Madyes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Madyes was a
 In the 8th and 7th centuries BCE, a significant movement of the nomads of the Eurasian steppe brought the Scythians into Southwest Asia. This movement started when another nomadic Iranic tribe closely related to the Scythians, either the Massagetae or the
In the 8th and 7th centuries BCE, a significant movement of the nomads of the Eurasian steppe brought the Scythians into Southwest Asia. This movement started when another nomadic Iranic tribe closely related to the Scythians, either the Massagetae or the
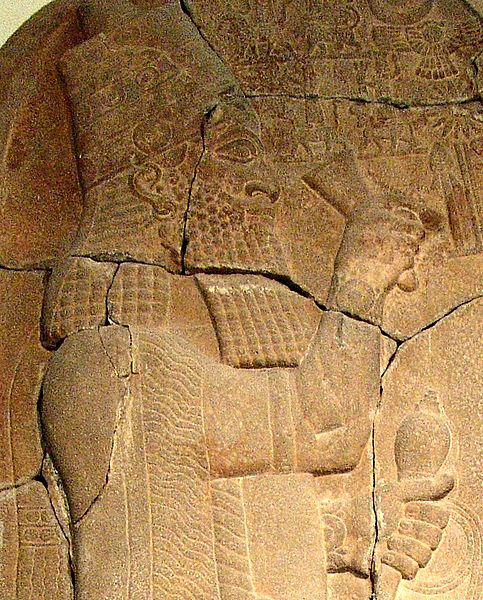



 Madyes soon expanded the Scythian hegemony to the state of Urartu as well, with Media, Mannai and Urartu all continuing to exist as kingdoms under Scythian suzerainty.
Madyes soon expanded the Scythian hegemony to the state of Urartu as well, with Media, Mannai and Urartu all continuing to exist as kingdoms under Scythian suzerainty.
 In 637 BCE, the
In 637 BCE, the
 By the 620s BCE, the Neo-Assyrian Empire began unravelling after the death of Ashurbanipal in 631 BCE: in addition to internal instability within Assyria itself,
By the 620s BCE, the Neo-Assyrian Empire began unravelling after the death of Ashurbanipal in 631 BCE: in addition to internal instability within Assyria itself,
 Madyes's relationship with the Scythian kings after him and the identity of his successor are both unknown, although shortly after his assassination, some time between 623 and 616 BCE, the Scythians took advantage of the power vacuum created by the crumbling of the power of their former Assyrian allies and overran the
Madyes's relationship with the Scythian kings after him and the identity of his successor are both unknown, although shortly after his assassination, some time between 623 and 616 BCE, the Scythians took advantage of the power vacuum created by the crumbling of the power of their former Assyrian allies and overran the
Scythian
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC fr ...
king who ruled during the period of the Scythian presence in West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
in the 7th century BCE.
Madyes was the son of the Scythian king Bartatua and the Assyrian princess Šērūʾa-ēṭirat, and, as an ally of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East and parts of South Caucasus, Nort ...
, which was then the superpower of West Asia and whose king Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal (, meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir")—or Osnappar ()—was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BC to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Ashurbanipal inherited the th ...
was his uncle, he brought Scythian power to its peak in West Asia.
After the Neo-Assyrian Empire started unravelling, Madyes was assassinated by the Median king Cyaxares, who expelled the Scythians from West Asia.
Name
The name is the Latinised form of (), which is itself the Ancient Greek form of an Old Iranic name. Iranologist had initially suggested that the original form of Madyes's name wasScythian
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC fr ...
, meaning "mead", derived from a term for honey, .
However, the Iranic sound had evolved into in Proto-Scythian, and later evolved into in Scythian, due to which the Proto-Iranic term had become in Scythian, hence why the scholar considered the derivation of from as unlikely, and, noting that the name of Madyes was transmitted through Persian sources to the Greek authors who recorded it, proposed that the name instead originated from a Western Iranic form , meaning "Median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “ ...
".
Historical background
 In the 8th and 7th centuries BCE, a significant movement of the nomads of the Eurasian steppe brought the Scythians into Southwest Asia. This movement started when another nomadic Iranic tribe closely related to the Scythians, either the Massagetae or the
In the 8th and 7th centuries BCE, a significant movement of the nomads of the Eurasian steppe brought the Scythians into Southwest Asia. This movement started when another nomadic Iranic tribe closely related to the Scythians, either the Massagetae or the Issedones
The Issedones () were an ancient people of Central Asia at the end of the trade route leading north-east from Scythia, described in the lost ''Arimaspeia'' of Aristeas, by Herodotus in his ''History'' (IV.16-25) and by Ptolemy in his ''Geography''. ...
, migrated westwards, forcing the Early Scythians of the to the west across the Araxes river, following which the Scythians moved into the Caspian Steppe from where they displaced the Cimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
.
Under Scythian pressure, the Cimmerians migrated to the south along the coast of the Black Sea and reached Anatolia, and the Scythians in turn later expanded to the south, following the coast of the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
and arrived in the steppes in the Northern Caucasus, from where they expanded into the region of present-day Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
, where they settled and turned eastern Transcaucasia
The South Caucasus, also known as Transcaucasia or the Transcaucasus, is a geographical region on the border of Eastern Europe and West Asia, straddling the southern Caucasus Mountains. The South Caucasus roughly corresponds to modern Armenia, ...
into their centre of operations in West Asia until the early 6th century BCE, with this presence in West Asia being an extension of the Scythian kingdom of the steppes. During this period, the Scythian kings' headquarters were located in the steppes to the north of Caucasus, and contact with the civilisation of West Asia would have an important influence on the formation of Scythian culture.
Life and reign

Background
Madyes was the son of the previous Scythian king, Bartatua, and possibly the grandson of Bartatua's predecessor, Išpakaia. Išpakaia had been an enemy of the then superpower in West Asia, theNeo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East and parts of South Caucasus, Nort ...
, and was killed in battle against the Assyrian king Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon (, also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 681 to 669 BC. The third king of the S ...
, after which Bartatua became the king of the Scythians and instead sought to ally with the Assyrians.
The name of Madyes's mother is not recorded, but, since Bartatua had asked in marriage the hand of the Assyrian princess Šērūʾa-ēṭirat, who was the daughter of Esarhaddon and the sister of his successors Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal (, meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir")—or Osnappar ()—was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BC to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Ashurbanipal inherited the th ...
and Shamash-shum-ukin, and there was a close alliance between the Scythians and Assyria under the reigns of Bartatua and Madyes, this suggests that the Assyrian priests did approve of this marriage between a daughter of an Assyrian king and a nomadic lord, which had never happened before in Assyrian history; the Scythians were thus brought into a marital alliance with Assyria, and Šērūʾa-ēṭirat was likely the mother of Bartatua's son Madyes.
Bartatua's marriage to Šērūʾa-ēṭirat required that he would pledge allegiance to Assyria as a vassal, and in accordance to Assyrian law, the territories ruled by him would be his fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal alle ...
granted by the Assyrian king, which made the Scythian presence in West Asia a nominal extension of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. Under this arrangement, the power of the Scythians in West Asia heavily depended on their cooperation with the Assyrian Empire; henceforth, the Scythians remained allies of the Assyrian Empire. Around this time, the Urartian king Rusa II might also have enlisted Scythian troops to guard his western borderlands.
The marital alliance between the Scythian king and the Assyrian ruling dynasty, as well as the proximity of the Scythians with Mannai and Urartu
Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Armenia.Kleiss, Wo ...
, placed the Scythians under the strong influence of Assyrian culture. After Bartatua's death, Madyes succeeded him.
Conquest of Media
When, following a period of Assyrian decline over the course of the 650s BCE, Esarhaddon's other son, Shamash-shum-ukin, who had succeeded him as the king of Babylon, revolted against his brother Ashurbanipal in 652 BCE, the Medes supported him, and Madyes helped Ashurbanipal suppress the revolt externally by invading the Medes. The Median king Phraortes was killed in battle, either against the Assyrians or against Madyes himself, who then imposed Scythian hegemony overMedia
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Means of communication, tools and channels used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Interactive media, media that is inter ...
for twenty-eight years on behalf of the Assyrians, thus starting a period which Greek authors called the "Scythian rule over Asia."


Defeat of the Cimmerians
During the 7th century BCE, the bulk of theCimmerians
The Cimmerians were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranic Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into W ...
were operating in Anatolia, where they constituted a threat against the Scythians' Assyrian allies, who since 669 BCE were ruled by Madyes's uncle, that is Esarhaddon's son and Šērūʾa-ēṭirat's brother, Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal (, meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir")—or Osnappar ()—was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BC to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Ashurbanipal inherited the th ...
. Assyrian records in 657 BCE might have referred to a threat against or a conquest of the western possessions of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, and these Cimmerian aggressions worried Ashurbanipal about the security of his empire's north-west border. By 657 BCE the Assyrian divinatory records were calling the Cimmerian king Tugdammi by the title of (" King of the Universe"), which could normally belong only to the Neo-Assyrian King: thus, Tugdammi's successes against Assyria meant that he had become recognised in ancient West Asia as equally powerful as Ashurbanipal, and the kingship over the Universe, which rightfully belonged to the Assyrian king, had been usurped by the Cimmerians and had to be won back by Assyria. This situation continued throughout the rest of the 650s BCE and the early 640s BCE.
In 644 BCE, the Cimmerians, led by Tugdammi, attacked the kingdom of Lydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis.
At some point before 800 BC, ...
, defeated the Lydians and captured the Lydian capital, Sardis
Sardis ( ) or Sardes ( ; Lydian language, Lydian: , romanized: ; ; ) was an ancient city best known as the capital of the Lydian Empire. After the fall of the Lydian Empire, it became the capital of the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Lydia (satrapy) ...
; the Lydian king Gyges died during this attack. After sacking Sardis, Tugdammi led the Cimmerians into invading the Greek city-states of Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
and Aeolis
Aeolis (; ), or Aeolia (; ), was an area that comprised the west and northwestern region of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), mostly along the coast, and also several offshore islands (particularly Lesbos), where the Aeolian Greek city-states w ...
on the western coast of Anatolia. After this attack on Lydia and the Asian Greek cities, around 640 BCE the Cimmerians moved to Cilicia
Cilicia () is a geographical region in southern Anatolia, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population ranging over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilician plain (). The region inclu ...
on the north-west border of the Neo-Assyrian empire, where, after Tugdammi faced a revolt against himself, he allied with Assyria and acknowledged Assyrian overlordship, and sent tribute to Ashurbanipal, to whom he swore an oath. Tugdammi soon broke this oath and attacked the Neo-Assyrian Empire again, but he fell ill and died in 640 BCE, and was succeeded by his son Sandakšatru.
 In 637 BCE, the
In 637 BCE, the Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, ...
Treres tribe who had migrated across the Thracian Bosporos and invaded Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, under their king Kōbos and in alliance with Sandakšatru's Cimmerians and the Lycians
Lycians () is the name of various peoples who lived, at different times, in Lycia, a geopolitical area in Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor).
History
The earliest known inhabitants of the area were the ''Solymoi'' (or ''Solymi''), also kn ...
, attacked Lydia during the seventh year of the reign of Gyges's son Ardys. They defeated the Lydians and captured their capital of Sardis except for its citadel, and Ardys might have been killed in this attack. Ardys's son and successor, Sadyattes, might possibly also have been killed in another Cimmerian attack on Lydia in 635 BCE.
Soon after 635 BCE, with Assyrian approval: A Scythian army, acting in conformity with Assyrian policy, entered Pontis to crush the last of the Cimmerians. and in alliance with the Lydians, the Scythians under Madyes entered Anatolia, expelled the Treres from Asia Minor, and defeated the Cimmerians so that they no longer constituted a threat again, following which the Scythians extended their domination to Central Anatolia. This final defeat of the Cimmerians was carried out by the joint forces of Madyes, whom Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
credits with expelling the Treres and Cimmerians from Asia Minor, and of Sadyattes's son, Ardys's grandson, and Gyges's great-grandson, the king Alyattes
Alyattes ( Lydian language: ; ; reigned c. 635 – c. 585 BC), sometimes described as Alyattes I, was the fourth king of the Mermnad dynasty in Lydia, the son of Sadyattes, grandson of Ardys, and great-grandson of Gyges. He died after a r ...
of Lydia, whom Herodotus of Halicarnassus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histories ...
and Polyaenus
Polyaenus or Polyenus ( ; see ae (æ) vs. e; , "much-praised") was a 2nd-century Roman Macedonian author and rhetorician, known best for his ''Stratagems in War'' (), which has been preserved. He was born in Bithynia, Asia Minor. The ''Suda'' c ...
claim finally defeated the Cimmerians.
In Polyaenus' account of the defeat of the Cimmerians, he claimed that Alyattes used "war dogs" to expel them from Asia Minor, with the term "war dogs" being a Greek folkloric reinterpretation of young Scythian warriors who, following the Indo-European passage rite of the , would ritually take on the role of wolf- or dog-warriors.
Scythian power in West Asia thus reached its peak under Madyes, with the territories ruled by the Scythians extending from the Halys river Halys may refer to:
* Health-adjusted life years (HALYs), a type of disability-adjusted life year which are used in attempts to quantify the burden of disease or disability in populations
* Halys River, a western name for the Kızılırmak River ...
in Anatolia in the west to the Caspian Sea and the eastern borders of Media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Means of communication, tools and channels used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Interactive media, media that is inter ...
in the east, and from Transcaucasia in the north to the northern borders of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in the south.
Revolt of Media and death
 By the 620s BCE, the Neo-Assyrian Empire began unravelling after the death of Ashurbanipal in 631 BCE: in addition to internal instability within Assyria itself,
By the 620s BCE, the Neo-Assyrian Empire began unravelling after the death of Ashurbanipal in 631 BCE: in addition to internal instability within Assyria itself, Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
revolted against the Assyrians in 626 BCE under the leadership of Nabopolassar
Nabopolassar (, meaning "Nabu, protect the son") was the founder and first king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from his coronation as king of Babylon in 626 BC to his death in 605 BC. Though initially only aimed at restoring and securing ...
. The next year, in 625 BCE, Cyaxares, the son of Phraortes and his successor to the Median kingship, overthrew the Scythian yoke over the Medes by inviting the Scythian rulers to a banquet and then murdering them all, including Madyes, after getting them drunk.
Aftermath
 Madyes's relationship with the Scythian kings after him and the identity of his successor are both unknown, although shortly after his assassination, some time between 623 and 616 BCE, the Scythians took advantage of the power vacuum created by the crumbling of the power of their former Assyrian allies and overran the
Madyes's relationship with the Scythian kings after him and the identity of his successor are both unknown, although shortly after his assassination, some time between 623 and 616 BCE, the Scythians took advantage of the power vacuum created by the crumbling of the power of their former Assyrian allies and overran the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and reached as far south as Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
till the borders of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, where their advance was stopped by the marshes of the Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the eas ...
, after which the pharaoh Psamtik I
Wahibre Psamtik I (Ancient Egyptian: ) was the first pharaoh of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt, the Saite period, ruling from the city of Sais in the Nile delta between 664 and 610 BC. He was installed by Ashurbanipal of the Neo-Assyrian E ...
met them and convinced them to turn back by offering them gifts. The Scythians retreated by passing through Askalon largely without any incident, although some stragglers looted the temple of Astarte
Astarte (; , ) is the Greek language, Hellenized form of the Religions of the ancient Near East, Ancient Near Eastern goddess ʿAṯtart. ʿAṯtart was the Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic equivalent of the East Semitic language ...
in the city, which was considered to be the most ancient of all temples to that goddess, as a result of which the perpetrators of this sacrilege and their descendants were allegedly cursed by Astarte with a "female disease," due to which they became a class of transvestite diviners called the (meaning "unmanly" in Scythian
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people who had migrated during the 9th to 8th centuries BC fr ...
).
According to Babylonian records, around 615 BCE the Scythians were operating as allies of Cyaxares and the Medes in their war against Assyria. The Scythians were finally expelled from West Asia by the Medes in the 600s BCE, after which they retreated into the Pontic Steppe
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to:
The Black Sea Places
* The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores
* Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores
* The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from n ...
.
Legacy
TheGraeco-Roman
The Greco-Roman world , also Greco-Roman civilization, Greco-Roman culture or Greco-Latin culture (spelled Græco-Roman or Graeco-Roman in British English), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and co ...
authors conflated Madyes with his predecessors and successors into a single figure by claiming that it was Madyes himself who led the Scythians from Central Asia into chasing the Cimmerians out of their homeland and then defeating the Medes and the legendary Egyptian king Sesostris
Sesostris () is the name of a king of ancient Egypt who, according to Herodotus, led a military expedition into parts of Europe. Tales of Sesostris are probably based on the life of Senusret I, Senusret III and perhaps other Pharaohs such as Sho ...
and imposing their rule over Asia for many years before returning to Scythia
Scythia (, ) or Scythica (, ) was a geographic region defined in the ancient Graeco-Roman world that encompassed the Pontic steppe. It was inhabited by Scythians, an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people.
Etymology
The names ...
. Later Graeco-Roman authors named this Scythian king as Idanthyrsos or Tanausis, although this Idanthyrsos is a legendary figure separate from the later historical Scythian king Idanthyrsus, from whom the Graeco-Romans derived merely his name.
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * , - {{Median topics Scythian kings 7th-century BC deaths Year of birth unknown 7th-century BC monarchs in Asia