M2-F1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The NASA M2-F1 is a lightweight, unpowered prototype aircraft, developed to flight-test the wingless
 The first flight tests of the M2-F1 were at
The first flight tests of the M2-F1 were at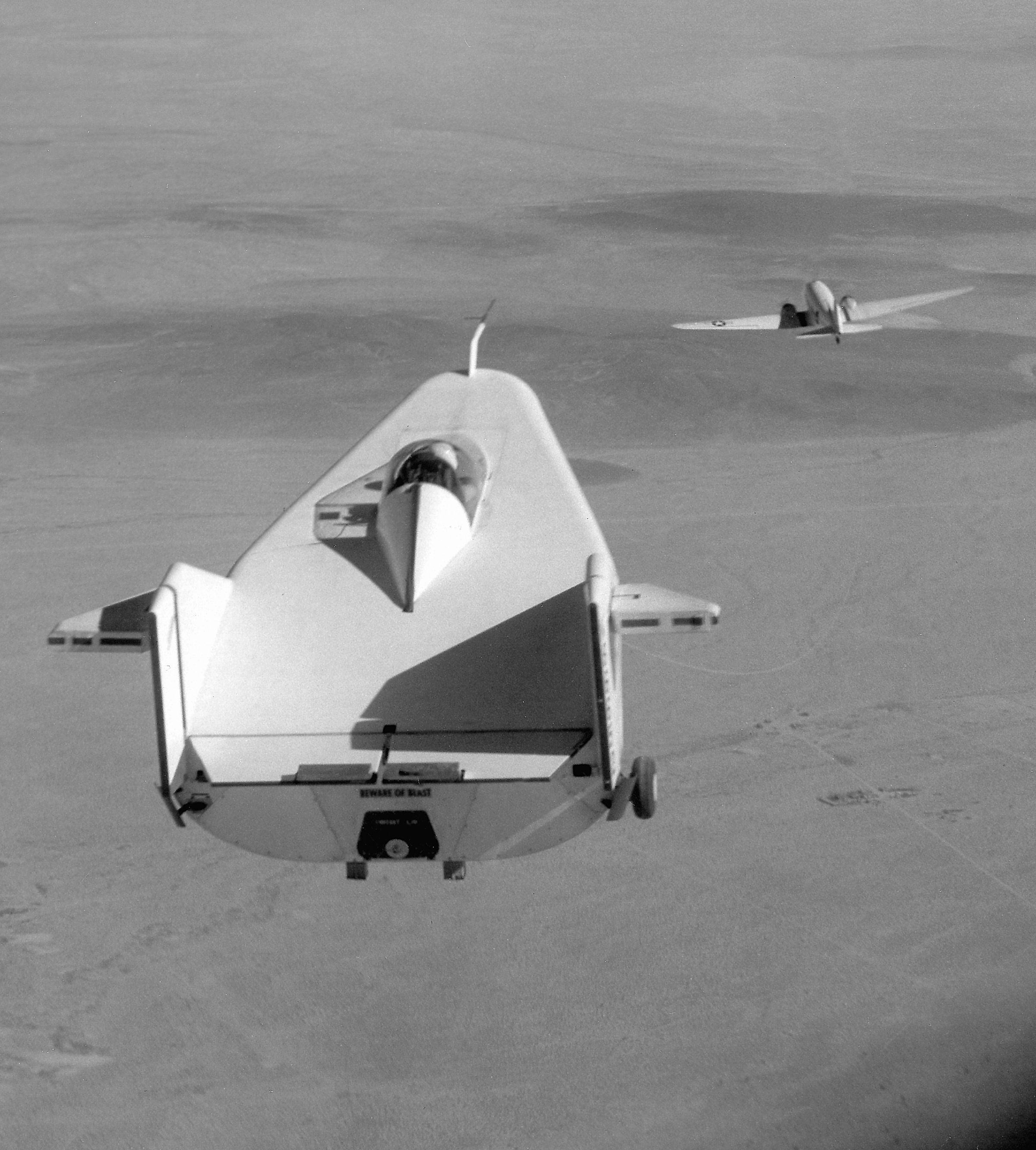  These initial tests produced enough flight data about the M2-F1 to proceed with flights behind a NASA R4D tow plane at greater altitudes.
These initial tests produced enough flight data about the M2-F1 to proceed with flights behind a NASA R4D tow plane at greater altitudes.
lifting body
A lifting body is a fixed-wing aircraft or spacecraft configuration in which the body itself produces lift (force), lift. In contrast to a flying wing, which is a wing with minimal or no conventional fuselage, a lifting body can be thought of as ...
concept. Its unusual appearance earned it the nickname "flying bathtub" and was designated the M2-F1, the M referring to "manned", and F referring to "flight" version. In 1962
The year saw the Cuban Missile Crisis, which is often considered the closest the world came to a Nuclear warfare, nuclear confrontation during the Cold War.
Events January
* January 1 – Samoa, Western Samoa becomes independent from Ne ...
, NASA Dryden management approved a program to build a lightweight, unpowered lifting-body prototype. It featured a plywood shell placed over a tubular steel frame crafted at Dryden. Construction was completed in 1963
Events January
* January 1 – Bogle–Chandler case: Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation scientist Dr. Gilbert Bogle and Mrs. Margaret Chandler are found dead (presumed poisoned), in bushland near the Lane Cove ...
.
Development
The lifting-body concept originated in the mid-1950s at theNational Advisory Committee for Aeronautics
The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) was a United States federal agency that was founded on March 3, 1915, to undertake, promote, and institutionalize aeronautical research. On October 1, 1958, the agency was dissolved and its ...
' Ames Aeronautical Laboratory
The Ames Research Center (ARC), also known as NASA Ames, is a major NASA research center at Moffett Federal Airfield in California's Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1939 as the second National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) laborat ...
, Mountain View, California
Mountain View is a city in Santa Clara County, California, United States, part of the San Francisco Bay Area. Named for its views of the Santa Cruz Mountains, the population was 82,376 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census.
Mountain V ...
. By February 1962, a series of possible shapes had been developed, and R. Dale Reed was working to gain support for a research vehicle.
The construction of the M2-F1 was a joint effort by Dryden and a local glider manufacturer, the Briegleb Glider Company. The budget was US$30,000. NASA craftsmen and engineers built the tubular steel interior frame. Its mahogany plywood shell was handmade by Gus Briegleb and company. Ernie Lowder, a NASA craftsman who had worked on Howard Hughes
Howard Robard Hughes Jr. (December 24, 1905 – April 5, 1976) was an American Aerospace engineering, aerospace engineer, business magnate, film producer, and investor. He was The World's Billionaires, one of the richest and most influential peo ...
's H-4 Hercules ("Spruce Goose"), was assigned to help Briegleb.
Final assembly of the remaining components (including aluminum tail surfaces, pushrod controls, and landing gear from a Cessna 150
The Cessna 150 is a two-seat tricycle gear general aviation airplane that was designed for flight training, touring and personal use.Plane and Pilot: ''1978 Aircraft Directory'', pages 22-23. Werner & Werner Corp, Santa Monica CA, 1977. In 19 ...
, later replaced by Cessna 180
The Cessna 180 Skywagon is a four- or six-seat, fixed conventional gear general aviation airplane which was produced between 1953 and 1981. Though the design is no longer in production, many of these aircraft are still in use as personal airc ...
landing gear) was done at the NASA facility.
The wingless, lifting-body aircraft design was initially conceived as a means of landing a spacecraft horizontally after atmospheric reentry. The absence of wings would make the extreme heat of reentry less damaging to the vehicle. Rather than using a ballistic reentry trajectory like a Command Module, very limited in maneuvering range, a lifting-body vehicle had a landing footprint
A landing footprint, also called a landing ellipse, is the area of uncertainty of a spacecraft's landing zone on an astronomical body. After atmospheric entry, the landing point of a spacecraft will depend upon the degree of control (if any), ent ...
of the size of California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
.
Tow testing
 The first flight tests of the M2-F1 were at
The first flight tests of the M2-F1 were at Rogers Dry Lake
Rogers Dry Lake is an endorheic desert salt pan in the Mojave Desert of Kern County, California. The lake derives its name from the Anglicization from the Spanish name, Rodriguez Dry Lake. It is the central part of Edwards Air Force Base as its ...
, at the end of a tow rope attached to a 1963 Pontiac Catalina
The Pontiac Catalina is a full-size automobile produced by Pontiac (automobile), Pontiac from 1950 to 1981. Initially, the name was a trim line on hardtop body styles, first appearing in the 1950 Chieftain Eight and DeLuxe Eight lines. In 1959, it ...
convertible. On April 5, 1963 test pilot Milt Thompson lifted the M2-F1's nose off the ground for the first time while being towed. The speed was . The little craft seemed to bounce uncontrollably between the main landing gear wheels, and stopped when he lowered the nose to the ground. He tried again, but each time with the same results. He felt it was a landing gear problem that could have caused the aircraft to roll on its back if he had lifted the main gear off the ground.
After looking at movies of the tests, it was decided that the bouncing was probably caused by unwanted rudder
A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium (usually air or water). On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw ...
movements. The control system was modified so that the joystick controlled the elevons
Elevons or tailerons are aircraft control surfaces that combine the functions of the elevator (used for pitch control) and the aileron (used for roll control), hence the name. They are frequently used on tailless aircraft such as flying wings. ...
rather than the rudder, which solved the problem.
It was found that the car used to tow the aircraft was not powerful enough to lift the M2-F1 entirely off the ground, so the FRC arranged to have the tow car hot-rodded by Bill Straub: the modifications tuned the engine for increased power, added a rollbar, and turned the front passenger seat to face aft so the passenger could observe the aircraft. This proved successful, and tow tests continued.
Speeds on tow inched up to , which allowed Thompson to climb to about , then glide for about 20 seconds after releasing the line. That was the most that could be expected during an auto tow.
 These initial tests produced enough flight data about the M2-F1 to proceed with flights behind a NASA R4D tow plane at greater altitudes.
These initial tests produced enough flight data about the M2-F1 to proceed with flights behind a NASA R4D tow plane at greater altitudes.
Flight testing
A NASA R4D, the Navy designation for the Douglas DC-3, was used for all of the air tows. The first was on August 16, 1963. The M2-F1 had recently been equipped with an ejection seat and small rockets – referred to by the test team as "instant L/D" – in the tail to extend thelanding flare
The landing flare, also referred to as the round out, is a maneuver or stage during the landing of an aircraft.
The flare follows the final approach phase and precedes the touchdown and roll-out phases of landing. In the flare, the nose of ...
for about 5 seconds if needed, and Thompson prepared for the flight with a few more tows behind the Pontiac.
Forward visibility in the M2-F1 was very limited on tow, requiring Thompson to fly about higher than the R4D, so he could see the plane through the nose window. Towing speed was about .
The R4D took the craft to an altitude of , where free flights back to Rogers Dry Lake began. Pilot for the first series of flights of the M2-F1 was NASA research pilot Milt Thompson. Typical glide flights with the M2-F1 lasted about two minutes and reached speeds of .
Tow release was at . The lifting body descended at an average rate of about 3,600 feet per minute (1,100 m/min). At above the ground, the nose was lowered to increase speed to about , flare was at from a 20° dive. The landing was smooth, and the lifting-body program was on its way.
The M2-F1 was flown until August 16, 1966. It proved the lifting-body concept and led the way for subsequent metal "heavyweight" designs. Chuck Yeager
Brigadier general (United States), Brigadier General Charles Elwood Yeager ( , February 13, 1923December 7, 2020) was a United States Air Force officer, flying ace, and record-setting test pilot who in October 1947 became the first pilot in his ...
, Bruce Peterson
Bruce A. Peterson (May 23, 1933 – May 1, 2006) was an American aeronautical engineer, and test pilot for NASA.
Biography Early life and education
Peterson was born on May 23, 1933. A native of Washburn, North Dakota, he attended the Univ ...
and Donald L. Mallick
Donald L. Mallick (born October 4, 1930) is an American former pilot at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center from 1963 to 1981. He later became the deputy chief for the Dryden Aircraft Operations Division.Northrop M2-F2
The Northrop M2-F2 was a heavyweight lifting body based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers and built by the Northrop Corporation in 1966.
Development
The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and cons ...
and the Northrop HL-10
The Northrop HL-10 is one of five US heavyweight lifting body designs flown at NASA's Flight Research Center (FRC—later Dryden Flight Research Center) in Edwards, California, from July 1966 to November 1975 to study and validate the concept ...
, both built by the Northrop Corporation, and the U.S. Air Force's X-24 program. The lifting-body program also heavily influenced the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
program.
The M2-F1 program demonstrated the feasibility of the lifting-body concept for horizontal landings of atmospheric entry vehicles. It also demonstrated a procurement and management concept for prototype flight research vehicles that produced rapid results at very low cost (approximately US$50,000, excluding salaries of government employees assigned to the project).
Pilots
* Milt Thompson – 45 flights *Bruce Peterson
Bruce A. Peterson (May 23, 1933 – May 1, 2006) was an American aeronautical engineer, and test pilot for NASA.
Biography Early life and education
Peterson was born on May 23, 1933. A native of Washburn, North Dakota, he attended the Univ ...
– 17 flights
* Chuck Yeager
Brigadier general (United States), Brigadier General Charles Elwood Yeager ( , February 13, 1923December 7, 2020) was a United States Air Force officer, flying ace, and record-setting test pilot who in October 1947 became the first pilot in his ...
– 5 flights
* Donald M. Sorlie – 5 flights
* Donald L. Mallick
Donald L. Mallick (born October 4, 1930) is an American former pilot at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center from 1963 to 1981. He later became the deputy chief for the Dryden Aircraft Operations Division.Jerauld R. Gentry – 2 flights
*
Project Habu: M2-F1
/ref>
NASA Dryden M2-F1 Photo Collection
{{X-planes Lifting bodies M2-F1, NASA NASA M2-F1 Lifting Body NASA aircraft Aircraft manufactured in the United States Aircraft first flown in 1963
Bill Dana
William Szathmary (October 5, 1924 June 15, 2017), known as Bill Dana, was an American comedian, actor, and screenwriter. He often appeared on television shows such as The Steve Allen Show, frequently in the guise of a heavily accented Bolivian ...
– 1 flight
* James W. Wood
James Wayne Wood (August 9, 1924 – January 1, 1990), (Colonel (United States), Col, United States Air Force, USAF), was an American aeronautical engineer, U.S. Air Force, U.S. Air Force officer, test pilot, and astronaut in the Boeing X-20 Dyna ...
– 1 ground tow
* Fred Haise
Fred Wallace Haise Jr. ( ; born November 14, 1933) is an American former NASA astronaut, engineer, fighter pilot with the United States Marine Corps Aviation, U.S. Marine Corps and United States Air Force, U.S. Air Force, and a test pilot. He ...
– 1 ground tow
* Joe Engle
Joe Henry Engle (August 26, 1932 – July 10, 2024) was an American pilot, aeronautical engineer, and NASA astronaut. He was the commander of two Space Shuttle missions including STS-2 in 1981, the program's second orbital flight. He also flew ...
– 1 ground tow
Aircraft serial number
* NASA M2-F1 – N86652, 77 flights, 400 ground towsAircraft on display
As of January 23, 2015, M2-F1 N86652 is on display at theAir Force Flight Test Museum
The Air Force Flight Test Museum is an aviation museum located at Edwards Air Force Base near Rosamond, California focused on the history of the Air Force Flight Test Center.
History
The Flight Test Museum Foundation was founded in 1983 by Car ...
on Edwards Air Force Base
Edwards Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in California. Most of the base sits in Kern County, California, Kern County, but its eastern end is in San Bernardino County, California, San Bernardino County and a souther ...
, California./ref>
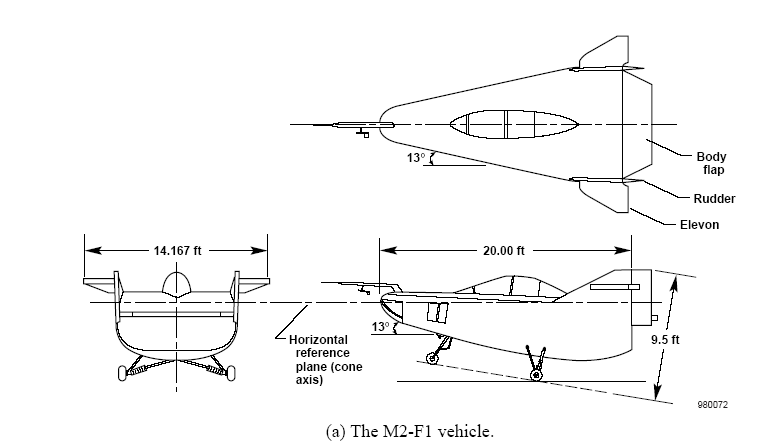
Specifications

Flights
See also
References
NASA Dryden M2-F1 Photo Collection
{{X-planes Lifting bodies M2-F1, NASA NASA M2-F1 Lifting Body NASA aircraft Aircraft manufactured in the United States Aircraft first flown in 1963