|
Roman Roads
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of Military history of ancient Rome, armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and Roman commerce, trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, Bridle path, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
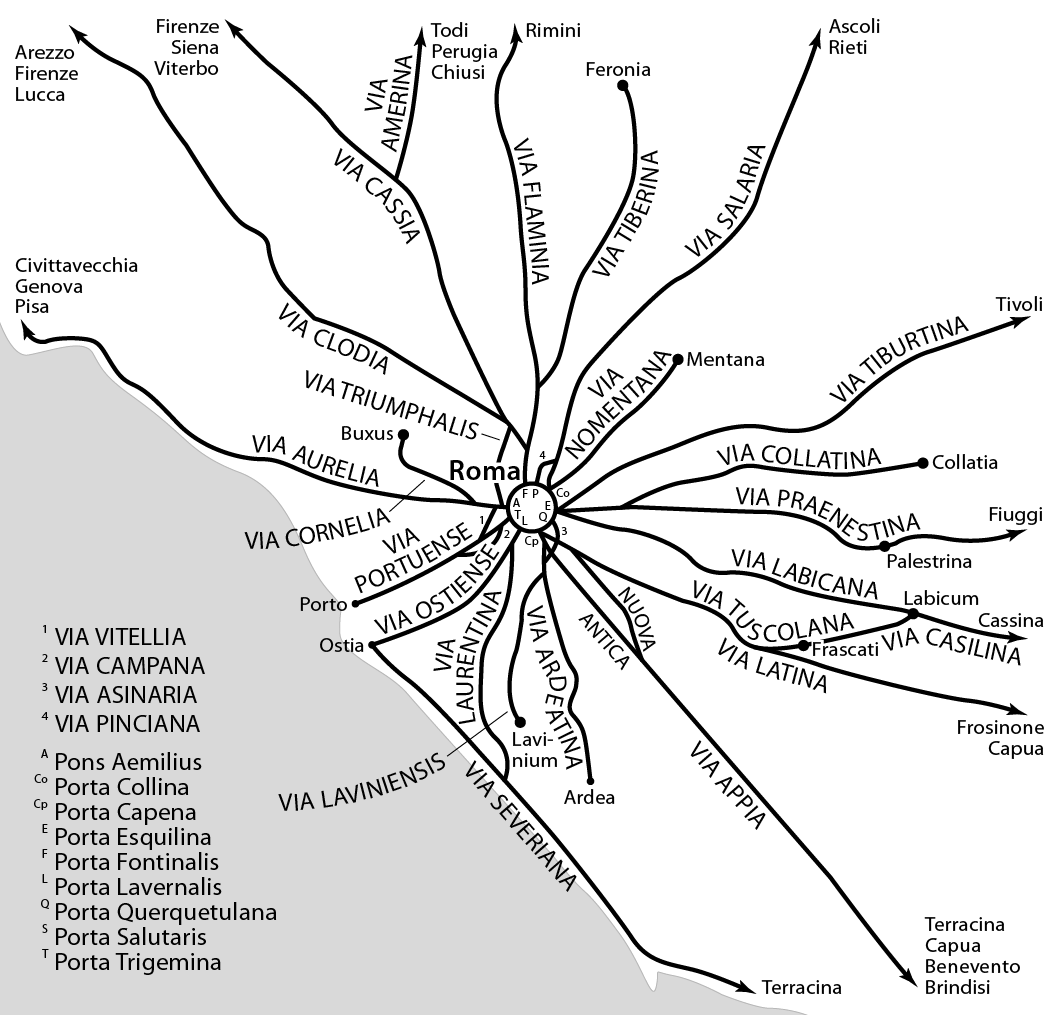
Roman Roads Around Rome
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of Roman civilization *Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter written by Paul, found in the New Testament of the Christian Bible *Ar-Rum (), the 30th sura of the Quran. Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music *Romans (band), a Japanese pop group *Roman (album), ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 *Roman (EP), ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *"Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio *Roman (film), ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film *Romans (2013 film), ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film *Romans (2017 film), ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film *The Romans (Doctor Who), ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
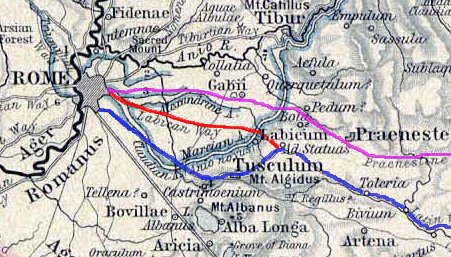
Via Praenestina
The Via Praenestina (modern Italian: Via Prenestina) was an ancient Roman road in central Italy. Initially called Via Gabiana, from Gabii, the ancient city of Old Latium to which it ran, it received a new name having been extended as far as Praeneste (modern Palestrina). Once past Praeneste the road continued towards the Apennines and the source of the Anio River. At the ninth mile the road crosses a ravine by the well-preserved and lofty Ponte di Nona, with seven arches, the finest ancient bridge in the neighbourhood of Rome. The line of the road is, considering the difficulty of the country beyond Gabii, very straight. Half-way between Gabii and Praeneste is a well-preserved single-arched bridge, Ponte Amato. Ashby cites his own contribution to ''Papers of the British School at Rome'', i. 149 sqq. References Roman roads in Italy, Praenestina Rome Q. VII Prenestino-Labicano Rome Q. VI Tiburtino Rome Q. XIX Prenestino-Centocelle Rome Q. XXII Collatino Rome Q. XXII ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Trackway
Historic roads (or historic trails in the US and Canada) are paths or routes that have historical importance due to their use over a period of time. Examples exist from prehistoric times until the early 20th century. They include ancient trackways, long-lasting roads, important trade routes, and migration trails. Many historic routes, such as the Silk Road, the Amber Road, and the Royal Road of the Persian Empire, covered great distances and their impact on human settlements remain today. The Post Track, a prehistoric causeway in the valley of the River Brue in the Somerset Levels, England, is one of the oldest known constructed trackways and dates from around 3800 BCE. The world's oldest known paved road was constructed in Egypt some time between 2600 and 2200 BC. The Roman roads, Romans were the most significant road builders of the ancient world. At the peak of the Roman Empire there were more than of roads, of which over were stone-paved. Another empire, that of the Inca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf. The Euphrates is the List of longest rivers of Asia, fifteenth-longest river in Asia and the longest in West Asia, at about , with a drainage area of that covers six countries. Etymology The term ''Euphrates'' derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Euphrátēs'' (), adapted from , itself from . The Elamite name is ultimately derived from cuneiform 𒌓𒄒𒉣; read as ''Buranun'' in Sumerian language, Sumerian and ''Purattu'' in Akkadian language, Akkadian; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest south into the Black Sea. A large and historically important river, it was once a frontier of the Roman Empire. In the 21st century, it connects ten European countries, running through their territories or marking a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine. Among the many List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river are four national capitals: Vienna, Bratislava, Budapest, and Belgrade. Its drainage basin amounts to and extends into nine more countries. The Danube's longest headstream, the Breg (river), Breg, rises in Furtwangen im Schwarzwald, while the river carries its name from its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Switzerland border, Swiss-Austrian border. From Lake Constance downstream, it forms part of the Germany-Switzerland border, Swiss-German border. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border. It then flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally, the Rhine turns to flow predominantly west to enter the Netherlands, eventually emptying into the North Sea. It drains an area of 185,000 km2. Its name derives from the Gaulish language, Gaulish ''Rēnos''. There are two States of Germany, German states named after the river, North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate, in addition to several districts of Germany, districts (e.g. Rhein-Sieg-Kreis, Rhein-Sieg). The departments of France, department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall (, also known as the ''Roman Wall'', Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Aelium'' in Latin) is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Roman Britain, Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. Running from Wallsend on the River Tyne in the east to Bowness-on-Solway in the west of what is now northern England, it was a stone wall with large ditches in front and behind, stretching across the whole width of the island. Soldiers were garrisoned along the line of the wall in large Castra, forts, smaller milecastles, and intervening Turret (Hadrian's Wall), turrets. In addition to the wall's defensive military role, its gates may have been customs posts. Hadrian's Wall Path generally runs close along the wall. Almost all the standing masonry of the wall was removed in early modern times and used for local roads and farmhouses. None of it stands to its original height, but modern work has exposed much of the footings, and some segments d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to present-day Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Poland and Ukraine. A Dacian kingdom that united the Dacians and the Getae was formed under the rule of Burebista in 82 BC and lasted until the Roman conquest in AD 106. As a result of the Trajan's Dacian Wars, wars with the Roman Empire, after the conquest of Dacia, the population was dispersed, and the capital city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans. However, the Romans built a settlement bearing the same name, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetuza, 40 km away, to serve as the capital of the newly established Roman Dacia, Roman province of Dacia. A group of "Free Dacians" may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itinerary Of Antoninus
The Antonine Itinerary (, "Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is an , a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly in part from a survey carried out under Augustus, it describes the roads of the Roman Empire. Owing to the scarcity of other extant records of this type, it is a valuable historical record. Publication History Manuscripts Almost nothing is known of its author or the conditions of its compilation. Numerous manuscripts survive, the eight oldest dating to some point between the 7th to 10th centuries after the onset of the Carolingian Renaissance. Despite the title seeming to ascribe the work to the patronage of the 2nd-century Antoninus Pius, all surviving editions seem to trace to an original towards the end of the reign of Diocletian in the early 4th century. The most likely imperial patron—if the work had one—would have been Caracalla. Stemma There are many manuscripts preserving the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Salaria
The Via Salaria was an ancient Roman road in Italy. It eventually ran from Rome (from Porta Salaria of the Aurelian Walls) to ''Castrum Truentinum'' ( Porto d'Ascoli) on the Adriatic coast, a distance of 242 km. The road also passed through Reate (Rieti) and Asculum (Ascoli Piceno). Strada statale 4 Via Salaria (SS4) is the modern state highway that maintains the old road's name and runs on the same path from Rome to the Adriatic Sea. History The Via Salaria owes its name to the Latin word for "salt", since it was the route by which the Sabines living nearer the Tyrrhenian Sea came to fetch salt from the marshes at the mouth of the river Tiber, the Campus Salinarum (near Portus). Peoples nearer the Adriatic Sea used it to fetch it from production sites there. It was one of many ancient salt roads in Europe, and some historians, amongst whom Francesco Palmegiani, consider the Salaria and the trade in salt to have been the origin of the settlement of Rome. Some remains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Labicana
The Via Labicana was an ancient road of Italy, leading east-southeast from Rome. The course after the first six miles from Rome is not taken by any modern road, but it can be clearly traced from remains of pavement and buildings. It seems possible that the road at first led to Tusculum, was then extended to Labici, and later became a road for through traffic. As the preferred way to the southeast, the Via Labicana may even have superseded the Via Latina. The Via Labicana's summit just west of the Mount Algidus pass, calls for some less of a climb overall. Beyond the two roads' reunion, the route was probably called Via Latina rather than Via Labicana. Ashby cites his own contribution to ''Papers of the British School at Rome'', i .215 sqq. Via Labicana entered Rome through the Aurelian walls via the ancient monumental gate of Porta Prenestina, and reached, after an internal part, the Servian Wall, entering through the Porta Esquilina, decorated with the arch of Gallienus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Via Nomentana
The Via Nomentana was an ancient Roman road in Italy, leading North-East from Rome Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ... to Nomentum (modern Mentana), a distance of . It originally bore the name "Via Ficulensis", from the old Latin village of Ficulea, about from Rome. It was subsequently extended to Nomentum, but never became an important high road, and merged in the Via Salaria a few kilometers beyond Nomentum. It is followed as far as Nomentum by the modern state road, but some traces of its pavement still exist. Ashby cites his own contribution to ''Papers of British School at Rome'', iii. 38 sqq. The road started at the Porta Collina in the Servian Walls until the third century, when emperor Aurelian built the Porta Nomentana in his Aurelian Walls, new set of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |