|
Combinational Logic
In automata theory, combinational logic (also referred to as time-independent logic) is a type of digital logic that is implemented by Boolean circuits, where the output is a pure function of the present input only. This is in contrast to sequential logic, in which the output depends not only on the present input but also on the history of the input. In other words, sequential logic has ''memory'' while combinational logic does not. Combinational logic is used in computer circuits to perform Boolean algebra on input signals and on stored data. Practical computer circuits normally contain a mixture of combinational and sequential logic. For example, the part of an arithmetic logic unit, or ALU, that does mathematical calculations is constructed using combinational logic. Other circuits used in computers, such as half adders, full adders, half subtractors, full subtractors, multiplexers, demultiplexers, encoders and decoders are also made by using combinational logic. Prac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinatory Logic
Combinatory logic is a notation to eliminate the need for quantified variables in mathematical logic. It was introduced by Moses Schönfinkel and Haskell Curry, and has more recently been used in computer science as a theoretical model of computation and also as a basis for the design of functional programming languages. It is based on combinators, which were introduced by Schönfinkel in 1920 with the idea of providing an analogous way to build up functions—and to remove any mention of variables—particularly in predicate logic. A combinator is a higher-order function that uses only function application and earlier defined combinators to define a result from its arguments. In mathematics Combinatory logic was originally intended as a 'pre-logic' that would clarify the role of quantified variables in logic, essentially by eliminating them. Another way of eliminating quantified variables is Quine's predicate functor logic. While the expressive power of combinatory log ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Decoder
In digital electronics, a binary decoder is a combinational logic circuit that converts binary information from the n coded inputs to a maximum of 2n unique outputs. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including instruction decoding, data multiplexing and data demultiplexing, seven segment displays, and as address decoders for memory and port-mapped I/O. There are several types of binary decoders, but in all cases a decoder is an electronic circuit with multiple input and multiple output signals, which converts every unique combination of input states to a specific combination of output states. In addition to integer data inputs, some decoders also have one or more "enable" inputs. When the enable input is negated (disabled), all decoder outputs are forced to their inactive states. Depending on its function, a binary decoder will convert binary information from n input signals to as many as 2n unique output signals. Some decoders have less than 2n output lines; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tseytin Transformation
The Tseytin transformation, alternatively written Tseitin transformation, takes as input an arbitrary combinatorial logic circuit and produces an equisatisfiable boolean formula in conjunctive normal form (CNF). The length of the formula is linear in the size of the circuit. Input vectors that make the circuit output "true" are in 1-to-1 correspondence with assignments that satisfy the formula. This reduces the problem of circuit satisfiability on any circuit (including any formula) to the satisfiability problem on 3-CNF formulas. It was discovered by the Russian scientist Grigori Tseitin. Motivation The naive approach is to write the circuit as a Boolean expression, and use De Morgan's law and the distributive property to convert it to CNF. However, this can result in an exponential increase in equation size. The Tseytin transformation outputs a formula whose size grows linearly relative to the input circuit's. Approach The output equation is the constant 1 set equal to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequential Logic
In automata theory, sequential logic is a type of logic circuit whose output depends on the present value of its input signals and on the sequence of past inputs, the input history. This is in contrast to '' combinational logic'', whose output is a function of only the present input. That is, sequential logic has ''state'' (''memory'') while combinational logic does not. Sequential logic is used to construct finite-state machines, a basic building block in all digital circuitry. Virtually all circuits in practical digital devices are a mixture of combinational and sequential logic. A familiar example of a device with sequential logic is a television set with "channel up" and "channel down" buttons. Pressing the "up" button gives the television an input telling it to switch to the next channel above the one it is currently receiving. If the television is on channel 5, pressing "up" switches it to receive channel 6. However, if the television is on channel 8, pressing "up" switch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
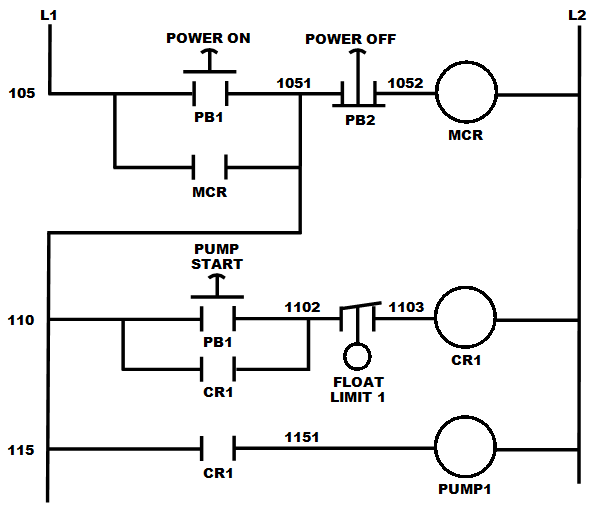
Relay Logic
Relay logic is a method of implementing combinational logic in electrical control circuits by using several electrical relays wired in a particular configuration. Ladder logic The schematic diagrams for relay logic circuits are often called line diagrams, because the inputs and outputs are essentially drawn in a series of lines. A relay logic circuit is an electrical network consisting of lines, or rungs, in which each line or rung must have continuity to enable the output device. A typical circuit consists of a number of rungs, with each rung controlling an output. This output is controlled by a combination of input or output conditions, such as input switches and control relays. The conditions that represent the inputs are connected in series, parallel, or series-parallel to obtain the logic required to drive the output. The relay logic circuit forms an electrical schematic diagram for the control of input and output devices. Relay logic diagrams represent the physical in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Logic Controller
A programmable logic controller (PLC) or programmable controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that requires high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis. PLCs can range from small modular devices with tens of Input/output, inputs and outputs (I/O), in a housing integral with the processor, to large rack-mounted modular devices with thousands of I/O, and which are often networked to other PLC and SCADA systems. They can be designed for many arrangements of digital and analog I/O, extended temperature ranges, immunity to electrical noise, and resistance to vibration and impact. PLCs were first developed in the automobile manufacturing industry to provide flexible, rugged and easily programmable controllers to replace hard-wired relay logic systems. Dick Morley, who invented the first PLC, the Modicon 084, for Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladder Logic
Ladder logic was originally a written method to document the design and construction of relay logic, relay racks as used in manufacturing and process control. Each device in the relay rack would be represented by a symbol on the ladder diagram with connections between those devices shown. In addition, other items external to the relay rack such as pumps, heaters, and so forth would also be shown on the ladder diagram. Ladder logic has evolved into a programming language that represents a program by a graphical diagram based on the circuit diagrams of relay logic hardware. Ladder logic is used to develop software for programmable logic controllers (PLCs) used in industrial control applications. The name is based on the observation that programs in this language resemble ladders, with two vertical rails and a series of horizontal rungs between them. Ladder diagrams were once the only way to record programmable controller programs, but today, other forms are standardized in IEC 6113 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Verification
In the context of hardware and software systems, formal verification is the act of proving or disproving the correctness of a system with respect to a certain formal specification or property, using formal methods of mathematics. Formal verification is a key incentive for formal specification of systems, and is at the core of formal methods. It represents an important dimension of analysis and verification in electronic design automation and is one approach to software verification. The use of formal verification enables the highest Evaluation Assurance Level ( EAL7) in the framework of common criteria for computer security certification. Formal verification can be helpful in proving the correctness of systems such as: cryptographic protocols, combinational circuits, digital circuits with internal memory, and software expressed as source code in a programming language. Prominent examples of verified software systems include the CompCert verified C compiler and the seL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-programmable Gate Array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of an array of programmable logic device, programmable logic block, logic blocks with a connecting grid, that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are often used in limited (low) quantity production of custom-made products, and in research and development, where the higher cost of individual FPGAs is not as important, and where creating and manufacturing a custom circuit would not be feasible. Other applications for FPGAs include the telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which benefit from their flexibility, high signal processing speed, and parallel processing abilities. A FPGA configuration is generally written using a hardware descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asynchronous Circuit
Asynchronous circuit (clockless or self-timed circuit) is a sequential logic, sequential digital logic electrical network, circuit that does not use a global clock circuit or clock signal, signal generator to synchronize its components. Instead, the components are driven by a handshaking circuit which indicates a completion of a set of instructions. Handshaking works by simple data transfer Communications protocol, protocols. Many synchronous circuits were developed in early 1950s as part of bigger asynchronous systems (e.g. ORDVAC). Asynchronous circuits and theory surrounding is a part of several steps in integrated circuit design, a field of digital electronics engineering. Asynchronous circuits are contrasted with synchronous circuits, in which changes to the signal values in the circuit are triggered by repetitive pulses called a clock signal. Most digital devices today use synchronous circuits. However asynchronous circuits have a potential to be much faster, have a lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinational Circuit
In automata theory, combinational logic (also referred to as time-independent logic) is a type of digital logic that is implemented by Boolean circuits, where the output is a pure function of the present input only. This is in contrast to sequential logic, in which the output depends not only on the present input but also on the history of the input. In other words, sequential logic has ''computer storage, memory'' while combinational logic does not. Combinational logic is used in computer circuits to perform Boolean algebra (logic), Boolean algebra on input signals and on stored data. Practical computer circuits normally contain a mixture of combinational and sequential logic. For example, the part of an arithmetic logic unit, or ALU, that does mathematical calculations is constructed using combinational logic. Other circuits used in computers, such as half adders, full adders, half subtractors, Half subtractor, full subtractors, multiplexers, Multiplexer, demultiplexers, Simpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic Optimization
Logic optimization is a process of finding an equivalent representation of the specified logic circuit under one or more specified constraints. This process is a part of a logic synthesis applied in digital electronics and integrated circuit design. Generally, the circuit is constrained to a minimum chip area meeting a predefined response delay. The goal of logic optimization of a given circuit is to obtain the smallest logic circuit that evaluates to the same values as the original one. Usually, the smaller circuit with the same function is cheaper, takes less space, consumes less power, has shorter latency, and minimizes risks of unexpected cross-talk, hazard of delayed signal processing, and other issues present at the nano-scale level of metallic structures on an integrated circuit. In terms of Boolean algebra, the optimization of a complex Boolean expression is a process of finding a simpler one, which would upon evaluation ultimately produce the same results as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |