Maratha (caste) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Maratha caste is composed of 96
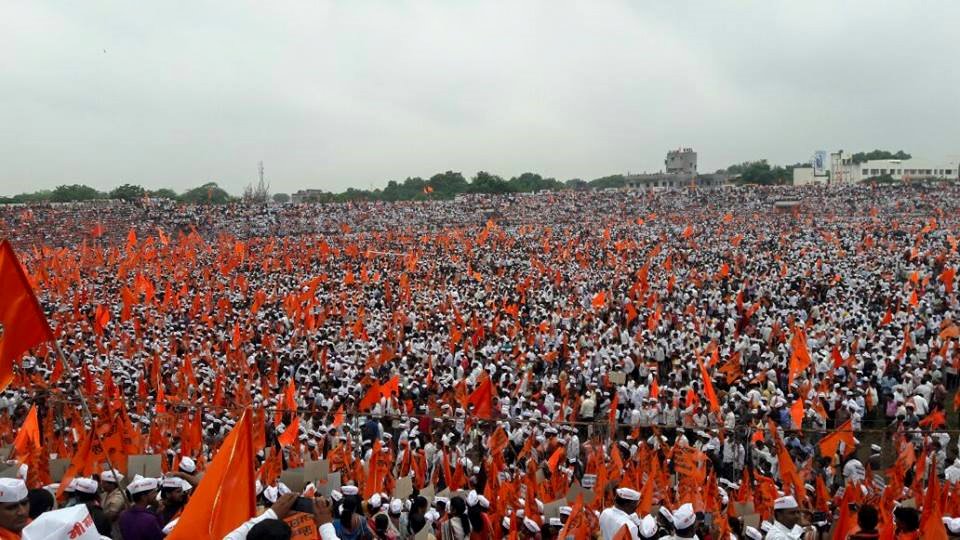 In 2018, several incidents of violence were reported due to agitation over the delay of the inclusion of the Maratha caste in the Other Backward Class category. The agitation was started by the
In 2018, several incidents of violence were reported due to agitation over the delay of the inclusion of the Maratha caste in the Other Backward Class category. The agitation was started by the
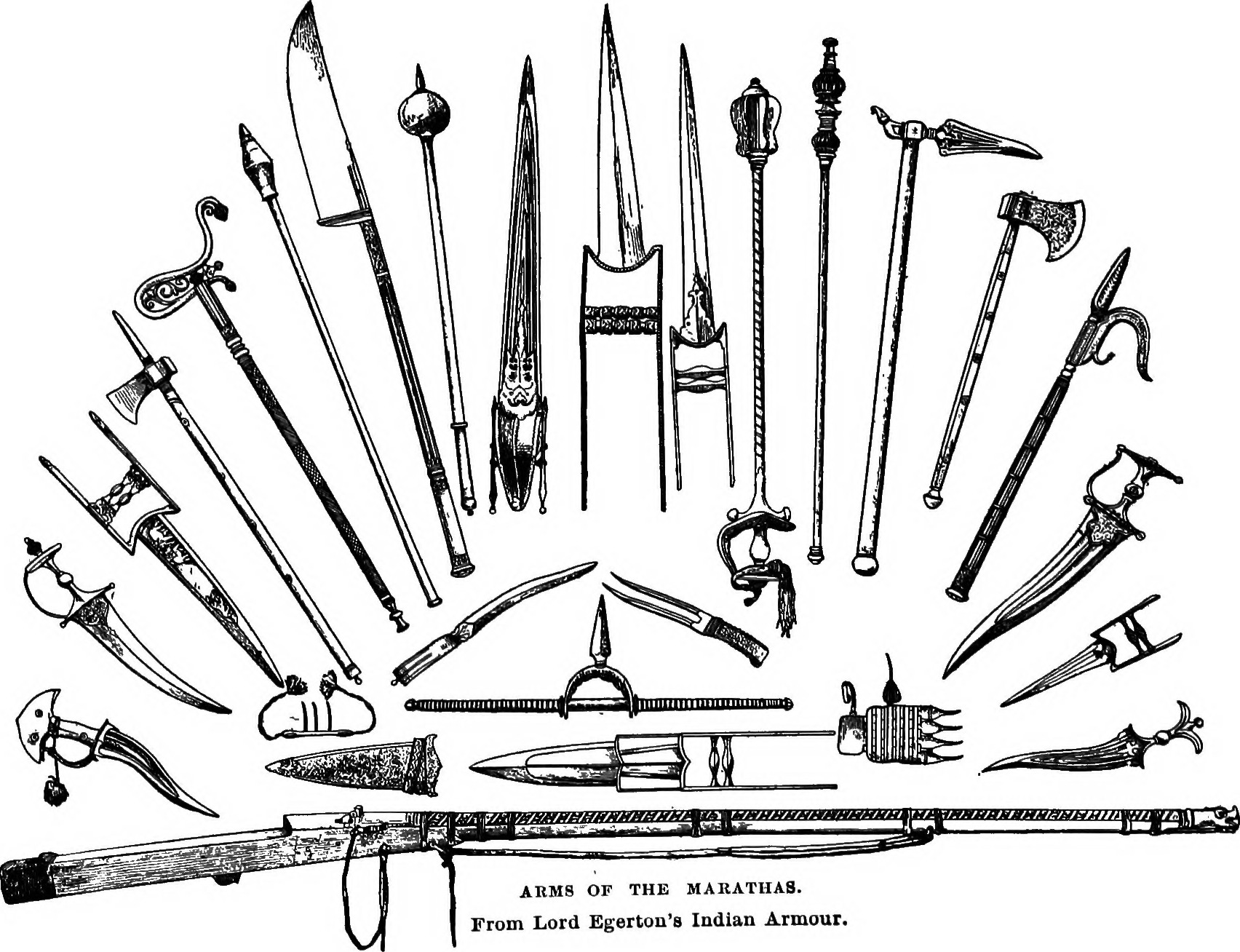 The Duke of Wellington, after defeating the Marathas, noted that the Marathas, though poorly led by their Generals, had regular infantry and artillery that matched the level of that of the Europeans and warned other British officers from underestimating the Marathas on the battlefield. He cautioned one British general that: "You must never allow Maratha infantry to attack head on or in close hand to hand combat as in that your army will cover itself with utter disgrace".
Norman Gash says that the Maratha infantry was equal to that of British infantry. After the Third Anglo-Maratha war in 1818, Britain listed the Marathas as one of the Martial Races to serve in the British Indian Army although it was unclear whether this categorisation referred to the Maratha caste or a subset of some Marathi castes. Despite praising the military prowess of the Marathas, the British considered them inferior to Sikhs and Gurkhas in terms of other masculine traits due to prevailing Christian notions of being a "man at arm" in battlefield i.e., they disapproved of Maratha utilisation of guerrilla warfare in combat along with their uncharitable and ruthless attitudes. However, racial theories have been discredited.
Lord Roberts, commander-in-chief of the Indian Army 1885–1893, who came up with the " Martial Race" theory, stated that in order to improve the quality of the army, there was a need to use "more warlike and hardy races" instead of the current sepoys from Bengal, the Tamils, Telugus and the Marathas. Based on this theory, Gurkhas and
The Duke of Wellington, after defeating the Marathas, noted that the Marathas, though poorly led by their Generals, had regular infantry and artillery that matched the level of that of the Europeans and warned other British officers from underestimating the Marathas on the battlefield. He cautioned one British general that: "You must never allow Maratha infantry to attack head on or in close hand to hand combat as in that your army will cover itself with utter disgrace".
Norman Gash says that the Maratha infantry was equal to that of British infantry. After the Third Anglo-Maratha war in 1818, Britain listed the Marathas as one of the Martial Races to serve in the British Indian Army although it was unclear whether this categorisation referred to the Maratha caste or a subset of some Marathi castes. Despite praising the military prowess of the Marathas, the British considered them inferior to Sikhs and Gurkhas in terms of other masculine traits due to prevailing Christian notions of being a "man at arm" in battlefield i.e., they disapproved of Maratha utilisation of guerrilla warfare in combat along with their uncharitable and ruthless attitudes. However, racial theories have been discredited.
Lord Roberts, commander-in-chief of the Indian Army 1885–1893, who came up with the " Martial Race" theory, stated that in order to improve the quality of the army, there was a need to use "more warlike and hardy races" instead of the current sepoys from Bengal, the Tamils, Telugus and the Marathas. Based on this theory, Gurkhas and
Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
clans originally formed in the earlier centuries from the amalgamation of families from the peasant ( Kunbi), shepherd (Dhangar
Dhangar is a herding caste of people found in the Indian states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. They are referred as Gavli in southern Maharashtra, Goa and northern Karnataka, Golla (caste), Golla in Andhra Prad ...
), pastoral ( Gavli), blacksmith ( Lohar), carpenter (Sutar), Bhandari
Bhandari or Bhandary or Bhanderi is a surname found in various Hindu castes and communities in India and Nepal. Bhandari or Bhanderi means ''treasurer'', keeper of a storehouse. In Punjab, Bhandaris belong to the Khatri caste. In Nepal, the sur ...
, Thakar and Koli castes in Maharashtra. Many of them took to military service in the 16th century for the Deccan sultanates or the Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. Later in the 17th and 18th centuries, they served in the armies of the Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian confederation that came to dominate much of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of S ...
, founded by Shivaji
Shivaji Bhonsale I (; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680), also referred to as Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle Maratha clan. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the declining Adi ...
, a Maratha Kunbi by caste. Many Marathas were granted hereditary fiefs by the Sultanates, and Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
for their service."The name of the 'caste-cluster of agriculturalists-turned-warriors' inhabiting the north-west Dakhan, Mahārās̲h̲tra 'the great country', a term which is extended to all Marāt́hī speakers":
According to the Maharashtrian historian B. R. Sunthankar, and scholars such as Rajendra Vora, the "Marathas" are a "middle-peasantry" caste which formed the bulk of the Maharashtrian society together with the other Kunbi peasant caste. Vora adds that the Maratha caste is the largest caste of India and dominate the power structure in Maharashtra because of their numerical strength, especially in the rural society.
According to Jeremy Black, British historian at the University of Exeter
, mottoeng = "We Follow the Light"
, established = 1838 - St Luke's College1855 - Exeter School of Art1863 - Exeter School of Science 1955 - University of Exeter (received royal charter)
, type = Public
, ...
, "Maratha caste is a coalescence of peasants, shepherds, ironworkers, etc. as a result of serving in the military in the 17th and 18th century". They are dominant caste in rural areas and mainly constitute the landed peasantry. As of 2018, 80% of the members of the Maratha caste were farmers.
Marathas are subdivided into 96 different clans, known as the '' 96 Kuli Marathas'' or ''Shahānnau Kule.'' Three clan lists exist but the general body of lists are often at great variance with each other. These lists were compiled in the 19th century.
There is not much social distinction between the Marathas and Kunbis since the 1950s.
The Maratha king Shivaji
Shivaji Bhonsale I (; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680), also referred to as Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle Maratha clan. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the declining Adi ...
founded the Maratha empire that included warriors and other notables from Maratha and several other castes from Maharashtra. This empire was the dominant in India for much of 18th century.
History
The term ''Maratha'' referred broadly to all the speakers of theMarathi language
Marathi (; ''Marāṭhī'', ) is an Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by Marathi people in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the official language of Maharashtra, and additional official language in the state of Goa. It is one o ...
. In the 17th century, it also served as a designation for peasants from the Deccan Plateau
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by t ...
who served as soldiers in the armies of Muslim rulers and later in the armies of Shivaji. Thus, the term ''Maratha'' became a marker of an endogamous caste for them. A number of Maratha warriors, including Shivaji's father, Shahaji, originally served in those Muslim armies. By the mid-1660s, Shivaji had established an independent Maratha kingdom. After Shivaji's death, Marathas fought under his sons and defeated Aurangzeb in the Mughal–Maratha Wars. The Maratha empire was further expanded into a vast empire by the Maratha Confederacy including Peshwa
The Peshwa (Pronunciation: e(ː)ʃʋaː was the appointed (later becoming hereditary) prime minister of the Maratha Empire of the Indian subcontinent. Originally, the Peshwas served as subordinates to the Chhatrapati (the Maratha king); later ...
s, stretching from central India in the south to Peshawar (in modern-day Pakistan) on the Afghanistan border in the north, and with expeditions in Bengal
The Maratha invasions of Bengal (1741-1751), also known as the Maratha expeditions in Bengal, refers to the frequent invasions by the Maratha forces in the Bengal Subah (Bengal, Bihar, parts of modern Orissa), after their successful campaign i ...
to the east.
By the 19th century, the empire had become a confederacy of individual states controlled by chiefs such as the Peshwa, Gaekwads of Baroda, the Holkar
The Holkar (Pronunciation: �o(ː)ɭkəɾ dynasty was a Maratha clan of Dhangar origin in India. The Holkars were generals under Peshwa Baji Rao I, and later became Maharajas of Indore in Central India as an independent member of the Mar ...
s of Indore, the Scindia
The Scindia dynasty (anglicized from Shinde) is a Hindu Maratha dynasty of maratha origin that ruled the erstwhile State of Gwalior. It had the Patil-ship of Kumberkerrab in Wai. It was founded by Ranoji Scindia, who started as a personal serv ...
s of Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the ...
, the Puars of Dhar and Dewas, and Bhonsles of Nagpur
Nagpur (pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, aːɡpuːɾ is the third largest city and the winter capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the 13th largest city in India by population and according to an Oxford's Economics report, Nag ...
. The Confederacy remained the pre-eminent power in India until their defeat by the British East India Company in the Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817–1818).
By the 19th century, the term ''Maratha'' had several interpretations in the British administrative records. In the Thane District
Thane district (Pronunciation: �ʰaːɳe previously named Taana or Thana) is a district in the Konkan Division of Maharashtra, India. At the 2011 Census it was the most populated district in the country, with 11,060,148 inhabitants; however, ...
Gazetteer of 1882, the term was used to denote elite layers within various castes: for example, "Maratha-Agri" within the Agri caste and "Maratha-Koli" within the Koli caste. In the Pune District, the words Kunbi and Maratha had become synonymous, giving rise to the Maratha-Kunbi caste complex. The Pune District Gazetteer of 1882 divided the Kunbis into two classes: Marathas and other Kunbis. The 1901 census listed three groups within the Maratha-Kunbi caste complex: "Marathas proper", "Maratha Kunbis" and Konkan Maratha.
According to Steele, in the early 19th century, Kunbis, who were agriculturists, and the Marathas who claimed Rajput descent and Kshatriya status, were distinguished by their customs related to widow remarriage. The Kunbis allowed it and the higher status Marathas prohibited it. However, there is no statistical evidence for this. However, the Kunbis and Marathas had hypergamous inter-community marriages – a rich Kunbi could always marry his daughter to a poor Maratha.
Historically, the Maratha population comprised more than 31% of the population in Maharashtra and the Kunbi was 7%, whereas the upper castes, Marathi Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests ( purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers ( ...
s, Saraswat Brahmins, and Prabhus, were earlier only about 4% of the population. The Other Backward Class population (other than the Kunbi) was 27% while the population of the Mahars was 12%.
Gradually, the term ''Maratha'' came to denote an endogamous caste. From 1900 onwards, the Satyashodhak Samaj movement defined the Marathas as a broader social category of non-Brahmin groups. These non-Brahmins gained prominence in the Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British ...
during the Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British rule in India. It lasted from 1857 to 1947.
The first nationalistic revolutionary movement for Indian independence emerged ...
. In independent India, these Marathas became the dominant political force in the newly formed state of Maharashtra.
The ritual caste hierarchy in Maharashtra is led by the Deshasthas, Chitpawan
The Chitpavan Brahmin or Konkanastha Brahmin is a Hindu Maharashtrian Brahmin community inhabiting Konkan, the coastal region of the state of Maharashtra. Initially working as messengers and spies in the late seventeenth century, the community ...
s, Karhades, Saraswats and the Chandraseniya Kayastha Prabhus. The Maratha are ranked lower under this classification than the above castes but are considered higher than the Kunbi, backward castes and castes that were considered ritually impure. According to the Chairperson of the Centre for Social Justice and Governance, this caste ranking is significant even in recent times in inter-caste matrimonial alliances between Maharashtrians.
Origin
Modern research has revealed that the Marathas and Kunbi have the same origin. Most recently, the Kunbi origin of the Maratha has been explained in detail by historians Richard Eaton and Stewart Gordon. Marathas who were distinguished from the Kunbi, in the past claimed genealogical connections with Rajputs of northern India. However, modern researchers demonstrate, giving examples, that these claims are not factual. Modern scholars agree that Marathas and Kunbi are the same. Anthropologist J. V. Ferreira writes: "The Maratha claim to belong to the ancient 96 Kshatriya families has no foundation in fact and may have been adopted after the Marathas became with Shivaji a power to be reckoned with". Gordon writes how the Maratha caste was generated from the Kunbis who served the Muslim rulers, prospered, and over time adopted different customs like different dressing styles, employed genealogists, started identifying as Maratha, and caste boundaries solidified between them. In the nineteenth century, economic prosperity rather than martial service to the Muslims replaced the mobility into Maratha identity. Eaton gives an example of the Holkar family that originally belonged to theDhangar
Dhangar is a herding caste of people found in the Indian states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. They are referred as Gavli in southern Maharashtra, Goa and northern Karnataka, Golla (caste), Golla in Andhra Prad ...
(shepherd) caste but was given a Maratha or even an "arch-Maratha" identity. The other example, given by Susan Bayly, is of the Bhonsles who originated among Maratha and Kunbi populations of the Deccani tiller-plainsmen. Similarly, scholars write that the Shinde
Shinde (pronunciation: �in̪d̪e is a clan of the Maratha clan system of Kunbi (Kurmi) origin; variations of the name include Scindia and '' Sindhia'', '' Sindia''. The ''Shinde'' last name may be also found in the Dalit community.
The Scind ...
( also known as Scindia) Maratha clan originated from the Kunbi caste and the Scindia's founder was a servant of the Peshwa who would carry his slippers. Dhanmanjiri Sathe states that "The line between Marathas and Kunbis is thin and sometimes difficult to ascertain". Iravati Karve, an anthropologist, showed how the Maratha caste was generated from Kunbis who simply started calling themselves "Maratha". She states that Maratha, Kunbi and Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Ma ...
are the three main farming communities of Maharashtra – the difference being that the Marathas and Kunbis were "dry farmers" whereas the Mali farmed throughout the year. Cynthia Talbot quotes a saying in Maharashtra, "when a Kunbi prospers he becomes Maratha". The Kunbi origin has been one of the factors on the basis of which the head of Maharashtra State Backward Class Commission (MSBCC), a Judge, M.G. Gaikwad, and some others in 2018, stated that Maratha associations have submitted historical proofs and petitions to be included in the Other Backward Class. The decision for giving reservation in jobs and education for Marathas based on the petitions that Marathas and Kunbis are one and the same caste was upheld by the Mumbai court in 2019.
Internal diaspora
Expansion of Maratha Empire also resulted in the voluntary relocation of substantial numbers of Maratha and other Marathi-speaking people outside Maharashtra, and across a big part of India. Today several significant communities descended from these emigrants live in the north, south and west of India. These descendant communities tend often to speak the local languages, although many also speak Marathi in addition. Notable Maratha families outside Maharashtra include Bhonsle of Tanjore,Scindia
The Scindia dynasty (anglicized from Shinde) is a Hindu Maratha dynasty of maratha origin that ruled the erstwhile State of Gwalior. It had the Patil-ship of Kumberkerrab in Wai. It was founded by Ranoji Scindia, who started as a personal serv ...
of Gwalior
Gwalior() is a major city in the central Indian state of Madhya Pradesh; it lies in northern part of Madhya Pradesh and is one of the Counter-magnet cities. Located south of Delhi, the capital city of India, from Agra and from Bhopal, the ...
, Gaekwad of Baroda, Holkar
The Holkar (Pronunciation: �o(ː)ɭkəɾ dynasty was a Maratha clan of Dhangar origin in India. The Holkars were generals under Peshwa Baji Rao I, and later became Maharajas of Indore in Central India as an independent member of the Mar ...
of Indore, Puar Puar may refer to:
* Pawar, Maratha rulers of Dhar State and Dewas State.
* Pu'ar, a character in ''Dragon Ball''
People with the name
* Hemendra Singh Rao Pawar, present titular Maharaja of Dhar State
* Tukojirao III (Tukoji Rao III Puar of Dew ...
of Dewas and Dhar, Ghorpade of Mudhol.
Culture
Literacy
In 17th century Maharashtra, the Brahmins and CKPs were the communities that had a system of higher education inGurukula
A or ( sa, गुरुकुल, gurukul) is a type of education system in ancient India with ('students' or 'disciples') living near or with the guru, in the same house. The guru-shishya tradition is a sacred one in Hinduism and possibly a ...
or lower-level education in clerical work or book-keeping. Education of all other castes and communities consisted of listening to oral reproductions from sacred texts like the Puranas and Kirtan
Kirtana ( sa, कीर्तन; ), also rendered as Kirtan, is a Sanskrit word that means "narrating, reciting, telling, describing" of an idea or story, specifically in Indian religions. It also refers to a genre of religious performance arts ...
s. However, despite lack of education, the Maratha caste due to their long tradition of service in military of the Yadavas and later the Muslim sultanates produced good soldiers and commanders.
Stewart Gordon writes that the prominent Ghorpade Maratha family, for instance, was not literate and had to use Brahmins as record keepers.
Gail Omvedt concludes that during the British era, the overall literacy of Brahmins and CKPs was overwhelmingly high as compared to the literacy of the Maratha and Kunbi communities where it was strikingly low. The artisan castes were intermediate in terms of literacy. For all castes, men were more literate than the women from that caste(respectively). Female literacy, as well as English literacy, showed the same pattern among castes.
A Bhandari author from 1920s quotes, according to Monika Vaidya, that Brahmins are not to blame for the lack of education of Marathas, as shown by other non-Brahmin communities whose occupations required education, like the Prabhus, Saraswats and CKP
Chandraseniya Kayastha Prabhu (CKP) is a caste group mainly found in Maharashtra. Historically, they made equally good warriors, statesmen as well as writers. They held the posts such as Deshpandes and Gadkaris and according to the historian, ...
. These communities got education despite the barriers imposed by the Brahmins and it has been argued that the need for reservations does not arise if each community tries for its own development.
Marriages
Like other Maharashtrian communities such as Kunbis,Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Ma ...
s, Mahars, etc., the marriage of a man to his maternal uncle's (''mama'' in Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Marathi people
*Palaiosouda, also known as Marathi, a small island in Greece
See also
*
* ...
) daughter is common in the Maratha community. Maratha and Kunbis intermarried in a hypergamous way i.e. a rich Kunbi's daughter could always marry a poor Maratha. Anthropologist Donald Attwood shows giving an example of the Karekars of Ahmednagar that this trend continues even in recent times indicating that the social order is fluid and flexible.
Dowry Issues
Being a politically dominant caste, the Marathas have not been able to progress beyond the social practices ofDowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment ...
(Dowry refers to the durable goods, cash, and real or movable property that the bride's family gives to the bridegroom, his parents, or his relatives as a condition of the marriage.). 80% of the Maratha community are farmers and there have been cases where the Maratha farmers had to sell their lands just to get their daughters married. Data compiled by the Maratha Kranti Morcha members showed that the expenditure incurred by an average low income and poor Maratha family has doubled in the last 10 years when it comes to dowry. A member said (in 2018), "The dowry amount ranges from Rs 7 lakh to Rs 50 lakh, depending on the profession of the groom. The lower-middle class Marathas too often have to bear an expenditure of Rs 7 lakh to Rs 10 lakh for a daughter's wedding. Even in the remote villages, a small and marginal farmer spends Rs 2 lakh to Rs 3.5 lakh on a daughter's wedding." Some caste members tried to use the Morcha to address the issue of Dowry but they did not get a positive response. Dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment ...
has now attained a status symbol in the community and that is part of the issue.
Widows
Research by a sociologist has shown that the restrictions faced by widows among Brahmins, Saraswats and CKP were significantly more than those faced by widows in Maratha caste.Festivals and Gods
Rosalind O'Hanlon, Professor at theUniversity of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the world's second-oldest university in contin ...
stated that the Hindu God Khandoba, also known by the name Mhasoba Mhasoba, pronounced "MUH-SO-BAA", is a horned buffalo deity of pastoral tribes in Western and Southern India. In Maharashtra, many Gawlis (tribes making their living cow-herding and by selling milk and milk products) have been worshipping this deit ...
, is traditionally very popular in the Maratha caste. She quotes about the devotion of the Marathas in the 19th century to Mhasoba as follows:
Mhasoba was also worshiped by the Bhonsles.
The other Hindu deity popular in the Maratha community is the Goddess Bhavani of Tuljapur.
Maratha leaders said that "Chhatrapati Shivaji is worshiped by the Maratha community, while different sections of society hold him in high esteem". "Shivaji Jayanti" (his birthday) is celebrated with folk dances, songs, plays and Puja. There was some controversy over the date but it is now celebrated on 19 February. Earlier, the regional Marathi political parties – Shiv Sena as well as the Maharashtra Navnirman Sena
The Maharashtra Navnirman Sena (translation: Maharashtra Reformation Army; MNS) is a Regionalist far-right Indian political party based in the state of Maharashtra and operates on the ideology of " Hindutva" and "Marathi" Manus. It was found ...
were celebrating it as per the Tithi according to the Hindu Calendar
The Hindu calendar, Panchanga () or Panjika is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a ...
("Falgun Vadya Tritiya" – third day of the month of Falgun), whereas the State Government was celebrating it as per the Gregorian Calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years di ...
.
Varna status
Research by modern anthropologists and historians has shown that the Maratha caste originated from the amalgamation of families from the peasant communities that belonged to theShudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four ''Varna (Hinduism), varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoret ...
Varna. However, after gaining political prominence with Shivaji's rise to power, this caste started claiming Kshatriya descent and genealogies were fabricated including those for Shivaji. Thus, the "96 clans"(Kuls)(''96 Kuli Marathas'' or ''Shahānnau Kule'') genealogies were concocted most likely after Shivaji came to power. Gordon explains that there are three such lists for the 96 clans compiled in the 19th century and they are "impossible to reconcile" due to this nature of origin of the caste. Jaffrelot writes that this process where Shudras pretend to be Kshatriyas and follow their customs is called "Kshatriyatization" and is a variation of Sanskritization
Sanskritisation (or Sanskritization) is a term in sociology which refers to the process by which castes or tribes placed lower in the caste hierarchy seek 'upward' mobility by emulating the rituals and practices of the dominant castes or upper ...
.
Modern scholars such as M. S. A. Rao and Francine Frankel
Francine R. Frankel (born 1935) is founding director of the Center for the Advanced Study of India and Professor of Political Science at the University of Pennsylvania. An authority on India's politics, economics and foreign polic she spent Academi ...
also agree that the Varna of Marathas remained Shudra, an indication being: "the maratha practice of hypergamy which permitted inter-marriage with rising peasant kunbi lineages, and created a hierarchy of maratha kuls, whose boundaries were flexible enough to incorporate, by the twentieth century, most of the kunbi population".
By the late 19th century, some Brahmins made public proclamations of their Shudra status but some moderate Brahmins were keen to ally with the influential Marathas of Bombay
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the '' de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the sec ...
in the interests of Indian independence from Britain. These Brahmins, motivated by such political reasons, supported the Maratha claim to Kshatriya status, but the success in this political alliance
A political group is a group consisting of political parties or legislators of aligned ideologies. A technical group is similar to a political group, but with members of differing ideologies.
International terms
Equivalent terms are used diffe ...
was sporadic and fell apart entirely following independence in 1947.
As late as the turn of 20th century, the Brahmin priests of Shahu, the Maratha ruler of Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. In, around 2 C.E. Kolapur's name was 'Kuntal'.
Kolhapur is k ...
refused to use Vedic mantras and would not take a bath before chanting, on the grounds that even the leading Marathas such as Shahu and his family belonged to the Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four ''Varna (Hinduism), varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoret ...
varna. This opinion about the Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four ''Varna (Hinduism), varnas'' of the Hindu caste system and social order in ancient India. Various sources translate it into English as a caste, or alternatively as a social class. Theoret ...
varna was supported by Brahmin Councils in Maharashtra and they stuck to their opinion even when they (the Brahmins) were threatened with the loss of land and property. This led to Shahu supporting Arya Samaj
Arya Samaj ( hi, आर्य समाज, lit=Noble Society, ) is a monotheistic Indian Hindu reform movement that promotes values and practices based on the belief in the infallible authority of the Vedas. The samaj was founded by the san ...
and Satyashodhak Samaj as well as campaigning for the rights of the Maratha community. He soon became the leader of the non-Brahmin movement and united the Marathas under his banner.
Gaikwad, the leader of Sambhaji Brigade, a prominent Maratha caste organisation, stated in an interview, that before Indian Independence, "Backward Class federation had raised the concerns of the Shudra communities including the Marathas".
Maratha caste does not have the upanayanam or "sacred thread ceremony" of ritually upper caste Hindus. However, despite the ritual status, the Marathas have significant political power.
