Logic gates on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A logic gate is a device that performs a
A logic gate is a device that performs a
10:00 min
/ref> Using this property of electrical switches to implement logic is the fundamental concept that underlies all electronic digital
 There are two sets of symbols for elementary logic gates in common use, both defined in
There are two sets of symbols for elementary logic gates in common use, both defined in
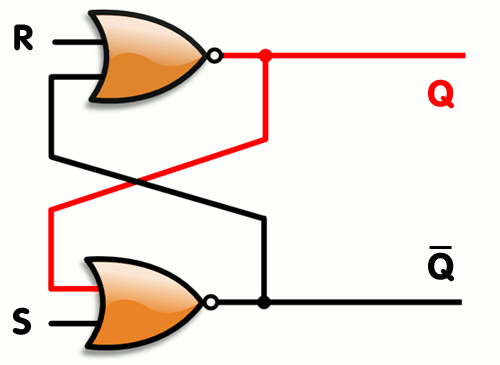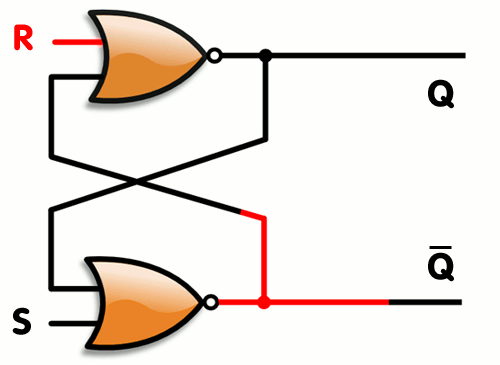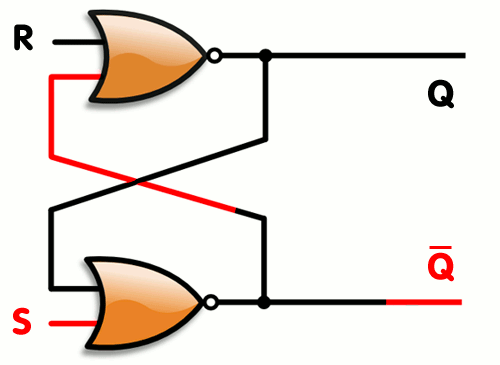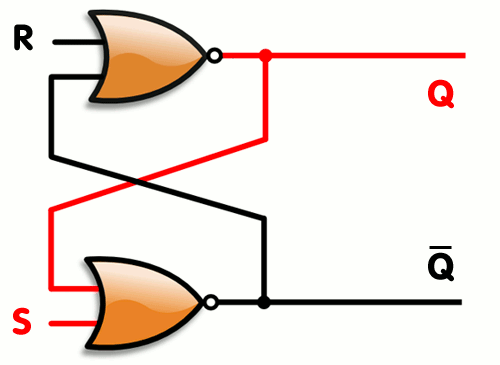 Logic gates can also be used to hold a state, allowing data storage. A storage element can be constructed by connecting several gates in a "
Logic gates can also be used to hold a state, allowing data storage. A storage element can be constructed by connecting several gates in a "
 As integrated circuits became more complex, bipolar transistors were replaced with smaller
As integrated circuits became more complex, bipolar transistors were replaced with smaller
 A three-state logic gate is a type of logic gate that can have three different outputs: high (H), low (L) and high-impedance (Z). The high-impedance state plays no role in the logic, which is strictly binary. These devices are used on
A three-state logic gate is a type of logic gate that can have three different outputs: high (H), low (L) and high-impedance (Z). The high-impedance state plays no role in the logic, which is strictly binary. These devices are used on
Boolean function
In mathematics, a Boolean function is a function whose arguments and result assume values from a two-element set (usually , or ). Alternative names are switching function, used especially in older computer science literature, and truth functi ...
