Lithium Aluminum Hydride on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lithium (from , , ) is a
 The
The  Lithium's
Lithium's

 Lithium is also found in
Lithium is also found in
. By USGS definitions, the reserve base "may encompass those parts of the resources that have a reasonable potential for becoming economically available within planning horizons beyond those that assume proven technology and current economics. The reserve base includes those resources that are currently economic (reserves), marginally economic (marginal reserves), and some of those that are currently subeconomic (subeconomic resources)." of lithium is in the

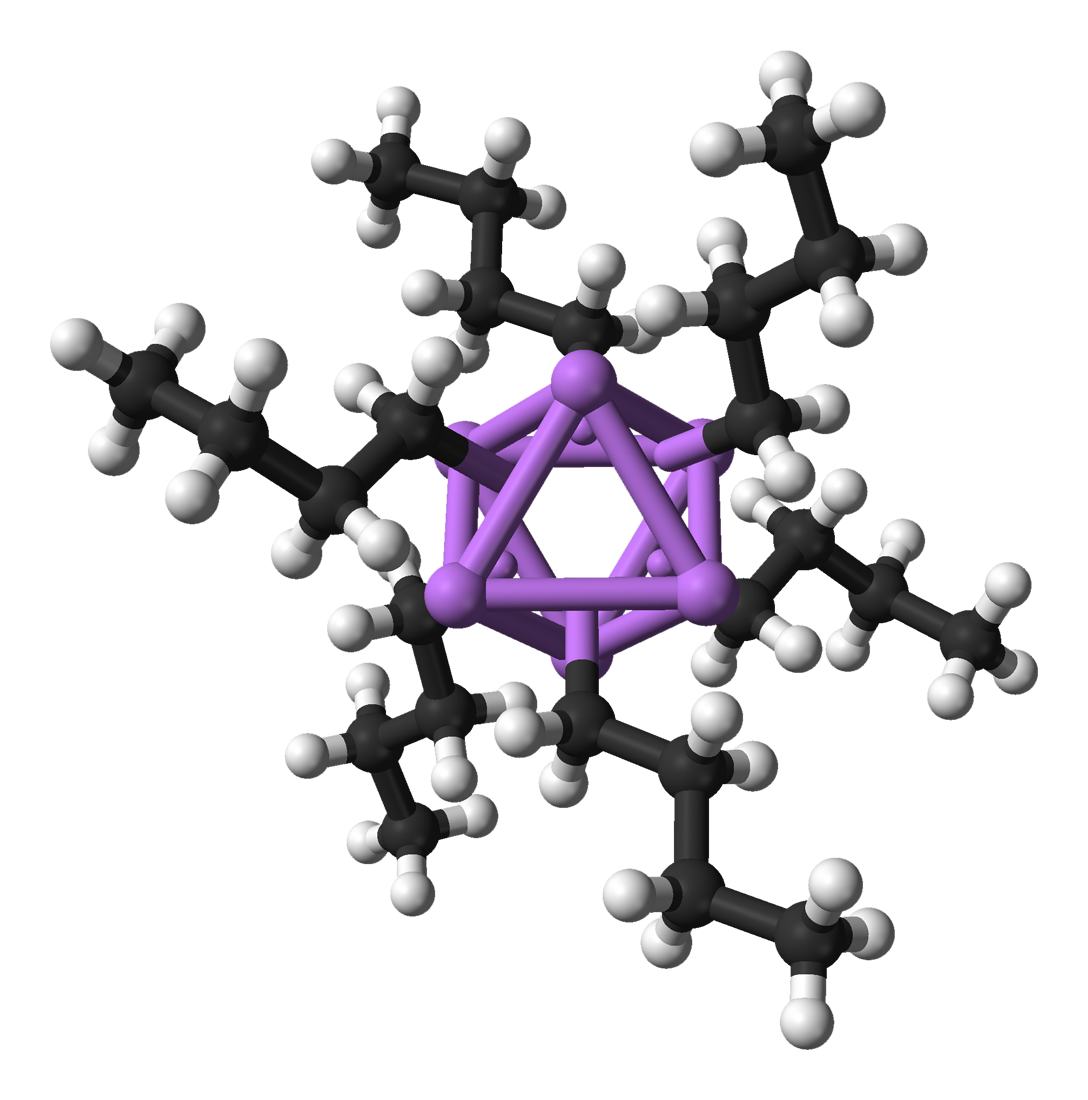 Organolithium compounds are numerous and useful. They are defined by the presence of a covalent bond, bond between carbon and lithium. They serve as metal-stabilized carbanions, although their solution and solid-state structures are more complex than this simplistic view. Thus, these are extremely powerful base (chemistry), bases and carbon nucleophile, nucleophiles. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoricity, pyrophoric.
Like its inorganic compounds, almost all organic compounds of lithium formally follow the duet rule (e.g., N-Butyllithium, BuLi, Methyllithium, MeLi). However, it is important to note that in the absence of coordinating solvents or ligands, organolithium compounds form dimeric, tetrameric, and hexameric clusters (e.g., BuLi is actually [BuLi]6 and MeLi is actually [MeLi]4) which feature multi-center bonding and increase the coordination number around lithium. These clusters are broken down into smaller or monomeric units in the presence of solvents like dimethoxyethane (DME) or ligands like tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA). As an exception to the duet rule, a two-coordinate lithate complex with four electrons around lithium, [Li(thf)4]+[((Me3Si)3C)2Li]–, has been characterized crystallographically.
Organolithium compounds are numerous and useful. They are defined by the presence of a covalent bond, bond between carbon and lithium. They serve as metal-stabilized carbanions, although their solution and solid-state structures are more complex than this simplistic view. Thus, these are extremely powerful base (chemistry), bases and carbon nucleophile, nucleophiles. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoricity, pyrophoric.
Like its inorganic compounds, almost all organic compounds of lithium formally follow the duet rule (e.g., N-Butyllithium, BuLi, Methyllithium, MeLi). However, it is important to note that in the absence of coordinating solvents or ligands, organolithium compounds form dimeric, tetrameric, and hexameric clusters (e.g., BuLi is actually [BuLi]6 and MeLi is actually [MeLi]4) which feature multi-center bonding and increase the coordination number around lithium. These clusters are broken down into smaller or monomeric units in the presence of solvents like dimethoxyethane (DME) or ligands like tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA). As an exception to the duet rule, a two-coordinate lithate complex with four electrons around lithium, [Li(thf)4]+[((Me3Si)3C)2Li]–, has been characterized crystallographically.
 The small ionic size makes it difficult for lithium to be included in early stages of mineral crystallization. As a result, lithium remains in the molten phases, where it gets enriched, until it gets solidified in the final stages. Such lithium enrichment is responsible for all commercially promising lithium ore deposits. Brines (and dry salt) are another important source of Li+. Although the number of known lithium-containing deposits and brines is large, most of them are either small or have too low Li+ concentrations. Thus, only a few appear to be of commercial value.
The US Geological Survey (USGS) estimated worldwide identified lithium reserves in 2022 and 2023 to be 26 million and 28 million tonnes, respectively. An accurate estimate of world lithium reserves is difficult. One reason for this is that most lithium classification schemes are developed for solid ore deposits, whereas brine is a fluid that is problematic to treat with the same classification scheme due to varying concentrations and pumping effects.
In 2019, world production of lithium from spodumene was around 80,000t per annum, primarily from the Greenbushes, Western Australia, Greenbushes pegmatite and from some China, Chinese and Chilean sources. The Talison mine in Greenbushes is reported to be the largest and to have the highest grade of ore at 2.4% Li2O (2012 figures).
The small ionic size makes it difficult for lithium to be included in early stages of mineral crystallization. As a result, lithium remains in the molten phases, where it gets enriched, until it gets solidified in the final stages. Such lithium enrichment is responsible for all commercially promising lithium ore deposits. Brines (and dry salt) are another important source of Li+. Although the number of known lithium-containing deposits and brines is large, most of them are either small or have too low Li+ concentrations. Thus, only a few appear to be of commercial value.
The US Geological Survey (USGS) estimated worldwide identified lithium reserves in 2022 and 2023 to be 26 million and 28 million tonnes, respectively. An accurate estimate of world lithium reserves is difficult. One reason for this is that most lithium classification schemes are developed for solid ore deposits, whereas brine is a fluid that is problematic to treat with the same classification scheme due to varying concentrations and pumping effects.
In 2019, world production of lithium from spodumene was around 80,000t per annum, primarily from the Greenbushes, Western Australia, Greenbushes pegmatite and from some China, Chinese and Chilean sources. The Talison mine in Greenbushes is reported to be the largest and to have the highest grade of ore at 2.4% Li2O (2012 figures).
, retrieved 13 October 2022 Operational mining began in 2022. A deposit discovered in 2013 in Wyoming's Rock Springs Uplift is estimated to contain 228,000 tons. Additional deposits in the same formation were estimated to be as much as 18 million tons. Similarly in Nevada, the McDermitt Caldera hosts lithium-bearing volcanic muds that consist of the largest known deposits of lithium within the United States. The Pampean Pegmatite Province in Argentina is known to have a total of at least 200,000 tons of
Mining Geothermal Resources
. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Recovery of this type of lithium has been demonstrated in the field; the lithium is separated by simple filtration.Patel, P. (16 November 2011
Startup to Capture Lithium from Geothermal Plants
. technologyreview.com Reserves are more limited than those of brine reservoirs and hard rock.
 In 1998, the price of lithium metal was about (or US$43/Pound (mass), lb). After the 2008 financial crisis, major suppliers, such as Sociedad Química y Minera (SQM), dropped lithium carbonate pricing by 20%. Prices rose in 2012. A 2012 Bloomberg Businessweek, Business Week article outlined an oligopoly in the lithium space: "SQM, controlled by billionaire Julio Ponce Lerou, Julio Ponce, is the second-largest, followed by Albemarle Corporation#Acquisition of Rockwood Holdings, Rockwood, which is backed by Henry Kravis's KKR & Co., and Philadelphia-based FMC", with Talison Minerals, Talison mentioned as the biggest producer. Global consumption may jump to 300,000 metric tons a year by 2020 from about 150,000 tons in 2012, to match the demand for lithium batteries that has been growing at about 25% a year, outpacing the 4% to 5% overall gain in lithium production.
The price information service ISE – Institute of Rare Earths Elements and Strategic Metals – gives for various lithium substances in the average of March to August 2022 the following kilo prices stable in the course: Lithium carbonate, purity 99.5% min, from various producers between 63 and 72 EUR/kg. Lithium hydroxide monohydrate LiOH 56.5% min, China, at 66 to 72 EUR/kg; delivered South Korea – 73 EUR/kg. Lithium metal 99.9% min, delivered China – 42 EUR/kg.
In 1998, the price of lithium metal was about (or US$43/Pound (mass), lb). After the 2008 financial crisis, major suppliers, such as Sociedad Química y Minera (SQM), dropped lithium carbonate pricing by 20%. Prices rose in 2012. A 2012 Bloomberg Businessweek, Business Week article outlined an oligopoly in the lithium space: "SQM, controlled by billionaire Julio Ponce Lerou, Julio Ponce, is the second-largest, followed by Albemarle Corporation#Acquisition of Rockwood Holdings, Rockwood, which is backed by Henry Kravis's KKR & Co., and Philadelphia-based FMC", with Talison Minerals, Talison mentioned as the biggest producer. Global consumption may jump to 300,000 metric tons a year by 2020 from about 150,000 tons in 2012, to match the demand for lithium batteries that has been growing at about 25% a year, outpacing the 4% to 5% overall gain in lithium production.
The price information service ISE – Institute of Rare Earths Elements and Strategic Metals – gives for various lithium substances in the average of March to August 2022 the following kilo prices stable in the course: Lithium carbonate, purity 99.5% min, from various producers between 63 and 72 EUR/kg. Lithium hydroxide monohydrate LiOH 56.5% min, China, at 66 to 72 EUR/kg; delivered South Korea – 73 EUR/kg. Lithium metal 99.9% min, delivered China – 42 EUR/kg.

 Lithium deuteride was the nuclear fusion, fusion fuel of choice in early versions of the Nuclear weapon, hydrogen bomb. When bombarded by neutrons, both 6Li and 7Li produce tritium — this reaction, which was not fully understood when Teller-Ulam design, hydrogen bombs were first tested, was responsible for the runaway yield of the Castle Bravo nuclear test. Tritium fuses with
Lithium deuteride was the nuclear fusion, fusion fuel of choice in early versions of the Nuclear weapon, hydrogen bomb. When bombarded by neutrons, both 6Li and 7Li produce tritium — this reaction, which was not fully understood when Teller-Ulam design, hydrogen bombs were first tested, was responsible for the runaway yield of the Castle Bravo nuclear test. Tritium fuses with
McKinsey review of 2018
(PDF)
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
International Lithium Alliance
(archived, August 2009)
USGS: Lithium Statistics and Information
Lithium Supply & Markets 2009 IM Conference 2009 Sustainable lithium supplies through 2020 in the face of sustainable market growth
University of Southampton, Mountbatten Centre for International Studies, Nuclear History Working Paper No5.
(PDF) (archived February 26 February 2008)
Lithium reserves by Country
at investingnews.com {{Authority control Lithium, Chemical elements Alkali metals Reducing agents Chemical elements with body-centered cubic structure
chemical element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its ...
; it has symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
Li and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of its atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei composed of protons and neutrons, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of pro ...
3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
. Under standard conditions
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) or standard conditions for temperature and pressure are various standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements used to allow comparisons to be made between different sets of data. The most used ...
, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. It exhibits a metallic luster. It corrodes quickly in air to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It does not occur freely in nature, but occurs mainly as pegmatitic
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic ...
minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brine
Brine (or briny water) is a high-concentration solution of salt (typically sodium chloride or calcium chloride) in water. In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawat ...
s. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorid ...
and potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a sa ...
.
The nucleus
Nucleus (: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucleu ...
of the lithium atom verges on instability, since the two stable lithium isotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
s found in nature have among the lowest binding energies per nucleon
In physics and chemistry, a nucleon is either a proton or a neutron, considered in its role as a component of an atomic nucleus. The number of nucleons in a nucleus defines the atom's mass number.
Until the 1960s, nucleons were thought to be ele ...
of all stable nuclide
Nuclides (or nucleides, from nucleus, also known as nuclear species) are a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, ''Z'', their number of neutrons, ''N'', and their nuclear energy state.
The word ''nuclide'' was coined by the A ...
s. Because of its relative nuclear instability, lithium is less common in the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
than 25 of the first 32 chemical elements even though its nuclei are very light: it is an exception to the trend that heavier nuclei are less common.Numerical data from: Graphed at :File:SolarSystemAbundances.jpg For related reasons, lithium has important uses in nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies th ...
. The transmutation of lithium atoms to helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
in 1932 was the first fully human-made nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two atomic nucleus, nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a t ...
, and lithium deuteride
Lithium hydride is an inorganic compound with the formula Lithium, LiHydride, H. This alkali metal hydride is a colorless solid, although commercial samples are grey. Characteristic of a Hydride#Ionic hydrides, salt-like (ionic) hydride, it has a ...
serves as a fusion fuel in staged thermonuclear weapons.
Lithium and its compounds have several industrial applications, including heat-resistant glass and ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
s, lithium grease
Lithium soap is a soap consisting of a lithium salt of a fatty acid. Sodium-based and potassium-based soaps are used as cleaning agents in domestic and industrial applications, whereas lithium soaps are used as components of lithium grease (white ...
lubricants, flux additives for iron, steel and aluminium production, lithium metal batteries, and lithium-ion batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy ...
. These uses consume more than three-quarters of lithium production.
Lithium is present in biological systems in trace amounts. It has no established metabolic function in humans. Lithium-based drugs are useful as a mood stabilizer and antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction.
Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathi ...
in the treatment of mental illness such as bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
.
Properties
Atomic and physical
alkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
s are also called the lithium family, after its leading element. Like the other alkali metals (which are sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
(Na), potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
(K), rubidium
Rubidium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Rb and atomic number 37. It is a very soft, whitish-grey solid in the alkali metal group, similar to potassium and caesium. Rubidium is the first alkali metal in the group to have ...
(Rb), caesium
Caesium (IUPAC spelling; also spelled cesium in American English) is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-golden alkali metal with a melting point of , which makes it one of only f ...
(Cs), and francium
Francium is a chemical element; it has symbol Fr and atomic number 87. It is extremely radioactive; its most stable isotope, francium-223 (originally called '' actinium K'' after the natural decay chain in which it appears), has a half-l ...
(Fr)), lithium has a single valence electron
In chemistry and physics, valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outermost shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair forms with b ...
that, in the presence of solvents, is easily released to form Li+. Because of this, lithium is a good conductor of heat and electricity as well as a highly reactive element, though it is the least reactive of the alkali metals. Lithium's lower reactivity is due to the proximity of its valence electron to its nucleus
Nucleus (: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucleu ...
(the remaining two electrons are in the 1s orbital
In quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital () is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function describes an electron's charge distribution around the atom's nucleus, and can be used to calc ...
, much lower in energy, and do not participate in chemical bonds). Molten lithium is significantly more reactive than its solid form.
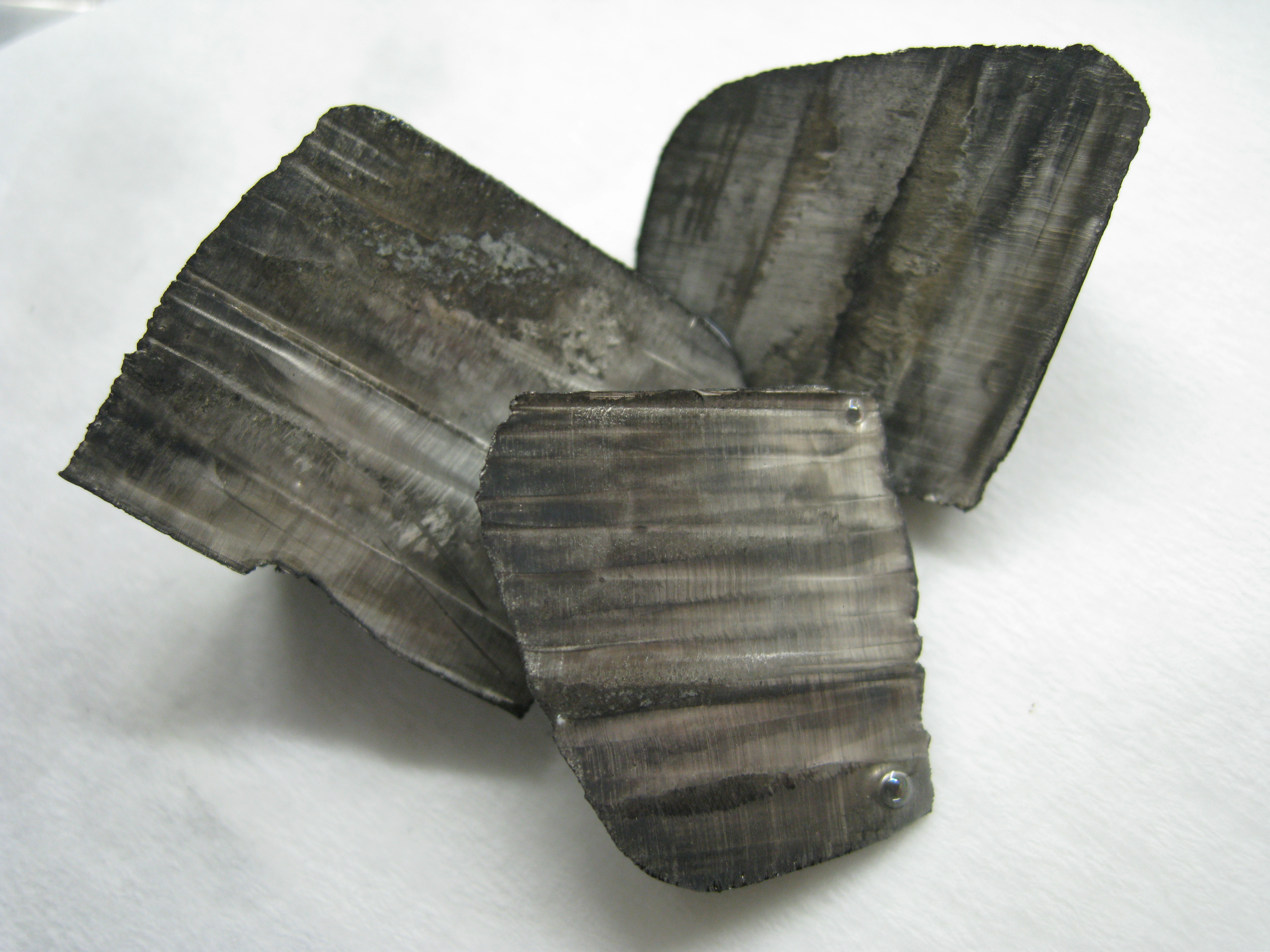
Lithium metal is soft enough to be cut with a knife. It is silvery-white. In air it oxidizes to lithium oxide
Lithium oxide (Lithium, Oxygen, O) or lithia is an Inorganic compound, inorganic chemical compound. It is a white or pale yellow solid. Although not specifically important, many materials are assessed on the basis of their Li2O content. For examp ...
. Its melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state of matter, state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase (matter), phase exist in Thermodynamic equilib ...
of and its boiling point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding envi ...
of are each the highest of all the alkali metals while its density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be u ...
of 0.534 g/cm3 is the lowest.
Lithium has a very low density (0.534 g/cm3), comparable with pine wood
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
. It is the least dense of all elements that are solids at room temperature; the next lightest solid element (potassium, at 0.862 g/cm3) is more than 60% denser. Apart from helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
and hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
, as a solid it is less dense than any other element as a liquid, being only two-thirds as dense as liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen (LN2) is nitrogen in a liquid state at cryogenics, low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, mobile liquid whose vis ...
(0.808 g/cm3). Lithium can float on the lightest hydrocarbon oils and is one of only three metals that can float on water, the other two being sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
and potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
.
 Lithium's
Lithium's coefficient of thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions).
Substances usually contract with decreasing temp ...
is twice that of aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
and almost four times that of iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
. Lithium is superconductive
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in superconductors: materials where electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic fields are expelled from the material. Unlike an ordinary metallic conductor, whose resistance decreases gr ...
below 400 μK at standard pressure and at higher temperatures (more than 9 K) at very high pressures (>20 GPa). At temperatures below 70 K, lithium, like sodium, undergoes diffusionless phase change transformations. At 4.2 K it has a rhombohedral crystal system
In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal family is one of the six crystal families, which includes two crystal systems (hexagonal and trigonal) and two lattice systems (hexagonal and rhombohedral). While commonly confused, the trigonal crystal ...
(with a nine-layer repeat spacing); at higher temperatures it transforms to face-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties o ...
and then body-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the Crystal structure#Unit cell, unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There ...
. At liquid-helium temperatures (4 K) the rhombohedral structure is prevalent. Multiple allotropic forms have been identified for lithium at high pressures.
Lithium has a mass specific heat capacity
In thermodynamics, the specific heat capacity (symbol ) of a substance is the amount of heat that must be added to one unit of mass of the substance in order to cause an increase of one unit in temperature. It is also referred to as massic heat ...
of 3.58 kilojoules per kilogram-kelvin, the highest of all solids. Because of this, lithium metal is often used in coolant
A coolant is a substance, typically liquid, that is used to reduce or regulate the temperature of a system. An ideal coolant has high thermal capacity, low viscosity, is low-cost, non-toxic, chemically inert and neither causes nor promotes corr ...
s for heat transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems. Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, ...
applications.
Isotopes
Naturally occurring lithium is composed of two stableisotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
s, 6Li and 7Li, the latter being the more abundant (95.15% natural abundance
In physics, natural abundance (NA) refers to the abundance of isotopes of a chemical element as naturally found on a planet. The relative atomic mass (a weighted average, weighted by mole-fraction abundance figures) of these isotopes is the ato ...
). Both natural isotopes have anomalously low nuclear binding energy
Nuclear binding energy in experimental physics is the minimum energy that is required to disassemble the nucleus of an atom into its constituent protons and neutrons, known collectively as nucleons. The binding energy for stable nuclei is alwa ...
per nucleon (compared to the neighboring elements on the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other s ...
, helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
and beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, hard, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with ...
); lithium is the only low numbered element that can produce net energy through nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radioactiv ...
. The two lithium nuclei have lower binding energies per nucleon than any other stable nuclides other than hydrogen-1
Hydrogen (H) has three naturally occurring isotopes: H, H, and H. H and H are stable, while H has a half-life of years. Heavier isotopes also exist; all are synthetic and have a half-life of less than 1 zeptosecond (10 s).
Of these, H is ...
, deuterium
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more c ...
and helium-3
Helium-3 (3He see also helion) is a light, stable isotope of helium with two protons and one neutron. (In contrast, the most common isotope, helium-4, has two protons and two neutrons.) Helium-3 and hydrogen-1 are the only stable nuclides with ...
. :File:Binding energy curve - common isotopes.svg shows binding energies of stable nuclides graphically; the source of the data-set is given in the figure background. As a result of this, though very light in atomic weight, lithium is less common in the Solar System than 25 of the first 32 chemical elements. Seven radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess numbers of either neutrons or protons, giving it excess nuclear energy, and making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ...
s have been characterized, the most stable being 8Li with a half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of 838 ms and 9Li with a half-life of 178 ms. All of the remaining radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is conside ...
isotopes have half-lives that are shorter than 8.6 ms. The shortest-lived isotope of lithium is 4Li, which decays through proton emission
Proton emission (also known as proton radioactivity) is a rare type of radioactive decay in which a proton is ejected from a atomic nucleus, nucleus. Proton emission can occur from high-lying excited states in a nucleus following a beta decay ...
and has a half-life of 7.6 × 10−23 s. The 6Li isotope is one of only five stable nuclides to have both an odd number of protons and an odd number of neutrons, the other four stable odd-odd nuclides being hydrogen-2
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more c ...
, boron-10
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three v ...
