Mesenosaurinae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Varanopidae is an extinct
 No known varanopids developed a sail like ''
No known varanopids developed a sail like ''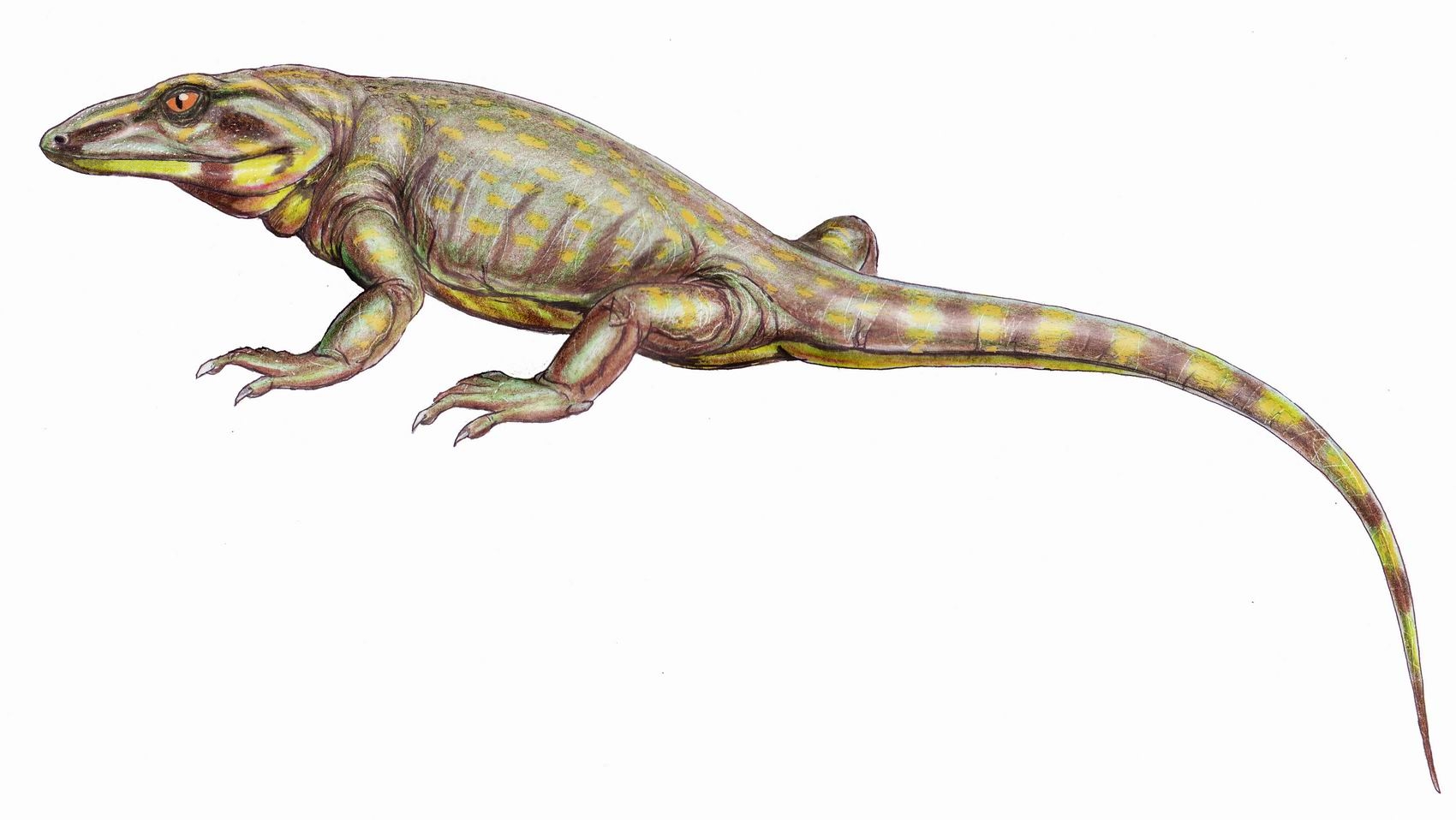
 The genus ''
The genus ''
 Family Varanopidae
*'' Apsisaurus''
*'' Archaeovenator''
*''
Family Varanopidae
*'' Apsisaurus''
*'' Archaeovenator''
*''
Varanopseidae
- at Palaeos {{Taxonbar, from=Q136615 Pennsylvanian first appearances Guadalupian extinctions Prehistoric synapsid families Taxa named by Llewellyn Ivor Price Taxa named by Alfred Romer
family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
of amniotes
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibious stem tetrapod ancestors during the ...
known from the Late Carboniferous
Late or LATE may refer to:
Everyday usage
* Tardy, or late, not being on time
* Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead
Music
* Late (The 77s album), ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000
* Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993
* Late!, a pseudo ...
to Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0. ...
that resembled monitor lizard
Monitor lizards are lizards in the genus ''Varanus,'' the only extant genus in the family Varanidae. They are native to Africa, Asia, and Oceania, and West African Nile monitor, one species is also found in south America as an invasive species. A ...
s (with the name of the group deriving from the monitor lizard genus ''Varanus'') and may have filled a similar niche. Typically, they are considered to be relatively basal synapsids
Synapsida is a diverse group of tetrapod vertebrates that includes all mammals and their extinct relatives. It is one of the two major clades of the group Amniota, the other being the more diverse group Sauropsida (which includes all extant rept ...
(and thus more closely related to mammals than to reptiles), although some studies from the late 2010s recovered them being taxonomically closer to diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The earliest traditionally identified diapsids, the araeosc ...
reptiles
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
, recent studies from the early 2020s support their traditional placement as synapsids on the basis of high degree of bone labyrinth ossification, maxillary canal morphology and phylogenetic analyses. A varanopid from the late Middle Permian ''Pristerognathus'' Assemblage Zone (Capitanian
In the geologic timescale, the Capitanian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the uppermost or latest of three subdivisions of the Guadalupian Epoch or Series. The Capitanian lasted between and million years ago. It was preceded by t ...
) is the youngest known varanopid and the last member of the "pelycosaur" group of synapsids. Thus, Varanopidae vanishes from the fossil record at the same time as dinocephalians, plausibly as a result of a major mass extinction event that has been called the "Dinocephalian extinction event".
Description
 No known varanopids developed a sail like ''
No known varanopids developed a sail like ''Dimetrodon
''Dimetrodon'' ( or ; ) is an extinct genus of sphenacodontid synapsid that lived during the Cisuralian (Early Permian) Epoch (geology), epoch of the Permian period, around 295–272 million years ago. With most species measuring long and ...
''. The length of known varanopids, including the tail, varies from . Varanopids already showed some advanced characteristics of true pelycosaurs such as their deep, narrow, elongated skulls. Their jaws were long and their teeth were sharp. However, they were still primitive by mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
ian standards. They had long tails, lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic isla ...
-like bodies, and thin legs. The varanopids were mostly carnivorous, but as they were reduced in size, their diets changed from a carnivorous to an insectivorous lifestyle. Compared to the other animals in Early Permian 01 or 01 may refer to:
* The year 2001, or any year ending with 01
* The month of January
* 1 (number)
Music
* '01 (Richard Müller album), ''01'' (Richard Müller album), 2001
* 01 (Urban Zakapa album), ''01'' (Urban Zakapa album), 2011
* ''01011 ...
, varanopids were agile creatures.
 The genus ''
The genus ''Ascendonanus
''Ascendonanus'' (meaning "climbing dwarf") is an extinct genus of varanopid amniote from the Early Permian of Germany. It is one of the earliest specialized arboreal (tree-living) tetrapods currently known and outwardly resembled a small lizar ...
'' provides the first extensive skin impressions for ancient amniotes, revealing scales akin to those of squamates
Squamata (, Latin ''squamatus'', 'scaly, having scales') is the largest order of reptiles; most members of which are commonly known as lizards, with the group also including snakes. With over 11,991 species, it is also the second-largest order ...
. Parental care is known in ''Heleosaurus
''Heleosaurus scholtzi'' is an extinct species of basal synapsids, known as pelycosaurs, in the family of Varanopidae during the middle Permian.Reisz, R. R. & Modesto, S. P. 2007. ''Heleosaurus scholtzi'' from the Permian of South Africa: a varan ...
'', suggesting that it is ancestral to synapsids as a whole.
Varanopids are small to medium-sized possible synapsids that have been discovered throughout the supercontinent Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia (continent), Siberia during the Carboniferous period ...
. Varanopids are found in formerly areas of North America, Russia, Europe, and South Africa. The authors Romer and Price (1940) discussed the original positioning of Varanopidae within Synapsida and considered them as the suborder Sphenacodontia. Most phylogenetic analyses have place Varanopidae as a basal member of Synapsida and due to their positioning, a better understanding of the morphology and phylogeny of varanopids is needed for synapsid evolution. The phylogeny of varanopids is based mostly on cranial morphology. The atlas−axis complex can be described with little effort with variation of this structure within a small clade. Varanopids, members of synapsid predators have well preserved atlas−axes permitting a descriptions and examination of morphological variation between taxon. The size of the transverse processes on the axis and the shape of the axial neural spine can be variable. For the small mycterosaurine varanopids, they have a small transverse processes that point posteroventrally, and the axial spine is dorsoventrally short, with a flattened dorsal margin in lateral view. The larger varanodontine varanopids have large transverse processes with a broad base, and a much taller axial spine with a rounded dorsal margin in lateral view. Using outgroup comparisons, the morphology of the transverse processes is considered a derived trait in varanodontines, while in mycterosaurines the morphology of the axial spine is the derived trait.
Ecology
At least some varanopids like ''Ascendonanus
''Ascendonanus'' (meaning "climbing dwarf") is an extinct genus of varanopid amniote from the Early Permian of Germany. It is one of the earliest specialized arboreal (tree-living) tetrapods currently known and outwardly resembled a small lizar ...
'' and ''Eoscansor
''Eoscansor'' (EE-oh-SKAN-sor; meaning "dawn climber") is a species of small varanopid amniote that lives from the upper Pennsylvanian subperiod in northern New Mexico, United States 305 million years ago. The species ''Eoscansor cobrensis'' w ...
'' are amongst the oldest known tree climbing (arboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally (scansorial), but others are exclusively arboreal. The hab ...
) animals, with limbs and digits adapted for grasping. Other varanopids lacked these adaptations and were probably terrestrial.
Classification
 Family Varanopidae
*'' Apsisaurus''
*'' Archaeovenator''
*''
Family Varanopidae
*'' Apsisaurus''
*'' Archaeovenator''
*''Ascendonanus
''Ascendonanus'' (meaning "climbing dwarf") is an extinct genus of varanopid amniote from the Early Permian of Germany. It is one of the earliest specialized arboreal (tree-living) tetrapods currently known and outwardly resembled a small lizar ...
''
*'' Basicranodon'' (possible junior synonym
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently.
...
of ''Mycterosaurus'')
*''Eoscansor
''Eoscansor'' (EE-oh-SKAN-sor; meaning "dawn climber") is a species of small varanopid amniote that lives from the upper Pennsylvanian subperiod in northern New Mexico, United States 305 million years ago. The species ''Eoscansor cobrensis'' w ...
''
*'' Dendromaia''
*'' Pyozia''
*'' Thrausmosaurus?'' (''nomen dubium
In binomial nomenclature, a ''nomen dubium'' (Latin for "doubtful name", plural ''nomina dubia'') is a scientific name that is of unknown or doubtful application.
Zoology
In case of a ''nomen dubium,'' it may be impossible to determine whether a ...
'')
*Clade Neovaranopsia
**Subfamily Mesenosaurinae
***'' Cabarzia''
***''Mesenosaurus
''Mesenosaurus'' is an extinct genus of synapsid belonging to the family Varanopidae. This genus includes two species: the type species ''Mesenosaurus romeri'' from the middle Permian (upper Kazanian) Mezen River Basin of northern Russia, and '' ...
''
***Clade Afrothyra
****'' Anningia''
****'' Elliotsmithia''
****''Heleosaurus
''Heleosaurus scholtzi'' is an extinct species of basal synapsids, known as pelycosaurs, in the family of Varanopidae during the middle Permian.Reisz, R. R. & Modesto, S. P. 2007. ''Heleosaurus scholtzi'' from the Permian of South Africa: a varan ...
''
****'' Microvaranops''
**Subfamily Varanodontinae
***''Aerosaurus
''Aerosaurus'' (meaning "copper lizard") is an extinct genus within Varanopidae, a family of non-mammalian synapsids. It lived between 252-299 million years ago during the Early Permian in North America. The name comes from Latin ''aes'' (''aeris ...
