Measuring Rod on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A measuring rod is a tool used to physically measure lengths and survey areas of various sizes. Most measuring rods are round or square sectioned; however, they can also be flat boards. Some have markings at regular intervals. It is likely that the measuring rod was used before the line, chain or steel tapes used in modern measurement.
A measuring rod is a tool used to physically measure lengths and survey areas of various sizes. Most measuring rods are round or square sectioned; however, they can also be flat boards. Some have markings at regular intervals. It is likely that the measuring rod was used before the line, chain or steel tapes used in modern measurement.

 Cubit-rods of wood or stone were used in Ancient Egypt. Fourteen of these were described and compared by Lepsius in 1865.
Cubit-rods of wood or stone were used in Ancient Egypt. Fourteen of these were described and compared by Lepsius in 1865.
 Large public works and imperial expansion, particularly the large network of
Large public works and imperial expansion, particularly the large network of
 Two statues of
Two statues of

 A measuring rod is a tool used to physically measure lengths and survey areas of various sizes. Most measuring rods are round or square sectioned; however, they can also be flat boards. Some have markings at regular intervals. It is likely that the measuring rod was used before the line, chain or steel tapes used in modern measurement.
A measuring rod is a tool used to physically measure lengths and survey areas of various sizes. Most measuring rods are round or square sectioned; however, they can also be flat boards. Some have markings at regular intervals. It is likely that the measuring rod was used before the line, chain or steel tapes used in modern measurement.
History
Ancient Sumer
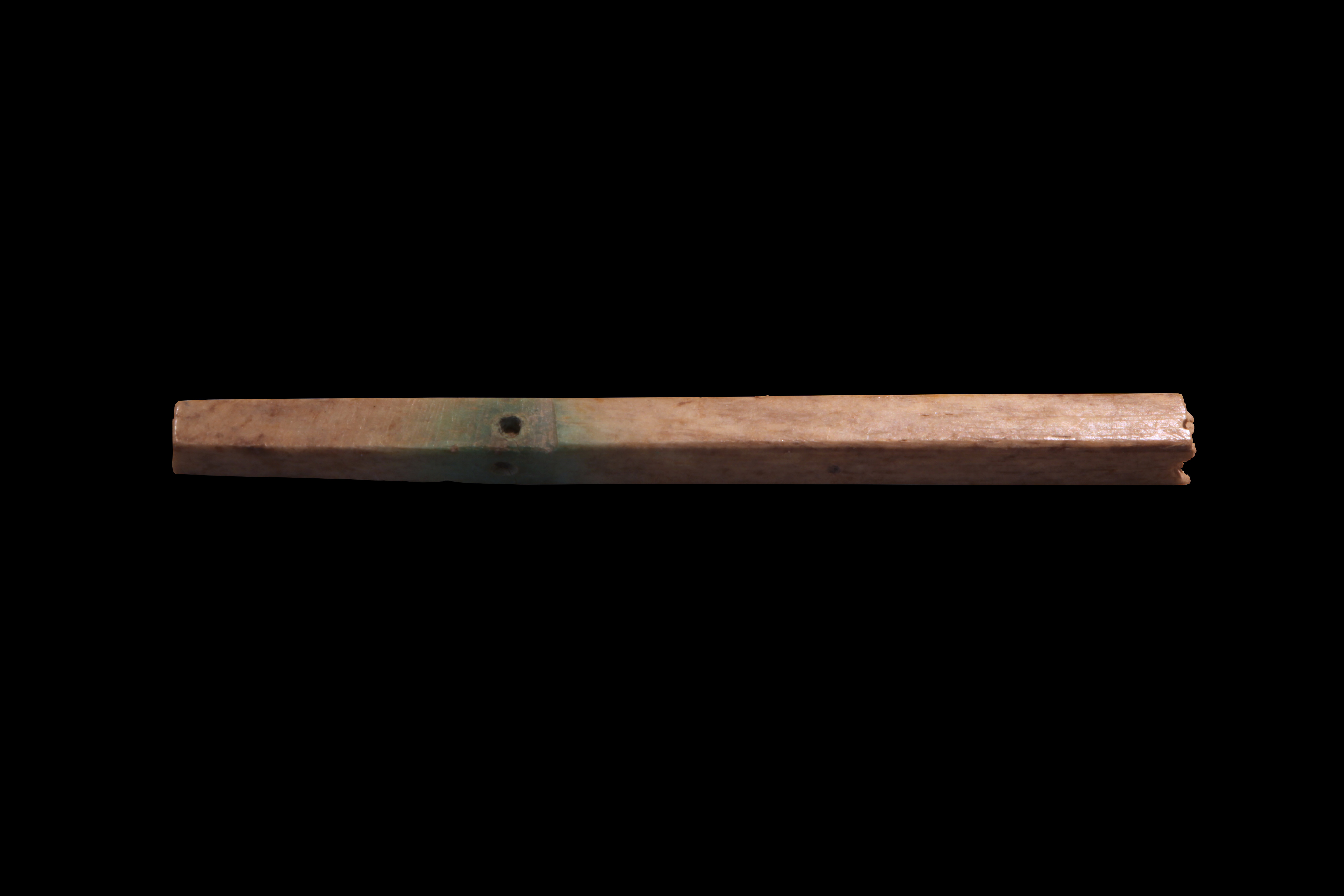
The oldest preserved measuring rod is acopper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
-alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
bar which was found by the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
Assyriologist
Assyriology (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ''Assyriā''; and , ''-logy, -logia''), also known as Cuneiform studies or Ancient Near East studies, is the archaeological, anthropological, historical, and linguistic study of the cultures that used cune ...
Eckhard Unger
Eckhard Unger ( Landsberg an der Warthe, 11 April 1884 – 24 July 1966) was a German assyriologist.
Unger who was the curator of the Istanbul museum described the remains of Balawat Gates that are still in the Istanbul Museum. Unger was fully ...
while excavating at Nippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"I. E. S. Edwards, C. J. Gadd, N. G. L. Hammond, ''The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory'': Vol. 1, Part 1, Ca ...
(pictured below). The bar dates from c. 2650 BC. and Unger claimed it was used as a measurement standard. This irregularly formed and irregularly marked ''graduated rule'' supposedly defined the ''Sumerian cubit'' as about , although this does not agree with other evidence from the statues of Gudea
Gudea ( Sumerian: , ''Gu3-de2-a''; died 2124 BC) was a Sumerian ruler ('' ensi'') of the state of Lagash in Southern Mesopotamia, who ruled –2060 BC ( short chronology) or 2144–2124 BC ( middle chronology). He probably did not come from the ...
from the same region, five centuries later.
Ancient India
Rulers made from ivory were in use by the Indus Valley Civilization in what today is Pakistan, and in some parts of Western India prior to 1500 BCE. Excavations at Lothal dating to 2400 BCE have yielded one such ruler calibrated to about Ian Whitelaw (2007) holds that 'The Mohenjo-Daro ruler is divided into units corresponding to and these are marked out in decimal subdivisions with remarkable accuracy—to within . Ancient bricks found throughout the region have dimensions that correspond to these units.' The sum total of ten graduations from Lothal is approximate to the angula in the Arthashastra.Ancient East Asia
Measuring rods for different purposes and sizes (construction, tailoring and land survey) have been found from China and elsewhere dating to the early 2nd millennium B.C.E.Ancient Egypt
 Cubit-rods of wood or stone were used in Ancient Egypt. Fourteen of these were described and compared by Lepsius in 1865.
Cubit-rods of wood or stone were used in Ancient Egypt. Fourteen of these were described and compared by Lepsius in 1865. Flinders Petrie
Sir William Matthew Flinders Petrie ( – ), commonly known as simply Sir Flinders Petrie, was an English people, English Egyptology, Egyptologist and a pioneer of systematic methodology in archaeology and the preservation of artefacts. ...
reported on a rod that shows a length of 520.5 mm, a few millimetres less than the Egyptian cubit
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term ''cubit'' is found in the Bible regarding Noah ...
. A slate measuring rod was also found, divided into fractions of a Royal Cubit and dating to the time of Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton ( ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning 'Effective for the Aten'), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eig ...
.
Further cubit rods have been found in the tombs of officials. Two examples are known from the tomb of Maya
Maya may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Mayan languages, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (East Africa), a p ...
—the treasurer of the 18th dynasty
The Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt (notated Dynasty XVIII, alternatively 18th Dynasty or Dynasty 18) is classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. The Eighteenth Dynasty ...
pharaoh Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun or Tutankhamen, (; ), was an Egyptian pharaoh who ruled during the late Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt. Born Tutankhaten, he instituted the restoration of the traditional polytheistic form of an ...
—in Saqqara
Saqqara ( : saqqāra ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in the markaz (county) of Badrashin in the Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for ...
. Another was found in the tomb of Kha (TT8
The tomb of Kha and Merit, also known by its tomb number Theban Tomb 8 or TT8, is the funerary chapel and burial place of the ancient Egyptian foreman Kha and his wife Merit, in the northern cemetery of the workmen's village of Deir el-Medin ...
) in Thebes. These cubits are ca long and are divided into seven palms, each palm is divided into four fingers and the fingers are further subdivided.Marshall Clagett, Ancient Egyptian Science, A Source Book. Volume Three: Ancient Egyptian Mathematics, American Philosophical Society, 1999 Another wooden cubit rod was found in Theban tomb TT40
The Theban Tomb TT40 is located in Qurnet Murai, part of the Theban Necropolis, on the west bank of the Nile, opposite to Luxor. It is the burial place of the ancient Egyptian Viceroy of Kush named Amenhotep called Huy, who lived during the ...
(Huy) bearing the throne name of Tutankhamun (Nebkheperure).
Egyptian measuring rods also had marks for the Remen measurement of approximately , used in construction of the Pyramids
A pyramid () is a Nonbuilding structure, structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a Pyramid (geometry), pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid ca ...
.
Ancient Europe
Anoak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
rod from the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
fortified settlement at Borre Fen
Borremose is a raised bog in central Himmerland, Denmark south east of the town of Aars. The name translates directly as 'Borre'-bog, where 'Borre' might well be a derivation of the old word ''burgh'' meaning fortified place, as seen in many other ...
in Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
measured , with marks dividing it up into eight parts of , corresponding quite closely to half a Doric Pous
The pous ( podes; , ''poús'') or Greek foot ( feet) was a Greek unit of length of approximately 300mm or 12 inches. It had various subdivisions whose lengths varied by place and over time. 100 podes made up one plethron, 600 podes made ...
(a Greek foot). A hazel
Hazels are plants of the genus ''Corylus'' of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family, Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K ...
measuring rod recovered from a Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
burial mound in Borum Eshøj
Borum is a village in Aarhus Municipality, Central Denmark Region in Denmark. Borum is situated 2.5 kilometres south of Sabro and 3 kilometres west of the Aarhus suburb of Tilst and has a population of 308 (1 January 2024). About 2 kilometres wes ...
, East Jutland by P. V. Glob
Peter Vilhelm Glob (20 February 1911 – 20 July 1985), also known as P. V. Glob, was a Denmark, Danish archaeologist.
Glob was most noted for his investigations of Denmark's bog body, bog bodies such as the Tollund Man and Grauballe Man, mummifi ...
in 1875 measured corresponding remarkably well to the traditional Danish foot. The megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging geographically f ...
ic structures of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
has been hypothesized to have been built by a " Megalithic Yard", though some authorities believe these structures have been measured out by pacing. Several tentative Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
bone fragments have been suggested as being parts of a measuring rod for this hypothetical measurement.
Roman Empire
 Large public works and imperial expansion, particularly the large network of
Large public works and imperial expansion, particularly the large network of Roman roads
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Em ...
and the many milecastle
A milecastle was a small fort (fortlet), a rectangular fortification built during the period of the Roman Empire. They were placed at intervals of approximately one Roman mile along several major frontiers, for example Hadrian's Wall in Great Br ...
s, made the measuring rod an indispensable part of both the military and civilian aspects of Roman life. Republican Rome
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of classical Roman civilisation beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War o ...
used several measures, including the various Greek feet measurements and the Oscan foot of 27.5 cm. Standardisation was introduced by Agrippa
Agrippa may refer to:
People Antiquity
* Agrippa (mythology), semi-mythological king of Alba Longa
* Agrippa (astronomer), Greek astronomer from the late 1st century
* Agrippa the Skeptic, Skeptic philosopher at the end of the 1st century
* Ag ...
in 29 BC, replacing all previous measurements by a Roman foot
The units of measurement of ancient Rome were generally consistent and well documented.
Length
The basic unit of Roman linear measurement was the ''pes'' (plural: ''pedes'') or Roman foot. Investigation of its relation to the English units#Leng ...
of 29.6 cm, which became the foot of Imperial Rome
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Romans conquered most of this during the Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC ...
.
The Roman measuring rod was 10 Roman feet long, and hence called a ''decempeda'', Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for 'ten-footer'. It was usually of square section capped at both ends by a metal shoe, and painted in alternating colours. Together with the '' groma'' and ''dioptra
A dioptra (sometimes also named dioptre or diopter, from ) is a classical astronomical and surveying instrument, dating from the 3rd century BC. The dioptra was a sighting tube or, alternatively, a rod with a sight at both ends, attached ...
'', the ''decempeda'' formed the basic kit for the Roman surveyors. The measuring rod is frequently found depicted in Roman art showing the surveyors at work. A shorter folding yardstick
A metre-stick, metrestick (or meter-stick and meterstick as alternative spellings); or yardstick is either a straightedge or foldable ruler used to Measurement, measure length, and is especially common in the construction industry. They are of ...
one Roman foot long is known from excavations of a Roman fort in Niederburg, Germany.
Middle Ages
In theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, bars were used as standards of length when surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the land, terrestrial Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional or Three-dimensional space#In Euclidean geometry, three-dimensional positions of Point (geom ...
land.
These bars often used a unit of measure called a rod, of length
Length is a measure of distance. In the International System of Quantities, length is a quantity with Dimension (physical quantity), dimension distance. In most systems of measurement a Base unit (measurement), base unit for length is chosen, ...
equal to 5.5 yard
The yard (symbol: yd) is an English units, English unit of length in both the British imperial units, imperial and US United States customary units, customary systems of measurement equalling 3 foot (unit), feet or 36 inches. Sinc ...
s, 5.0292 metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
s, 16.5 feet
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of ...
, or of a statute mile
The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of length; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English ...
. A rod is the same length as a ''perch
Perch is a common name for freshwater fish from the genus ''Perca'', which belongs to the family Percidae of the large order Perciformes. The name comes from , meaning the type species of this genus, the European perch (''P. fluviatilis'') ...
'' or a ''pole''. In Old English, the term ''lug'' is also used. The length is equal to the standardized length of the ox goad
The goad is a traditional farming implement, used to spur or guide livestock, usually oxen, which are pulling a plow or a cart; used also to round up cattle. It is a type of long stick with a pointed end, also known as the cattle prod.
The wo ...
used for teams of eight oxen by medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
English ploughmen. The lengths of the perch (one rod unit) and ''chain
A chain is a serial assembly of connected pieces, called links, typically made of metal, with an overall character similar to that of a rope in that it is flexible and curved in compression but linear, rigid, and load-bearing in tension. A ...
'' (four rods) were standardized in 1607 by Edmund Gunter
Edmund Gunter (158110 December 1626), was an English clergyman, mathematician, geometer and astronomer of Welsh descent. He is best remembered for his mathematical contributions, which include the invention of the Gunter's chain, the #Gunter's q ...
. The rod unit was still in use as a common unit of measurement in the mid-19th century, when Henry David Thoreau
Henry David Thoreau (born David Henry Thoreau; July 12, 1817May 6, 1862) was an American naturalist, essayist, poet, and philosopher. A leading Transcendentalism, transcendentalist, he is best known for his book ''Walden'', a reflection upon sim ...
used it frequently when describing distances in his work ''Walden
''Walden'' (; first published as ''Walden; or, Life in the Woods'') is an 1854 book by American transcendentalism, transcendentalist writer Henry David Thoreau. The text is a reflection upon the author's simple living in natural surroundings. T ...
''.
In culture
Iconography
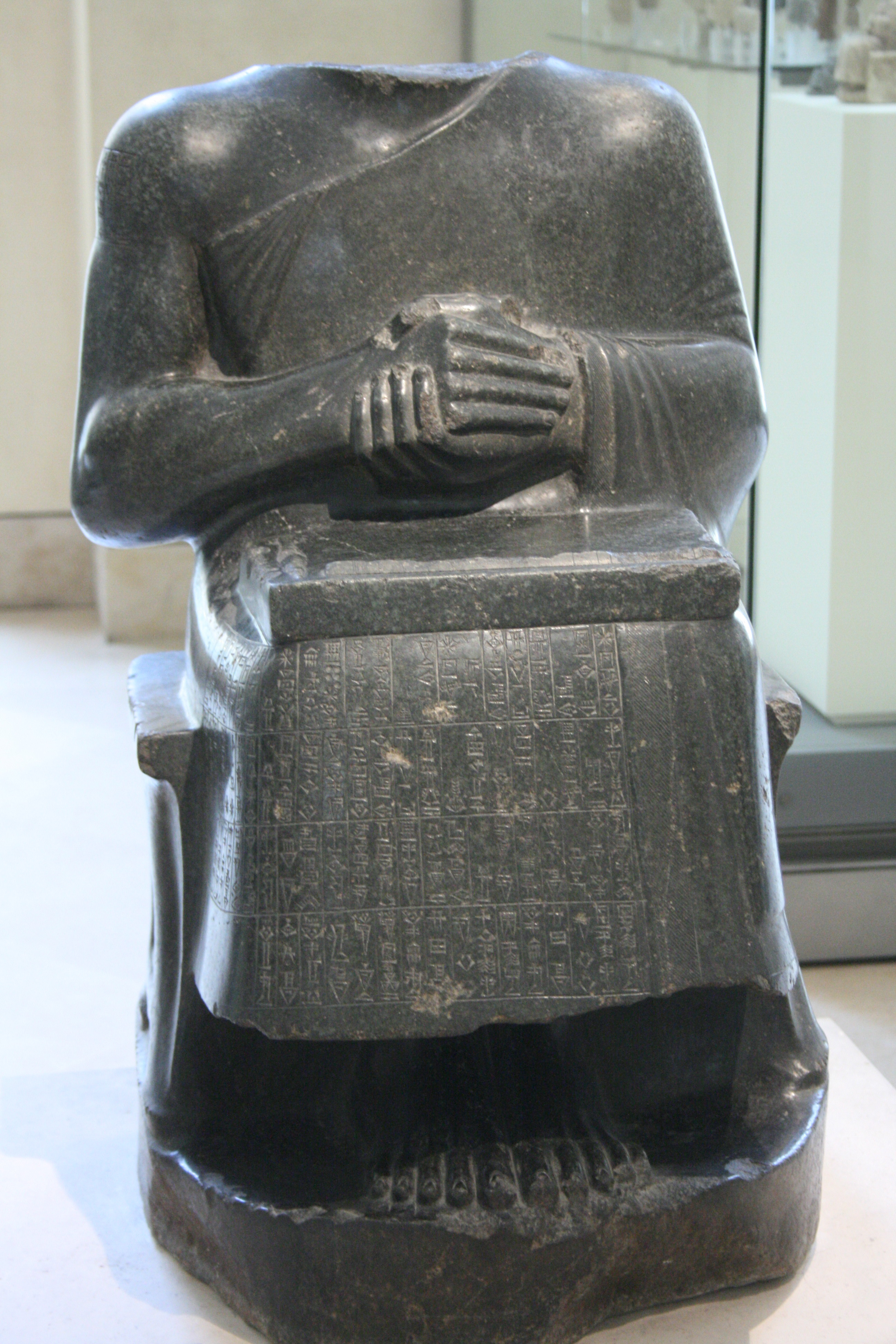
 Two statues of
Two statues of Gudea of Lagash
Gudea (Sumerian language, Sumerian: , ''Gu3-de2-a''; died 2124 BC) was a Sumer, Sumerian ruler (''Ensí, ensi'') of the state of Lagash in Southern Mesopotamia, who ruled –2060 BC (short chronology) or 2144–2124 BC (middle chronology). He pr ...
in the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arron ...
depict him sitting with a tablet on his lap, upon which are placed surveyors tools including a measuring rod.
Seal 154 recovered from Alalakh
Alalakh (''Tell Atchana''; Hittite: Alalaḫ) is an ancient archaeological site approximately northeast of Antakya (historic Antioch) in what is now Turkey's Hatay Province. It flourished as an urban settlement in the Middle and Late Bronze Age ...
, now in the Biblioteque Nationale show a seated figure with a wedge shaped measuring rod.
The Tablet of Shamash
The Tablet of Shamash (also known as the Sun God Tablet or the Nabuapaliddina Tablet) is a stele recovered from the ancient Babylonian city of Sippar in southern Iraq in 1881; it is now a major piece in the British Museum's ancient Middle East co ...
recovered from the ancient Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
ian city of Sippar
Sippar (Sumerian language, Sumerian: , Zimbir) (also Sippir or Sippara) was an ancient Near Eastern Sumerian and later Babylonian city on the east bank of the Euphrates river. Its ''Tell (archaeology), tell'' is located at the site of modern Tell ...
and dated to the 9th century BC shows Shamash
Shamash (Akkadian language, Akkadian: ''šamaš''), also known as Utu (Sumerian language, Sumerian: dutu "Sun") was the List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian Solar deity, sun god. He was believed to see everything that happened in t ...
, the Sun God awarding the measuring rod and coiled rope to newly trained surveyor
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the terrestrial two-dimensional or three-dimensional positions of points and the distances and angles between them. These points are usually on the ...
s.
A similar scene with measuring rod and coiled rope is shown on the top part of the diorite
Diorite ( ) is an intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock formed by the slow cooling underground of magma (molten rock) that has a moderate content of silica and a relatively low content of alkali metals. It is Intermediate composition, inter ...
stele
A stele ( ) or stela ( )The plural in English is sometimes stelai ( ) based on direct transliteration of the Greek, sometimes stelae or stelæ ( ) based on the inflection of Greek nouns in Latin, and sometimes anglicized to steles ( ) or stela ...
above the Code of Hammurabi
The Code of Hammurabi is a Babylonian legal text composed during 1755–1750 BC. It is the longest, best-organized, and best-preserved legal text from the ancient Near East. It is written in the Old Babylonian dialect of Akkadian language, Akkadi ...
in the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arron ...
, Paris, dating to ca. 1700 BC.
The "measuring rod" or tally stick
A tally stick (or simply a tally) was an ancient memory aid used to record and document numbers, quantities, and messages. Tally sticks first appear as animal bones carved with notches during the Upper Palaeolithic; a notable example is the Is ...
is common in the iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
Goddess Nemesis
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Nemesis (; ) also called Rhamnousia (or Rhamnusia; ), was the goddess who personified retribution for the sin of hubris: arrogance before the gods.
Etymology
The name ''Nemesis'' is derived from the Greek ...
.
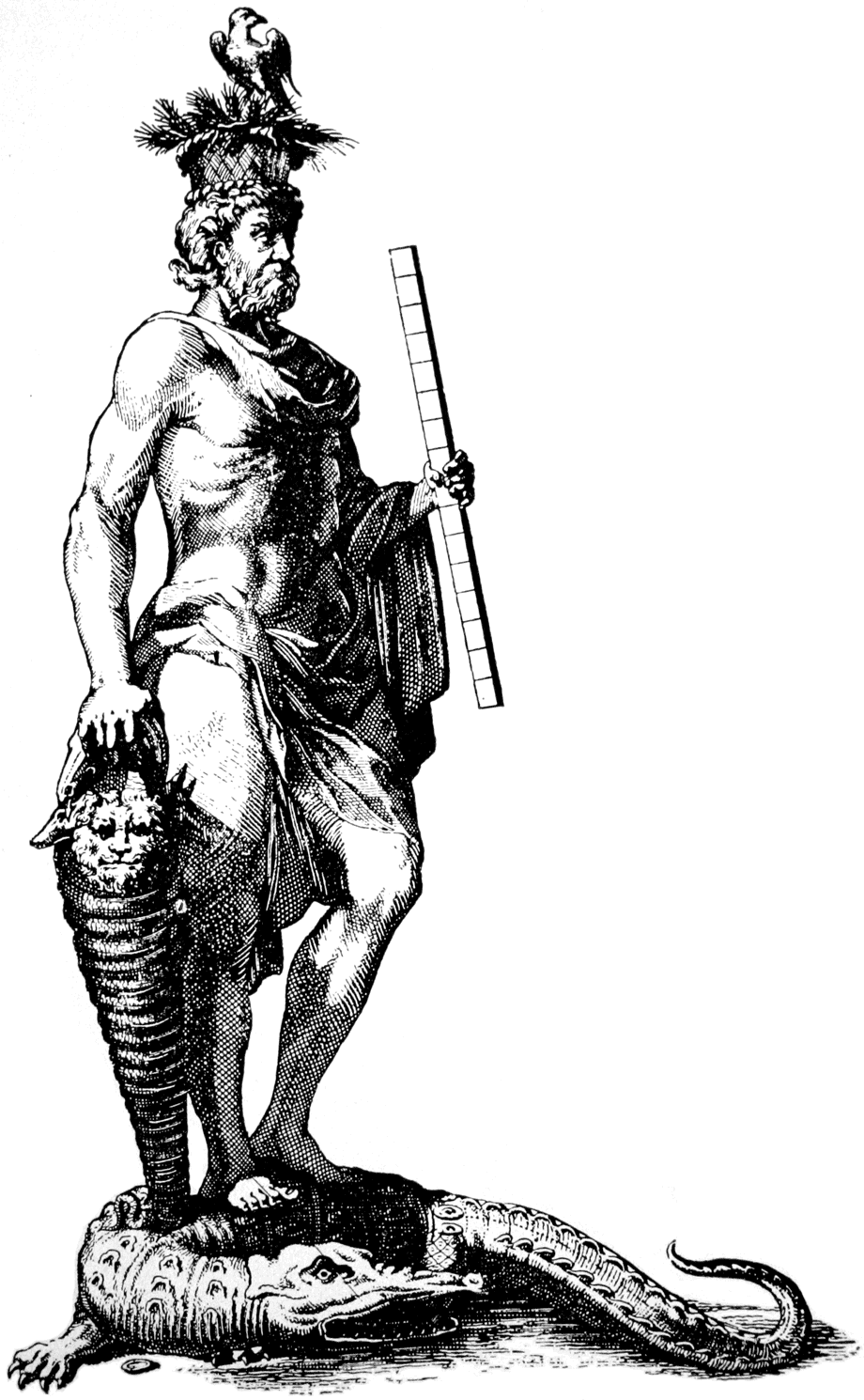
The Graeco-Egyptian God Serapis
Serapis or Sarapis is a Egyptian Greeks, Graeco-Egyptian god. A Religious syncretism, syncretic deity derived from the worship of the Egyptian Osiris and Apis (deity), Apis, Serapis was extensively popularized in the third century BC on the ord ...
is also depicted in images and on coins with a measuring rod in hand and a vessel on his head.
The most elaborate depiction is found on the Ur-Nammu
Ur-Nammu (or Ur-Namma, Ur-Engur, Ur-Gur, Sumerian language, Sumerian: ; died 2094 BC) founded the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur, in southern Mesopotamia, following several centuries of Akkadian Empire, Akkadian and Gutian period, Gutian rule. Thou ...
-stela, where the winding of the cords has been detailed by the sculptor. This has also been described as a "staff and a chaplet of beads".
Mythology
The myth ofInanna
Inanna is the List of Mesopotamian deities, ancient Mesopotamian goddess of war, love, and fertility. She is also associated with political power, divine law, sensuality, and procreation. Originally worshipped in Sumer, she was known by the Akk ...
's descent to the nether world describes how the goddess dresses and prepares herself:
Lachesis
Lachesis ( ; ; from , 'to obtain by lot, by fate, or by the will of the gods'), in ancient Greek religion, was the middle of the Three Fates, or Moirai; the others were her sisters, Clotho and Atropos. Normally seen clothed in white, Laches ...
in Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories conc ...
was one of the three Moirai
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, the Moirai ()often known in English as the Fateswere the personifications of fate, destiny. They were three sisters: Clotho (the spinner), Lachesis (mythology), Lachesis (the allotter ...
(or Fates) and "allotter" (or drawer of lots). She measured the thread of life allotted to each person with her measuring rod. Her Roman equivalent was '' Decima'' (the 'Tenth').
Varuna
Varuna (; , ) is a Hindu god. He is one of the earliest deities in pantheon, whose role underwent a significant transformation from the Vedic to the Puranic periods. In the early Vedic era, Varuna is seen as the god-sovereign, ruling the sky ...
in the Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
, is described as using the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
as a measuring rod to lay out space in a creation myth
A creation myth or cosmogonic myth is a type of cosmogony, a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it., "Creation myths are symbolic stories describing how the universe and its inhabitants came to be. Cre ...
. W. R. Lethaby has commented on how the measurers were seen as solar deities and noted how Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
''"measured the regions of the Earth"''.
Bible
Measuring rods or reeds are mentioned several times in theBible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
. In the Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Isr ...
or Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' Yahweh Yahweh was an Ancient Semitic religion, ancient Semitic deity of Weather god, weather and List of war deities, war in the History of the ancient Levant, ancient Levant, the national god of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Judah, Judah and Kingdom ...
in . '' Yahweh Yahweh was an Ancient Semitic religion, ancient Semitic deity of Weather god, weather and List of war deities, war in the History of the ancient Levant, ancient Levant, the national god of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Judah, Judah and Kingdom ...
Ezekiel
Ezekiel, also spelled Ezechiel (; ; ), was an Israelite priest. The Book of Ezekiel, relating his visions and acts, is named after him.
The Abrahamic religions acknowledge Ezekiel as a prophet. According to the narrative, Ezekiel prophesied ...
40:2-3: One of the eight visions seen by the prophet Zechariah involves a man with a measuring line.: NKJV
The New King James Version (NKJV) is a translation of the Bible in contemporary English, working as a revision of the King James Version. Published by Thomas Nelson, the complete NKJV was released in 1982. With regard to its textual basis, the ...
(English verse numbering)
In the New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianit ...
, Revelation
Revelation, or divine revelation, is the disclosing of some form of Religious views on truth, truth or Knowledge#Religion, knowledge through communication with a deity (god) or other supernatural entity or entities in the view of religion and t ...
11:1 says that the author:
The measuring rod also appears in connection with foundation stone
A cornerstone (or foundation stone or setting stone) is the first stone set in the construction of a masonry Foundation (engineering), foundation. All other stones will be set in reference to this stone, thus determining the position of the entir ...
rites in Revelation
Revelation, or divine revelation, is the disclosing of some form of Religious views on truth, truth or Knowledge#Religion, knowledge through communication with a deity (god) or other supernatural entity or entities in the view of religion and t ...
21:14-15:
See also
*Ancient Egyptian units of measurement The ancient Egyptian units of measurement are those used by the dynasties of ancient Egypt prior to its incorporation in the Roman Empire and general adoption of Roman, Greek, and Byzantine units of measurement. The units of length seem to have o ...
* Ancient Greek units of measurement Ancient Greek units of measurement varied according to location and epoch. Systems of ancient weights and measures evolved as needs changed; Solon and other lawgivers also reformed them ''en bloc''. Some units of measurement were found to be conven ...
* Ancient Mesopotamian units of measurement
Ancient Mesopotamian units of measurement originated in the loosely organized city-states of Early Dynastic Sumer. Each city, kingdom and trade guild had its own standards until the formation of the Akkadian Empire when Sargon of Akkad issued ...
* Distance measurement
Length measurement, distance measurement, or range measurement (ranging) all refer to the many ways in which length, distance, or range can be measured. The most commonly used approaches are the rulers, followed by transit-time methods and the ...
* Levelling rod
Levelling or leveling (American English; see spelling differences) is a branch of surveying, the object of which is to establish or verify or measure the height of specified points relative to a datum. It is widely used in geodesy and cartogra ...
* Rod (unit)
The rod, perch, or pole (sometimes also lug) is a surveyor's tool and unit of length of various historical definitions. In British imperial and US customary units, it is defined as feet, equal to exactly of a mile, or yards (a quarter ...
* Rod-and-ring symbol
* Ruler
A ruler, sometimes called a rule, scale, line gauge, or metre/meter stick, is an instrument used to make length measurements, whereby a length is read from a series of markings called "rules" along an edge of the device. Usually, the instr ...
* Shen ring
In ancient Egypt, a shen ring was a circle with a line tangent to it, represented in hieroglyphs as a stylised loop of a rope, bound to a stick. The tool used by builders and architects. Shen rings can most often be seen in the clutches of Horu ...
* Surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the land, terrestrial Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional or Three-dimensional space#In Euclidean geometry, three-dimensional positions of Point (geom ...
* Units of measurement
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other qua ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Measuring Rod Length, distance, or range measuring devices Hand tools Ancient technology Surveying instruments