In the 21st century, the Government of Maharashtra
The Government of Maharashtra is the state governing authority for the states of india, state of Maharashtra, India. It is a democratically elected State governments of India, government with 288 Member of the Legislative Assembly (India), MLAs ...
cited historical incidents for the claim of Shudra status of prominent Maratha families to form a case for reservation __NOTOC__
Reservation may refer to: Places
Types of places:
* Indian reservation, in the United States
* Military base, often called reservations
* Nature reserve
Government and law
* Reservation (law), a caveat to a treaty
* Reservation in India, ...
for the Marathas in the state. Additionally, a report by an independent commission in November 2018 concluded that the Maratha caste is educationally, socially and economically a backward community.
Affirmative Action
In Karnataka, the Marathas are classified as Other Backward Class with the exception of the Marathas ofKodagu
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State.
It occupie ...
district who are classified as a Scheduled Tribe
The Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) are officially designated groups of people and among the most disadvantaged socio-economic groups in India. The terms are recognized in the Constitution of India and the groups are designa ...
. In Maharashtra, they were classified as a Forward caste by the Mandal commission. In 2018, they were classified as Socially and Educationally Backward (SEBC) and were granted 16% reservation in jobs and education. In 2019, the court upheld the quota but recommended that the quota be cut to 12%.
In November 2022, the Government of Maharashtra declared that needy Maratha students who live in hostels would be getting a stipend of Indian Rupees sixty thousand per year.
Inter-caste issues
Anti-Marwadi/Anti-Brahmin Deccan riots of 1875
Claude Markovits, director of center of Indian and South-Asian studies, writes, that in 1875, in places such asPune
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, ( the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million As of 2021, Pune Metropolitan Region is the largest i ...
and Ahmednagar
Ahmednagar (), is a city located in the Ahmednagar district in the state of Maharashtra, India, about 120 km northeast of Pune and 114 km from Aurangabad. Ahmednagar takes its name from Ahmad Nizam Shah I, who founded the town in 1 ...
, Marwadi moneylenders became victims of coordinated attacks by the "local peasantry of the Maratha caste". Historian, David Ludlen states that the motivation for the violence was destroying the debt agreements that the moneylenders held over the Maratha farmers. These riots were known as the "Deccan riots". According to John McLane, the victims were mostly Marwadi moneylenders but Marathi speaking Brahmin moneylenders were usually spared. However, according to Lele, in Ahmednagar, Poona and Satara, the Marathas led the riots to challenge the Brahmins, who were a majority of the money lenders.
Anti-Brahmin Violence
Following the assassination of Gandhi in 1948 by Nathuram Godse, aChitpawan Brahmin
The Chitpavan Brahmin or Konkanastha Brahmin is a Hindu Maharashtrian Brahmin community inhabiting Konkan, the coastal region of the state of Maharashtra. Initially working as messengers and spies in the late seventeenth century, the communit ...
from Pune, other Brahmins in Maharashtra became targets of violence, mostly from elements from the Maratha caste. Later, in Sangli, Jains and Lingayats joined the Marathas in their attacks against the Brahmins. Thousands of offices and homes were also set on fire. Molestation incidents were also reported during these attacks. On the first day alone, the number of deaths in Bombay were 15, and 50 in Pune.
One scholar has observed, "It will be too much to believe that the riots took place because of the intense love of Gandhiji on the part of the Marathas. Godse became a very convenient hate symbol to damn the Brahmins and burn their properties."
Donald Rosenthal opines that the motivation for the violence was the historic discrimination and humiliation that the Maratha community faced due to their caste status. He writes, "Even today, local Brahmins claim that the Marathas organized the riots to take political advantage of the situation".
In Satara alone, the official reports show that about 1000 houses were burnt in about 300 villages. There were "cruel, cold-blooded killings" as well – for example, one family whose last name happened to be 'Godse' had three of its male members killed. Brahmins suffered from serious physical violence as well as economic violence in the form of looting.
Maureen Patterson concludes that the greatest violence took place not in the cities of Mumbai, Pune and Nagpur – but in Satara, Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. In, around 2 C.E. Kolapur's name was 'Kuntal'.
Kolhapur is k ...
and Belgaum. Destruction was extensive in Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the administrative headquarter of the Kolhapur district. In, around 2 C.E. Kolapur's name was 'Kuntal'.
Kolhapur is k ...
. Earlier in the century, Shahu of Kolhapur had actively collaborated with the British against the Indian freedom struggle which he identified being led by Chitpavan Brahmins such as Bal Gangadhar Tilak. Shahu was also actively involved in the anti-Brahmin movement as well. During the 1948 disturbances, in Sangli, the local Jain and the Lingayat communities joined the Marathas in the attacks against the Brahmins. Here, specifically, the factories owned by the Chitpawan Brahmin
The Chitpavan Brahmin or Konkanastha Brahmin is a Hindu Maharashtrian Brahmin community inhabiting Konkan, the coastal region of the state of Maharashtra. Initially working as messengers and spies in the late seventeenth century, the communit ...
s were destroyed. This event led to the hasty integration of the Patwardhan
Patwardhan may refer to the surname most commonly used by members of Indian Chitpavan Brahmin families belonging to the Kaundinya gotra. The Karhade Patwardhans belong to the Kashyapa and Naidhruva Gotra and their history in the Rajapur region of ...
ruled princely states into the Bombay Province by March 1948.
Worli BDD Chawl violence
The BDDChawl
A chawl is a type of residential building found in western India, similar to a tenement. Typically low quality housing, chawls are generally associated with poverty. The first chawls were constructed in the early 1700s, as housing for industr ...
in the Worli inner suburb of Mumbai is a complex of buildings which were built in 1920s to house workers employed by the textile mills.
In the 1970s, at the height of the Dalit Panther
The Dalit Panthers are a social organisation that seeks to combat caste discrimination. It was led by a group of Mahar writers and poets, including Raja Dhale, Namdeo Dhasal, and J. V. Pawar in some time between the second and the third semes ...
movement, fights between the Chawl's dominant Maratha population and the Neo-Buddhists living in 20-odd buildings resulted in full-scale riots. Violence between the communities continued through the 1970s to the early 1990s.
Other incidents of caste related violence
Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute
Sambhaji Brigade is a branch of "Maratha Seva Sangh"(a Maratha caste organisation) and has committed acts of violence. In 2004, a mob of 150 Maratha activists attacked the Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute - the reason being a book by James Laine. The vandalism led to loss of valuable historic documents and an estimated loss of Rs 1.25 crore. Sanskrit and religious documents dating back to the 16th century were destroyed, translation of theRigVeda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' ( ', from ' "praise" and ' "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts ('' śruti'') known as the Vedas. Only one ...
by the Shankaracharya was thrown on the road. A woman who tried to call the police had bricks pelted at her by the mob.
Ram Ganesh Gadkari Statue
In 2017, the statue of Ram Ganesh Gadkari, a noted playwright and poet who showed Sambhaji in a poor light in his 1919 play 'Rajsanyas', was uprooted and thrown in the river by Sambhaji Brigade. The Chandraseniya Kayastha Prabhu(CKP
Chandraseniya Kayastha Prabhu (CKP) is a caste group mainly found in Maharashtra. Historically, they made equally good warriors, statesmen as well as writers. They held the posts such as Deshpandes and Gadkaris and according to the historian, ...
), the community to which Gadkari belonged later organised a meeting to protest this incident at the "Ram Ganesh Gadkari Rangayatan"(a theatre named after Gadkari) in Thane
Thane (; also known as Thana, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city in Maharashtra, India. It is situated in the north-eastern portion of the Salsette Island. Thane city is entirely within Thane taluka, one of the seven talu ...
. BJP leader Nitesh Rane later rewarded the vandals and made inflammatory remarks claiming that he had announced a reward earlier in 2016 for removing the bust, and was proud of the act carried out by the accused.
Violence related to inclusion in the Other Backward Caste(OBC)
 In 2018, several incidents of violence were reported due to agitation over the delay of the inclusion of the Maratha caste in the Other Backward Class category. The agitation was started by the
In 2018, several incidents of violence were reported due to agitation over the delay of the inclusion of the Maratha caste in the Other Backward Class category. The agitation was started by the Maratha Kranti Morcha
The Maratha Kranti Morcha, loosely translated as "Maratha revolutionary demonstration" in the Marathi language, is a series of silent and pragmatic protests organized by the Maratha community in various cities across India as well as overseas. ...
. In June 2018, the Marathas threatened violent protests if their demands were not met. In July, Maratha protests turned violent as the protesters attacked police and torched police vehicles. Several incidents, including some deaths, were reported in other locations as well – several police were injured by the mobs, public property was damaged and private cars were torched. In Navi Mumbai itself, hundreds of vehicles were torched and buses were set on fire in cities such as Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the secon ...
and Pune
Pune (; ; also known as Poona, ( the official name from 1818 until 1978) is one of the most important industrial and educational hubs of India, with an estimated population of 7.4 million As of 2021, Pune Metropolitan Region is the largest i ...
.
Other inter caste issues
Medha Khole Incident
In a widely publicised 2017 incident, a Brahmin scientist by the name of Medha Vinayak Khole(Deputy Director-General for the weather forecasting section) filed a police complaint against her Maratha domestic worker, Nirmala Yadav, for hiding her caste and "violating ritual purity and sanctity". Khole even insulted the latter's Gods, Khandoba (a popular God worshipped by most Marathi Hindu communities) andMhasoba Mhasoba, pronounced "MUH-SO-BAA", is a horned buffalo deity of pastoral tribes in Western and Southern India. In Maharashtra, many Gawlis (tribes making their living cow-herding and by selling milk and milk products) have been worshipping this deit ...
(a Hindu God worshiped by Pastoral communities and very popular in the Marathas). The "Akhil Bhartiya Bramhan Mahasangh" initially came out in support of Khole. However, there were widespread protests not just by Maratha caste organisations but also by non-caste organisations like Domestic Workers Unions and Women's organisations and Khole was widely criticised.
Political participation
The 1919 Montagu–Chelmsford Reforms of the British colonial government called for caste based representation in legislative council. In anticipation a Maratha league party was formed. The league and other groups came together to form the non-Brahmins party in the Marathi speaking areas in the early 1920s under the leadership of Maratha leadersKeshavrao Jedhe
Keshavrao Marutrao Jedhe (Deshmukh) (25 April 1896 – 12 November 1959) was an Indian independence activist and politician from Pune. He served as a leading figure in the Indian National Congress, and in the Samyukta Maharashtra movement durin ...
and Baburao Javalkar. Their early goals in that period were capturing the Ganpati and Shivaji festivals from Brahmin domination. They combined nationalism with anti-casteism as the party's aims. Later on in the 1930s, Jedhe merged the non-Brahmin party with the Congress party and changed the Congress party in the Maharashtra region from an upper-caste dominated body to a more broadly based but Maratha-dominated party. Apart from Jedhe, most Congress leaders from the Maratha /Kunbi community remained aloof from the Samyukta Maharashtra campaign of the 1950s. However, they have dominated the state politics of Maharashtra since its inception in 1960.
The INC was the preferred party of the Maratha/Kunbi community in the early days of Maharashtra and the party was long without a major challenger, and enjoyed overwhelming support from the Maratha dominated sugar co-operatives and thousands of other cooperative organisations involved in the rural agricultural economy of the state such as marketing of dairy and vegetable produce, credit union
A credit union, a type of financial institution similar to a commercial bank, is a member-owned nonprofit financial cooperative. Credit unions generally provide services to members similar to retail banks, including deposit accounts, provision ...
s etc. The domination by Marathas of the cooperative institutions and with it the rural economic power allowed the community to control politics from the village level up to the Assembly and Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, constitutionally the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-pas ...
seats. Since the 1980s, this group has also been active in setting up private educational institutions. Major past political figures of Congress party from Maharashtra such as Panjabrao Deshmukh, Keshavrao Jedhe
Keshavrao Marutrao Jedhe (Deshmukh) (25 April 1896 – 12 November 1959) was an Indian independence activist and politician from Pune. He served as a leading figure in the Indian National Congress, and in the Samyukta Maharashtra movement durin ...
, Yashwantrao Chavan, Shankarrao Chavan and Vilasrao Deshmukh have been from this group.
Sharad Pawar, who has been a towering figure in Maharashtrian and national politics, belongs to this group.
The state has had many Maratha government ministers and officials, as well as in local municipal councils, and panchayats. Marathas comprise around 32 per cent of the state population. 10 out of 16 chief ministers of Maharashtra hailed from the Maratha community as of 2012.
The rise of the Hindu Nationalist Shiv Sena and Bharatiya Janata Party
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; ; ) is a political party in India, and one of the two major List of political parties in India, Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. Since 2014, it has been the List of ruling p ...
in recent years have not dented Maratha representation in Maharashtra Legislative assembly.
Shiv Sena's strength mainly came from the Maratha support which it drew away from the Congress. In 1990, 24 MLAs elected from Shiv Sena were Marathas which increased to 33 in 2004 (more than 50%). Thus, researcher Vora concludes that the Shiv Sena has been emerging as a "Maratha Party".
Maratha Seva Sangh, a Maratha caste based organisation and its youth wing Sambhaji Brigade came into the political scene after the BORI attack. The group distances itself from the Hindu nationalist parties like the BJP and Shiv Sena and invokes a secular anti-Brahmin genealogy from Shivaji
Shivaji Bhonsale I (; 19 February 1630 – 3 April 1680), also referred to as Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, was an Indian ruler and a member of the Bhonsle Maratha clan. Shivaji carved out his own independent kingdom from the declining Adi ...
, Tukaram, Jyotirao Phule and B. R. Ambedkar. In late 2004, Maratha Seva Sangh announced that they had established a new religion called ''Shiv Dharma'' to protest "Vedic Brahminism" and oppose Hinduism. The details of this are published in ''Jijau Brigade va Sambhaji Brigade Sanskarmala, Maratha Sanskarmala I''.
Military service
 The Duke of Wellington, after defeating the Marathas, noted that the Marathas, though poorly led by their Generals, had regular infantry and artillery that matched the level of that of the Europeans and warned other British officers from underestimating the Marathas on the battlefield. He cautioned one British general that: "You must never allow Maratha infantry to attack head on or in close hand to hand combat as in that your army will cover itself with utter disgrace".
Norman Gash says that the Maratha infantry was equal to that of British infantry. After the Third Anglo-Maratha war in 1818, Britain listed the Marathas as one of the Martial Races to serve in the British Indian Army although it was unclear whether this categorisation referred to the Maratha caste or a subset of some Marathi castes. Despite praising the military prowess of the Marathas, the British considered them inferior to Sikhs and Gurkhas in terms of other masculine traits due to prevailing Christian notions of being a "man at arm" in battlefield i.e., they disapproved of Maratha utilisation of guerrilla warfare in combat along with their uncharitable and ruthless attitudes. However, racial theories have been discredited.
Lord Roberts, commander-in-chief of the Indian Army 1885–1893, who came up with the " Martial Race" theory, stated that in order to improve the quality of the army, there was a need to use "more warlike and hardy races" instead of the current sepoys from Bengal, the Tamils, Telugus and the Marathas. Based on this theory, Gurkhas and
The Duke of Wellington, after defeating the Marathas, noted that the Marathas, though poorly led by their Generals, had regular infantry and artillery that matched the level of that of the Europeans and warned other British officers from underestimating the Marathas on the battlefield. He cautioned one British general that: "You must never allow Maratha infantry to attack head on or in close hand to hand combat as in that your army will cover itself with utter disgrace".
Norman Gash says that the Maratha infantry was equal to that of British infantry. After the Third Anglo-Maratha war in 1818, Britain listed the Marathas as one of the Martial Races to serve in the British Indian Army although it was unclear whether this categorisation referred to the Maratha caste or a subset of some Marathi castes. Despite praising the military prowess of the Marathas, the British considered them inferior to Sikhs and Gurkhas in terms of other masculine traits due to prevailing Christian notions of being a "man at arm" in battlefield i.e., they disapproved of Maratha utilisation of guerrilla warfare in combat along with their uncharitable and ruthless attitudes. However, racial theories have been discredited.
Lord Roberts, commander-in-chief of the Indian Army 1885–1893, who came up with the " Martial Race" theory, stated that in order to improve the quality of the army, there was a need to use "more warlike and hardy races" instead of the current sepoys from Bengal, the Tamils, Telugus and the Marathas. Based on this theory, Gurkhas and Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
were recruited by the British army and they were "construed as martial races" in preference to other races in India. Historian Sikata Banerjee notes a dissonance in British military opinions of the Maratha, wherein the British portrayed them as both "formidable opponents" and yet not "properly qualified" for fighting in the western manner, criticising the Maratha guerrilla tactics as an improper way of war. Banerjee cites an 1859 statement as emblematic of this disparity:
The Maratha Light Infantry regiment is one of the "oldest and most renowned" regiments of the Indian Army. Its First Battalion, also known as the ''Jangi Paltan'' ("Warrior Platoon"), traces its origins to 1768 as part of the Bombay Sepoys.
The battle cry of Maratha Light Infantry is ''Bol Shri Chattrapati Shivaji Maharaj ki Jai!'' ("Hail Victory to Emperor Shivaji!") in tribute to the Maratha sovereign and their motto is ''Shatrujeet'' (victory over enemy).
See also
* Maratha clan system * List of Maratha dynasties and states * List of notable Maratha People * Marhatta region * Thanjavur Marathi people * Marathi People in Uttar PradeshFootnotes
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Social groups of Maharashtra Social groups of Maharashtra Indian castes Marathi people Maharashtra Social groups of Goa