, nitrogen-14
Natural nitrogen (7N) consists of two stable isotopes: the vast majority (99.6%) of naturally occurring nitrogen is nitrogen-14, with the remainder being nitrogen-15. Thirteen radioisotopes are also known, with atomic masses ranging from 9 to 23, ...
, and tantalum-180m
Natural tantalum (73Ta) consists of two stable isotopes: 181Ta (99.988%) and 180mTa (0.012%).
There are also 35 known artificial radioisotopes, the longest-lived of which are 179Ta with a half-life of 1.82 years, 182Ta with a half-life of 114.43 ...
.
7Li is one of the primordial elements
In geochemistry, geophysics and nuclear physics, primordial nuclides, also known as primordial isotopes, are nuclides found on Earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Primordial nuclides were present in the ...
(or, more properly, primordial nuclide
Nuclides (or nucleides, from nucleus, also known as nuclear species) are a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, ''Z'', their number of neutrons, ''N'', and their nuclear energy state.
The word ''nuclide'' was coined by the A ...
s) produced in Big Bang nucleosynthesis
In physical cosmology, Big Bang nucleosynthesis (also known as primordial nucleosynthesis, and abbreviated as BBN) is a model for the production of light nuclei, deuterium, 3He, 4He, 7Li, between 0.01s and 200s in the lifetime of the universe ...
. A small amount of both 6Li and 7Li are produced in stars during stellar nucleosynthesis
In astrophysics, stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. As a ...
, but it is further " burned" as fast as produced. 7Li can also be generated in carbon star
A carbon star (C-type star) is typically an asymptotic giant branch star, a luminous red giant, whose Stellar atmosphere, atmosphere contains more carbon than oxygen. The two elements combine in the upper layers of the star, forming carbon monox ...
s. Additional small amounts of both 6Li and 7Li may be generated from solar wind, cosmic rays hitting heavier atoms, and from early solar system 7 Be radioactive decay.
Lithium isotopes fractionate substantially during a wide variety of natural processes, including mineral formation (chemical precipitation), metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
, and ion exchange
Ion exchange is a reversible interchange of one species of ion present in an insoluble solid with another of like charge present in a solution surrounding the solid. Ion exchange is used in softening or demineralizing of water, purification of ch ...
. Lithium ions substitute for magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
and iron in octahedral sites in clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolinite, ). Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impuriti ...
minerals, where 6Li is preferred to 7Li, resulting in enrichment of the light isotope in processes of hyperfiltration and rock alteration. The exotic 11Li is known to exhibit a neutron halo, with 2 neutrons orbiting around its nucleus of 3 protons and 6 neutrons. The process known as laser isotope separation can be used to separate lithium isotopes, in particular 7Li from 6Li.
Nuclear weapons manufacture and other nuclear physics applications are a major source of artificial lithium fractionation, with the light isotope 6Li being retained by industry and military stockpiles to such an extent that it has caused slight but measurable change in the 6Li to 7Li ratios in natural sources, such as rivers. This has led to unusual uncertainty in the standardized atomic weight
Relative atomic mass (symbol: ''A''; sometimes abbreviated RAM or r.a.m.), also known by the deprecated synonym atomic weight, is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a giv ...
of lithium, since this quantity depends on the natural abundance ratios of these naturally-occurring stable lithium isotopes, as they are available in commercial lithium mineral sources.
Both stable isotopes of lithium can be laser cooled and were used to produce the first quantum degenerate Bose
Bose may refer to:
* Bose (crater), a lunar crater.
* ''Bose'' (film), a 2004 Indian Tamil film starring Srikanth and Sneha
* Bose (surname), a surname (and list of people with the name)
* Bose (given name), a given name
* Bose, Italy, a ''fra ...
– Fermi mixture.
Occurrence
Astronomical
Although it was synthesized in theBig Bang
The Big Bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models based on the Big Bang concept explain a broad range of phenomena, including th ...
, lithium (together with beryllium and boron) is markedly less abundant in the universe than other elements. This is a result of the comparatively low stellar temperatures necessary to destroy lithium, along with a lack of common processes to produce it.
According to modern cosmological theory, lithium—in both stable isotopes (lithium-6 and lithium-7)—was one of the three elements synthesized in the Big Bang. Though the amount of lithium generated in Big Bang nucleosynthesis
In physical cosmology, Big Bang nucleosynthesis (also known as primordial nucleosynthesis, and abbreviated as BBN) is a model for the production of light nuclei, deuterium, 3He, 4He, 7Li, between 0.01s and 200s in the lifetime of the universe ...
is dependent upon the number of photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s per baryon
In particle physics, a baryon is a type of composite particle, composite subatomic particle that contains an odd number of valence quarks, conventionally three. proton, Protons and neutron, neutrons are examples of baryons; because baryons are ...
, for accepted values the lithium abundance can be calculated, and there is a " cosmological lithium discrepancy" in the universe: older stars seem to have less lithium than they should, and some younger stars have much more. The lack of lithium in older stars is apparently caused by the "mixing" of lithium into the interior of stars, where it is destroyed, while lithium is produced in younger stars. Although it transmutes into two atoms of helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
due to collision with a proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
at temperatures above 2.4 million degrees Celsius (most stars easily attain this temperature in their interiors), lithium is more abundant than computations would predict in later-generation stars.
 Lithium is also found in
Lithium is also found in brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big en ...
substellar objects and certain anomalous orange stars. Because lithium is present in cooler, less-massive brown dwarfs, but is destroyed in hotter red dwarf
A red dwarf is the smallest kind of star on the main sequence. Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of fusing star in the Milky Way, at least in the neighborhood of the Sun. However, due to their low luminosity, individual red dwarfs are ...
stars, its presence in the stars' spectra can be used in the "lithium test" to differentiate the two, as both are smaller than the Sun. Certain orange stars can also contain a high concentration of lithium. Those orange stars found to have a higher than usual concentration of lithium (such as Centaurus X-4) orbit massive objects—neutron stars or black holes—whose gravity evidently pulls heavier lithium to the surface of a hydrogen-helium star, causing more lithium to be observed.
On 27 May 2020, astronomers reported that classical nova
A nova ( novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. All observed novae involve white ...
explosions are galactic producers of lithium-7.
Terrestrial
Although lithium is widely distributed on Earth, it does not naturally occur in elemental form due to its high reactivity. The total lithium content of seawater is very large and is estimated as 230 billion tonnes, where the element exists at a relatively constant concentration of 0.14 to 0.25 parts per million (ppm), or 25micromolar
Molar concentration (also called molarity, amount concentration or substance concentration) is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. Specifically, It is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular, of a s ...
; higher concentrations approaching 7 ppm are found near hydrothermal vents
Hydrothermal vents are fissures on the seabed from which geothermally heated water discharges. They are commonly found near volcanically active places, areas where tectonic plates are moving apart at mid-ocean ridges, ocean basins, and hots ...
.
Estimates for the Earth's crustal content range from 20 to 70 ppm by weight. In keeping with its name, lithium forms a minor part of igneous rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
s, with the largest concentrations in granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
s. Granitic pegmatite
A pegmatite is an igneous rock showing a very coarse texture, with large interlocking crystals usually greater in size than and sometimes greater than . Most pegmatites are composed of quartz, feldspar, and mica, having a similar silicic c ...
s also provide the greatest abundance of lithium-containing minerals, with spodumene
Spodumene is a pyroxene mineral consisting of lithium aluminium inosilicate, Li Al( Si O3)2, and is a commercially important source of lithium. It occurs as colorless to yellowish, purplish, or lilac kunzite (see below), or alternatively yellow ...
and petalite
Petalite, also known as castorite, is a lithium aluminum phyllosilicate mineral Li Al Si4 O10, crystallizing in the monoclinic system. Petalite occurs as colorless, pink, grey, yellow, yellow grey, to white tabular crystals and columnar masses. ...
being the most commercially viable sources. Another significant mineral of lithium is lepidolite
Lepidolite is the common name for a lilac-gray or rose-colored series of minerals in the mica group. The mineralogical name for this series is the polylithionite-trilithionite series. Lepidolite has a chemical formula of . It is the most abundan ...
which is now an obsolete name for a series formed by polylithionite and trilithionite. Another source for lithium is hectorite
Hectorite is a rare soft, greasy, white clay mineral with a chemical formula of .
Hectorite was first described in 1941 and named for an occurrence in the United States near Hector, California (in San Bernardino County, California, 30 miles east ...
clay, the only active development of which is through the Western Lithium Corporation in the United States. At 20 mg lithium per kg of Earth's crust, lithium is the 31st most abundant element.
According to the ''Handbook of Lithium and Natural Calcium'', "Lithium is a comparatively rare element, although it is found in many rocks and some brines, but always in very low concentrations. There are a fairly large number of both lithium mineral and brine deposits but only comparatively few of them are of actual or potential commercial value. Many are very small, others are too low in grade."
Chile is estimated (2020) to have the largest reserves by far (9.2 million tonnes), and Australia the highest annual production (40,000 tonnes). One of the largest ''reserve bases''Appendixes. By USGS definitions, the reserve base "may encompass those parts of the resources that have a reasonable potential for becoming economically available within planning horizons beyond those that assume proven technology and current economics. The reserve base includes those resources that are currently economic (reserves), marginally economic (marginal reserves), and some of those that are currently subeconomic (subeconomic resources)." of lithium is in the
Salar de Uyuni
Salar de Uyuni (or "Salar de Tunupa") is the world's largest salt flat, or playa, at in area. It is in the Daniel Campos Province in Potosí in southwest Bolivia, near the crest of the Andes at an elevation of above sea level.
The Salar wa ...
area of Bolivia, which has 5.4 million tonnes. Other major suppliers include Australia, Argentina and China. As of 2015, the Czech Geological Survey
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus
*Czech (surna ...
considered the entire Ore Mountains
The Ore Mountains (, or ; ) lie along the Czech–German border, separating the historical regions of Bohemia in the Czech Republic and Saxony in Germany. The highest peaks are the Klínovec in the Czech Republic (German: ''Keilberg'') at ab ...
in the Czech Republic as lithium province. Five deposits are registered, one near is considered as a potentially economical deposit, with 160 000 tonnes of lithium. In December 2019, Finnish mining company Keliber Oy reported its Rapasaari lithium deposit has estimated proven and probable ore reserves of 5.280 million tonnes.
In June 2010, ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'' reported that American geologists were conducting ground surveys on dry salt lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per liter). I ...
s in western Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
believing that large deposits of lithium are located there. These estimates are "based principally on old data, which was gathered mainly by the Soviets
The Soviet people () were the citizens and nationals of the Soviet Union. This demonym was presented in the ideology of the country as the "new historical unity of peoples of different nationalities" ().
Nationality policy in the Soviet Union ...
during their occupation of Afghanistan from 1979–1989". The Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Space Force, ...
estimated the lithium reserves in Afghanistan to amount to the ones in Bolivia and dubbed it as a potential "Saudi-Arabia of lithium". In Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
, England, the presence of brine rich in lithium was well known due to the region's historic mining industry
Mining is the extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a la ...
, and private investors have conducted tests to investigate potential lithium extraction in this area.
Biological
Lithium is found in trace amount in numerous plants, plankton, and invertebrates, at concentrations of 69 to 5,760parts per billion
In science and engineering, the parts-per notation is a set of pseudo-units to describe the small values of miscellaneous dimensionless quantities, e.g. mole fraction or mass fraction.
Since these fractions are quantity-per-quantity measur ...
(ppb). In vertebrates the concentration is slightly lower, and nearly all vertebrate tissue and body fluids contain lithium ranging from 21 to 763 ppb. Marine organisms tend to bioaccumulate lithium more than terrestrial organisms. Whether lithium has a physiological role in any of these organisms is unknown.
Lithium concentrations in human tissue averages about 24 ppb (4 ppb in blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
, and 1.3 ppm in bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
).
Lithium is easily absorbed by plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s and lithium concentration in plant tissue is typically around 1 ppm. Some plant families
Family (from ) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as ...
bioaccumulate
Bioaccumulation is the gradual accumulation of substances, such as pesticides or other chemicals, in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a substance faster than it can be lost or eliminated by catabolism and excretion. Th ...
more lithium than others. Dry weight
Vehicle weight is a measurement of wheeled motor vehicles; either an actual measured weight of the vehicle under defined conditions or a gross weight rating for its weight carrying capacity.
Curb or kerb weight
Curb weight (American English) or k ...
lithium concentrations for members of the family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
Solanaceae
Solanaceae (), commonly known as the nightshades, is a family of flowering plants in the order Solanales. It contains approximately 2,700 species, several of which are used as agricultural crops, medicinal plants, and ornamental plants. Many me ...
(which includes potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
es and tomato
The tomato (, ), ''Solanum lycopersicum'', is a plant whose fruit is an edible Berry (botany), berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originate ...
es), for instance, can be as high as 30 ppm while this can be as low as 0.05 ppb for corn grains.
Studies of lithium concentrations in mineral-rich soil give ranges between around 0.1 and 50−100 ppm, with some concentrations as high as 100−400 ppm, although it is unlikely that all of it is available for uptake by plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s.
Lithium accumulation does not appear to affect the essential nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
composition of plants. Tolerance to lithium varies by plant species and typically parallels sodium tolerance; maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
and Rhodes grass
''Chloris gayana'' is a species of Poaceae, grass known by the common name Rhodes grass. It is native to Africa but it can be found throughout the tropical and subtropical world as a introduced species, naturalized species.
It can grow in many t ...
, for example, are highly tolerant to lithium injury while avocado
The avocado, alligator pear or avocado pear (''Persea americana'') is an evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to Americas, the Americas and was first domesticated in Mesoamerica more than 5,000 years ago. It was priz ...
and soybean
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source o ...
are very sensitive. Similarly, lithium at concentrations of 5 ppm reduces seed germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
in some species (e.g. Asian rice
''Oryza sativa'', having the common name Asian cultivated rice, is the much more common of the two rice species cultivated as a cereal, the other species being '' O. glaberrima'', African rice. It was first domesticated in the Yangtze River ba ...
and chickpea
The chickpea or chick pea (''Cicer arietinum'') is an annual plant, annual legume of the family (biology), family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae, cultivated for its edible seeds. Its different types are variously known as gram," Bengal gram, ga ...
) but not in others (e.g. barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
and wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
).
Many of lithium's major biological effects can be explained by its competition with other ions.
The monovalent lithium ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
competes with other ions such as sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
(immediately below lithium on the periodic table
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows (" periods") and columns (" groups"). It is an icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other s ...
), which like lithium is also a monovalent alkali metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names ...
.
Lithium also competes with bivalent magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
ions, whose ionic radius
Ionic radius, ''r''ion, is the radius of a monatomic ion in an ionic crystal structure. Although neither atoms nor ions have sharp boundaries, they are treated as if they were hard spheres with radii such that the sum of ionic radii of the cati ...
(86 pm) is approximately that of the lithium ion (90 pm).
Mechanisms that transport sodium across cellular membranes also transport lithium.
For instance, sodium channel
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell (biology), cell's cell membrane, membrane. They belong to the Cation channel superfamily, superfamily of cation channels.
Classific ...
s (both voltage-gated and epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
) are particularly major pathways of entry for lithium.
Lithium ions can also permeate
In physics and engineering, permeation (also called imbuing) is the penetration of a permeate (a fluid such as a liquid, gas, or vapor) through a solid. It is directly related to the concentration gradient of the permeate, a material's intrinsi ...
through ligand-gated ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channels (LICs, LGIC), also commonly referred to as ionotropic receptors, are a group of transmembrane ion-channel proteins which open to allow ions such as sodium, Na+, potassium, K+, calcium, Ca2+, and/or chloride, Cl− to ...
s as well as cross both nuclear
Nuclear may refer to:
Physics
Relating to the nucleus of the atom:
*Nuclear engineering
*Nuclear physics
*Nuclear power
*Nuclear reactor
*Nuclear weapon
*Nuclear medicine
*Radiation therapy
*Nuclear warfare
Mathematics
* Nuclear space
*Nuclear ...
and mitochondrial
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
membrane
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Bi ...
s.
Like sodium, lithium can enter and partially block (although not permeate
In physics and engineering, permeation (also called imbuing) is the penetration of a permeate (a fluid such as a liquid, gas, or vapor) through a solid. It is directly related to the concentration gradient of the permeate, a material's intrinsi ...
) potassium channel
Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of ...
s and calcium channel
A calcium channel is an ion channel which shows selective permeability to calcium ions. It is sometimes synonymous with voltage-gated calcium channel, which are a type of calcium channel regulated by changes in membrane potential. Some calcium chan ...
s.
The biological effects of lithium are many and varied but its mechanisms of action are only partially understood.
For instance, studies of lithium-treated patients with bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
show that, among many other effects, lithium partially reverses telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see #Sequences, Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In ...
shortening
Shortening is any fat that is a solid at room temperature and is used to make crumbly pastry and other food products.
The idea of shortening dates back to at least the 18th century, well before the invention of modern, shelf-stable vegetable ...
in these patients and also increases mitochondrial function, although how lithium produces these pharmacological effect
In pharmacology, biological activity or pharmacological activity describes the beneficial or adverse effects of a drug on living matter. When a drug is a complex chemical mixture, this activity is exerted by the substance's active ingredient or ...
s is not understood.
Even the exact mechanisms involved in lithium toxicity
Lithium toxicity, also known as lithium overdose, is the condition of having too much lithium. Symptoms may include a tremor, increased reflexes, trouble walking, kidney problems, and an altered level of consciousness. Some symptoms may last for a ...
are not fully understood.
History

Petalite
Petalite, also known as castorite, is a lithium aluminum phyllosilicate mineral Li Al Si4 O10, crystallizing in the monoclinic system. Petalite occurs as colorless, pink, grey, yellow, yellow grey, to white tabular crystals and columnar masses. ...
(LiAlSi4O10) was discovered in 1800 by the Brazilian chemist and statesman José Bonifácio de Andrada e Silva in a mine on the island of Utö, Sweden, Utö, Sweden. However, it was not until 1817 that Johan August Arfwedson, then working in the laboratory of the chemist Jöns Jakob Berzelius, discovery of the chemical elements, detected the presence of a new element while analyzing petalite ore. This element formed compounds similar to those of sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
and potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
, though its lithium carbonate, carbonate and lithium hydroxide, hydroxide were less solubility, soluble in water and less Base (chemistry), alkaline. Berzelius gave the alkaline material the name "''lithion''/''lithina''", from the Greek word ''λιθoς'' (transliterated as ''lithos'', meaning "stone"), to reflect its discovery in a solid mineral, as opposed to potassium, which had been discovered in plant ashes, and sodium, which was known partly for its high abundance in animal blood. He named the new element "lithium".
Arfwedson later showed that this same element was present in the minerals spodumene
Spodumene is a pyroxene mineral consisting of lithium aluminium inosilicate, Li Al( Si O3)2, and is a commercially important source of lithium. It occurs as colorless to yellowish, purplish, or lilac kunzite (see below), or alternatively yellow ...
and lepidolite
Lepidolite is the common name for a lilac-gray or rose-colored series of minerals in the mica group. The mineralogical name for this series is the polylithionite-trilithionite series. Lepidolite has a chemical formula of . It is the most abundan ...
. In 1818, Christian Gmelin was the first to observe that lithium salts give a bright red color to flame. However, both Arfwedson and Gmelin tried and failed to isolate the pure element from its salts. It was not isolated until 1821, when William Thomas Brande obtained it by electrolysis of lithium oxide
Lithium oxide (Lithium, Oxygen, O) or lithia is an Inorganic compound, inorganic chemical compound. It is a white or pale yellow solid. Although not specifically important, many materials are assessed on the basis of their Li2O content. For examp ...
, a process that had previously been employed by the chemist Sir Humphry Davy to isolate the alkali metals potassium and sodium. Brande also described some pure salts of lithium, such as the chloride, and, estimating that lithia (lithium oxide
Lithium oxide (Lithium, Oxygen, O) or lithia is an Inorganic compound, inorganic chemical compound. It is a white or pale yellow solid. Although not specifically important, many materials are assessed on the basis of their Li2O content. For examp ...
) contained about 55% metal, estimated the atomic weight of lithium to be around 9.8 g/mol (modern value ~6.94 g/mol). In 1855, larger quantities of lithium were produced through the electrolysis of lithium chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorid ...
by Robert Bunsen and Augustus Matthiessen. The discovery of this procedure led to commercial production of lithium in 1923 by the German company Metallgesellschaft AG, which performed an electrolysis of a liquid mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a sa ...
.
Australian psychiatrist John Cade is credited with reintroducing and popularizing the use of lithium to treat mania in 1949. Shortly after, throughout the mid 20th century, lithium's mood stabilizing applicability for mania and Depression (mood), depression took off in Europe and the United States.
The production and use of lithium underwent several drastic changes in history. The first major application of lithium was in high-temperature lithium grease
Lithium soap is a soap consisting of a lithium salt of a fatty acid. Sodium-based and potassium-based soaps are used as cleaning agents in domestic and industrial applications, whereas lithium soaps are used as components of lithium grease (white ...
s for aircraft engines and similar applications in World War II and shortly after. This use was supported by the fact that lithium-based soaps have a higher melting point than other alkali soaps, and are less corrosive than calcium based soaps. The small demand for lithium soaps and lubricating greases was supported by several small mining operations, mostly in the US.
The demand for lithium increased dramatically during the Cold War with the production of Nuclear weapon design, nuclear fusion weapons. Both lithium-6 and lithium-7 produce tritium when irradiated by neutrons, and are thus useful for the production of tritium by itself, as well as a form of solid fusion fuel used inside hydrogen bombs in the form of lithium deuteride
Lithium hydride is an inorganic compound with the formula Lithium, LiHydride, H. This alkali metal hydride is a colorless solid, although commercial samples are grey. Characteristic of a Hydride#Ionic hydrides, salt-like (ionic) hydride, it has a ...
. The US became the prime producer of lithium between the late 1950s and the mid-1980s. At the end, the stockpile of lithium was roughly 42,000 tonnes of lithium hydroxide. The stockpiled lithium was depleted in lithium-6 by 75%, which was enough to affect the measured atomic weight
Relative atomic mass (symbol: ''A''; sometimes abbreviated RAM or r.a.m.), also known by the deprecated synonym atomic weight, is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a giv ...
of lithium in many standardized chemicals, and even the atomic weight of lithium in some "natural sources" of lithium ion which had been "contaminated" by lithium salts discharged from isotope separation facilities, which had found its way into ground water.
Lithium is used to decrease the melting temperature of glass and to improve the melting behavior of aluminium oxide in the Hall-Héroult process. These two uses dominated the market until the middle of the 1990s. After the end of the nuclear arms race, the demand for lithium decreased and the sale of department of energy stockpiles on the open market further reduced prices. In the mid-1990s, several companies started to isolate lithium from brine
Brine (or briny water) is a high-concentration solution of salt (typically sodium chloride or calcium chloride) in water. In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawat ...
which proved to be a less expensive option than underground or open-pit mining. Most of the mines closed or shifted their focus to other materials because only the ore from zoned pegmatites could be mined for a competitive price. For example, the US mines near Kings Mountain, North Carolina, Kings Mountain, North Carolina, closed before the beginning of the 21st century.
The development of lithium-ion batteries increased the demand for lithium and became the dominant use in 2007. With the surge of lithium demand in batteries in the 2000s, new companies have expanded brine isolation efforts to meet the rising demand.
Chemistry
Of lithium metal
Lithium reacts with water easily, but with noticeably less vigor than other alkali metals. The reaction formshydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
gas and lithium hydroxide. When placed over a flame, lithium compounds give off a striking crimson color, but when the metal burns strongly, the flame becomes a brilliant silver. Lithium will ignite and burn in oxygen when exposed to water or water vapor. In moist air, lithium rapidly tarnishes to form a black coating of lithium hydroxide (LiOH and LiOH·H2O), lithium nitride (Li3N) and lithium carbonate (Li2CO3, the result of a secondary reaction between LiOH and carbon dioxide, CO2). Lithium is one of the few metals that react with nitrogen gas.
Because of its reactivity with water, and especially nitrogen, lithium metal is usually stored in a hydrocarbon sealant, often petroleum jelly. Although the heavier alkali metals can be stored under mineral oil, lithium is not dense enough to fully submerge itself in these liquids.
Lithium has a diagonal relationship with magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, an element of similar atomic and ionic radius
Ionic radius, ''r''ion, is the radius of a monatomic ion in an ionic crystal structure. Although neither atoms nor ions have sharp boundaries, they are treated as if they were hard spheres with radii such that the sum of ionic radii of the cati ...
. Chemical resemblances between the two metals include the formation of a nitride by reaction with N2, the formation of an lithium oxide, oxide () and peroxide () when burnt in O2, salt (chemistry), salts with similar solubility, solubilities, and thermal instability of the carbonates and nitrides. The metal reacts with hydrogen gas at high temperatures to produce lithium hydride (LiH).
Lithium forms a variety of binary and ternary materials by direct reaction with the main group elements. These Zintl phases, although highly covalent, can be viewed as salts of polyatomic anions such as Si44-, P73-, and Te52-. With graphite, lithium forms a variety of intercalation compounds.
It dissolves in ammonia (and amines) to give [Li(NH3)4]+ and the solvated electron.
Inorganic compounds
Lithium forms salt-like derivatives with all halides and pseudohalides. Some examples include the halides lithium fluoride, LiF, lithium chloride, LiCl, lithium bromide, LiBr, Lithium iodide, LiI, as well as the pseudohalides and related anions. Lithium carbonate has been described as the most important compound of lithium. This white solid is the principal product of beneficiation of lithium ores. It is a precursor to other salts including ceramics and materials for lithium batteries. The compounds Lithium borohydride, and Lithium aluminium hydride, are useful reagents. These salts and many other lithium salts exhibit distinctively high solubility in ethers, in contrast with salts of heavier alkali metals. In aqueous solution, the coordination complex [Li(H2O)4]+ predominates for many lithium salts. Related complexes are known with amines and ethers.Organic chemistry
 Organolithium compounds are numerous and useful. They are defined by the presence of a covalent bond, bond between carbon and lithium. They serve as metal-stabilized carbanions, although their solution and solid-state structures are more complex than this simplistic view. Thus, these are extremely powerful base (chemistry), bases and carbon nucleophile, nucleophiles. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoricity, pyrophoric.
Like its inorganic compounds, almost all organic compounds of lithium formally follow the duet rule (e.g., N-Butyllithium, BuLi, Methyllithium, MeLi). However, it is important to note that in the absence of coordinating solvents or ligands, organolithium compounds form dimeric, tetrameric, and hexameric clusters (e.g., BuLi is actually [BuLi]6 and MeLi is actually [MeLi]4) which feature multi-center bonding and increase the coordination number around lithium. These clusters are broken down into smaller or monomeric units in the presence of solvents like dimethoxyethane (DME) or ligands like tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA). As an exception to the duet rule, a two-coordinate lithate complex with four electrons around lithium, [Li(thf)4]+[((Me3Si)3C)2Li]–, has been characterized crystallographically.
Organolithium compounds are numerous and useful. They are defined by the presence of a covalent bond, bond between carbon and lithium. They serve as metal-stabilized carbanions, although their solution and solid-state structures are more complex than this simplistic view. Thus, these are extremely powerful base (chemistry), bases and carbon nucleophile, nucleophiles. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoricity, pyrophoric.
Like its inorganic compounds, almost all organic compounds of lithium formally follow the duet rule (e.g., N-Butyllithium, BuLi, Methyllithium, MeLi). However, it is important to note that in the absence of coordinating solvents or ligands, organolithium compounds form dimeric, tetrameric, and hexameric clusters (e.g., BuLi is actually [BuLi]6 and MeLi is actually [MeLi]4) which feature multi-center bonding and increase the coordination number around lithium. These clusters are broken down into smaller or monomeric units in the presence of solvents like dimethoxyethane (DME) or ligands like tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA). As an exception to the duet rule, a two-coordinate lithate complex with four electrons around lithium, [Li(thf)4]+[((Me3Si)3C)2Li]–, has been characterized crystallographically.
Production
Lithium production has greatly increased since the end of World War II. The main sources of lithium arebrine
Brine (or briny water) is a high-concentration solution of salt (typically sodium chloride or calcium chloride) in water. In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawat ...
s and ores.
Lithium metal is produced through electrolysis applied to a mixture of fused 55% lithium chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorid ...
and 45% potassium chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a sa ...
at about 450 °C.
Lithium is one of the elements critical in a world running on renewable energy and dependent on batteries. This suggests that lithium will be one of the main objects of geopolitical competition, but this perspective has also been criticised for underestimating the power of economic incentives for expanded production.
Reserves and occurrence
 The small ionic size makes it difficult for lithium to be included in early stages of mineral crystallization. As a result, lithium remains in the molten phases, where it gets enriched, until it gets solidified in the final stages. Such lithium enrichment is responsible for all commercially promising lithium ore deposits. Brines (and dry salt) are another important source of Li+. Although the number of known lithium-containing deposits and brines is large, most of them are either small or have too low Li+ concentrations. Thus, only a few appear to be of commercial value.
The US Geological Survey (USGS) estimated worldwide identified lithium reserves in 2022 and 2023 to be 26 million and 28 million tonnes, respectively. An accurate estimate of world lithium reserves is difficult. One reason for this is that most lithium classification schemes are developed for solid ore deposits, whereas brine is a fluid that is problematic to treat with the same classification scheme due to varying concentrations and pumping effects.
In 2019, world production of lithium from spodumene was around 80,000t per annum, primarily from the Greenbushes, Western Australia, Greenbushes pegmatite and from some China, Chinese and Chilean sources. The Talison mine in Greenbushes is reported to be the largest and to have the highest grade of ore at 2.4% Li2O (2012 figures).
The small ionic size makes it difficult for lithium to be included in early stages of mineral crystallization. As a result, lithium remains in the molten phases, where it gets enriched, until it gets solidified in the final stages. Such lithium enrichment is responsible for all commercially promising lithium ore deposits. Brines (and dry salt) are another important source of Li+. Although the number of known lithium-containing deposits and brines is large, most of them are either small or have too low Li+ concentrations. Thus, only a few appear to be of commercial value.
The US Geological Survey (USGS) estimated worldwide identified lithium reserves in 2022 and 2023 to be 26 million and 28 million tonnes, respectively. An accurate estimate of world lithium reserves is difficult. One reason for this is that most lithium classification schemes are developed for solid ore deposits, whereas brine is a fluid that is problematic to treat with the same classification scheme due to varying concentrations and pumping effects.
In 2019, world production of lithium from spodumene was around 80,000t per annum, primarily from the Greenbushes, Western Australia, Greenbushes pegmatite and from some China, Chinese and Chilean sources. The Talison mine in Greenbushes is reported to be the largest and to have the highest grade of ore at 2.4% Li2O (2012 figures).
Lithium triangle and other brine sources
The world's top four lithium-producing countries in 2019, as reported by the US Geological Survey, were lithium mining in Australia, Australia, Chile, Economy of China, China and Economy of Argentina, Argentina. The three countries of Chile, Bolivia, and Argentina contain a region known as the Lithium Triangle. The Lithium Triangle is known for its high-quality salt flats, which include Bolivia'sSalar de Uyuni
Salar de Uyuni (or "Salar de Tunupa") is the world's largest salt flat, or playa, at in area. It is in the Daniel Campos Province in Potosí in southwest Bolivia, near the crest of the Andes at an elevation of above sea level.
The Salar wa ...
, Chile's Salar de Atacama, and Argentina's Salar de Arizaro. , the Lithium Triangle was estimated to contain over 75% of existing known lithium reserves. Deposits found in subsurface brines have also been found in South America throughout the Andes mountain chain. In 2010, Chile was the leading producer, followed by Argentina. Both countries recover lithium from brine pools. According to USGS, Bolivia's Uyuni Desert has 5.4 million tonnes of lithium. Half the world's known reserves are located in Bolivia along the central eastern slope of the Andes. The Bolivian government has invested US$900 million in lithium production and in 2021 successfully produced 540 tons. The brines in the salt pans of the Lithium Triangle vary widely in lithium content. Concentrations can also vary over time as brines are fluids that are changeable and mobile.
In the US, lithium is recovered from brine pools in Nevada. Projects are also under development in Lithium Valley in California and from brine in southwest Arkansas using a direct lithium extraction process, drawing on the deep brine resource in the Smackover Formation.
Hard-rock deposits
Since 2018 the Mining industry of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of Congo is known to have the largest lithiumspodumene
Spodumene is a pyroxene mineral consisting of lithium aluminium inosilicate, Li Al( Si O3)2, and is a commercially important source of lithium. It occurs as colorless to yellowish, purplish, or lilac kunzite (see below), or alternatively yellow ...
hard-rock deposit in the world. The deposit located in Manono, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Manono, Democratic Republic of the Congo, DRC, may hold up to 1.5 billion tons of lithium spodumene hard-rock. The two largest pegmatites (known as the Carriere de l'Este Pegmatite and the Roche Dure Pegmatite) are each of similar size or larger than the famous Greenbushes Pegmatite in Western Australia. Thus, the Mining industry of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of Congo is expected to be a significant supplier of lithium to the world with its high grade and low impurities.
On 16 July 2018 2.5 million tonnes of high-grade lithium resources and 124 million pounds of uranium resources were found in the Falchani hard rock deposit in the region Puno, Peru.
In 2020, Australia granted Major Project Status (MPS) to the Finniss Lithium Project for a strategically important lithium deposit: an estimated 3.45 million tonnes (Mt) of mineral resource at 1.4 percent lithium oxide
Lithium oxide (Lithium, Oxygen, O) or lithia is an Inorganic compound, inorganic chemical compound. It is a white or pale yellow solid. Although not specifically important, many materials are assessed on the basis of their Li2O content. For examp ...
.CORE Lithium : Finnis Lithium, retrieved 13 October 2022 Operational mining began in 2022. A deposit discovered in 2013 in Wyoming's Rock Springs Uplift is estimated to contain 228,000 tons. Additional deposits in the same formation were estimated to be as much as 18 million tons. Similarly in Nevada, the McDermitt Caldera hosts lithium-bearing volcanic muds that consist of the largest known deposits of lithium within the United States. The Pampean Pegmatite Province in Argentina is known to have a total of at least 200,000 tons of
spodumene
Spodumene is a pyroxene mineral consisting of lithium aluminium inosilicate, Li Al( Si O3)2, and is a commercially important source of lithium. It occurs as colorless to yellowish, purplish, or lilac kunzite (see below), or alternatively yellow ...
with lithium oxide
Lithium oxide (Lithium, Oxygen, O) or lithia is an Inorganic compound, inorganic chemical compound. It is a white or pale yellow solid. Although not specifically important, many materials are assessed on the basis of their Li2O content. For examp ...
