Manganite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Manganite is a
 Manganite occurs with other manganese oxides in deposits formed by circulating
Manganite occurs with other manganese oxides in deposits formed by circulating 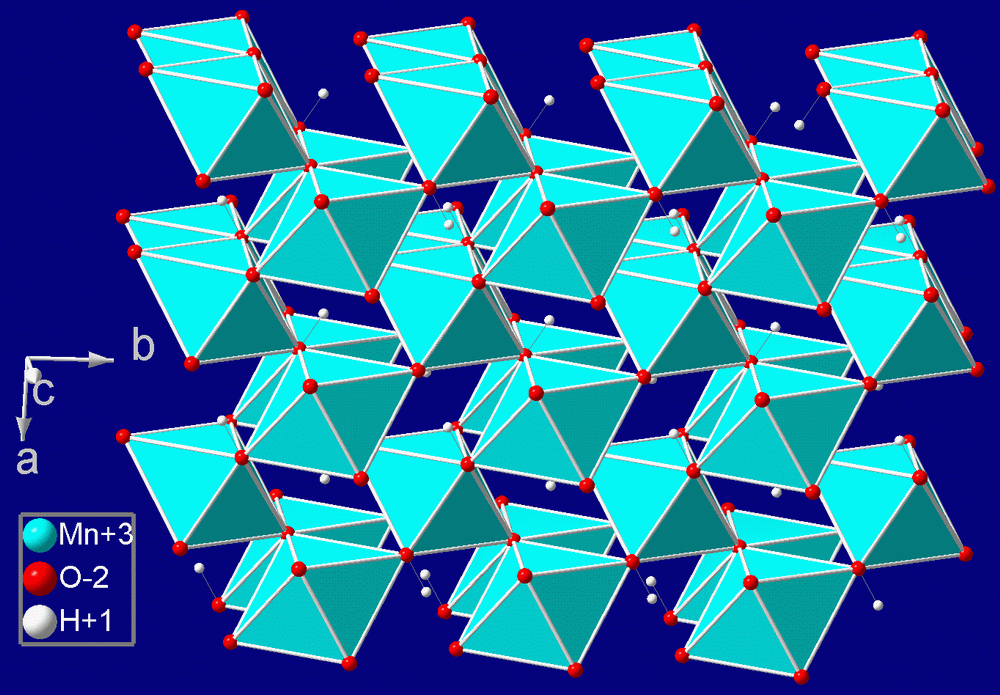
mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
composed of manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation st ...
-hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It ...
, MnO(OH), crystallizing in the monoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three Vector (geometric), vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in t ...
system (pseudo-orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic Lattice (group), lattices result from stretching a cubic crystal system, cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, res ...
). Crystals of manganite are prismatic and deeply striated parallel to their length; they are often grouped together in bundles. The color is dark steel-grey to iron-black, and the luster brilliant and submetallic. The streak is dark reddish brown. The hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
is 4, and the specific gravity
Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a dimensionless quantity defined as the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for solids and liquids is nea ...
is 4.3. There is a perfect cleavage parallel to the brachypinacoid, and less-perfect cleavage parallel to the prism faces. Twinned crystals are not infrequent.
The mineral contains 89.7% manganese sesquioxide; it dissolves in hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
with evolution of chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
.
Occurrence
 Manganite occurs with other manganese oxides in deposits formed by circulating
Manganite occurs with other manganese oxides in deposits formed by circulating meteoric water
Meteoric water, derived from precipitation such as snow and rain, includes water from lakes, rivers, and ice melts, all of which indirectly originate from precipitation. The journey of meteoric water from the atmosphere to the Earth's surface is a ...
in the weathering environment in clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
deposits and laterite
Laterite is a soil type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and prolo ...
s. It forms by low temperature hydrothermal
Hydrothermal circulation in its most general sense is the circulation of hot water (Ancient Greek ὕδωρ, ''water'',Liddell, H.G. & Scott, R. (1940). ''A Greek-English Lexicon. revised and augmented throughout by Sir Henry Stuart Jones. with th ...
action in veins
Veins () are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal c ...
in association with calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
, barite
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate (Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
, and siderite
Siderite is a mineral composed of iron(II) carbonate (FeCO3). Its name comes from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "iron". A valuable iron ore, it consists of 48% iron and lacks sulfur and phosphorus. Zinc, magnesium, and manganese commonly ...
. Often associated with pyrolusite
Pyrolusite is a mineral consisting essentially of manganese dioxide ( Mn O2) and is important as an ore of manganese.. It is a black, amorphous appearing mineral, often with a granular, fibrous, or columnar structure, sometimes forming reniform ...
, braunite
Braunite is a silicate mineral containing both di- and tri- valent manganese with the chemical formula:
Mn2+Mn3+6 SiO4 Common impurities include iron, calcium, boron, barium, titanium, aluminium, and magnesium.
Braunite forms grey/black tetragon ...
, hausmannite
Hausmannite is a complex oxide, or a mixed oxide, of manganese containing both Divalent, di- and Trivalent, tri-valent manganese. Its chemical formula can be represented as , or more simply noted as , or , as commonly done for magnetite (), the co ...
and goethite
Goethite (, ) is a mineral of the diaspore group, consisting of iron(III) oxide-hydroxide, specifically the α- polymorph. It is found in soil and other low-temperature environments such as sediment. Goethite has been well known since ancient t ...
.
Manganite occurs in specimens exhibiting good crystal form at Ilfeld
Ilfeld is a village and a former municipality in the district of Nordhausen, in Thuringia, Germany. It is situated at the south foot of the Harz, at the entrance to the Bährethal, north from Nordhausen by the railway to Wernigerode. Since 1 ...
in the Harz Mountains
The Harz (), also called the Harz Mountains, is a Mittelgebirge, highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The nam ...
of Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, where the mineral occurs with calcite and barite in veins traversing porphyry
Porphyry (; , ''Porphyrios'' "purple-clad") may refer to:
Geology
* Porphyry (geology), an igneous rock with large crystals in a fine-grained matrix, often purple, and prestigious Roman sculpture material
* Shoksha porphyry, quartzite of purple c ...
. Crystals have also been found at Ilmenau in Thuringia
Thuringia (; officially the Free State of Thuringia, ) is one of Germany, Germany's 16 States of Germany, states. With 2.1 million people, it is 12th-largest by population, and with 16,171 square kilometers, it is 11th-largest in area.
Er ...
, Neukirch near Sélestat
Sélestat (; Alsatian language, Alsatian: ''Schlettstàdt''; German: ''Schlettstadt'') is a Communes of France, commune in the Grand Est region of France. An administrative division (Subprefectures in France, sous-préfecture) of the Bas-Rhin Depa ...
in Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,9 ...
(newkirkite), Granam near Towie Towie may refer to:
* Towie, Aberdeenshire
* Towie Barclay Castle, Aberdeenshire
* Towie Castle, Kildrummy, Aberdeenshire
* Towie (game), a three-hand variant of Bridge
* ''The Only Way Is Essex'', a British reality television series
See also
...
in Aberdeenshire, and in Upton Pyne
Upton Pyne is a parish and village in Devon, England. The parish lies just north west of Exeter, mainly between the River Exe and River Creedy. The village is located north of Cowley and west of Brampford Speke and Stoke Canon
Stoke Canon ...
near Exeter
Exeter ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and the county town of Devon in South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter w ...
, UK and Negaunee, Michigan
Negaunee ( or ) is a city in Marquette County, Michigan, Marquette County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 4,627 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The city is located at the southwest corner of Negaunee Township, M ...
, United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, and in the Pilbara
The Pilbara () is a large, dry, sparsely populated regions of Western Australia, region in the north of Western Australia. It is known for its Indigenous Australians, Aboriginal people; wealth disparity; its ancient landscapes; the prevailing r ...
of Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
. Good crystals have also been found at Atikokan, Ontario and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
, Canada. As an ore
Ore is natural rock or sediment that contains one or more valuable minerals, typically including metals, concentrated above background levels, and that is economically viable to mine and process. The grade of ore refers to the concentration ...
of manganese it is much less abundant than pyrolusite
Pyrolusite is a mineral consisting essentially of manganese dioxide ( Mn O2) and is important as an ore of manganese.. It is a black, amorphous appearing mineral, often with a granular, fibrous, or columnar structure, sometimes forming reniform ...
or psilomelane
Psilomelane is a group name for hard black manganese oxides including hollandite and romanechite. Psilomelane consists of hydrous manganese oxide with variable amounts of barium and potassium. Psilomelane is erroneously, and uncommonly, known as ...
.
Although described with various other names as early as 1772, the name ''manganite'' was first applied in a publication by W. Haidinger in 1827.
Applications
The mineral was used in prehistoric times as a pigment, by humans, and as a fire starter by Neanderthalers. Manganite is believed to have been used in prehistoric times to start a wood fire. Manganite lowers the combustion temperature of wood from 350 degrees Celsius to 250 degrees Celsius. Manganite powder has been a common find inNeanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
archaeological sites.
See also
*Manganese oxide Manganese oxide is any of a variety of manganese oxides and hydroxides.Wells A.F. (1984) ''Structural inorganic chemistry'' 5th edition Oxford Science Publications, . These include
* Manganese(II) oxide, MnO
* Manganese(II,III) oxide, Mn3O4
* Man ...
* Groutite
Groutite is a manganese oxide mineral with formula Mn3+O(OH). It is a member of the diaspore group and is trimorphous with manganite and feitknechtite. It forms lustrous black crystals in the orthorhombic system.
It occurs in weathered banded i ...
References
* {{Authority control Manganese(III) minerals Hydroxide minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 14