''
***''Mycterosaurus
''Mycterosaurus'' (Greek as mykter/mykteros meaning nose/snout, sauros meaning "lizard") is an extinct genus of amniotes belonging to the family Varanopidae. It is classified in the varanopid subfamily Mycterosaurinae. ''Mycterosaurus'' is th ...
''
***''Ruthiromia
''Ruthiromia'' is an extinct genus of varanopid synapsids from the Early Permian of the United States.
See also
* List of pelycosaurs
This list of pelycosaurs is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera that have ever ...
''
***''Tambacarnifex
''Tambacarnifex'' (meaning " Tambach butcher") is an extinct genus of varanodontine synapsids known from the Early Permian Tambach Formation of Free State of Thuringia, central Germany. It was first named by David S. Berman, Amy C. Henrici, Stu ...
''
***''Varanodon
''Varanodon'' is an extinct genus of amniotes from the family Varanopidae. It has been found in the Chickasha Formation of Oklahoma, which dates to the Roadian stage of the Middle Permian. The largest varanopid known at the time of its descripti ...
''
***''Varanops
''Varanops'' is an extinct genus of Early Permian varanopid known from Texas and Oklahoma of the United States. It was first named by Samuel Wendell Williston in 1911 as a second species of ''Varanosaurus'', ''Varanosaurus brevirostris''. In 191 ...
''
***''Watongia
''Watongia'' is an extinct genus of non-mammalian synapsids from Middle Permian of Oklahoma. Only one species has been described, ''Watongia meieri'', from the Chickasha Formation. It was assigned to family Gorgonopsidae by Olson and to Eotita ...
''
'' Apsisaurus'' was formerly assigned as an "eosuchia
Eosuchians are an extinct order of diapsid reptiles. Depending on which taxa are included the order may have ranged from the late Carboniferous to the Eocene but the consensus is that eosuchians are confined to the Permian and Triassic.
Eosuchi ...
n" diapsid
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae, in each side of their skulls. The earliest traditionally identified diapsids, the araeosc ...
. In 2010, it was redescribed by Robert R. Reisz, Michel Laurin and David Marjanović; their phylogenetic analysis
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data ...
found it to be a basal varanopid synapsid
Synapsida is a diverse group of tetrapod vertebrates that includes all mammals and their extinct relatives. It is one of the two major clades of the group Amniota, the other being the more diverse group Sauropsida (which includes all extant rept ...
. The cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
below is modified after Reisz, Laurin and Marjanović, 2010.
The poorly known ''Basicranodon'' and ''Ruthiromia'' were tentatively assigned to Varanopidae by Reisz (1986), but have been neglected in more recent studies. They were included for the first time in a phylogenetic analysis by Benson (2012). ''Ruthiromia'' was found to be most closely related to ''Aerosaurus
''Aerosaurus'' (meaning "copper lizard") is an extinct genus within Varanopidae, a family of non-mammalian synapsids. It lived between 252-299 million years ago during the Early Permian in North America. The name comes from Latin ''aes'' (''aeris ...
''. ''Basicranodon'' was found to be a wildcard taxon due to its small amount of known materials, as it is based on a partial braincase
In human anatomy, the neurocranium, also known as the braincase, brainpan, brain-pan, or brainbox, is the upper and back part of the skull, which forms a protective case around the brain. In the human skull, the neurocranium includes the calv ...
from the ?Kungurian
In the geologic timescale, the Kungurian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is the latest or upper of four subdivisions of the Cisuralian Epoch or Series. The Kungurian lasted between and million years ago (Ma). It was preceded by the Arti ...
stage Richards Spur locality in Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northea ...
. It occupies two possible positions, falling either as a mycterosaurine, or as the sister taxon of '' Pyozia''. Although Reisz ''et al.'' (1997) considered ''Basicranodon'' as a subjective junior synonym of ''Mycterosaurus'', Benson (2012) found some differences in the distribution of teeth and shape of the dentigerous ventral platform medial to the basipterygoid processes that may indicate taxonomic distinction. Below is a cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
modified from the analysis of Benson (2012), after the exclusion of ''Basicranodon'':
References
External links
Varanopseidae
- at Palaeos {{Taxonbar, from=Q136615 Pennsylvanian first appearances Guadalupian extinctions Prehistoric synapsid families Taxa named by Llewellyn Ivor Price Taxa named by Alfred Romer