Megali Idea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
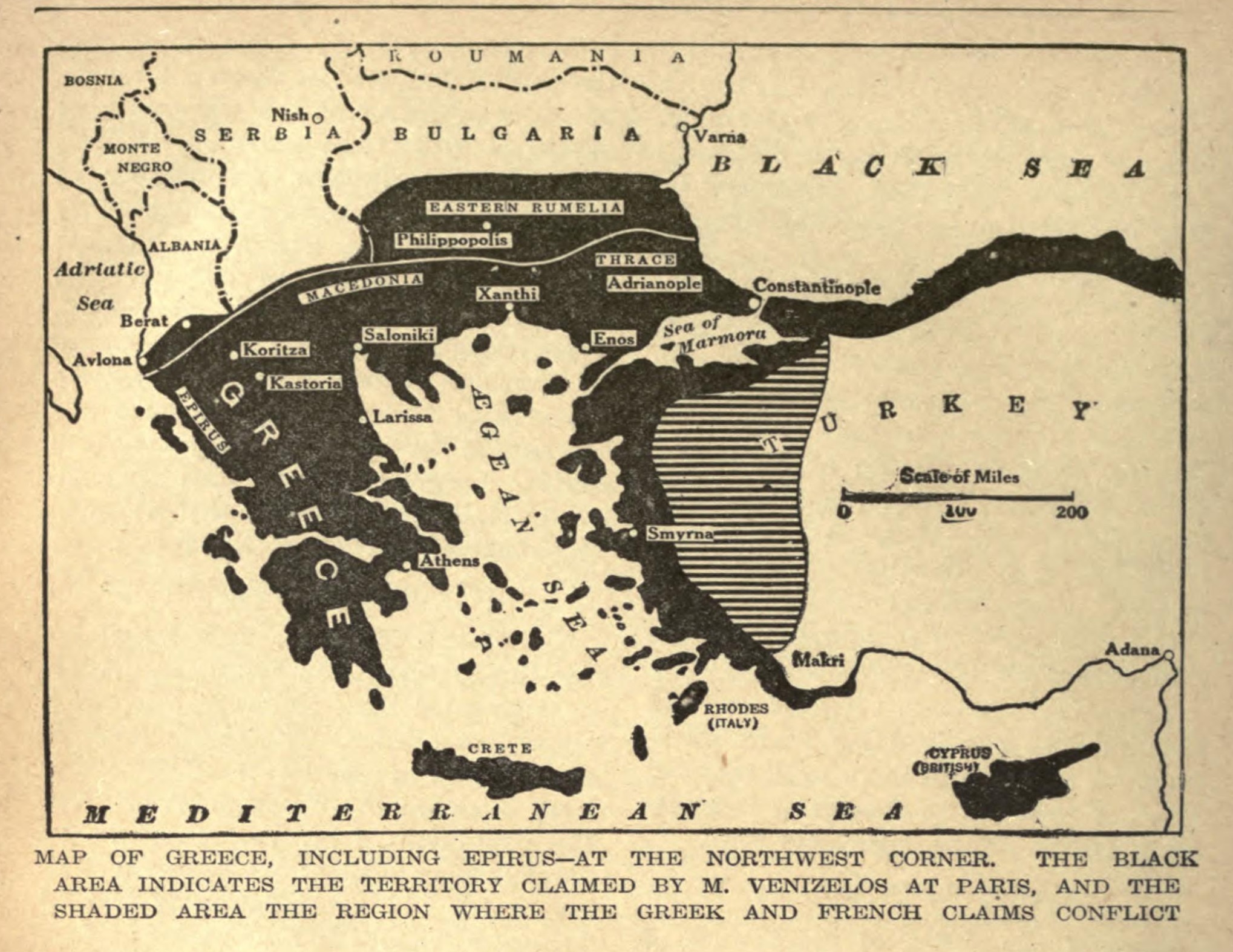
 The Megali Idea () is a
The Megali Idea () is a
Encyclopædia Britannica Online It came to dominate foreign relations and played a significant role in domestic politics for much of the first century of Greek independence. The expression was new in 1844 but the concept had roots in the Greek popular psyche, which long had hopes of liberation from Ottoman rule and restoration of the Byzantine Empire.
 The
The

 A major proponent of the Megali Idea was
A major proponent of the Megali Idea was
 Greece's efforts to take control of Smyrna in accordance with the Treaty of Sèvres were thwarted by
Greece's efforts to take control of Smyrna in accordance with the Treaty of Sèvres were thwarted by
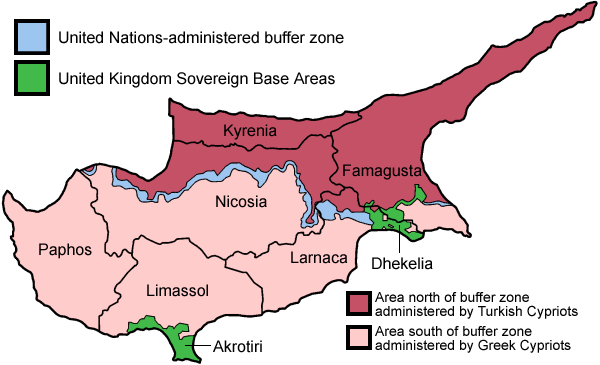 The Zürich Agreement of 1959 culminated in independence of the island with Greece, Turkey and UK as guarantee powers. The inter-ethnic clashes from 1960 led to the dispatch of a peacekeeping force of the
The Zürich Agreement of 1959 culminated in independence of the island with Greece, Turkey and UK as guarantee powers. The inter-ethnic clashes from 1960 led to the dispatch of a peacekeeping force of the

 The Megali Idea () is a
The Megali Idea () is a nationalist
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation,Anthony D. Smith, Smith, A ...
and irredentist
Irredentism () is one state's desire to annex the territory of another state. This desire can be motivated by ethnic reasons because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to or the same as the population of the parent state. Hist ...
concept that expresses the goal of reviving the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, by establishing a Greek state, which would include the large Greek populations that were still under Ottoman rule after the end of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
(1821–1829) and all the regions that had large Greek populations (parts of the southern Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
, Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
).
The term appeared for the first time during the debates of Prime Minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
Ioannis Kolettis with King Otto that preceded the promulgation of the 1844 constitution.''History of Greece''Encyclopædia Britannica Online It came to dominate foreign relations and played a significant role in domestic politics for much of the first century of Greek independence. The expression was new in 1844 but the concept had roots in the Greek popular psyche, which long had hopes of liberation from Ottoman rule and restoration of the Byzantine Empire.
Πάλι με χρόνια με καιρούς, :πάλι δικά μας θα 'ναι! (''Once more, as years and time go by, once more they shall be ours'').D. Bolukbasi and D. Bölükbaşı, ''Turkey And Greece: The Aegean Disputes'', Routledge Cavendish 2004The Megali Idea implies establishing a Greek state, which would be a territory encompassing mostly the former Byzantine lands from the
Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea (, ; or , ; , ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including Basilicata, Calabria, Sicily, and the Salento peninsula to the west, ...
in the west to Anatolia and the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
to the east and from Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
, Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
and Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
in the north to Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
and Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
to the south. This new state would have Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
as its capital: it would be the "Greece of Two Continents and Five Seas" (Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
and Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, the Ionian, Aegean, Marmara, Black and Libyan Seas). If realized, this would expand modern Greece to roughly the same size and extent of the later Byzantine Empire, after its restoration in 1261 AD.
The Megali Idea dominated foreign policy and domestic politics of Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
from the War of Independence
Wars of national liberation, also called wars of independence or wars of liberation, are conflicts fought by nations to gain independence. The term is used in conjunction with wars against foreign powers (or at least those perceived as foreign) ...
in the 1820s through the Balkan wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans, Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Montenegro, M ...
in the beginning of the 20th century. It started to fade after the Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922), followed by the population exchange between Greece and Turkey in 1923. Despite the end of the Megali Idea project in 1922, by then the Greek state had expanded four times, either through military conquest or diplomacy (often with British support). After the creation of Greece in 1830, it acquired the Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands (Modern Greek: , ; Ancient Greek, Katharevousa: , ) are a archipelago, group of islands in the Ionian Sea, west of mainland Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese ("Seven Islands"; , ''Heptanēsa'' or , ''Heptanē ...
( Treaty of London, 1864), Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
(Convention of Constantinople (1881)
The Convention of Constantinople was signed between the Kingdom of Greece and the Ottoman Empire on 2 July 1881, resulting in the cession of the region of Thessaly (apart from Elassona) and a part of southern Epirus (the Arta Prefecture) to Gre ...
), Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
, Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, (southern) Epirus and the Eastern Aegean Islands ( Treaty of Bucharest), and Western Thrace ( Treaty of Neuilly, 1920). The Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; , ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger and 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. This island group generally define ...
were acquired after the Second World War ( Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947).
A related concept is ''enosis
''Enosis'' (, , "union") is an irredentist ideology held by various Greek communities living outside Greece that calls for them and the regions that they inhabit to be incorporated into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea ...
''.
Fall of Constantinople
 The
The Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
was Eastern Roman in origin and was called the "Roman Empire" by its inhabitants, though often not by the Latin West, which regarded it as Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
. After its fall, Hieronymus Wolf popularized the usage of "Byzantium". An informal cultural division had existed within the Roman Empire for centuries. Although Latin was the official language of the empire, Greek was the lingua franca in the East and was regularly used alongside Latin in official business. The division of the Empire following the death of Emperor Theodosius in AD 395 added a formal political layer to the informal cultural division. Following the adoption of Christianity in the 4th century, Greek was also the dominant liturgical language, as exemplified by the fact the New Testament was written in Greek. These factors ultimately led to Greek replacing Latin as the official language in AD 620.
Byzantium held out against numerous invasions over the centuries and during the 10th and early 11th centuries managed to reclaim considerable territory in the Balkans, Anatolia and to a lesser extent Syria. The Turkish invasion of the mid to late 11th century however greatly weakened the Empire and, although it partially recovered under the Komnenos dynasty
The House of Komnenos ( Komnenoi; , , ), Latinized as Comnenus ( Comneni), was a Byzantine Greek noble family who ruled the Byzantine Empire in the 11th and 12th centuries. The first reigning member, Isaac I Komnenos, ruled from 1057 to 1059. T ...
, it never managed to regain control of the Anatolian interior, cutting the empire off from a valuable source of manpower and tax revenue. In 1204 Constantinople was besieged and sacked during the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
and became the Capital of what has come to be known as the Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantin ...
, a French dominated crusader state, until it was liberated by the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea (), also known as the Nicene Empire, was the largest of the three Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by Walter Abel Heurtley, W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C ...
, the Byzantine state in exile, in 1261. However, Byzantine strength would rapidly diminish towards the end of the 13th century and evaporated almost entirely during the 14th century, to the extent that by 1400 little remained of the Empire except Constantinople, the city’s immediate surroundings and some small territories in modern-day Greece. In 1453 the Ottoman Turks besieged and captured Constantinople officially marking the end of the Roman Empire and also the end of Greek predominance in the city; although it would continue to have a considerable Greek speaking population and the Patriarch of Constantinople continued to reside in the city.
Greeks under Ottoman rule
Under the ''millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most millets belong to the tribe Paniceae.
Millets are important crops in the Semi-arid climate, ...
'' system which was in force during the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, the population was classified according to religion rather than language or ethnicity. Orthodox Greeks were seen as part of the ''millet-i Rûm'' (literally "Roman community") which included all Orthodox Christians, including beside Greeks also Bulgarians
Bulgarians (, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and its neighbouring region, who share a common Bulgarian ancestry, culture, history and language. They form the majority of the population in Bulgaria, ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
, Vlachs
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula ...
, Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
, Georgians
Georgians, or Kartvelians (; ka, ქართველები, tr, ), are a nation and Peoples of the Caucasus, Caucasian ethnic group native to present-day Georgia (country), Georgia and surrounding areas historically associated with the Ge ...
, Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
and Albanians
The Albanians are an ethnic group native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, Albanian culture, culture, Albanian history, history and Albanian language, language. They are the main ethnic group of Albania and Kosovo, ...
, despite their differences in ethnicity and language and despite the fact that the religious hierarchy was Greek dominated. It is not clear to what extent one can speak of a Greek identity during those times as opposed to a Christian or Orthodox identity. In the late 1780s, Catherine II of Russia
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
and Joseph II of Austria intended to reclaim the Byzantine heritage and restore the Greek statehood as part of their joint Greek Plan.
During the Middle Ages and the Ottoman period, Greek-speaking Christians identified as ''Romans'' and thought of themselves as the descendants of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
(including the medieval Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
). The term ''Roman'' was often interpreted as synonymous with ''Christian'' throughout Europe and the Mediterranean during this time. The terms ''Greek'' or ''Hellene'' were largely seen by Ottoman Christians as referring to the ancient pagan peoples of the region. This changed during the late stages of the Ottoman Empire and the emergence of the Greek independence movement.
For much of the period of the '' Tourkokratia'', the Russians were viewed by the Greeks as the ''xanthon genos'', a fair-haired race and the sole Orthodox power that would liberate Constantinople from the Ottomans. The Greek legend of the ''xanthon genos'' eventually liberating Constantinople was also referenced in the 15th-century '' Tale on the Taking of Tsargrad'', which itself was widely circulated in Russia between the 16th and 18th centuries.
Greek War of Independence and later
After theGreek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
ended in 1829, a new southern Greek state was established, with assistance from the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
, Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from th ...
, and Imperial Russia
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor/empress, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* ...
. However, this new Greek state under John Capodistrias after the Greek War of Independence was, with Serbia, one of the only two countries of the era whose population was smaller than the population of the same ethnicity outside its borders; most ethnic Greeks still resided within the borders of the Ottoman Empire. This version of Greece was designed by the Great Powers, who had no desire to see a larger Greek state replace the Ottoman Empire.
The Great Idea embodied a desire to bring all ethnic Greeks into the Greek state, and subsequently revive the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
; it applied specifically to the Greeks in Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
, Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
, Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
, the Aegean Islands, Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
, parts of Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, and the city of Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
(which would replace Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
as the capital).
When the young Danish prince Wilhelm Georg was elected king in 1863, the title offered to him by the Greek National Assembly was ''not'' "King of Greece", the title of his deposed predecessor, King Otto; but rather "King of ''the Hellenes''". Implicit in the wording was that George I was to be king of all Greeks, regardless of whether they then lived within the borders of his new kingdom.
The first additional areas to be incorporated into the Kingdom were the Ionian islands
The Ionian Islands (Modern Greek: , ; Ancient Greek, Katharevousa: , ) are a archipelago, group of islands in the Ionian Sea, west of mainland Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese ("Seven Islands"; , ''Heptanēsa'' or , ''Heptanē ...
in 1864, and later Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
with the 1878 Treaty of Berlin.
Revolts, Cretan crisis and Greco-Turkish War (1897)
In January 1897, violence and disorder were escalating in Crete, polarizing the population. Massacres of the Christian population took place in Chania and Rethimno. The Greek government, pressured by public opinion, intransigent political elements, extreme nationalist groups (e.g. Ethniki Etairia) and with the Great Powers reluctant to intervene, decided to send warships and personnel to assist the Cretans. The Great Powers had no option then but to proceed with the occupation of the island, but they were too late. A Greek force of 1,500 men had landed at Kolymbari on 1 February 1897, and its commanding officer, ColonelTimoleon Vassos
Timoleon Vassos or Vasos ( or Βάσος; 1836–1929) was a Hellenic Army officer and general.
He was born in Athens in 1836, the younger son of the hero of the Greek Revolution Vasos Mavrovouniotis. He studied at the Hellenic Military Academ ...
, declared that he was taking over the island "in the name of the King of the Hellenes" and that he was announcing the union of Crete with Greece. This led to an uprising that spread immediately throughout the island. The Great Powers finally decided to land their troops and stopped the Greek army force from approaching Chania. At the same time their fleets blockaded Crete, preventing both Greeks and Turks from bringing any more troops to the island.
The Ottoman Empire, in reaction to the rebellion of Crete and the assistance sent by Greece, relocated a significant part of its army in the Balkans to the north of Thessaly, close to the borders with Greece. Greece in reply reinforced its borders in Thessaly. However, irregular Greek forces and followers of the Megali Idea acted without orders and raided Turkish outposts, leading the Ottoman Empire to declare war on Greece; the war is known as the Greco-Turkish War of 1897
The Greco-Turkish War of 1897 or the Ottoman-Greek War of 1897 ( or ), also called the Thirty Days' War and known in Greece as the Black '97 (, ''Mauro '97'') or the Unfortunate War (), was a war fought between the Kingdom of Greece and the O ...
. The Turkish army, far outnumbering the Greek, was also better prepared, due to the recent reforms carried out by a German mission under Baron von der Goltz. The Greek army fell back in retreat. The other Great Powers then intervened and an armistice was signed in May 1897. The war, however, only ended in December of that year.
The military failure in the Greco-Turkish war cost Greece small territorial losses along the border line in northern Thessaly, and a large sum of financial reparations that wrecked Greece's economy for years, while giving no lasting solution to the Cretan Question. The Great Powers (Britain, France, Russia, and Italy) in order to prevent future clashes and trying to avoid the creation of a revanchist climate in Greece, imposed what they thought of as a lasting solution; Crete was proclaimed an autonomous '' Cretan State''. The four Great Powers assumed the administration of Crete; and, in a decisive diplomatic victory for Greece, Prince George of Greece (second son of King George I) became High Commissioner.
Early 20th century
Balkan Wars

 A major proponent of the Megali Idea was
A major proponent of the Megali Idea was Eleftherios Venizelos
Eleftherios Kyriakou Venizelos (, ; – 18 March 1936) was a Cretan State, Cretan Greeks, Greek statesman and prominent leader of the Greek national liberation movement. As the leader of the Liberal Party (Greece), Liberal Party, Venizelos ser ...
, under whose leadership Greek territory doubled in the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans, Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Montenegro, M ...
of 1912–13 — southern Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, Lesbos
Lesbos or Lesvos ( ) is a Greek island located in the northeastern Aegean Sea. It has an area of , with approximately of coastline, making it the third largest island in Greece and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, eighth largest ...
, Chios
Chios (; , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greece, Greek list of islands of Greece, island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea, and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, tenth largest island in the Medi ...
, Ikaria, Samos
Samos (, also ; , ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese archipelago, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the Mycale Strait. It is also a separate reg ...
, Samothrace, Lemnos
Lemnos ( ) or Limnos ( ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos (regional unit), Lemnos regional unit, which is part of the North Aegean modern regions of Greece ...
and the majority of Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
were attached to Greece. Born and raised in Crete, in 1909 Venizelos was already a prominent Cretan and had influence in mainland Greece. As such, he was invited after the Goudi coup in 1909 by the Military League to become Prime Minister of Greece. Venizelos pressed forward a series of reforms in society, as well as the military and administration, which helped Greece succeed in its goals during the Balkan Wars.
World War I
Following the Greek gains in the Balkan Wars, the Ottomans began to persecute ethnic Greeks living in the Empire, which led toethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, or religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making the society ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal such as deportation or population transfer, it ...
in the Greek genocide. This persecution continued into World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
when the Ottomans declared for the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,; ; , ; were one of the two main coalitions that fought in World War I (1914–1918). It consisted of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulga ...
on late 1914. Greece remained neutral until 1917 when they joined the Allies. Refugees reports of Turkish atrocities as well as the Allied victory in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
seemed to promise an even greater realization of the Megali Idea. Greece gained a foothold in Asia Minor with a protectorate over Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; , or ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna ...
and its hinterland. Following 5 years of Greek administration, a referendum was to be held to determine whether the territory would revert to Ottoman control or join Greece. Greece also gained the islands of Imbros and Tenedos
Tenedos (, ''Tenedhos''; ), or Bozcaada in Turkish language, Turkish, is an island of Turkey in the northeastern part of the Aegean Sea. Administratively, the island constitutes the Bozcaada, Çanakkale, Bozcaada district of Çanakkale Provinc ...
, Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Eastern Thrace
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace, also known as Turkish Thrace or European Turkey, is the part of Turkey that is geographically in Southeast Europe. Turkish Thrace accounts for 3.03% of Turkey's land area and 15% of its population. The largest c ...
, the border then drawn a few miles from the walls of Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
.
Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)
 Greece's efforts to take control of Smyrna in accordance with the Treaty of Sèvres were thwarted by
Greece's efforts to take control of Smyrna in accordance with the Treaty of Sèvres were thwarted by Turkish revolutionaries
The Turkish National Movement (), also known as the Anatolian Movement (), the Nationalist Movement (), and the Kemalists (, ''Kemalciler'' or ''Kemalistler''), included political and military activities of the Turkish revolutionaries that resu ...
, who were resisting the Allies. The Turks finally prevailed and expelled the Greeks from Anatolia during the Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922) (part of the Turkish War of Independence
, strength1 = May 1919: 35,000November 1920: 86,000Turkish General Staff, ''Türk İstiklal Harbinde Batı Cephesi'', Edition II, Part 2, Ankara 1999, p. 225August 1922: 271,000Celâl Erikan, Rıdvan Akın: ''Kurtuluş Savaşı tarih ...
). The war was concluded by the Treaty of Lausanne which saw Greece cede Eastern Thrace, Imbros, Tenedos and Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; , or ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna ...
to the nascent Turkish Republic. To avoid any further territorial claims, both Greece and Turkey engaged in an " exchange of populations": During the conflict, 151,892 Greeks had already fled Asia Minor. The Treaty of Lausanne moved 1,104,216 Greeks from Turkey, while 380,000 Turks left the Greek territory for Turkey. The transfers ended any further appetite for pursuing the concept of a Greater Greece and ended the 3000 year Greek habitation of Asia Minor. Further population exchanges occurred after World War I, including 40,027 Greeks from Bulgaria, 58,522 from Russia (because of the defeat of the White Army led by Pyotr Wrangel) and 10,080 from other lands (for example Dodecanese
The Dodecanese (, ; , ''Dodekánisa'' , ) are a group of 15 larger and 150 smaller Greek islands in the southeastern Aegean Sea and Eastern Mediterranean, off the coast of Anatolia, of which 26 are inhabited. This island group generally define ...
or Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
), while 70,000 Bulgarians from Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
and Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
had moved to Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
. From the Bulgarian refugees ca. 66,000 were from Greek Macedonia.
The immediate reception of refugees to Greece cost 45 million francs, so the League of Nations arranged for a loan of 150 million francs to aid settlement of refugees. In 1930, Venizelos even went on an official visit to Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, where he proposed that Mustafa Kemal be awarded the Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize (Swedish language, Swedish and ) is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the Will and testament, will of Sweden, Swedish industrialist, inventor, and armaments manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Nobe ...
.
The Greek novelist Yiorgos Theotokas described the psychological impact of the defeat of 1922:"For a short time, while the Treaty of Serves ran its joyful but uncertain course, it seemed to them that the...long-buried hopes of their ancestors were to be fulfilled. But the terrible summer of 1922 came all too soon. From the hermitage of Arsenios they watched, tense with anxiety, the daily unfolding of the national tragedy, the last desperate efforts of the Royalist Governments of Greece to save the situation, the failure of King Constantine's attempt to take Constantinople, and the final Catastrophe.
In mid-August Mustapha Kemal broke through the Greek front and the Greek army, exhausted by ten years of warfare and the privations of the Asia Minor campaign, was vanquished in two weeks. The Turks, advancing rapidly, recaptured in quick succession Afion-Karahisar, Eski-Shehir, Kiutahia, Brussa, Oushak—and then Smyrna! Once again the banners of Islam floated proudly, tauntingly, over the Aegean coast opposite Chios and Mytilene. The whole of Ionia was in flames. Slaughter and pillage descended on the smiling city of Smyrna and in a few short days turned it into a ruin...As day succeeded day, Greece seemed to have become paralyzed, to have lost all will, all ability to resist the blows of fate. The swiftness of the catastrophe completely overwhelmed the State, flooded as it was by the thousands of fleeting soldiers and refugees who sought shelter on the Greek coasts.The nation was plunged into deep despair...
Greece had lost her big gamble and had been uprooted from Asia Minor. St. Sophia remained in the hands of the Moslems. The brilliant plans of 1918 were mocking visions, hallucinations, dreams. And the return of reality was truly heartbreaking. The tale of the years was not yet told, then, the historic hour, the fulfillment of the Great Idea, the moment they had longed for with such faith and such anxiety for five tortured, bloody centuries, had not yet come! It was all a lie!"
World War II, annexation of Dodecanese and Cyprus dispute
Although the Great Idea ceased to be a driving force behind Greek foreign policy, some remnants continued to influence Greek foreign policy throughout the remainder of the 20th century. Thus, after his coup d'état of 4 August 1936,Ioannis Metaxas
Ioannis Metaxas (; 12 April 187129 January 1941) was a Greek military officer and politician who was dictator of Greece from 1936 until his death in 1941. He governed constitutionally for the first four months of his tenure, and thereafter as th ...
proclaimed the advent of the "Third Hellenic Civilization", similar to Adolf Hitler's Third Reich (influenced by pan-Germanism
Pan-Germanism ( or '), also occasionally known as Pan-Germanicism, is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanism seeks to unify all ethnic Germans, German-speaking people, and possibly also non-German Germanic peoples – into a sin ...
). The attack by Italy from Albania and the Greek victories enabled Greece to conquer, during the winter of 1940–1941, parts of southern Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
(Northern Epirus
Northern Epirus (, ; ) is a term used for specific parts of southern Albania which were first claimed by the Kingdom of Greece in the Balkan Wars and later were associated with the Greek minority in Albania and Greece-Albania diplomatic relation ...
, as it is identified by Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
) which were administered as a province of Greece for a short time until the German offensive of April 1941.
The occupation, resistance and the civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
initially put the Great Idea in the background. Nevertheless, another very good diplomatic performance by the Greek side at the Paris Peace Conference, 1946 secured a further enlargement of Greek territory, in the form of the Dodecanese Islands, despite the very strong opposition of Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov (; – 8 November 1986) was a Soviet politician, diplomat, and revolutionary who was a leading figure in the government of the Soviet Union from the 1920s to the 1950s, as one of Joseph Stalin's closest allies. ...
and the Soviet delegates.
The British colony of Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
became the "apple of discord" between the two countries, putting an end to the positive Greco-Turkish relations that had existed since the Kemal-Venizelos agreement in the 1930s. In 1955, a Greek army colonel of Greek Cypriot origin, George Grivas, began a campaign of civil disobedience whose purpose was primarily to drive the British from the island, then move for ''Enosis
''Enosis'' (, , "union") is an irredentist ideology held by various Greek communities living outside Greece that calls for them and the regions that they inhabit to be incorporated into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea ...
'' with Greece. The Greek prime minister, Alexandros Papagos, was not unfavourable to this idea. There was increasing polarisation of opinion between the dominant Greek population and the minority Turks.
The problems in Cyprus affected the continent itself. In September 1955, in response to the demand for ''Énosis'', an anti-Greek riot took place in Istanbul. During the Istanbul Pogrom
The Istanbul pogrom, also known as the Istanbul riots, were a series of state-sponsored anti-Greek mob attacks directed primarily at Istanbul's Greek minority on 6–7 September 1955. The pogrom was orchestrated by the governing Democrat ...
4,000 stores, 100 hotels and restaurants and 70 churches were destroyed or damaged. This led to the last great wave of migration from Turkey to Greece.
 The Zürich Agreement of 1959 culminated in independence of the island with Greece, Turkey and UK as guarantee powers. The inter-ethnic clashes from 1960 led to the dispatch of a peacekeeping force of the
The Zürich Agreement of 1959 culminated in independence of the island with Greece, Turkey and UK as guarantee powers. The inter-ethnic clashes from 1960 led to the dispatch of a peacekeeping force of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
in 1964.
The Cyprus issue was revived by the dictatorship of the colonels, who presented their April 21, 1967, ''coup d'état'' as the only way to defend the traditional values of what they called the "Hellenic-Christian Civilization".
Brigadier General Ioannidis arranged, in July 1974, to overthrow Cypriot President Archbishop
In Christian denominations, an archbishop is a bishop of higher rank or office. In most cases, such as the Catholic Church, there are many archbishops who either have jurisdiction over an ecclesiastical province in addition to their own archdi ...
Makarios Macarius is a Latinized form of the old Greek given name Makários (Μακάριος), meaning "happy, fortunate, blessed"; compare the Latin ''beatus'' and ''felix''. Ancient Greeks applied the epithet ''Makarios'' to the gods.
In other la ...
, and proceed with ''Enosis
''Enosis'' (, , "union") is an irredentist ideology held by various Greek communities living outside Greece that calls for them and the regions that they inhabit to be incorporated into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea ...
'' (union with Greece). This led to Turkey invading the island in response, with the expulsion of Greek Cypriots in areas controlled by Turkey, and the flight of Turkish Cypriots from the south. In 1983, the north declared independence and to this day, Turkey is the only country that recognizes Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus, officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, island of Cyprus. It is List of states with limited recognition, recognis ...
.
Attempted revival by Golden Dawn
The ultra-nationalist Golden Dawn party, which had electoral support from 2010 to 2019, supports the Megali Idea, with party leader, Nikolaos Michaloliakos stating: Michaloliakos criticizedThessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area) and the capital cit ...
mayor Yiannis Boutaris for wanting to name a street after Atatürk, who was born in the city when it was still part of the Ottoman Empire.
In January 2013, a group of Golden Dawn supporters attacked the car of Turkish consul-general Osman İlhan Şener and hurled insults at Atatürk, during an anti-Turkey protest in Komotini.
Mihaloliakos has also called for the "liberation" of Northern Epirus. Golden Dawn and its former Cypriot counterpart ELAM
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
support enosis.
In 2015, close to 100 Golden Dawn members and leaders were arrested on a range of charges, including murder and racketeering. In 2019, the party's level of support, slumped to less than 2%. In October 2020, most of Golden Dawn's leadership was convicted, including Michaloliakos. As of 2023, the party, which never enjoyed electoral support above 10% of the popular vote, now has no remaining members in either the Hellenic or European Parliament.Gatopoulos, Derek; Becatoros, Elena (7 October 2020). "Greek court rules Golden Dawn party criminal organization". Associated Press. Retrieved January 3, 2020.
See also
*Greek diaspora
The Greek diaspora, also known as Omogenia (), are the communities of Greeks living outside of Greece and Cyprus.
Such places historically (dating to the ancient period) include, Greeks in Albania, Albania, Greeks in North Macedonia, North Maced ...
* Northern Epirus
Northern Epirus (, ; ) is a term used for specific parts of southern Albania which were first claimed by the Kingdom of Greece in the Balkan Wars and later were associated with the Greek minority in Albania and Greece-Albania diplomatic relation ...
* Autonomous Republic of Northern Epirus
* Occupation of Constantinople
* Irredentism
Irredentism () is one State (polity), state's desire to Annexation, annex the territory of another state. This desire can be motivated by Ethnicity, ethnic reasons because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to or the same as the ...
* Zone of Smyrna
* Republic of Pontus
The Republic of Pontus (, ''Dimokratía tou Póntou'') was a proposed Pontic Greek state on the southern coast of the Black Sea. Its territory would have encompassed much of historical Pontus in north-eastern Asia Minor, and today forms part of T ...
* Georgios Grivas
* Foreign relations of Greece
As one of the oldest Euro-Atlantic member states in the region of Southeast Europe, Greece enjoys a prominent geopolitical role as a middle power, due to its political and geographical proximity to Europe. Greece maintains strong relations with ...
* Succession of the Roman Empire
The continuation, succession, and revival of the Roman Empire is a running theme of the history of Europe and the Mediterranean Basin. It reflects the lasting memories of power, prestige, and unity associated with the Roman Empire.
Several pol ...
References
Sources
* {{Stateless nationalism in Europe National unifications Foreign relations of Greece Greece–Turkey relations History of modern Greece 19th century in the Ottoman Empire Greek nationalism Nationalist movements in Europe Pan-nationalism Political history of Greece Political movements of the Ottoman Empire