|
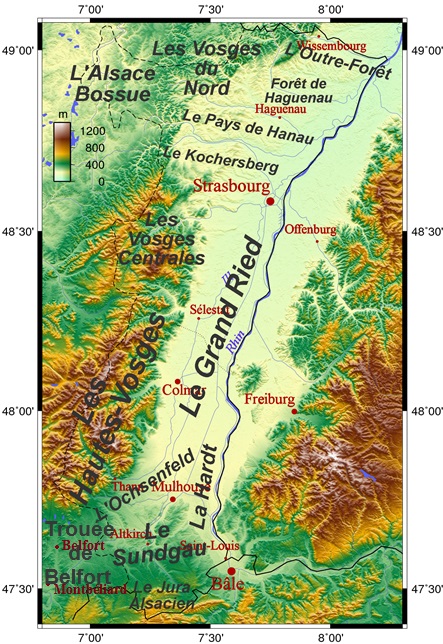
Sélestat
Sélestat (; Alsatian language, Alsatian: ''Schlettstàdt''; German: ''Schlettstadt'') is a Communes of France, commune in the Grand Est region of France. An administrative division (Subprefectures in France, sous-préfecture) of the Bas-Rhin Departments of France, department, the town lies on the Ill (France), Ill river, from the Rhine and the German border. Sélestat is located between the largest communes of Alsace, Strasbourg and Mulhouse. In 2019, Sélestat had a total population of 19,242. The Humanist Library of Sélestat is located there. Name The present name of the town is a Frenchification of the original Germanic name. It appeared soon after the French conquest in the 17th century. The town is called ''Schlettstàdt'' () in Alsatian language, Alsatian and () in German. Sélestat was first mentioned in 727 as ''Sclastat''.. It was mentioned as ''Scalistati'' in 775, as ''Slectistat'' in 881, as ''Sclezistat'' in 884 and as ''Slezestat'' in 1095. The current German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humanist Library Of Sélestat
The Humanist Library in Sélestat is one of the most important cultural treasures of Alsace, France. There are two Renaissance humanist libraries involved, the library of the Humanist School and the private library of the scholar, Beatus Rhenanus (1485–1547). The Library of the Humanist School In 1441, the municipal authorities of Sélestat – then a free city of the Holy Roman Empire – appointed Ludwig Dringenberg, born in Westphalia, to be the leader of the local Latin school. Under his leadership the school fostered Humanist thinking. His successors. Were Kraft Hofman (1477–1501), Hieronymus Gebwiler (1501–1509) and Hans Sapidus (1510–1525). The school also had a library. Notable alumni * Bonifacius Amerbach * Beatus Rhenanus The Library of Beatus Rhenanus Beatus Rhenanus bequeathed his entire private library to his home city of Sélestat. This library contained about 670 bound leather volumes at the time of his death in 1547, which Rhenanus had collected du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bas-Rhin
Bas-Rhin () is a department in Alsace which is a part of the Grand Est region of France. The name means 'Lower Rhine', referring to its lower altitude among the two French Rhine departments: it is downstream of the Haut-Rhin (Upper Rhine) department. Both belong to the European Upper Rhine region. It is, with the Haut-Rhin (Upper Rhine), one of the two departments of the traditional Alsace region which until 1871, also included the area now known as the Territoire de Belfort. The more populous and densely populated of the pair, it had 1,152,662 inhabitants in 2021. The prefecture is based in Strasbourg. The INSEE and Post Code is 67. On 1 January 2021, the departemental councils of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the European Collectivity of Alsace. The inhabitants of the department are known as or . Geography The Rhine has always been of great historical and economic importance to the area, and it forms the eastern border of Bas-Rhin. The area is also home to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in the Grand Est administrative region of northeastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine, next to Germany and Switzerland. In January 2021, it had a population of 1,919,745. Alsatian culture is characterized by a blend of German and French influences. Until 1871, Alsace included the area now known as the Territoire de Belfort, which formed its southernmost part. From 1982 to 2016, Alsace was the smallest administrative in metropolitan France, consisting of the Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin Departments of France, departments. Territorial reform passed by the French Parliament in 2014 resulted in the merger of the Alsace administrative region with Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine to form Grand Est. On 1 January 2021, the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the new European Collectivity of Alsace but remained part of the region Grand Est. Alsatian dialect, Alsatian is an Alemannic German, Alemannic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lièpvre
Lièpvre (; ; ) is a commune in the Haut-Rhin department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. A monastery was built here in the eighth century by Saint Fulrad, who filled it with relics of Saint Cucuphas and Saint Alexander. Geography The municipality is nestled in the Liepvrette river valley as the river descends from the main chain of the Vosges into the Col des Bagenelles, a mountain pass in the Vosges. The Liepvrette runs northeast through Sainte-Marie-aux-Mines before reaching Lièpvre. Below Lièpvre, the river runs between the ruins of Frankenbourg castle in the north and the castle of Haut-Koenigsbourg in the south then across the municipality of Scherwiller. The Liepvrette then joins the river Giessen (Scheer in former times), which flows from the Val de Villé, before emptying into the river Ill near Sélestat. The municipality of Lièpvre is bordered by several summits in the Vosges: Brézouard (1229 m), Taennchel (992 m), and High-Koenigsbourg (775 m) to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbey Church Of Saint Foy
The Abbey Church of Sainte-Foy in Conques, France, was a popular stop for pilgrims traveling the Way of St. James to Santiago de Compostela, in what is now Spain. The main draw for medieval pilgrims at Conques were the remains of Sainte-Foy, a young woman martyred during the fourth century. The relics of Sainte-Foy arrived in Conques through theft in 866. After unsuccessful attempts to acquire the relics of Saint Vincent of Saragossa and then the relics of St. Vincent Pompejac in Agen, the abbey authorities set their sights on the relics of Sainte-Foy at the ancient St. Faith's Church, Sélestat. The Conques abbey opened a priory next to the shrine in Sélestat. A monk from Conques posed as a loyal monk in Agen for nearly a decade in order to get close enough to the relics to steal them. The abbey church has been a listed monument since 1840. Architecture The original monastery building at Conques was an eighth-century oratory built by monks fleeing the Saracens in Spain. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Ried