, a logical operation
In logic, a logical connective (also called a logical operator, sentential connective, or sentential operator) is a logical constant. Connectives can be used to connect logical formulas. For instance in the syntax of propositional logic, th ...
performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has, for instance, zero rise time
In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time is the time taken by a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value. These values may be expressed as ratiosSee for example , and . or, equiva ...
and unlimited fan-out
In digital electronics, the fan-out is the number of gate inputs driven by the output of another single logic gate.
In most designs, logic gates are connected to form more complex circuits. While no logic gate input can be fed by more than one ...
, or it may refer to a non-ideal physical device (see ideal and real op-amps for comparison).
The primary way of building logic gates uses diode
A diode is a two-Terminal (electronics), terminal electronic component that conducts electric current primarily in One-way traffic, one direction (asymmetric electrical conductance, conductance). It has low (ideally zero) Electrical resistance ...
s or transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s acting as electronic switches. Today, most logic gates are made from MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
s (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three termi ...
s). ''From Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
'' They can also be constructed using vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
s, electromagnetic relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switc ...
s with relay logic
Relay logic is a method of implementing combinational logic in electrical control circuits by using several electrical relays wired in a particular configuration.
Ladder logic
The schematic diagrams for relay logic circuits are often called ...
, fluidic logic
Fluidics, or fluidic logic, is the use of a fluid to perform analog or digital operations similar to those performed with electronics.
The physical basis of fluidics is pneumatics and hydraulics, based on the theoretical foundation of fluid d ...
, pneumatic logic, optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
, molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry ...
, acoustics, or even mechanical
Mechanical may refer to:
Machine
* Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement
* Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations o ...
or thermal elements.
Logic gates can be cascaded in the same way that Boolean functions can be composed, allowing the construction of a physical model of all of Boolean logic
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variable (mathematics), variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denot ...
, and therefore, all of the algorithms and mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
that can be described with Boolean logic. Logic circuits include such devices as multiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several Analog signal, analog or Digital signal (electronics), digital input signals and forwards the sel ...
s, registers, arithmetic logic unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a Combinational logic, combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on ...
s (ALUs), and computer memory
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the terms ''RAM,'' ''main memory,'' or ''primary storage.'' Archaic synonyms for main memory include ...
, all the way up through complete microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
s, which may contain more than 100 million logic gates.
Compound logic gates AND-OR-invert
AND-OR-invert (AOI) logic and AOI gates are two-level compound (or complex) logic functions constructed from the combination of one or more AND gates followed by a NOR gate (equivalent to an OR gate through an Inverter gate, which is the "OI" part ...
(AOI) and OR-AND-invert OR-AND-invert gates, or OAI-gates, are logic gates comprising OR gates followed by a NAND gate. They can be efficiently implemented in logic families like CMOS and Transistor–transistor logic, TTL. They are Duality_(mathematics)#Duality_in_logic_a ...
(OAI) are often employed in circuit design because their construction using MOSFETs is simpler and more efficient than the sum of the individual gates.
History and development
The binary number system was refined byGottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz (or Leibnitz; – 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat who is credited, alongside Sir Isaac Newton, with the creation of calculus in addition to ...
(published in 1705), influenced by the ancient ''I Ching
The ''I Ching'' or ''Yijing'' ( ), usually translated ''Book of Changes'' or ''Classic of Changes'', is an ancient Chinese divination text that is among the oldest of the Chinese classics. The ''I Ching'' was originally a divination manual in ...
''s binary system. Leibniz established that using the binary system combined the principles of arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms.
...
and logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
.
The analytical engine devised by Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage (; 26 December 1791 – 18 October 1871) was an English polymath. A mathematician, philosopher, inventor and mechanical engineer, Babbage originated the concept of a digital programmable computer.
Babbage is considered ...
in 1837 used mechanical logic gates based on gears.
In an 1886 letter, Charles Sanders Peirce
Charles Sanders Peirce ( ; September 10, 1839 – April 19, 1914) was an American scientist, mathematician, logician, and philosopher who is sometimes known as "the father of pragmatism". According to philosopher Paul Weiss (philosopher), Paul ...
described how logical operations could be carried out by electrical switching circuits.Peirce, C. S., "Letter, Peirce to A. Marquand", dated 1886, '' Writings of Charles S. Peirce'', v. 5, 1993, pp. 420–423. See Early Electromechanical computer
A mechanical computer is a computer built from mechanical components such as levers and gears rather than electronic components. The most common examples are adding machines and mechanical counters, which use the turning of gears to increment ...
s were constructed from switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type o ...
es and relay logic
Relay logic is a method of implementing combinational logic in electrical control circuits by using several electrical relays wired in a particular configuration.
Ladder logic
The schematic diagrams for relay logic circuits are often called ...
rather than the later innovations of vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
s (thermionic valves) or transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s (from which later electronic computers were constructed). Ludwig Wittgenstein
Ludwig Josef Johann Wittgenstein ( ; ; 26 April 1889 – 29 April 1951) was an Austrian philosopher who worked primarily in logic, the philosophy of mathematics, the philosophy of mind, and the philosophy of language.
From 1929 to 1947, Witt ...
introduced a version of the 16-row truth table
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arg ...
as proposition 5.101 of ''Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus
The ''Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus'' (widely abbreviated and Citation, cited as TLP) is the only book-length philosophical work by the Austrian philosopher Ludwig Wittgenstein that was published during his lifetime. The project had a broad goal ...
'' (1921). Walther Bothe
Walther Wilhelm Georg Bothe (; 8 January 1891 – 8 February 1957) was a German physicist who shared the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics with Max Born "for the coincidence method and his discoveries made therewith".
He served in the military durin ...
, inventor of the coincidence circuit
In physics and electrical engineering, a coincidence circuit or coincidence gate is an electronic device with one output and two (or more) inputs. The output activates only when the circuit receives signals within a time window accepted as ''at th ...
, got part of the 1954 Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; ; ) are awards administered by the Nobel Foundation and granted in accordance with the principle of "for the greatest benefit to humankind". The prizes were first awarded in 1901, marking the fifth anniversary of Alfred N ...
in physics, for the first modern electronic AND gate in 1924. Konrad Zuse
Konrad Ernst Otto Zuse (; ; 22 June 1910 – 18 December 1995) was a German civil engineer, List of pioneers in computer science, pioneering computer scientist, inventor and businessman. His greatest achievement was the world's first programm ...
designed and built electromechanical logic gates for his computer Z1 (from 1935 to 1938).
From 1934 to 1936, NEC
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered at the NEC Supertower in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. It provides IT and network solutions, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), Inte ...
engineer Akira Nakashima, Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, computer scientist, cryptographer and inventor known as the "father of information theory" and the man who laid the foundations of th ...
and Victor Shestakov introduced switching circuit theory in a series of papers showing that two-valued Boolean algebra
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variable (mathematics), variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denot ...
, which they discovered independently, can describe the operation of switching circuits. (3+207+1 pages10:00 min
/ref> Using this property of electrical switches to implement logic is the fundamental concept that underlies all electronic digital
computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
s. Switching circuit theory became the foundation of digital circuit
In theoretical computer science, a circuit is a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function. Circuits of this kind provide a generalization of Boolean circuits and a mathematica ...
design, as it became widely known in the electrical engineering community during and after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, with theoretical rigor superseding the ''ad hoc'' methods that had prevailed previously.
In 1948, Bardeen and Brattain patented an insulated-gate transistor (IGFET) with an inversion layer. Their concept forms the basis of CMOS technology today. In 1957 Frosch and Derick were able to manufacture PMOS and NMOS planar gates. Later a team at Bell Labs demonstrated a working MOS with PMOS and NMOS gates. Both types were later combined and adapted into complementary MOS (CMOS) logic by Chih-Tang Sah
Chih-Tang "Tom" Sah (; born in November 1932 in Beijing, China) is a Chinese-American electronics engineer and condensed matter physicist. He is best known for inventing CMOS (complementary MOS) logic with Frank Wanlass at Fairchild Semiconduc ...
and Frank Wanlass at Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument by the " traitorous eight" who defected from Shockley Semi ...
in 1963.
