...
(CTA) must then transform these toxic chemicals into non-toxic forms to protect the cell. In this process, electrons from methanol are not captured as usable energy by the cell, and are thus lost.
References
Further reading
* EC 1.1.1 NADH-dependent enzymes Enzymes of unknown structureDehydrogenase
A dehydrogenase is an enzyme belonging to the group of oxidoreductases that oxidizes a substrate by reducing an electron acceptor, usually NAD+/NADP+ or a flavin coenzyme such as FAD or FMN. Like all catalysts, they catalyze reverse as well as ...
{{1.1.1-enzyme-stub