{{more citations needed, date=September 2014 The Grand Ried is an Alsatian natural region which is part of the Ried. It shows landscapes typical of the Ried. To the west, it is delimited by the Ill, and by the Rhine to the east. It stretches between Strasbourg and Colmar. It was formed by the meandering Rhine (and Ill), before it was canalised. The Rhine used to spread its sediments when inundations occurred. Today the Rhine is corseted between embankments. The Erstein polder is used to regulate the flow of the Rhine, thus avoiding inundations. It has been listed as a national nature reserve since 1989. As a matter of fact, it is still possible to discover in the reserve the biodiversity which used to exist when the Grand Ried was wild and the Rhine was not canalised. The commune of Rhinau presents a unique feature: it possesses an area of almost 1000 ha directly at the border, however on German soil. This is Rheinau. The landscape is characterised by numerous ''Baggersee' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick I, Duke Of Swabia
Frederick I (c. 1050 – 1105 before 21 July) was Duke of Swabia from 1079 to his death, the first ruler from the House of Hohenstaufen (''Staufer''). Life Frederick was the son of Frederick of Büren (c. 1020–1053), Count in the Riesgau and Swabian Count Palatine, with Hildegard of Egisheim- Dagsburg, a niece of Pope Leo IX, daughter of Otto II, Duke of Swabia and founder of the Abbey of Saint Faith in Schlettstadt, Alsace. When Frederick succeeded his father, he had Hohenstaufen Castle erected on the eponymous mountain in the Swabian Jura range, which became the ancestral seat of the dynasty. He also founded a Benedictine abbey at the site of former Lorch castle about 1100. By his mother he ruled over large Alsatian estates around Schlettstadt and Hagenau. When during the Investiture Controversy the Swabian duke Rudolf of Rheinfelden was elected anti-king to King Henry IV of Germany, Frederick remained a loyal supporter of the ruling Salian dynasty. In turn Henry veste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Est
Grand Est (; ) is an Regions of France, administrative region in northeastern France. It superseded three former administrative regions, Alsace, Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine, on 1 January 2016 under the provisional name of Alsace-Champagne-Ardenne-Lorraine (; ACAL or, less commonly, ALCALIA), as a result of territorial reform which had been passed by the French Parliament in 2014. The region sits astride three water basins (Seine, Meuse and Rhine), spanning an area of , the fifth largest in France; it includes two mountain ranges (Vosges and Ardennes). It shares borders with Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany and Switzerland. As of 2021, it had a population of 5,561,287 inhabitants. The Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city is Strasbourg. The East of France has a rich and diverse culture, being situated at a crossroads between the Gallo-Romance languages, Gallic-Latin and Germanic languages, Germanic worlds. This history is reflected in the variety of languages spoken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ill (France)
The Ill ( ; , ) is a river in Alsace, in north-eastern France, and a left-bank, or western, tributary of the Rhine. It is long. It starts down from its source near the village of Winkel, Haut-Rhin, Winkel, in the Jura mountains, with a resurgence near Ligsdorf, turns around Ferrette on its east side, and then runs northward through Alsace, flowing parallel to the Rhine. Taking apart the Largue, also coming from the Jura mountains near Illfurth, it receives several tributaries from the west bank Vosges mountains after passing through Altkirch: the Doller (river), Doller in Mulhouse, the Thur (France), Thur near Ensisheim, the Lauch in Colmar, the Fecht (river), Fecht in Illhaeusern, the Giessen in Sélestat, the Andlau near Fegersheim, the Ehn near Geispolsheim, the Bruche (river), Bruche next to Strasbourg and the Souffel upstream from La Wantzenau before meeting with the Rhine downstream from Gambsheim's Lock (water transport), lock. As the Ill nears the city of Mulhouse, most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AD 727
__NOTOC__ Year 727 ( DCCXXVII) was a common year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 727 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * A revolt breaks out in Greece against the religious policies of Emperor Leo III (see 726). A rebel fleet under Agallianos Kontoskeles sets out for Constantinople with Kosmas, an anti-emperor, but is destroyed by the Byzantine fleet through the use of Greek fire. * Siege of Nicaea: Muslim forces under Mu'awiya ibn Hisham (son of Umayyad caliph Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik) penetrate deep into Asia Minor, and sack the fortress city of Gangra, but unsuccessfully lay siege to Nicaea (northwestern Anatolia). Europe * A revolt breaks out in Italy against Leo's Iconoclasm; this results in the independence of the Exarchate of Ravenna, after part of a Byzantine invasion force is lost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in Epipaleolithic Near East, the Levant and Epipaleolithic Caucasus, Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and the Middle East, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 Before Present, BP; in the Middle East (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 Before Present, BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |