Live birth (human) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
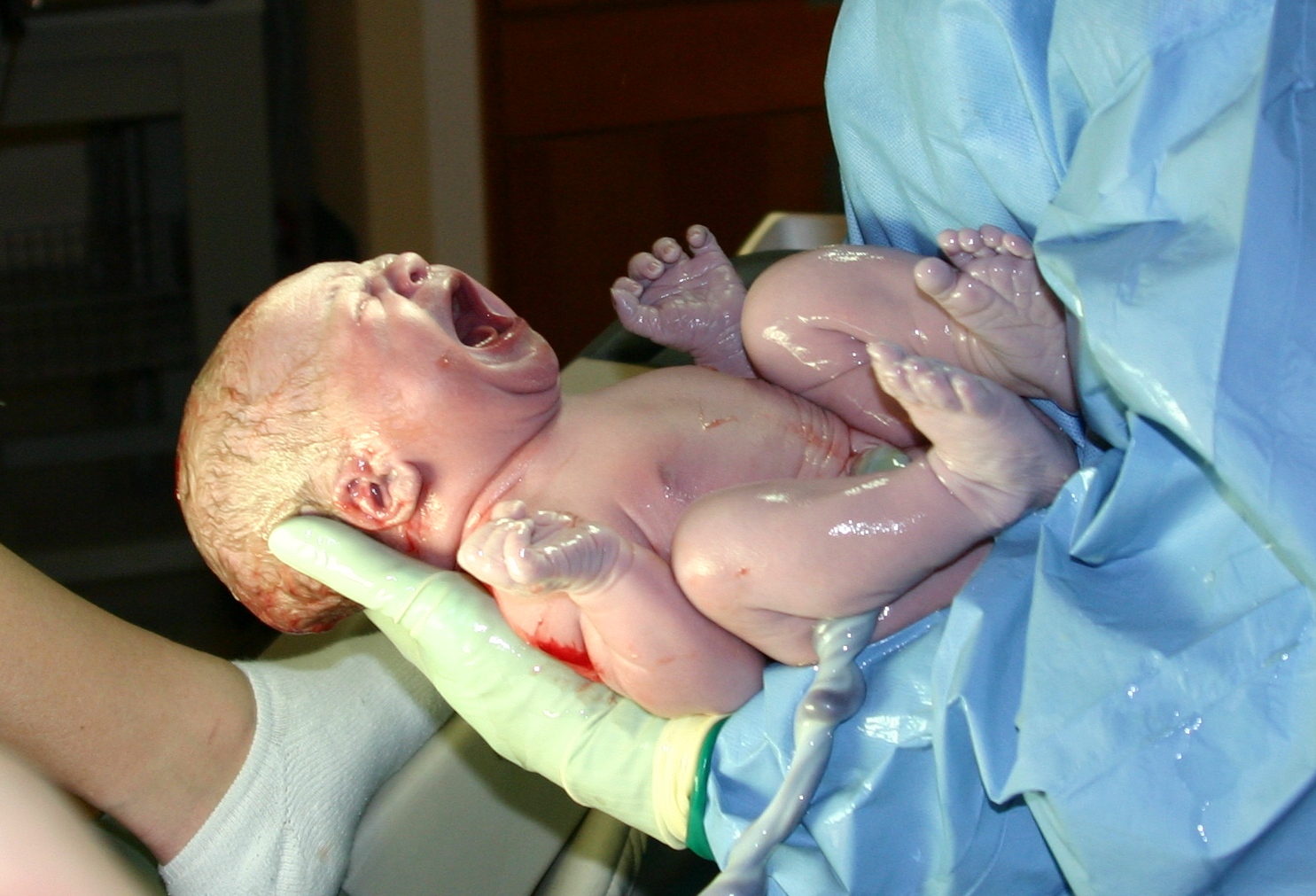 In
In
human reproduction
Human sexual reproduction, to produce offspring, begins with fertilization. Successful reproduction typically involves sexual intercourse between a healthy, sexually mature and fertile male and female. During sexual intercourse, sperm cells are ...
, a live birth occurs when a fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
exits a pregnant
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
person showing any definite sign of life, such as voluntary movement, heartbeat or pulsation of the umbilical cord
In Placentalia, placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord i ...
, for however brief a time, and regardless of whether the umbilical cord or placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
are intact. After the fetus leaves the womb
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more fertilized eggs until bi ...
it is called a neonate
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to Juvenile (orga ...
. It is a "live birth" whether the birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
is vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vag ...
l or by caesarean section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section, cesarean, or caesarean delivery, is the Surgery, surgical procedure by which one or more babies are Childbirth, delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen. It is often performed because va ...
, and whether the neonate is ultimately viable.
The definition of the term "live birth" was created by the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
in 1950, and is chiefly used for public health and statistical purposes. However, the term "live birth" was in common use long before 1950.
In the United States, the term "born alive" is defined by federal law known as the born alive rule. Live births are recorded on a U.S. Standard Certificate of Live Birth, also known as a birth certificate
A birth certificate is a vital record that documents the Childbirth, birth of a person. The term "birth certificate" can refer to either the original document certifying the circumstances of the birth or to a certified copy of or representation ...
. The United States recorded 3,605,201 live births in 2020 which is a 4% decrease from 2019 and the 6th consecutive year of decline in births.
Not all pregnancies result in live births. A woman may elect to end her pregnancy by induced abortion
Abortion is the early termination of a pregnancy by removal or expulsion of an embryo or fetus. Abortions that occur without intervention are known as miscarriages or "spontaneous abortions", and occur in roughly 30–40% of all pregnan ...
. The natural death of an embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
or fetus before it is able to survive independently is termed miscarriage
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion, is an end to pregnancy resulting in the loss and expulsion of an embryo or fetus from the womb before it can fetal viability, survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks ...
or pregnancy loss. Some use the cutoff of 20 weeks of gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregn ...
for miscarriage, after which fetal death is known as stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetus, fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without vital signs, signs of life. A stillbirth can often result in the feeling of guilt (emotio ...
. The death of the fetus or neonate at the end of the pregnancy, during labour and delivery, or just after birth, is counted as perinatal mortality
Perinatal mortality (PNM) is the death of a fetus or neonate and is the basis to calculate the perinatal mortality rate. ''Perinatal'' means "relating to the period starting a few weeks before birth and including the birth and a few weeks after bi ...
.
Statistical significance
Factors affecting viability
Gestational age
Measured in weeks, gestational age is a term used to describe how far along a pregnancy is starting from the first day of the woman's last menstrual cycle to the current date. A baby born "at term" is between the gestational age of 37 weeks to 41 weeks. Apreterm
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is betwee ...
baby is born before the gestational age of 37 weeks. A pregnancy that lasts 41 weeks up to 42 weeks is called late-term and a pregnancy longer than 42 weeks is called post-term. The general consensus is that a fetus is viable at 24 weeks, however, a live birth may occur earlier in gestation with the assistance from neonatal intensive care unit
A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. The NICU is divided into several areas, including a critical c ...
(NICU) resources. Gestational age is the main determinant of whether a baby will be able to live and survive outside of the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
.
Other factors
While gestational age is the most significant predictor of fetal viability, the condition of the neonate at birth also significantly indicates how well it tolerates life outside of the mother. Factors measured at birth include birth weight, head circumference, and body length. AnApgar score
The Apgar score is a quick way for health professionals to evaluate the health of all newborns at 1 and 5 minutes after birth and in response to resuscitation. It was originally developed in 1952 by an anesthesiologist at Columbia University, ...
is given at the time of birth to report the status of the newborn infant and the response to resuscitation if needed.
Recovery
The maternal recovery period directly following the events of humanchildbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy, where one or more Fetus, fetuses exits the Womb, internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section and becomes a newborn to ...
, regardless of whether it is a live birth, is called the postpartum period
The postpartum (or postnatal) period begins after childbirth and is typically considered to last for six to eight weeks. There are three distinct phases of the postnatal period; the acute phase, lasting for six to twelve hours after birth; the ...
.
Special cases
There is one case report of a woman having a live birth derived from a frozen embryo obtained before she began cancer treatment.See also
*Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy, where one or more Fetus, fetuses exits the Womb, internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section and becomes a newborn to ...
* Maternal death
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Live Birth Obstetrics Demography Midwifery Infancy Reproduction in mammals Childbirth