Symbols
 There are two sets of symbols for elementary logic gates in common use, both defined in
There are two sets of symbols for elementary logic gates in common use, both defined in ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organiz ...
/IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE ...
Std 91-1984 and its supplement ANSI/IEEE Std 91a-1991. The "distinctive shape" set, based on traditional schematics, is used for simple drawings and derives from United States Military Standard
A United States defense standard, often called a military standard, "MIL-STD", "MIL-SPEC", or (informally) "MilSpecs", is used to help achieve standardization objectives by the United States Department of Defense.
Standardization is beneficial ...
MIL-STD-806 of the 1950s and 1960s. It is sometimes unofficially described as "military", reflecting its origin. The "rectangular shape" set, based on ANSI Y32.14 and other early industry standards as later refined by IEEE and IEC, has rectangular outlines for all types of gate and allows representation of a much wider range of devices than is possible with the traditional symbols. The IEC standard, IEC 60617-12, has been adopted by other standards, such as EN 60617-12:1999 in Europe, BS EN 60617-12:1999 in the United Kingdom, and DIN
DIN or Din or din may refer to:
People and language
* Din (name), people with the name
* Dīn, an Arabic word with three general senses: judgment, custom, and religion from which the name originates
* Dinka language (ISO 639 code: din), spoken ...
EN 60617-12:1998 in Germany.
The mutual goal of IEEE Std 91-1984 and IEC 617-12 was to provide a uniform method of describing the complex logic functions of digital circuits with schematic symbols. These functions were more complex than simple AND and OR gates. They could be medium-scale circuits such as a 4-bit counter to a large-scale circuit such as a microprocessor.
IEC 617-12 and its renumbered successor IEC 60617-12 do not explicitly show the "distinctive shape" symbols, but do not prohibit them. These are, however, shown in ANSI/IEEE Std 91 (and 91a) with this note: "The distinctive-shape symbol is, according to IEC Publication 617, Part 12, not preferred, but is not considered to be in contradiction to that standard." IEC 60617-12 correspondingly contains the note (Section 2.1) "Although non-preferred, the use of other symbols recognized by official national standards, that is distinctive shapes in place of symbols ist of basic gates shall not be considered to be in contradiction with this standard. Usage of these other symbols in combination to form complex symbols (for example, use as embedded symbols) is discouraged." This compromise was reached between the respective IEEE and IEC working groups to permit the IEEE and IEC standards to be in mutual compliance with one another.
In the 1980s, schematics were the predominant method to design both circuit boards and custom ICs known as gate array
A gate array is an approach to the design and manufacture of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) using a semiconductor device fabrication, prefabricated chip with components that are later interconnected into logic devices (e.g. NAN ...
s. Today custom ICs and the field-programmable gate array are typically designed with Hardware Description Languages
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, usually to design application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) and to progra ...
(HDL) such as Verilog
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits, with the highest level of abstraction being at the re ...
or VHDL
VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Program, VHSIC Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that can model the behavior and structure of Digital electronics, digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ran ...
.
De Morgan equivalent symbols
By use ofDe Morgan's laws
In propositional calculus, propositional logic and Boolean algebra, De Morgan's laws, also known as De Morgan's theorem, are a pair of transformation rules that are both Validity (logic), valid rule of inference, rules of inference. They are nam ...
, an ''AND'' function is identical to an ''OR'' function with negated inputs and outputs. Likewise, an ''OR'' function is identical to an ''AND'' function with negated inputs and outputs. A NAND gate is equivalent to an OR gate with negated inputs, and a NOR gate is equivalent to an AND gate with negated inputs.
This leads to an alternative set of symbols for basic gates that use the opposite core symbol (''AND'' or ''OR'') but with the inputs and outputs negated. Use of these alternative symbols can make logic circuit diagrams much clearer and help to show accidental connection of an active high output to an active low input or vice versa. Any connection that has logic negations at both ends can be replaced by a negationless connection and a suitable change of gate or vice versa. Any connection that has a negation at one end and no negation at the other can be made easier to interpret by instead using the De Morgan equivalent symbol at either of the two ends. When negation or polarity indicators on both ends of a connection match, there is no logic negation in that path (effectively, bubbles "cancel"), making it easier to follow logic states from one symbol to the next. This is commonly seen in real logic diagrams – thus the reader must not get into the habit of associating the shapes exclusively as OR or AND shapes, but also take into account the bubbles at both inputs and outputs in order to determine the "true" logic function indicated.
A De Morgan symbol can show more clearly a gate's primary logical purpose and the polarity of its nodes that are considered in the "signaled" (active, on) state. Consider the simplified case where a two-input NAND gate is used to drive a motor when either of its inputs are brought low by a switch. The "signaled" state (motor on) occurs when either one OR the other switch is on. Unlike a regular NAND symbol, which suggests AND logic, the De Morgan version, a two negative-input OR gate, correctly shows that OR is of interest. The regular NAND symbol has a bubble at the output and none at the inputs (the opposite of the states that will turn the motor on), but the De Morgan symbol shows both inputs and output in the polarity that will drive the motor.
De Morgan's theorem is most commonly used to implement logic gates as combinations of only NAND gates, or as combinations of only NOR gates, for economic reasons.
Truth tables
Output comparison of various logic gates:Universal logic gates
Charles Sanders Peirce
Charles Sanders Peirce ( ; September 10, 1839 – April 19, 1914) was an American scientist, mathematician, logician, and philosopher who is sometimes known as "the father of pragmatism". According to philosopher Paul Weiss (philosopher), Paul ...
(during 1880–1881) showed that NOR gates alone (or alternatively NAND gates alone) can be used to reproduce the functions of all the other logic gates, but his work on it was unpublished until 1933. The first published proof was by Henry M. Sheffer in 1913, so the NAND logical operation is sometimes called ''Sheffer stroke
In Boolean functions and propositional calculus, the Sheffer stroke denotes a logical operation that is equivalent to the negation of the conjunction operation, expressed in ordinary language as "not both". It is also called non-conjunction, ...
''; the logical NOR
In Boolean logic, logical NOR, non-disjunction, or joint denial is a truth-functional operator which produces a result that is the negation of logical or. That is, a sentence of the form (''p'' NOR ''q'') is true precisely when neither ''p' ...
is sometimes called '' Peirce's arrow''. Consequently, these gates are sometimes called ''universal logic gates''.
Data storage and sequential logic
 Logic gates can also be used to hold a state, allowing data storage. A storage element can be constructed by connecting several gates in a "
Logic gates can also be used to hold a state, allowing data storage. A storage element can be constructed by connecting several gates in a "latch
A latch or catch (called sneck in Northern England and Scotland) is a type of mechanical fastener that joins two or more objects or surfaces while allowing for their regular separation. A latch typically engages another piece of hardware on the ...
" circuit. Latching circuitry is used in static random-access memory
Static random-access memory (static RAM or SRAM) is a type of random-access memory (RAM) that uses latching circuitry (flip-flop) to store each bit. SRAM is volatile memory; data is lost when power is removed.
The ''static'' qualifier diffe ...
. More complicated designs that use clock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') is an electronic logic signal (voltage or current) which oscillates between a high and a low state at a constant frequency and ...
s and that change only on a rising or falling edge of the clock are called edge-triggered "flip-flops
Flip-flops are a type of light sandal-like shoe, typically worn as a form of casual footwear. They consist of a flat sole held loosely on the foot by a Y-shaped strap known as a toe thong that passes between the first and second toes and around ...
". Formally, a flip-flop is called a bistable circuit, because it has two stable states which it can maintain indefinitely. The combination of multiple flip-flops in parallel, to store a multiple-bit value, is known as a register. When using any of these gate setups the overall system has memory; it is then called a sequential logic
In automata theory, sequential logic is a type of logic circuit whose output depends on the present value of its input signals and on the sequence of past inputs, the input history. This is in contrast to '' combinational logic'', whose output i ...
system since its output can be influenced by its previous state(s), i.e. by the ''sequence'' of input states. In contrast, the output from combinational logic
In automata theory, combinational logic (also referred to as time-independent logic) is a type of digital logic that is implemented by Boolean circuits, where the output is a pure function of the present input only. This is in contrast to sequ ...
is purely a combination of its present inputs, unaffected by the previous input and output states.
These logic circuits are used in computer memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembe ...
. They vary in performance, based on factors of speed
In kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a non-negative scalar quantity. Intro ...
, complexity, and reliability of storage, and many different types of designs are used based on the application.
Manufacturing
Electronic gates
A functionally complete logic system may be composed ofrelay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switc ...
s, valves (vacuum tubes), or transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s.
Electronic logic gates differ significantly from their relay-and-switch equivalents. They are much faster, consume much less power, and are much smaller (all by a factor of a million or more in most cases). Also, there is a fundamental structural difference. The switch circuit creates a continuous metallic path for current to flow (in either direction) between its input and its output. The semiconductor logic gate, on the other hand, acts as a high- gain voltage
Voltage, also known as (electrical) potential difference, electric pressure, or electric tension, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a Electrostatics, static electric field, it corresponds to the Work (electrical), ...
amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power su ...
, which sinks a tiny current at its input and produces a low-impedance voltage at its output. It is not possible for current to flow between the output and the input of a semiconductor logic gate.
For small-scale logic, designers now use prefabricated logic gates from families of devices such as the TTL 7400 series
The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs).
In 1964, Texas Instruments introduced the SN5400 series of logic chips, in a ceramic semiconductor package. A low-cost plastic package ...
by Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American multinational semiconductor company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog ...
, the CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
4000 series by RCA
RCA Corporation was a major American electronics company, which was founded in 1919 as the Radio Corporation of America. It was initially a patent pool, patent trust owned by General Electric (GE), Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghou ...
, and their more recent descendants. Increasingly, these fixed-function logic gates are being replaced by programmable logic device
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, the function of a PLD is undefined at the time of m ...
s, which allow designers to pack many mixed logic gates into a single integrated circuit. The field-programmable nature of programmable logic device
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, the function of a PLD is undefined at the time of m ...
s such as FPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of a ...
s has reduced the 'hard' property of hardware; it is now possible to change the logic design of a hardware system by reprogramming some of its components, thus allowing the features or function of a hardware implementation of a logic system to be changed.
An important advantage of standardized integrated circuit logic families, such as the 7400 and 4000 families, is that they can be cascaded. This means that the output of one gate can be wired to the inputs of one or several other gates, and so on. Systems with varying degrees of complexity can be built without great concern of the designer for the internal workings of the gates, provided the limitations of each integrated circuit are considered.
The output of one gate can only drive a finite number of inputs to other gates, a number called the 'fan-out
In digital electronics, the fan-out is the number of gate inputs driven by the output of another single logic gate.
In most designs, logic gates are connected to form more complex circuits. While no logic gate input can be fed by more than one ...
limit'. Also, there is always a delay, called the 'propagation delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination, for example in the electromagnetic field, a wire, speed of sound, gas, fluid or seismic wave, solid body.
Physics
* An electromagnetic wave travelling through ...
', from a change in input of a gate to the corresponding change in its output. When gates are cascaded, the total propagation delay is approximately the sum of the individual delays, an effect which can become a problem in high-speed synchronous circuit
In digital electronics, a synchronous circuit is a digital circuit in which the changes in the state (computer science), state of memory elements are synchronized by a clock signal. In a sequential logic, sequential digital logic circuit, data ...
s. Additional delay can be caused when many inputs are connected to an output, due to the distributed capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related ...
of all the inputs and wiring and the finite amount of current that each output can provide.
Logic families
There are severallogic families
In computer engineering, a logic family is one of two related concepts:
* A logic family of monolithic digital integrated circuit devices is a group of electronic logic gates constructed using one of several different designs, usually with compati ...
with different characteristics (power consumption, speed, cost, size) such as: RDL (resistor–diode logic), RTL (resistor-transistor logic), DTL (diode–transistor logic), TTL (transistor–transistor logic) and CMOS. There are also sub-variants, e.g. standard CMOS logic vs. advanced types using still CMOS technology, but with some optimizations for avoiding loss of speed due to slower PMOS transistors.
The simplest family of logic gates uses bipolar transistors
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A ...
, and is called resistor–transistor logic
Resistor–transistor logic (RTL), sometimes also known as transistor–resistor logic (TRL), is a class of digital circuits built using resistors as the input network and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) as switching devices. RTL is the earlies ...
(RTL). Unlike simple diode logic gates (which do not have a gain element), RTL gates can be cascaded indefinitely to produce more complex logic functions. RTL gates were used in early integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s. For higher speed and better density, the resistors used in RTL were replaced by diodes resulting in diode–transistor logic
Diode–transistor logic (DTL) is a class of digital circuits that is the direct ancestor of transistor–transistor logic. It is called so because the logic gating functions AND and OR are performed by diode logic, while logical inversi ...
(DTL). Transistor–transistor logic
Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function (the first "transistor") and the amplifying function (the second "transistor" ...
(TTL) then supplanted DTL.
field-effect transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three termi ...
s (MOSFET
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
s); see PMOS and NMOS. To reduce power consumption still further, most contemporary chip implementations of digital systems now use CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
logic. CMOS uses complementary (both n-channel and p-channel) MOSFET devices to achieve a high speed with low power dissipation.
Other types of logic gates include, but are not limited to:
Three-state logic gates
buses
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a motor vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van, but fewer than the average rail transport. It is most commonly used ...
of the CPU to allow multiple chips to send data. A group of three-state outputs driving a line with a suitable control circuit is basically equivalent to a multiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several Analog signal, analog or Digital signal (electronics), digital input signals and forwards the sel ...
, which may be physically distributed over separate devices or plug-in cards.
In electronics, a high output would mean the output is sourcing current from the positive power terminal (positive voltage). A low output would mean the output is sinking current to the negative power terminal (zero voltage). High impedance would mean that the output is effectively disconnected from the circuit.
Non-electronic logic gates
Non-electronic implementations are varied, though few of them are used in practical applications. Many early electromechanical digital computers, such as theHarvard Mark I
The Harvard Mark I, or IBM Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator (ASCC), was one of the earliest general-purpose electromechanical computers used in the war effort during the last part of World War II.
One of the first programs to run on th ...
, were built from relay logic
Relay logic is a method of implementing combinational logic in electrical control circuits by using several electrical relays wired in a particular configuration.
Ladder logic
The schematic diagrams for relay logic circuits are often called ...
gates, using electro-mechanical relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switc ...
s. Logic gates can be made using pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek 'wind, breath') is the use of gas or pressurized air in mechanical systems.
Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located a ...
devices, such as the Sorteberg relay or mechanical logic gates, including on a molecular scale. Various types of fundamental logic gates have been constructed using molecules ( molecular logic gates), which are based on chemical inputs and spectroscopic outputs. Logic gates have been made out of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
(see DNA nanotechnology) and used to create a computer called MAYA (see MAYA-II). Logic gates can be made from quantum mechanical
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of a ...
effects, see quantum logic gate
In quantum computing and specifically the quantum circuit model of computation, a quantum logic gate (or simply quantum gate) is a basic quantum circuit operating on a small number of qubits. Quantum logic gates are the building blocks of qua ...
. Photonic logic gates use nonlinear optical
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typicall ...
effects.
In principle any method that leads to a gate that is functionally complete (for example, either a NOR or a NAND gate) can be used to make any kind of digital logic circuit. Note that the use of 3-state logic for bus systems is not needed, and can be replaced by digital multiplexers, which can be built using only simple logic gates (such as NAND gates, NOR gates, or AND and OR gates).
See also
* And-inverter graph * Boolean algebra topics *Boolean function
In mathematics, a Boolean function is a function whose arguments and result assume values from a two-element set (usually , or ). Alternative names are switching function, used especially in older computer science literature, and truth functi ...
* Depletion-load NMOS logic
In integrated circuits, depletion-load NMOS is a form of digital logic family that uses only a single power supply voltage, unlike earlier NMOS logic, NMOS (n-type metal-oxide semiconductor) logic families that needed multiple power supply voltag ...
* Digital circuit
In theoretical computer science, a circuit is a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function. Circuits of this kind provide a generalization of Boolean circuits and a mathematica ...
* Electronic symbol
* Espresso heuristic logic minimizer
* Emitter-coupled logic
In electronics, emitter-coupled logic (ECL) is a high-speed integrated circuit bipolar transistor logic family. ECL uses a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) differential amplifier with single-ended input and limited emitter current to avoid th ...
* Fan-out
In digital electronics, the fan-out is the number of gate inputs driven by the output of another single logic gate.
In most designs, logic gates are connected to form more complex circuits. While no logic gate input can be fed by more than one ...
* Field-programmable gate array (FPGA)
* Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, flip-flops and latches are electronic circuit, circuits that have two stable states that can store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control ...
* Functional completeness
In Mathematical logic, logic, a functionally complete set of logical connectives or Boolean function, Boolean operators is one that can be used to express all possible truth tables by combining members of the Set (mathematics), set into a Boolean ...
* Integrated injection logic
* Karnaugh map
A Karnaugh map (KM or K-map) is a diagram that can be used to simplify a Boolean algebra expression. Maurice Karnaugh introduced the technique in 1953 as a refinement of Edward W. Veitch's 1952 Veitch chart, which itself was a rediscovery of ...
* Combinational logic
In automata theory, combinational logic (also referred to as time-independent logic) is a type of digital logic that is implemented by Boolean circuits, where the output is a pure function of the present input only. This is in contrast to sequ ...
* List of 4000 series integrated circuits
* List of 7400 series integrated circuits
The following is a list of 7400-series digital logic integrated circuits. In the mid-1960s, the original 7400-series integrated circuits, 7400-series integrated circuits were introduced by Texas Instruments with the prefix "SN" to create the name ...
* Logic family
In computer engineering, a logic family is one of two related concepts:
* A logic family of monolithic digital integrated circuit devices is a group of electronic logic gates constructed using one of several different designs, usually with compati ...
* Logic level
In digital circuits, a logic level is one of a finite number of states that a digital signal can inhabit. Logic levels are usually represented by the voltage difference between the signal and ground, although other standards exist. The range of ...
* Logical graph
An existential graph is a type of diagrammatic or visual notation for logical expressions, created by Charles Sanders Peirce, who wrote on graphical logic as early as 1882, and continued to develop the method until his death in 1914. They include ...
* Magnetic logic
* NMOS logic
NMOS or nMOS logic (from N-type metal–oxide–semiconductor) uses n-type (-) MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits.
NMOS transistors operate by creating an inv ...
* Parametron
* Processor design
Processor design is a subfield of computer science and computer engineering (fabrication) that deals with creating a processor, a key component of computer hardware.
The design process involves choosing an instruction set and a certain execution ...
* Programmable logic controller
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that ...
(PLC)
* Programmable logic device
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, the function of a PLD is undefined at the time of m ...
(PLD)
* Propositional calculus
The propositional calculus is a branch of logic. It is also called propositional logic, statement logic, sentential calculus, sentential logic, or sometimes zeroth-order logic. Sometimes, it is called ''first-order'' propositional logic to contra ...
* Race hazard
* Reversible computing
Reversible computing is any model of computation where every step of the process is time-reversible. This means that, given the output of a computation, it's possible to perfectly reconstruct the input. In systems that progress deterministica ...
* Superconducting computing
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where Electrical resistance and conductance, electrical resistance vanishes and Magnetic field, magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ord ...
* Truth table
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arg ...
* Unconventional computing
References
Further reading
* *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Logic Gate Charles Sanders Peirce