|
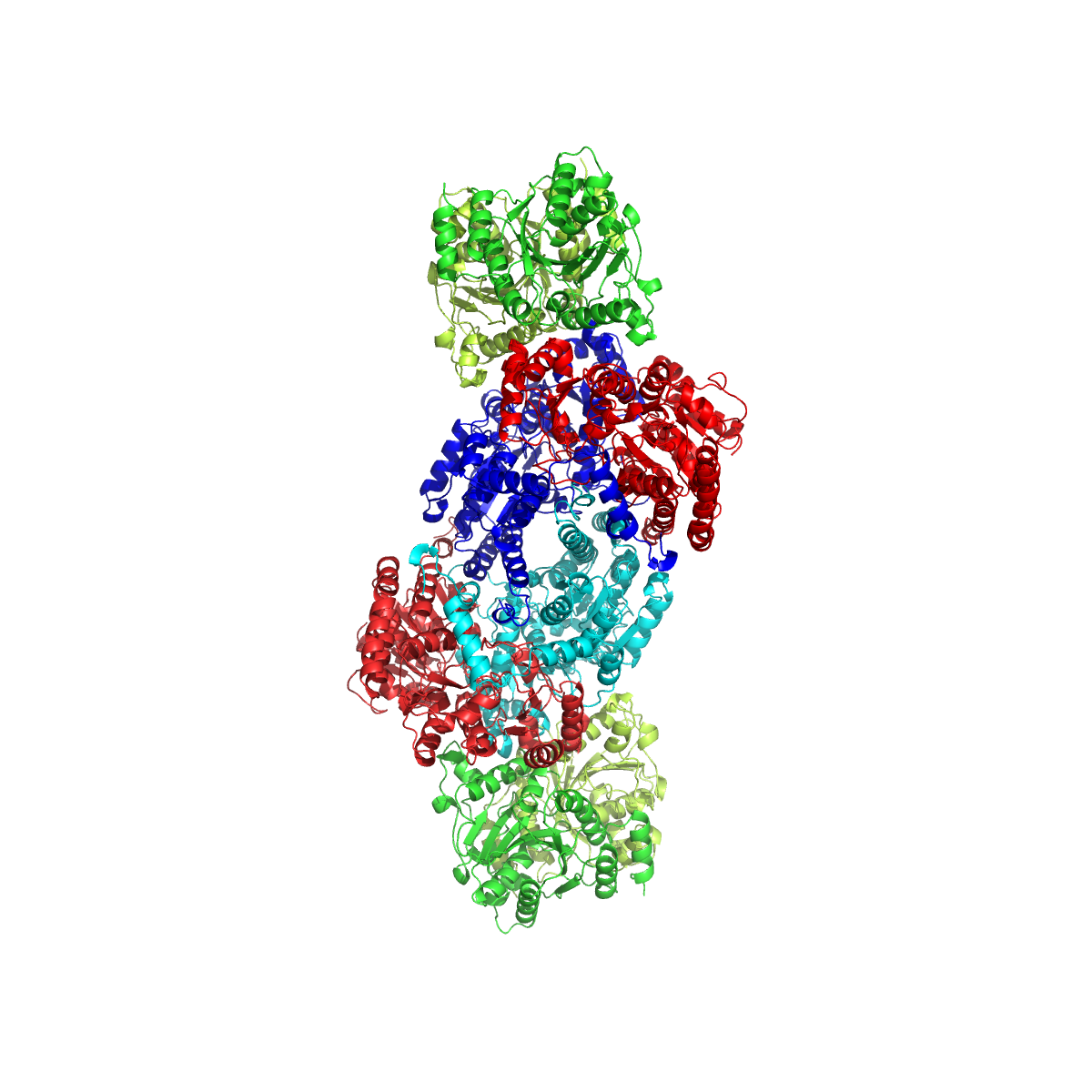
Nitrogenase
Nitrogenases are enzymes () that are produced by certain bacteria, such as cyanobacteria (blue-green bacteria) and rhizobacteria. These enzymes are responsible for the reduction of nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3). Nitrogenases are the only family of enzymes known to catalyze this reaction, which is a step in the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation is required for all forms of life, with nitrogen being essential for the biosynthesis of molecules (nucleotides, amino acids) that create plants, animals and other organisms. They are encoded by the Nif genes or homologs. They are related to protochlorophyllide reductase. Classification and structure Although the equilibrium formation of ammonia from molecular hydrogen and nitrogen has an overall negative enthalpy of reaction ( \Delta H^ = -45.2 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm \; \mathrm ), the activation energy is very high ( E_\mathrm = 230-420 \ \mathrm \, \mathrm ). Nitrogenase acts as a catalyst, reducing this energy barrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Fixation
Nitrogen fixation is a chemical process by which molecular dinitrogen () is converted into ammonia (). It occurs both biologically and abiological nitrogen fixation, abiologically in chemical industry, chemical industries. Biological nitrogen fixation or ''diazotrophy'' is catalyzed by enzymes called nitrogenases. These enzyme complexes are encoded by the Nif gene, ''Nif'' genes (or ''Nif'' homologs) and contain iron, often with a second metal (usually molybdenum, but sometimes vanadium). Some nitrogen-fixing bacteria have symbiotic relationships with plants, especially legumes, mosses and aquatic ferns such as ''Azolla''. Looser non-symbiotic relationships between diazotrophs and plants are often referred to as associative, as seen in nitrogen fixation on rice roots. Nitrogen fixation occurs between some termites and fungus, fungi. It occurs naturally in the air by means of NOx, NOx production by lightning. Fixed nitrogen is essential to life on Earth. Organic compounds such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
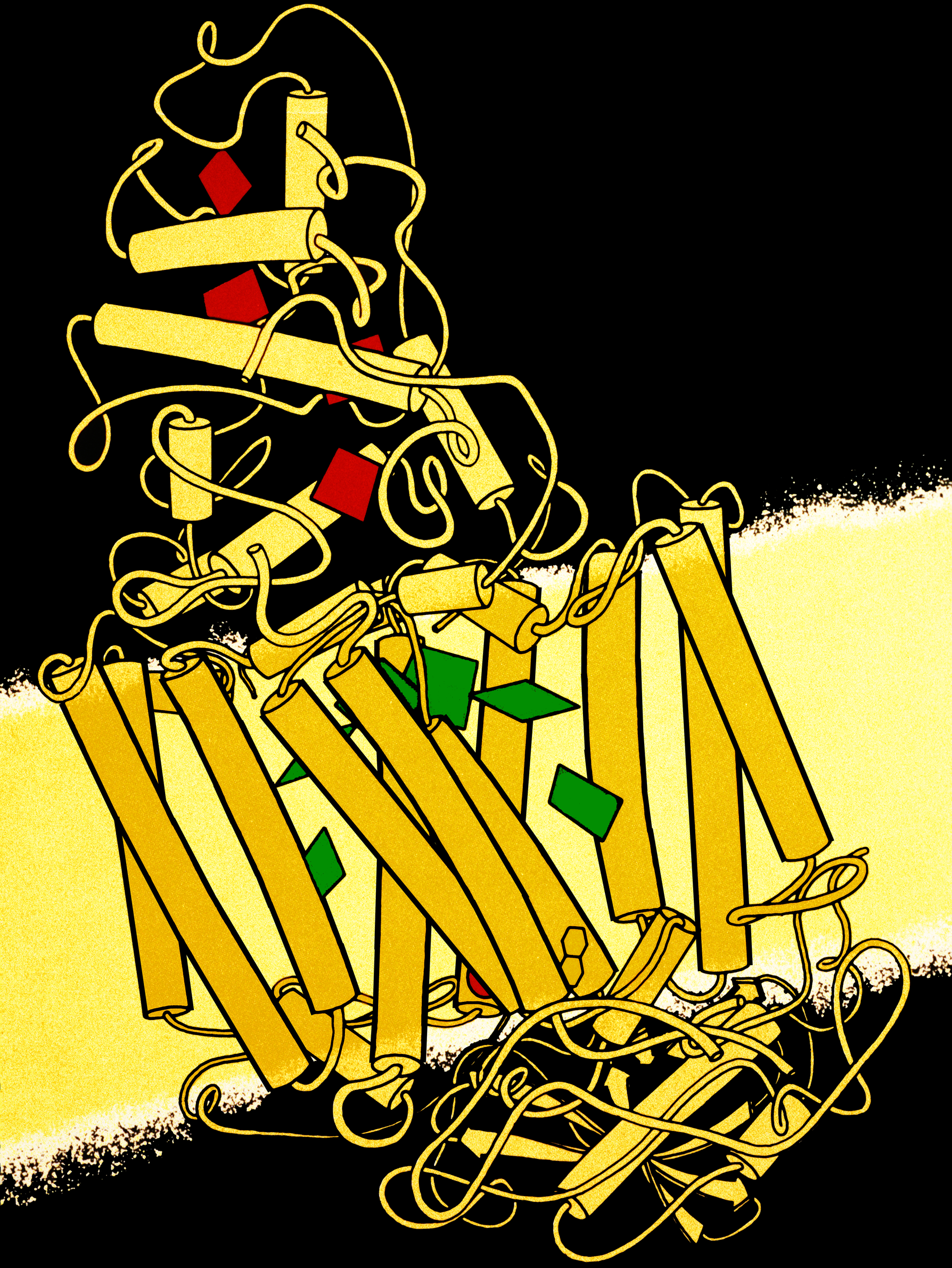
FeMoco Cluster
FeMoco ( cofactor) or M-cluster is the primary cofactor of nitrogenase. Nitrogenase is the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen molecules N2 into ammonia (NH3) through the process known as nitrogen fixation. Because it contains iron and molybdenum, the cofactor is called FeMoco. Its stoichiometry is Fe7MoS9C. Structure The FeMo cofactor is a cluster with composition Fe7MoS9C. This cluster can be viewed as two subunits composed of one Fe4S3 ( iron(III) sulfide) cluster and one MoFe3S3 cluster. The two clusters are linked by three sulfide ligands and a bridging carbon atom. The unique iron (Fe) is anchored to the protein by a cysteine. It is also bound to three sulfides, resulting in tetrahedral molecular geometry. The additional six Fe centers in the cluster are each bonded to three sulfides. These six internal Fe centers define a trigonal prismatic arrangement around a central carbide center. The molybdenum is attached to three sulfides and is anchored t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferredoxin
Ferredoxins (from Latin ''ferrum'': iron + redox, often abbreviated "fd") are iron–sulfur proteins that mediate electron transfer in a range of metabolic reactions. The term "ferredoxin" was coined by D.C. Wharton of the DuPont Co. and applied to the "iron protein" first purified in 1962 by Mortenson, Valentine, and Carnahan from the anaerobic organism, anaerobic bacterium ''Clostridium pasteurianum''. Another redox protein, isolated from spinach chloroplasts, was termed "chloroplast ferredoxin". The chloroplast ferredoxin is involved in both cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation reactions of photosynthesis. In non-cyclic photophosphorylation, ferredoxin is the last electron acceptor thus reducing the enzyme NADP+ reductase. It accepts electrons produced from sunlight-Electron excitation, excited chlorophyll and transfers them to the enzyme ferredoxin: NADP+ oxidoreductase . Ferredoxins are small proteins containing iron and sulfur atoms organized as iron–sulfur clusters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizobacteria
Rhizobacteria are root-associated bacteria that can have a detrimental (parasitic varieties), neutral or beneficial effect on plant growth. The name comes from the Greek ''rhiza'', meaning root. The term usually refers to bacteria that form symbiotic relationships with many plants ( mutualism). Rhizobacteria are often referred to as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, or PGPRs. The term PGPRs was first used by Joseph W. Kloepper in the late 1970s and has become commonly used in scientific literature. Generally, about 2–5% of rhizosphere bacteria are PGPR. They are an important group of microorganisms used in biofertilizer. Biofertilization accounts for about 65% of the nitrogen supply to crops worldwide. PGPRs have different relationships with different species of host plants. The two major classes of relationships are rhizospheric and endophytic. Rhizospheric relationships consist of the PGPRs that colonize the surface of the root, or superficial intercellular spaces of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthetic Reaction Center
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex of several proteins, biological pigments, and other co-factors that together execute the primary energy conversion reactions of photosynthesis. Molecular excitations, either originating directly from sunlight or transferred as excitation energy via light-harvesting antenna systems, give rise to electron transfer reactions along the path of a series of protein-bound co-factors. These co-factors are light-absorbing molecules (also named chromophores or pigments) such as chlorophyll and pheophytin, as well as quinones. The energy of the photon is used to excite an electron of a pigment. The free energy created is then used, via a chain of nearby electron acceptors, for a transfer of hydrogen atoms (as protons and electrons) from H2O or hydrogen sulfide towards carbon dioxide, eventually producing glucose. These electron transfer steps ultimately result in the conversion of the energy of photons to chemical energy. Transforming light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenase
A hydrogenase is an enzyme that Catalysis, catalyses the reversible Redox, oxidation of molecular hydrogen (H2), as shown below: Hydrogen oxidation () is coupled to the reduction of electron acceptors such as oxygen, nitrate, Ferric, ferric ion, sulfate, carbon dioxide (), and fumarate. On the other hand, proton reduction () is coupled to the oxidation of electron donors such as ferredoxin (FNR), and serves to dispose excess electrons in cells (essential in pyruvate fermentation). Both low-molecular weight compounds and proteins such as FNRs, cytochrome ''c''3, and cytochrome ''c''6 can act as physiological electron donors or acceptors for hydrogenases. Structural classification It has been estimated that 99% of all organisms utilize hydrogen, H2. Most of these species are microbes and their ability to use H2 as a metabolite arises from the expression of metalloenzymes known as hydrogenases. Hydrogenases are sub-classified into three different types based on the active site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homodimeric
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", '' di-'' + '' -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins while a protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors have the ability to form both homo- and heterodimer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
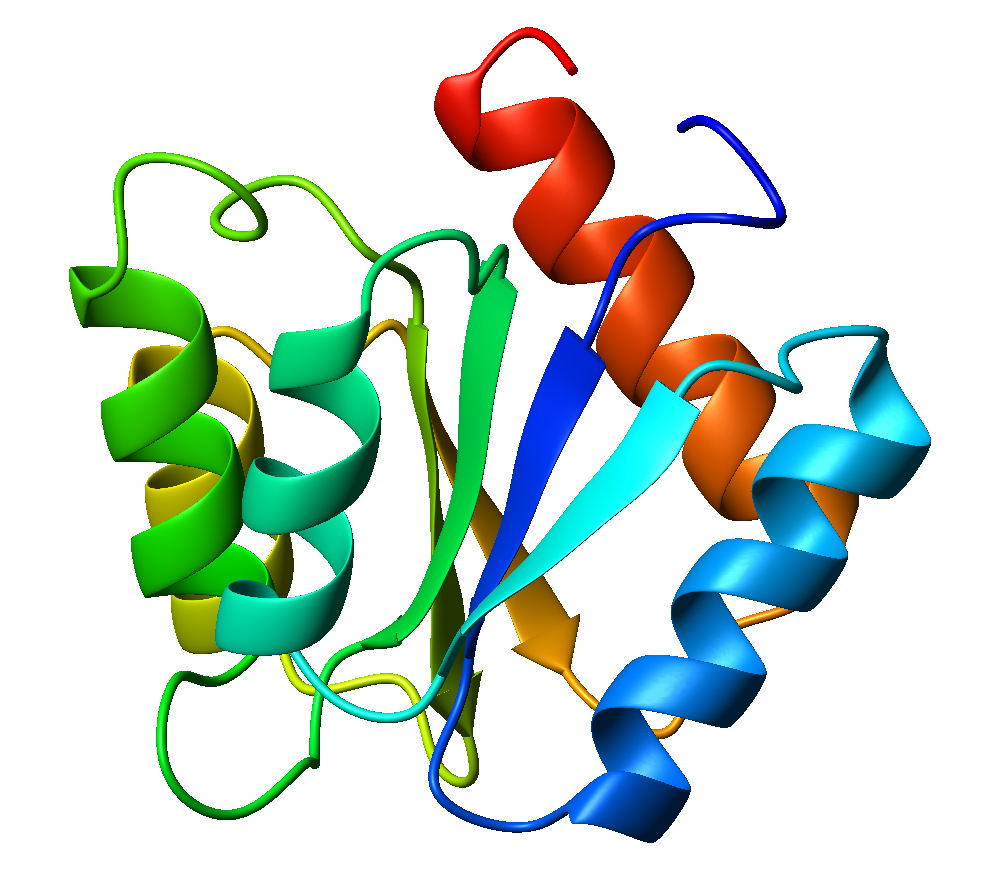
Flavodoxin
Flavodoxins (Fld) are small, soluble electron-transfer proteins. Flavodoxins contains flavin mononucleotide as prosthetic group. The structure of flavodoxin is characterized by a five-stranded parallel beta sheet, surrounded by five alpha helices. They have been isolated from prokaryotes, cyanobacteria, and some eukaryotic algae. Background Originally found in cyanobacteria and clostridia, flavodoxins were discovered over 50 years ago. These proteins evolved from an anaerobic environment, due to Selective pressure, selective pressures. Ferredoxin, another redox protein, was the only protein able to be used in this manner. However, when oxygen became present in the environment, iron became limited. Ferredoxin is iron-dependant as well as oxidant-sensitive. Under these limited iron conditions, ferredoxin was no longer preferred. Flavodoxin on the other hand is the opposite of these traits, as it is oxidant-resistant and has iron-free isofunctional counterparts. Therefore, for some t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |