Metal Cluster Compound on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Metal cluster compounds are a molecular ion or neutral compound composed of three or more metals and featuring significant metal-metal interactions.
Metal cluster compounds are a molecular ion or neutral compound composed of three or more metals and featuring significant metal-metal interactions.
 Many metal carbonyl clusters contain ligands aside from CO. For example, the CO ligand can be replaced with myriad alternatives such as phosphines, isocyanides, alkenes, hydride, etc. Some carbonyl clusters contain two or more metals. Others contain carbon vertices. One example is the methylidyne-tricobalt cluster o3(CH)(CO)9 The above-mentioned cluster serves as an example of an overall zero-charged (neutral) cluster. In addition, ''cationic'' (positively charged) rather than neutral organometallic trimolybdenum or tritungsten clusters are also known. The first representative of these ionic organometallic clusters is o3(CCH3)2(O2CCH3)6(H2O)3sup>2+.
Many metal carbonyl clusters contain ligands aside from CO. For example, the CO ligand can be replaced with myriad alternatives such as phosphines, isocyanides, alkenes, hydride, etc. Some carbonyl clusters contain two or more metals. Others contain carbon vertices. One example is the methylidyne-tricobalt cluster o3(CH)(CO)9 The above-mentioned cluster serves as an example of an overall zero-charged (neutral) cluster. In addition, ''cationic'' (positively charged) rather than neutral organometallic trimolybdenum or tritungsten clusters are also known. The first representative of these ionic organometallic clusters is o3(CCH3)2(O2CCH3)6(H2O)3sup>2+.
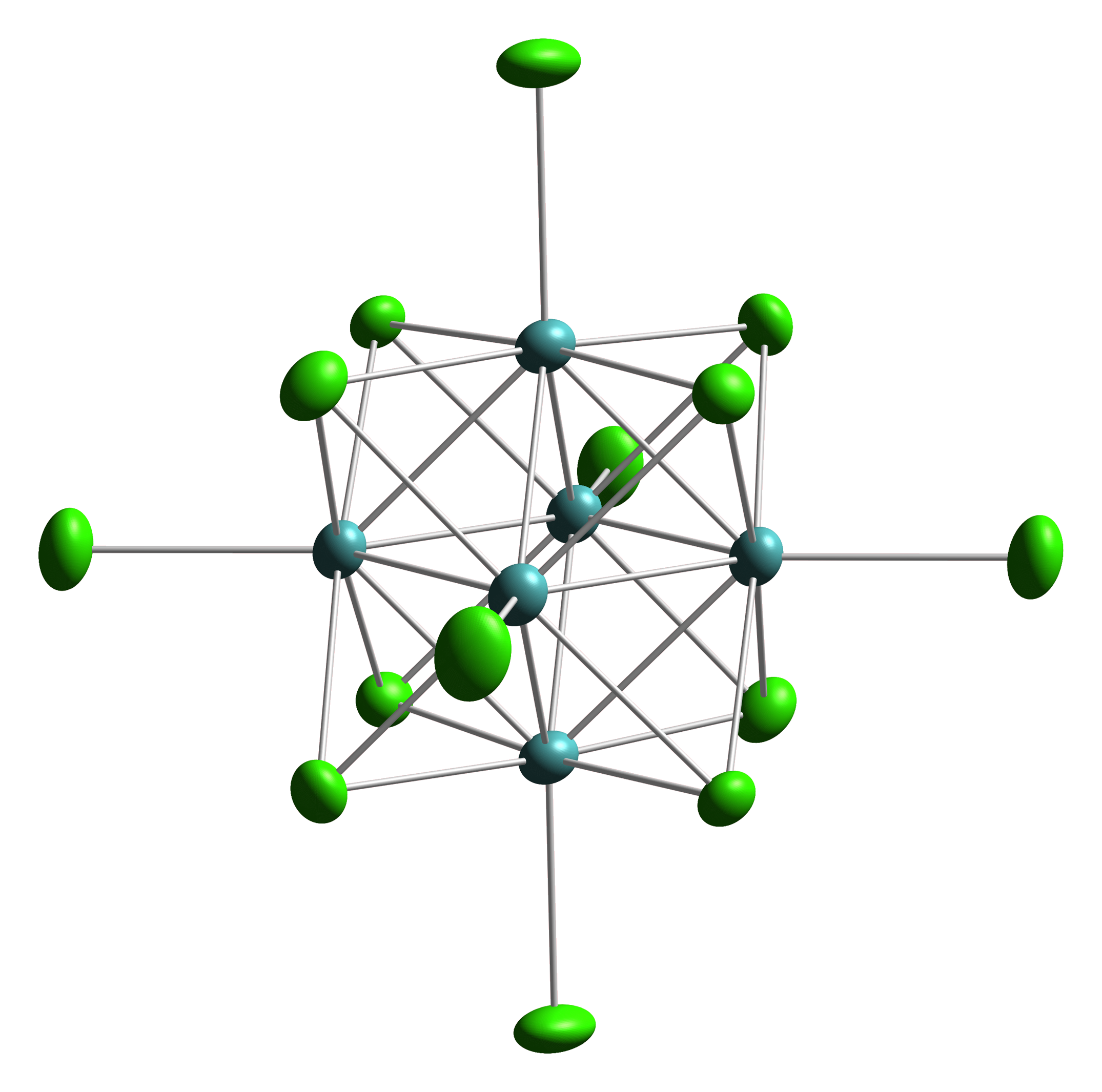 The halides of low-valent early metals often are clusters with extensive M-M bonding. The situation contrasts with the higher halides of these metals and virtually all halides of the late transition metals, where metal-halide bonding is replete.
Transition metal halide clusters are prevalent for the heavier metals: Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, Mo, W, and Re. For the earliest metals Zr and Hf, interstitial carbide ligands are also common. One example is Zr6CCl12.Arndt Simon "Metal clusters inside out" Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010 vol. 368, 1285-1299. One structure type features six terminal halides and 12 edge-bridging halides. This motif is exemplified by tungsten(III) chloride, a6Cl18sup>4−, Another common structure has six terminal halides and 8 bridging halides, e.g. Mo6Cl142−.
Many of the early metal clusters can only be prepared when they incorporate interstitial atoms.
In terms of history,
The halides of low-valent early metals often are clusters with extensive M-M bonding. The situation contrasts with the higher halides of these metals and virtually all halides of the late transition metals, where metal-halide bonding is replete.
Transition metal halide clusters are prevalent for the heavier metals: Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, Mo, W, and Re. For the earliest metals Zr and Hf, interstitial carbide ligands are also common. One example is Zr6CCl12.Arndt Simon "Metal clusters inside out" Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010 vol. 368, 1285-1299. One structure type features six terminal halides and 12 edge-bridging halides. This motif is exemplified by tungsten(III) chloride, a6Cl18sup>4−, Another common structure has six terminal halides and 8 bridging halides, e.g. Mo6Cl142−.
Many of the early metal clusters can only be prepared when they incorporate interstitial atoms.
In terms of history,

 Metal cluster compounds are a molecular ion or neutral compound composed of three or more metals and featuring significant metal-metal interactions.
Metal cluster compounds are a molecular ion or neutral compound composed of three or more metals and featuring significant metal-metal interactions.
Transition metal carbonyl clusters
The development of metal carbonyl clusters such as Ni(CO)4 and Fe(CO)5 led quickly to the isolation of Fe2(CO)9 and Fe3(CO)12. Rundle and Dahl discovered that Mn2(CO)10 featured an "unsupported" Mn-Mn bond, thereby verifying the ability of metals to bond to one another in molecules. In the 1970s, Paolo Chini demonstrated that very large clusters could be prepared from the platinum metals, one example being h13(CO)24H3sup>2−. This area of cluster chemistry has benefited from single-crystalX-ray diffraction
X-ray diffraction is a generic term for phenomena associated with changes in the direction of X-ray beams due to interactions with the electrons around atoms. It occurs due to elastic scattering, when there is no change in the energy of the waves. ...
.
 Many metal carbonyl clusters contain ligands aside from CO. For example, the CO ligand can be replaced with myriad alternatives such as phosphines, isocyanides, alkenes, hydride, etc. Some carbonyl clusters contain two or more metals. Others contain carbon vertices. One example is the methylidyne-tricobalt cluster o3(CH)(CO)9 The above-mentioned cluster serves as an example of an overall zero-charged (neutral) cluster. In addition, ''cationic'' (positively charged) rather than neutral organometallic trimolybdenum or tritungsten clusters are also known. The first representative of these ionic organometallic clusters is o3(CCH3)2(O2CCH3)6(H2O)3sup>2+.
Many metal carbonyl clusters contain ligands aside from CO. For example, the CO ligand can be replaced with myriad alternatives such as phosphines, isocyanides, alkenes, hydride, etc. Some carbonyl clusters contain two or more metals. Others contain carbon vertices. One example is the methylidyne-tricobalt cluster o3(CH)(CO)9 The above-mentioned cluster serves as an example of an overall zero-charged (neutral) cluster. In addition, ''cationic'' (positively charged) rather than neutral organometallic trimolybdenum or tritungsten clusters are also known. The first representative of these ionic organometallic clusters is o3(CCH3)2(O2CCH3)6(H2O)3sup>2+.
Transition metal halide clusters
 The halides of low-valent early metals often are clusters with extensive M-M bonding. The situation contrasts with the higher halides of these metals and virtually all halides of the late transition metals, where metal-halide bonding is replete.
Transition metal halide clusters are prevalent for the heavier metals: Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, Mo, W, and Re. For the earliest metals Zr and Hf, interstitial carbide ligands are also common. One example is Zr6CCl12.Arndt Simon "Metal clusters inside out" Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010 vol. 368, 1285-1299. One structure type features six terminal halides and 12 edge-bridging halides. This motif is exemplified by tungsten(III) chloride, a6Cl18sup>4−, Another common structure has six terminal halides and 8 bridging halides, e.g. Mo6Cl142−.
Many of the early metal clusters can only be prepared when they incorporate interstitial atoms.
In terms of history,
The halides of low-valent early metals often are clusters with extensive M-M bonding. The situation contrasts with the higher halides of these metals and virtually all halides of the late transition metals, where metal-halide bonding is replete.
Transition metal halide clusters are prevalent for the heavier metals: Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, Mo, W, and Re. For the earliest metals Zr and Hf, interstitial carbide ligands are also common. One example is Zr6CCl12.Arndt Simon "Metal clusters inside out" Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010 vol. 368, 1285-1299. One structure type features six terminal halides and 12 edge-bridging halides. This motif is exemplified by tungsten(III) chloride, a6Cl18sup>4−, Another common structure has six terminal halides and 8 bridging halides, e.g. Mo6Cl142−.
Many of the early metal clusters can only be prepared when they incorporate interstitial atoms.
In terms of history, Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling ( ; February 28, 1901August 19, 1994) was an American chemist and peace activist. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics. ''New Scientist'' called him one of the 20 gre ...
showed that " MoCl2" consisted of Mo6 octahedra. F. Albert Cotton established that " ReCl3" in fact features subunits of the cluster Re3Cl9, which could be converted to a host of adducts without breaking the Re-Re bonds. Because this compound is diamagnetic
Diamagnetism is the property of materials that are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagn ...
and not paramagnetic
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
the rhenium
Rhenium is a chemical element; it has symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an estimated average concentration of 1 part per billion (ppb), rhenium is one ...
bonds are double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betw ...
s and not single bonds. In the solid state further bridging occurs between neighbours and when this compound is dissolved in hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
a Re3Cl123− complex forms. An example of a tetranuclear complex is hexadecamethoxytetratungsten W4(OCH3)12 with tungsten
Tungsten (also called wolfram) is a chemical element; it has symbol W and atomic number 74. It is a metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively in compounds with other elements. It was identified as a distinct element in 1781 and first ...
single bonds. A related group of clusters with the general formula MxMo6X8 such as PbMo6S8. These sulfido clusters are called Chevrel phase
Octahedral clusters are inorganic or organometallic cluster compounds composed of six metals in an octahedral array.Eric J. Welch and Jeffrey R. Long ''Atomlike Building Units of Adjustable Character: Solid-State and Solution Routes to Manipulating ...
s.
Fe-S clusters in biology
In the 1970s,ferredoxin
Ferredoxins (from Latin ''ferrum'': iron + redox, often abbreviated "fd") are iron–sulfur proteins that mediate electron transfer in a range of metabolic reactions. The term "ferredoxin" was coined by D.C. Wharton of the DuPont Co. and applied t ...
was demonstrated to contain Fe4S4 clusters and later nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes () that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only fa ...
was shown to contain a distinctive MoFe7S9 active site. The Fe-S clusters mainly serve as redox cofactors, but some have a catalytic function. In the area of bioinorganic chemistry
Bioinorganic chemistry is a field that examines the role of metals in biology. Bioinorganic chemistry includes the study of both natural phenomena such as the behavior of metalloproteins as well as artificially introduced metals, including those t ...
, a variety of Fe-S clusters have also been identified that have CO as ligands.
FeMoco
FeMoco ( cofactor) or M-cluster is the primary cofactor of nitrogenase. Nitrogenase is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen molecules N2 into ammonia (NH3) through the process known as nitrogen fixation. Because it con ...
, the active site of most nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes () that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only fa ...
s, features a Fe7MoS9C cluster.
Zintl clusters
Zintl compounds feature naked anionic clusters that are generated by reduction of heavy main group ''p'' elements, mostly metals or semimetals, with alkali metals, often as a solution in anhydrous liquidammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
or ethylenediamine
Ethylenediamine (abbreviated as en when a ligand) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NH2)2. This colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor is a basic amine. It is a widely used building block in chemical synthesis, with approximately ...
. Examples of Zintl anions are i3sup>3−, n9sup>4−, b9sup>4−, and b7sup>3−.''Zintl Ions: Principles and Recent Developments'', Book Series: ''Structure and Bonding''. T. F. Fässler (Ed.), Volume 140, Springer, Heidelberg, 2011 Although these species are called "naked clusters," they are usually strongly associated with alkali metal cations. Some examples have been isolated using cryptate complexes of the alkali metal cation, e.g., b10sup>2− anion, which features a capped square antiprism
In geometry, the square antiprism is the second in an infinite family of antiprisms formed by an even number, even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It is also known as an ''anticube''.
If all its faces are regular ...
atic shape. According to Wade's rules (2n+2) the number of cluster electrons is 22 and therefore a closo cluster
In chemistry the polyhedral skeletal electron pair theory (PSEPT) provides electron counting rules useful for predicting the structures of cluster compound, clusters such as Boranes, borane and carborane clusters. The electron counting rules were ...
. The compound is prepared from oxidation
Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ...
of K4Pb9 by Au+ in PPh3AuCl (by reaction of tetrachloroauric acid and triphenylphosphine
Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to P Ph3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a l ...
) in ethylene diamine
Ethylenediamine (abbreviated as en when a ligand) is the organic compound with the formula C2H4(NH2)2. This colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor is a basic amine. It is a widely used building block in chemical synthesis, with approximately 5 ...
with 2.2.2-crypt. This type of cluster was already known as is the endohedral Ni@Pb102− (the cage contains one nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
atom). The icosahedral
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons".
There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrical tha ...
tin
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the ...
cluster Sn122− or stannaspherene anion is another closed shell
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon ato ...
structure observed (but not isolated) with photoelectron spectroscopy
Photoemission spectroscopy (PES), also known as photoelectron spectroscopy, refers to energy measurement of electrons emitted from solids, gases or liquids by the photoelectric effect, in order to determine the binding energies of electrons in t ...
. With an internal diameter of 6.1 Ã…ngstrom
The angstrom (; ) is a unit of length equal to m; that is, one ten-billionth of a metre, a hundred-millionth of a centimetre, 0.1 nanometre, or 100 picometres. The unit is named after the Swedish physicist Anders Jonas Ångström (1814–18 ...
, it is of comparable size to fullerene
A fullerene is an allotropes of carbon, allotrope of carbon whose molecules consist of carbon atoms connected by single and double bonds so as to form a closed or partially closed mesh, with fused rings of five to six atoms. The molecules may ...
and should be capable of containing small atoms in the same manner as endohedral fullerene
Endohedral fullerenes, also called endofullerenes, are fullerenes that have additional atoms, ions, or clusters enclosed within their inner spheres. The first lanthanum C60 complex called La@C60 was synthesized in 1985. The @ (at sign) in t ...
s, and indeed exists a Sn12 cluster that contains an Ir atom: r@Sn12sup>3−.
Metalloid clusters
Elementoid clusters are ligand-stabilized clusters of metal compounds that possess more direct element-element than element-ligand contacts. Examples of structurally characterized clusters feature ligand stabilized cores of Al77, Ga84, and Pd145.Intermetalloid clusters
These clusters consist of at least two different (semi)metallic elements, and possess more direct metal-metal than metal-ligand contacts. The suffix "oid" designate that such clusters possess at a molecular scale, atom arrangements that appear in bulk intermetallic compounds with high coordination numbers of the atoms, such as for example inLaves phase
Laves phases are intermetallic phase (matter), phases that have composition AB2 and are named for Fritz Laves who first described them. The phases are classified on the basis of geometry alone. While the problem of Close-packing of equal spheres ...
and Hume-Rothery phases. Ligand-free intermetalloid clusters include also endohedrally filled Zintl clusters. A synonym for ligand-stabilized intermetalloid clusters is "molecular alloy". The clusters appear as discrete units in intermetallic compounds separated from each other by electropositive atoms such as n@Cu12@Sn20sup>12−, as soluble ions s@Ni12@As20sup>3− or as ligand-stabilized molecules such as o(ZnCH3)9(ZnCp*)3
References
{{Authority control Cluster chemistry