Meningococcal Infections on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Meningococcal disease is a serious infection caused by ''
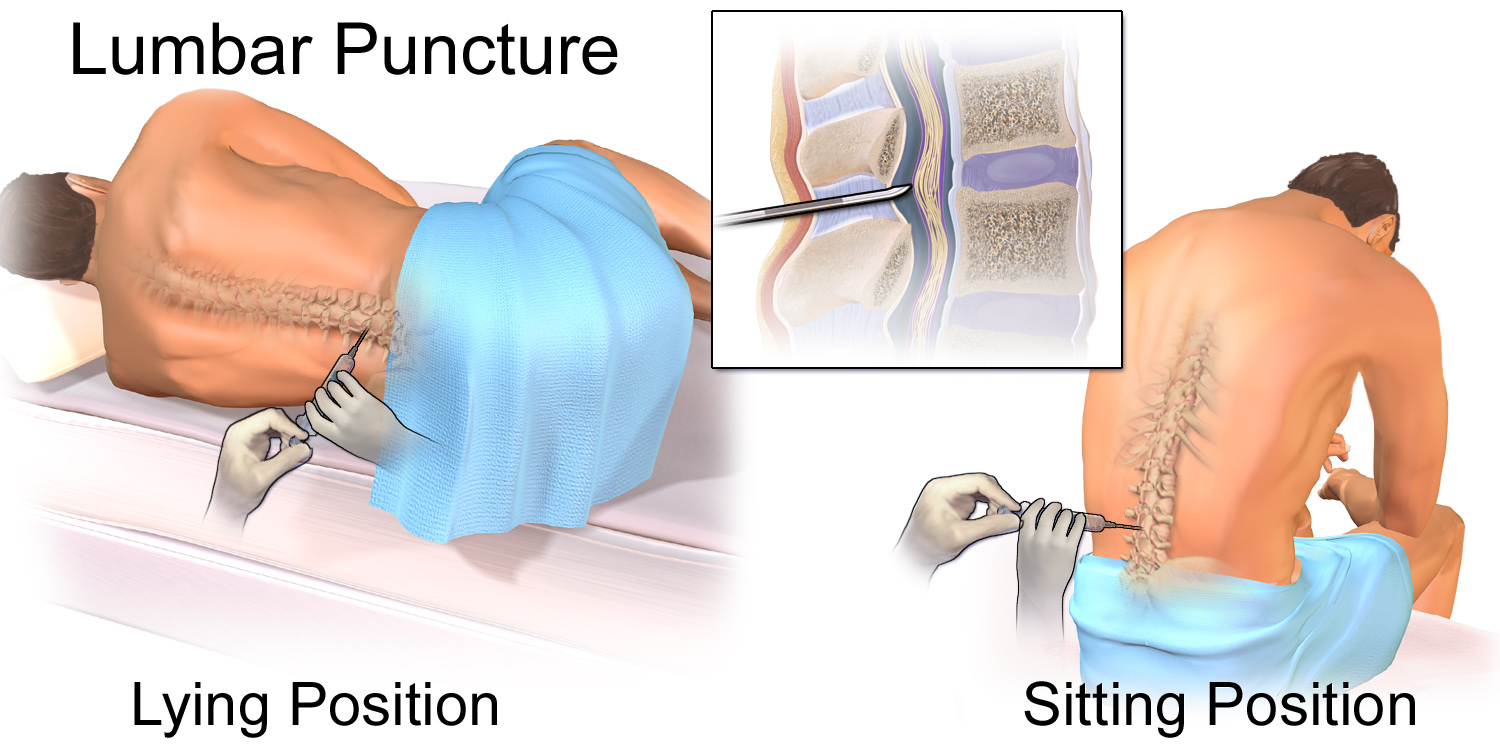 Diagnosis includes clinical evaluation based on symptoms blood cultures, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, basic metabolic panel, and possibly imaging.
Lumbar puncture is the gold standard for identifying a person has meningitis and rule out other causes of infection. This fluid covers the brain and spinal cord. This test should be completed unless a person has increased pressure in the brain such as swelling in the optic nerve or altered mental status.
Computer tomography (CT) can be used if diagnosis is unclear and if a person has depressed mental status.
Diagnosis includes clinical evaluation based on symptoms blood cultures, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, basic metabolic panel, and possibly imaging.
Lumbar puncture is the gold standard for identifying a person has meningitis and rule out other causes of infection. This fluid covers the brain and spinal cord. This test should be completed unless a person has increased pressure in the brain such as swelling in the optic nerve or altered mental status.
Computer tomography (CT) can be used if diagnosis is unclear and if a person has depressed mental status.
 When meningococcal disease is suspected, treatment must be started ''immediately'' and should not be delayed while waiting for investigations. Treatment in primary care usually involves prompt intramuscular administration of
When meningococcal disease is suspected, treatment must be started ''immediately'' and should not be delayed while waiting for investigations. Treatment in primary care usually involves prompt intramuscular administration of
Neisseria meningitidis
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as the meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to a ...
'', also known as meningococcus, a gram negative diplococcus. Meningococcal disease includes meningitis, meningococcal septicemia, or a combination of both, which can be life-threatening and rapidly progressive. If left untreated, the disease has a high mortality rate; however, it is preventable through vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
. Meningitis and meningococcal sepsis are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under-developed countries.
Meningococcal disease can be transmitted to others through saliva, close contact with an infected individual by inhaling respiratory air droplets. Initial symptoms may be subtle and similar to other bacterial infection, but can quickly progress to include fever, rash, body aches, photophobia and other complications. ''Neisseria meningitidis
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as the meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to a ...
'' colonizes a substantial proportion of the general population without issues, but it can invade the bloodstream, affecting the entire body, most notably limbs and brain, causing serious illness in a small percentage of individuals.
The global incidence of meningococcal disease is relatively low, ranging from 0.0 to 10.2 per 100,000 however cases in the United States are rising.Sanford Guide to antimicrobial therapy 2014 44th edition Serotypes of the bacteria range from various countries, with serotype B accounting for most new cases worldwide. Meningococcal vaccines
Meningococcal vaccine refers to any vaccine used to prevent infection by ''Neisseria meningitidis''. Different versions are effective against some or all of the following types of meningococcus: A, B, C, W-135, and Y. The vaccines are between ...
have sharply reduced the incidence of the disease in developed countries.
Vaccine has also shown to lessen cases of illness and their associated complications as well as death. Current vaccinations cover most of the bacterial strains that causes meningococcal disease. This has led to a decrease of incidence and burden from the disease.Treatment include supportive care, early administration of antibiotics and management of complications associated with infection. Ongoing research continues in an effort to understand specific aspects of meningococcal biology and host interactions; however, the development of improved treatments and effective vaccines is expected to depend on novel efforts by workers in many different fields.
Pathogenesis
Meningococcal disease causes life-threatening meningitis and sepsis conditions. In the case of meningitis, bacteria attack the lining between the brain and skull called themeninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid spac ...
. Infected fluid from the meninges then passes into the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
, causing symptoms including stiff neck, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
and rash
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
es. The meninges (and sometimes the brain itself) begin to swell, which affects the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
.
Even with antibiotics, approximately 1 in 10 people who have meningococcal meningitis will die; however, about as many survivors of the disease lose a limb or their hearing, or experience permanent brain damage
Brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating trauma-induced damage.
A common ...
.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Meningococcal disease among college students: ACIP modifies recommendations for meningitis vaccination. Press release. 1999 Oct 20 The sepsis type of infection is much more deadly, and results in a severe blood poisoning
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is compo ...
called meningococcal sepsis that affects the entire body. In this case, bacterial toxins rupture blood vessels and can rapidly shut down vital organs. Within hours, patient's health can change from seemingly good to mortally ill.Jeeri R. Reddy and Thiombiano S. Rigobert. Infections à méningocoques Maladies infectieuses et Africa. West Africa. Med. Bull. 2007
The ''N. meningitidis'' bacterium is surrounded by a slimy outer coat that contains disease-causing endotoxin
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), now more commonly known as endotoxin, is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as '' E. coli'' and ''Salmonella'' with a common structural archit ...
. While many bacteria produce endotoxin, the levels produced by meningococcal bacteria are 100 to 1,000 times greater (and accordingly more lethal) than normal. As the bacteria multiply and move through the bloodstream, it sheds concentrated amounts of toxin. The endotoxin directly affects the heart, reducing its ability to circulate blood, and also causes pressure on blood vessels throughout the body. As some blood vessels start to hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
, major organs like the lungs and kidneys are damaged.
Patients with meningococcal disease are treated with a large dose of antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
. The systemic antibiotic flowing through the bloodstream rapidly kills the bacteria but, as the bacteria are killed, even more toxin is released. It takes up to several days for the toxin to be neutralized from the body by using continuous liquid treatment and antibiotic therapy.
Classification
Meningococcemia
Meningococcemia, also known as meningococcal septicemia, is an infection of the bloodstream. Meningococcemia makes up about approximately 20% of meningococcal disease cases. Symptoms of meningoccemia may include fever, low blood pressure as well as organ failure. Like many othergram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists ...
blood infections it can cause disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking Microvessel, small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems ...
(DIC), which is the inappropriate clotting of blood within the vessels. DIC can cause ischemic
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
tissue damage when upstream thrombi obstruct blood flow and hemorrhage because clotting factors
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The process of coagulatio ...
are exhausted. Small bleeds into the skin cause the characteristic petechial
A petechia (; : petechiae) is a small red or purple spot ( 1 cm in diameter) and purpura (3 to 10 mm in diameter). The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant.
Causes Physical t ...
rash, which appears with a star-like shape and mostly appears on the extremity of the body. This is due to the release of toxins
A toxin is a naturally occurring poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. They occur especially as proteins, often conjugated. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived ...
into the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
that break down the walls of blood vessels
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the tissues of a body. They also take waste an ...
. A rash
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
can develop under the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
due to blood leakage that may leave red or brownish pinprick spots, which can develop into purple bruising. Meningococcal rash can usually be confirmed by a glass test in which the rash does not fade away under pressure.
Meningoccemia can also lead to Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome
Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome (WFS) is defined as adrenal gland failure due to hemorrhages in the adrenal glands, commonly caused by sepsis. Typically, the bacteria responsible for triggering the bleeding is '' Neisseria meningitidis''.
The ...
, which is associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation or thrombosis of multiple organs and extremities and necrosis of adrenal glands.
Meningitis
Meningococcal meningitis is a form of bacterialmeningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasion ...
caused by the ''Neisseria meningitidis
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as the meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to a ...
'' bacteria. Meningitis is a disease caused by inflammation and irritation of the meninges
In anatomy, the meninges (; meninx ; ) are the three membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord. In mammals, the meninges are the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. Cerebrospinal fluid is located in the subarachnoid spac ...
, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. In meningococcal meningitis this is caused by the bacteria invading the cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
and circulating through the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
. The classic presentation of meningitis includes fever, neck stiffness, and altered mental status; however these symptoms are typically present in less than 50% of cases. Symptoms also differentiate between age groups, with older individuals presenting with altered mental status and localized neurological impairments and younger children showing general symptoms such as irritability, lethargy, or inability to feed.
Atypical types of meningococcal disease
''N. meningitidis'' can also result in atypical presentations throughout the body. Atypical types of meningococcal disease include septic arthritis, meningococcal pneumonia, pericarditis and acute gastrointestinal or GI symptoms. GI symptoms from meningococcal disease includes nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. These symptoms are rare but can occur during the initial phases of infection. These symptoms can often be misdiagnosed asgastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of ...
, also known as a inflammation of the stomach and intestines.
Septic arthritic is also associated with meningococcal disease. Septic arthritis caused by ''Neisseria meningitidis'' can appear as joint pain, redness, warmth, and limited movement. It typically affects just one joint—most often the knee—and is more common in very young or older individuals.
Meningococcal pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
can appear during influenza pandemics and in military camps. This is a multi-lobar, rapidly evolving pneumonia, sometimes associated with septic shock. With prompt treatment, the prognosis is excellent. Meningococcal pneumonia typical occurs in older individuals and found to be associated with serotype W of ''N. meningitidis''. Although rare, meningococcal pericarditis
Pericarditis () is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe whe ...
can occur.
Signs and symptoms
Meningitis
The patient with meningococcal meningitis typically presents with high fever, nuchal rigidity (stiff neck), Kernig's sign, severe headache, vomiting,purpura
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, ...
, photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom, photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence o ...
, and sometimes chills, altered mental status, or seizures. Diarrhea or respiratory symptoms are less common. Petechiae
A petechia (; : petechiae) is a small red or purple spot ( 1 cm in diameter) and purpura (3 to 10 mm in diameter). The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant.
Causes Physical ...
are often also present, but do not always occur; their absence does not negate a diagnosis of meningococcal disease. Anyone with symptoms of meningococcal meningitis should receive intravenous antibiotics prior to the results of lumbar puncture being known, as delay in treatment can greatly worsen the prognosis.
Meningococcemia
Symptoms of meningococcemia are, at least initially, similar to those ofinfluenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
. Typically, the first symptoms include fever, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, myalgia, headache, arthralgia
Arthralgia () literally means ' joint pain'. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceuti ...
, chills
Chills is a feeling of coldness occurring during a high fever, but sometimes is also a common symptom which occurs alone in specific people. It occurs during fever due to the release of cytokines and prostaglandins as part of the inflammatory ...
, diarrhea, stiff neck, and malaise. Later symptoms include septic shock
Septic shock is a potentially fatal medical condition that occurs when sepsis, which is organ injury or damage in response to infection, leads to dangerously low blood pressure and abnormalities in cellular metabolism. The Third International C ...
, purpura
Purpura () is a condition of red or purple discolored spots on the skin that do not blanch on applying pressure. The spots are caused by bleeding underneath the skin secondary to platelet disorders, vascular disorders, coagulation disorders, ...
, hypotension, cyanosis, petechiae
A petechia (; : petechiae) is a small red or purple spot ( 1 cm in diameter) and purpura (3 to 10 mm in diameter). The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant.
Causes Physical ...
, seizures, anxiety, and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is altered organ function in an acutely ill patient requiring immediate medical intervention.
There are different stages of organ dysfunction for certain different organs, both in acute and in chronic ...
. Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin co ...
and altered mental status may also occur. The petechial rash appear with the 'star-like' shape. Meningococcal sepsis has a greater mortality rate than meningococcal meningitis, but the risk of neurologic sequelae is much lower.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing meningococcal disease is vital; death can occur in a person within 6-12 hours with initial signs and symptoms. Diagnosis includes clinical evaluation based on symptoms blood cultures, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, basic metabolic panel, and possibly imaging.
Lumbar puncture is the gold standard for identifying a person has meningitis and rule out other causes of infection. This fluid covers the brain and spinal cord. This test should be completed unless a person has increased pressure in the brain such as swelling in the optic nerve or altered mental status.
Computer tomography (CT) can be used if diagnosis is unclear and if a person has depressed mental status.
Diagnosis includes clinical evaluation based on symptoms blood cultures, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, basic metabolic panel, and possibly imaging.
Lumbar puncture is the gold standard for identifying a person has meningitis and rule out other causes of infection. This fluid covers the brain and spinal cord. This test should be completed unless a person has increased pressure in the brain such as swelling in the optic nerve or altered mental status.
Computer tomography (CT) can be used if diagnosis is unclear and if a person has depressed mental status.
Prevention
The most effective method of prevention is a vaccine against ''N. meningitidis''. Different countries have different strains of the bacteria and therefore use different vaccines. Twelve serogroups (strains) exist, with six having the potential to cause a major epidemic - A, B, C, X, Y and W135 are responsible for virtually all cases of the disease in humans. Vaccines are currently available against all six strains, including a newer vaccine against serogroup B. The first vaccine to prevent meningococcal serogroup B (meningitis B) disease was approved by theEuropean Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informall ...
on 22 January 2013.
Vaccines offer significant protection from three to five years (plain polysaccharide vaccine Menomune, Mencevax and NmVac-4) to more than eight years (conjugate vaccine Menactra).
Vaccinations
Children
Children 2–10 years of age who are at high risk for meningococcal disease such as certain chronic medical conditions and travel to or reside in countries with hyperendemic or epidemic meningococcal disease should receive primary immunization. Although safety and efficacy of the vaccine have not been established in children younger than 2 years of age and under outbreak control, the unconjugated vaccine can be considered.Adolescents
Primary immunization against meningococcal disease with meningitis A, C, Y and W-135 vaccines is recommended for all young adolescents at 11–12 years of age and all unvaccinated older adolescents at 15 years of age. Although conjugate vaccines are the preferred meningococcal vaccine in adolescents 11 years of age or older, polysaccharide vaccines are an acceptable alternative if the conjugated vaccine is unavailable.Adults
Primary immunization with meningitis A, C, Y and W-135 vaccines is recommended for college students who plan to live in dormitories, although the risk for meningococcal disease for college students 18–24 years of age is similar to that of the general population of similar age. Routine primary immunization against meningococcal disease is recommended for most adults living in areas where meningococcal disease is endemic or who are planning to travel to such areas. Although conjugate vaccines are the preferred meningococcal vaccine in adults 55 years of age or younger, polysaccharide vaccines are an acceptable alternative for adults in this age group if the conjugated vaccine is unavailable. Since safety and efficacy of conjugate vaccines in adults older than 55 years of age have not been established to date, polysaccharide vaccines should be used for primary immunization in this group.Medical staff
Health care people should receive routine immunization against meningococcal disease for laboratory personnel who are routinely exposed to isolates of ''N. meningitidis''. Laboratory personnel and medical staff are at risk of exposure to ''N. meningitides'' or to patients with meningococcal disease. Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee (HICPAC) recommendations regarding immunization of health-care workers that routine vaccination of health-care personnel is recommended, Any individual 11–55 years of age who wishes to reduce their risk of meningococcal disease may receive meningitis A, C, Y and W-135 vaccines and those older than 55 years of age. Under certain circumstances if unvaccinated health-care personnel cannot get vaccinated and who have intensive contact with oropharyngeal secretions of infected patients and who do not use proper precautions should receive anti-infective prophylaxis against meningococcal infection (i.e., 2-day regimen of oralrifampicin
Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires' disease. It is almost always used tog ...
or a single dose of IM ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joi ...
or a single dose of oral ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin ...
).
USA military recruits
Because the risk of meningococcal disease is increased among USA's military recruits, all military recruits routinely receive primary immunization against the disease.Travelers
Immunization against meningococcal disease is not a requirement for entry into any country, unlike yellow fever. OnlySaudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
requires that travelers to that country for the annual Hajj
Hajj (; ; also spelled Hadj, Haj or Haji) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for capable Muslims that must be carried out at least once in their lifetim ...
and Umrah
The Umrah () is an Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, the holiest city for Muslims, located in the Hejazi region of Saudi Arabia. It can be undertaken at any time of the year, in contrast to the '' Ḥajj'' (; "pilgrimage"), which has specific d ...
pilgrimage have a certificate of vaccination against meningococcal disease, issued not more than 3 years and not less than 10 days before arrival in Saudi Arabia.
Travelers to or residents of areas where ''N. meningitidis'' is highly endemic or epidemic are at risk of exposure should receive primary immunization against meningococcal disease.
HIV-infected individuals
HIV-infected individuals are likely to be at increased risk for meningococcal disease; HIV-infected individuals who wish to reduce their risk of meningococcal disease may receive primary immunization against meningococcal disease. Although efficacy of meningitis A, C, Y and W-135 vaccines have not been evaluated in HIV-infected individuals to date, HIV-infected individuals 11–55 years of age may receive primary immunization with the conjugated vaccine. Vaccination against meningitis does not decrease CD4+ T-cell counts or increase viral load in HIV-infected individuals, and there has been no evidence that the vaccines adversely affect survival.Janoff EN, Tasker S, Opstad NL et al. Impact of immunization of recent HIV-1 seroconverters. Proceedings of ICAAC New Orleans 1996. Abstract No. I60Close contacts
Protective levels of anticapsular antibodies are not achieved until 7–14 days following administration of a meningococcal vaccine, vaccination cannot prevent early onset disease in these contacts and usually is not recommended following sporadic cases of invasive meningococcal disease. Unlike developed countries, in sub-Saharan Africa and other under developed countries, entire families live in a single room of a house. Meningococcal infection is usually introduced into a household by an asymptomatic person. Carriage then spreads through the household, reaching infants usually after one or more other household members have been infected. Disease is most likely to occur in infants and young children who lack immunity to the strain of organism circulating and who subsequently acquire carriage of an invasive strain. Close contacts are defined as those persons who could have had intimate contact with the patient's oral secretions such as through kissing or sharing of food or drink. The importance of the carrier state in meningococcal disease is well known. In developed countries the disease transmission usually occurs in day care, schools and large gatherings where usually disease transmission could occur. Because the meningococcal organism is transmitted by respiratory droplets and is susceptible to drying, it has been postulated that close contact is necessary for transmission. Therefore, the disease transmission to other susceptible person cannot be prevented. Meningitis occurs sporadically throughout the year, and since the organism has no known reservoir outside of man, asymptomatic carriers are usually the source of transmission. Additionally, basichygiene
Hygiene is a set of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
measures, such as handwashing and not sharing drinking cups, can reduce the incidence of infection by limiting exposure. When a case is confirmed, all close contacts with the infected person can be offered antibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
to reduce the likelihood of the infection spreading to other people. However, rifampin-resistant strains have been reported and the indiscriminate use of antibiotics contributes to this problem. Chemoprophylaxis
Chemoprevention or chemoprophylaxis refers to the administration of a medication for the purpose of preventing disease or infection. Antibiotics, for example, may be administered to patients with disorders of immune system function to prevent bact ...
is commonly used to those close contacts who are at highest risk of carrying the pathogenic strains. Since vaccine duration is unknown, mass select vaccinations may be the most cost-effective means for controlling the transmission of the meningococcal disease, rather than mass routine vaccination schedules.
Chronic medical conditions
Persons with component deficiencies in the final common complement pathway (C3, C5-C9) are more susceptible to ''N. meningitidis'' infection than complement-satisfactory persons, and it was estimated that the risk of infection is 7000 times higher in such individuals. In addition, complement component-deficient populations frequently experience frequent meningococcal disease since their immune response to natural infection may be less complete than that of complement non-deficient persons. Inheritedproperdin deficiency
Properdin deficiency is a rare X-linked disease in which properdin, an important Complement system, complement factor responsible for the stabilization of the alternative C3 convertase, is deficient. There are three forms of properdin deficiencies ...
also is related, with an increased risk of contracting meningococcal disease. Persons with functional or anatomic asplenia may not efficiently clear encapsulated ''Neisseria meningitidis'' from the bloodstream Persons with other conditions associated with immunosuppression also may be at increased risk of developing meningococcal disease.
Antibiotics
An updated 2013Cochrane review
Cochrane is a British international charitable organisation formed to synthesize medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes ...
investigated the effectiveness of different antibiotics for prophylaxis against meningococcal disease and eradication of N. meningitidis particularly in people at risk of being carriers. The systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
included 24 studies with 6,885 participants. During follow up no cases of meningococcal disease were reported and thus true antibiotic preventative measures could not be directly assessed. However, the data suggested that rifampin
Rifampicin, also known as rifampin, is an ansamycin antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections, including tuberculosis (TB), ''Mycobacterium avium'' complex, leprosy, and Legionnaires' disease. It is almost always used tog ...
, ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joi ...
, ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin ...
and penicillin were equally effective for the eradication of ''N. meningitidis'' in potential carriers, although rifampin was associated with resistance to the antibiotic following treatment. Eighteen studies provided data on side effects and reported they were minimal but included nausea, abdominal pain, dizziness and pain at injection site.
Disease outbreak control
Meningitis A, C, Y and W-135 vaccines can be used for large-scale vaccination programs when an outbreak of meningococcal disease occurs in Africa and other regions of the world. Whenever sporadic or cluster cases or outbreaks of meningococcal disease occur in the US,chemoprophylaxis
Chemoprevention or chemoprophylaxis refers to the administration of a medication for the purpose of preventing disease or infection. Antibiotics, for example, may be administered to patients with disorders of immune system function to prevent bact ...
is the principal means of preventing secondary cases in household and other close contacts of individuals with invasive disease. Meningitis A, C, Y and W-135 vaccines rarely may be used as an adjunct to chemoprophylaxis,1 but only in situations where there is an ongoing risk of exposure (e.g., when cluster cases or outbreaks occur) and when a serogroup contained in the vaccine is involved.
It is important that clinicians promptly report all cases of suspected or confirmed meningococcal disease to local public health authorities and that the serogroup of the meningococcal strain involved be identified. The effectiveness of mass vaccination programs depends on early and accurate recognition of outbreaks. When a suspected outbreak of meningococcal disease occurs, public health authorities will then determine whether mass vaccinations (with or without mass chemoprophylaxis) is indicated and delineate the target population to be vaccinated based on risk assessment.
Treatment
 When meningococcal disease is suspected, treatment must be started ''immediately'' and should not be delayed while waiting for investigations. Treatment in primary care usually involves prompt intramuscular administration of
When meningococcal disease is suspected, treatment must be started ''immediately'' and should not be delayed while waiting for investigations. Treatment in primary care usually involves prompt intramuscular administration of benzylpenicillin
Benzylpenicillin, also known as penicillin G (PenG) or BENPEN, is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes pneumonia, strep throat, syphilis, necrotizing enterocolitis, diphtheria, gas gangrene, leptospiro ...
, and then an urgent transfer to hospital (hopefully, an academic level I medical center, or at least a hospital with round the clock neurological care, ideally with neurological intensive and critical care units) for further care. Once in the hospital, the antibiotics of choice are usually IV broad spectrum 3rd generation cephalosporins
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotic ...
, e.g., cefotaxime
Cefotaxime is an antibiotic used to treat several bacterial infections in humans, other animals, and plant tissue culture. Specifically in humans it is used to treat joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urin ...
or ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joi ...
. Benzylpenicillin and chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, pl ...
are also effective. Supportive measures include IV fluids, oxygen, inotropic support, e.g., dopamine or dobutamine and management of raised intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adu ...
. Steroid therapy may help in some adult patients, but is unlikely to affect long term outcomes.
There is some debate on which antibiotic is most effective at treating the illness. A systematic review
A systematic review is a scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from published studies on ...
compared two antibiotics. There was one trial: an open label (not blinded) non-inferiority trial of 510 people comparing two different types of antibiotics; ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone, sold under the brand name Rocephin, is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infections, endocarditis, meningitis, pneumonia, bone and joi ...
(in which there were 14 deaths out of 247), and chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, pl ...
(12 deaths out of 256). There were no reported side effects. Both antibiotics were considered equally effective. Antibiotic choice should be based on local antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resis ...
information.
Prognosis
Complications
Complications following meningococcal disease can be divided into early and late groups. Early complications include: raised intracranial pressure,disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition in which blood clots form throughout the body, blocking Microvessel, small blood vessels. Symptoms may include chest pain, shortness of breath, leg pain, problems speaking, or problems ...
, seizures, circulatory collapse and organ failure.
Later complications of meningococcal disease can be physical, neurological, or psychological. Physical effects, most commonly following meningococcal septicemia, may include limb malformation or amputation. These outcomes are more frequently observed in children who have experienced invasive meningococcal disease. Neurological complications, typically associated with meningococcal meningitis, can include hearing loss, cognitive impairments, and seizures. Psychological effects, observed in children, include post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and increased levels of anxiety.
Epidemiology
Africa
The importance of meningitis disease is as significant inAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
as HIV, TB and malaria. Cases of meningococcemia leading to severe meningoencephalitis
Meningoencephalitis (; from ; ; and the medical suffix ''-itis'', "inflammation"), also known as herpes meningoencephalitis, is a medical condition that simultaneously resembles both meningitis, which is an infection or inflammation of the mening ...
are common among young children and the elderly. Deaths occurring in less than 24 hours are more likely during the disease epidemic seasons in Africa and Sub-Saharan Africa is hit by meningitis disease outbreaks throughout the epidemic season. It may be that climate change contributes significantly the spread of the disease in Benin
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its po ...
, Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,87 ...
, Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
, the Central African Republic
The Central African Republic (CAR) is a landlocked country in Central Africa. It is bordered by Chad to Central African Republic–Chad border, the north, Sudan to Central African Republic–Sudan border, the northeast, South Sudan to Central ...
, Chad
Chad, officially the Republic of Chad, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North Africa, North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to Chad–Libya border, the north, Sudan to Chad–Sudan border, the east, the Central Afric ...
, Côte d'Ivoire
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire and officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital city of Yamoussoukro is located in the centre of the country, while its largest city and ...
, the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ...
, Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
, Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
and Togo
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to Ghana–Togo border, the west, Benin to Benin–Togo border, the east and Burkina Faso to Burkina Faso–Togo border, the north. It is one of the le ...
. This is an area of Africa where the disease is endemic: meningitis is "silently" present, and there are always a few cases. When the number of cases passes five per population of 100,000 in one week, teams are on alert. Epidemic levels are reached when there have been 100 cases per 100,000 populations over several weeks.
Further complicating efforts to halt the spread of meningitis in Africa is the fact that extremely dry, dusty weather conditions which characterize Niger and Burkina Faso from December to June favor the development of epidemics. Overcrowded villages are breeding grounds for bacterial transmission and lead to a high prevalence of respiratory tract infections, which leave the body more susceptible to infection, encouraging the spread of meningitis. IRIN Africa news has been providing the number of deaths for each country since 1995, and a mass vaccination campaign following a community outbreak of meningococcal disease in Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
was done by the CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
.
Florida
As of June 2022, there is an ongoing outbreak of the disease in Florida. The CDC has identified 26 cases of the disease. Seven deaths have been attributed to the disease.History and etymology
From theGreek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
''meninx'' (membrane) + ''kokkos'' (berry), meningococcal disease was first described by Gaspard Vieusseux during an outbreak in Geneva
Geneva ( , ; ) ; ; . is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland and the most populous in French-speaking Romandy. Situated in the southwest of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the ca ...
in 1805. In 1884, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
pathologists Ettore Marchiafava
Ettore Marchiafava (3 January 1847 – 22 October 1935) was an Italian physician, pathologist and neurologist. He spent most of his career as professor of medicine at the University of Rome (now Sapienza Università di Roma). His works on malar ...
and Angelo Celli described intracellular micrococci in cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, transcellular body fluid found within the meninges, meningeal tissue that surrounds the vertebrate brain and spinal cord, and in the ventricular system, ven ...
, and in 1887, Anton Wiechselbaum
Anton may refer to: People
*Anton (given name), a list of people with the given name
*Anton (surname), a list of people with the surname
Places
*Anton Municipality, Bulgaria
**Anton, Sofia Province, a village
*Antón District, Panama
**Antón, ...
identified the meningococcus (designated as ''Diplococcus intracellularis meningitidis'') in cerebrospinal fluid and established the connection between the organism and epidemic meningitis.
See also
*Endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, o ...
* Pathogenic bacteria
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and many are Probiotic, beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The nu ...
* Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome
Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome (WFS) is defined as adrenal gland failure due to hemorrhages in the adrenal glands, commonly caused by sepsis. Typically, the bacteria responsible for triggering the bleeding is '' Neisseria meningitidis''.
The ...
* African meningitis belt
* 2009–10 West African meningitis outbreak
* Meningococcal vaccine
Meningococcal vaccine refers to any vaccine used to prevent infection by '' Neisseria meningitidis''. Different versions are effective against some or all of the following types of meningococcus: A, B, C, W-135, and Y. The vaccines are between ...
* Meningitis Vaccine Project
References
Further reading
*External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Meningococcal Disease Bacterial diseases Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions Causes of amputation Sepsis Vaccine-preventable diseases