(Li2O) ore grade, grades varying between 5 and 8 wt %.
In Russia the largest lithium deposit Kolmozerskoye is located in Murmansk region. In 2023, Polar Lithium, a joint venture between Nornickel and Rosatom, has been granted the right to develop the deposit. The project aims to produce 45,000 tonnes of lithium carbonate and hydroxide per year and plans to reach full design capacity by 2030.
Sources
Another potential source of lithium was identified as the leachates of Geothermal electricity, geothermal wells, which are carried to the surface.Parker, AnnMining Geothermal Resources
. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Recovery of this type of lithium has been demonstrated in the field; the lithium is separated by simple filtration.Patel, P. (16 November 2011
Startup to Capture Lithium from Geothermal Plants
. technologyreview.com Reserves are more limited than those of brine reservoirs and hard rock.
Pricing
 In 1998, the price of lithium metal was about (or US$43/Pound (mass), lb). After the 2008 financial crisis, major suppliers, such as Sociedad Química y Minera (SQM), dropped lithium carbonate pricing by 20%. Prices rose in 2012. A 2012 Bloomberg Businessweek, Business Week article outlined an oligopoly in the lithium space: "SQM, controlled by billionaire Julio Ponce Lerou, Julio Ponce, is the second-largest, followed by Albemarle Corporation#Acquisition of Rockwood Holdings, Rockwood, which is backed by Henry Kravis's KKR & Co., and Philadelphia-based FMC", with Talison Minerals, Talison mentioned as the biggest producer. Global consumption may jump to 300,000 metric tons a year by 2020 from about 150,000 tons in 2012, to match the demand for lithium batteries that has been growing at about 25% a year, outpacing the 4% to 5% overall gain in lithium production.
The price information service ISE – Institute of Rare Earths Elements and Strategic Metals – gives for various lithium substances in the average of March to August 2022 the following kilo prices stable in the course: Lithium carbonate, purity 99.5% min, from various producers between 63 and 72 EUR/kg. Lithium hydroxide monohydrate LiOH 56.5% min, China, at 66 to 72 EUR/kg; delivered South Korea – 73 EUR/kg. Lithium metal 99.9% min, delivered China – 42 EUR/kg.
In 1998, the price of lithium metal was about (or US$43/Pound (mass), lb). After the 2008 financial crisis, major suppliers, such as Sociedad Química y Minera (SQM), dropped lithium carbonate pricing by 20%. Prices rose in 2012. A 2012 Bloomberg Businessweek, Business Week article outlined an oligopoly in the lithium space: "SQM, controlled by billionaire Julio Ponce Lerou, Julio Ponce, is the second-largest, followed by Albemarle Corporation#Acquisition of Rockwood Holdings, Rockwood, which is backed by Henry Kravis's KKR & Co., and Philadelphia-based FMC", with Talison Minerals, Talison mentioned as the biggest producer. Global consumption may jump to 300,000 metric tons a year by 2020 from about 150,000 tons in 2012, to match the demand for lithium batteries that has been growing at about 25% a year, outpacing the 4% to 5% overall gain in lithium production.
The price information service ISE – Institute of Rare Earths Elements and Strategic Metals – gives for various lithium substances in the average of March to August 2022 the following kilo prices stable in the course: Lithium carbonate, purity 99.5% min, from various producers between 63 and 72 EUR/kg. Lithium hydroxide monohydrate LiOH 56.5% min, China, at 66 to 72 EUR/kg; delivered South Korea – 73 EUR/kg. Lithium metal 99.9% min, delivered China – 42 EUR/kg.
Extraction
Lithium and its compounds were historically isolated and extracted from hard rock. However, by the 1990s mineral springs,brine
Brine (or briny water) is a high-concentration solution of salt (typically sodium chloride or calcium chloride) in water. In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawat ...
pools, and brine deposits had become the dominant source. Most of these were in Chile, Argentina and Bolivia and the lithium is extracted from the brine by evaporative processes. Large lithium-clay deposits under development in the McDermitt caldera (Nevada, United States) require concentrated sulfuric acid to leach lithium from the clay ore.
By early 2021, much of the lithium mined globally came from either "spodumene
Spodumene is a pyroxene mineral consisting of lithium aluminium inosilicate, Li Al( Si O3)2, and is a commercially important source of lithium. It occurs as colorless to yellowish, purplish, or lilac kunzite (see below), or alternatively yellow ...
, the mineral contained in hard rocks found in places such as Australia and North Carolina" or from salty brine pumped directly out of the ground, as it is in locations in Chile. In Chile's Salar de Atacama, the lithium concentration in the brine is raised by solar evaporation in a system of ponds. The enrichment by evaporation process may require up to one-and-a-half years, when the brine reaches a lithium content of 6%. The final processing in this example is done in Salar del Carmen and La Negra (industrial complex), La Negra near the coastal city of Antofagasta where pure lithium carbonate, lithium hydroxide, and lithium chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorid ...
are produced from the brine.
Direct Lithium Extraction (DLE) technologies are being developed as alternatives to the evaporitic technology long used to extract lithium salts from brine
Brine (or briny water) is a high-concentration solution of salt (typically sodium chloride or calcium chloride) in water. In diverse contexts, ''brine'' may refer to the salt solutions ranging from about 3.5% (a typical concentration of seawat ...
s. The traditional evaporitic technology is a long duration process requiring large amounts of land and intensive water use, and can only be applied to the large continental brines. In contrast, DLE technologies are proposed to tackle the environmental and techno–economic shortcomings by avoiding brine evaporation. Some recent lithium mining projects are attempting to bring DLE into commercial production by these non-evaporative DLE approaches.
One method direct lithium extraction, as well as other valuable minerals, is to process geothermal brine water through an electrolytic cell, located within a membrane.
The use of electrodialysis and electrochemical intercalation was proposed in 2020 to extract lithium compounds from seawater (which contains lithium at 0.2 parts per million). Ion-selective cells within a membrane in principle could collect lithium either by use of electric field or a concentration difference. In 2024, a redox/electrodialysis system was claimed to offer enormous cost savings, shorter timelines, and less environmental damage than traditional evaporation-based systems.
Environmental issues
The manufacturing processes of lithium, including the solvent and mining waste, presents significant environmental and health hazards. Lithium extraction can be fatal to aquatic life due to water pollution. It is known to cause surface water contamination, drinking water contamination, respiratory problems, ecosystem degradation and landscape damage. It also leads to unsustainable water consumption in arid regions (1.9 million liters per ton of lithium). Massive byproduct generation of lithium extraction also presents unsolved problems, such as large amounts ofmagnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
and Lime (material), lime waste.
Although lithium occurs naturally, it is a non-renewable resource yet is seen as crucial in the transition away from Fossil fuel phase-out, fossil fuels, and the extraction process has been criticised for long-term degradation of water resources.
In the United States, open-pit mining and mountaintop removal mining compete with Brine mining, brine extraction mining. Environmental concerns include wildlife habitat degradation, potable water pollution including arsenic and antimony contamination, unsustainable water table reduction, and massive mining waste, including radioactive uranium byproduct and sulfuric acid discharge.
During 2021, a 2021–2022 Serbian environmental protests, series of mass protests broke out in Serbia against the construction of a lithium mine in Western Serbia by the Rio Tinto (corporation), Rio Tinto corporation. In 2024, an EU backed lithium mining project created large scale 2024 Serbian environmental protests, protests in Serbia.
Some animal species associated to salt lakes in the Lithium Triangle are particularly threatened by the damages of lithium production to the local ecosystem, including the Andean flamingo and ''Orestias parinacotensis'', a small fish locally known as "karachi".
Human rights issues
A study of relationships between lithium extraction companies and indigenous peoples in Argentina indicated that the state may not have protected indigenous peoples' right to Free, prior and informed consent, free prior and informed consent, and that extraction companies generally controlled community access to information and set the terms for discussion of the projects and benefit sharing. In Zimbabwe, the global increase in lithium prices in the early 2020s triggered a 'lithium fever', that led to conflicts between small-scale artisanal miners and large-scale mining companies, often Chinese-owned, backed by the Zimbabwean government which had an interest in attracting foreign investments. Artisanal miners occupied parts of the Sandawana mines and a privately owned lithium claim area in Goromonzi, a rural area close to the capital Harare. The artisanal miners were later evicted after the area was cordoned off and shut down by Zimbabwe’s Environmental Management Agency. Development of the Thacker Pass Lithium Mine, Thacker Pass lithium mine in Nevada, United States, has met with protests and lawsuits from several indigenous tribes who have said they were not provided free prior and informed consent and that the project threatens cultural and sacred sites. They have also expressed concerns that development of the project will create risks to indigenous women, because resource extraction is linked to Missing and murdered Indigenous women, missing and murdered indigenous women. Protestors have been occupying the site of the proposed mine since January 2021.Applications

Batteries
In 2021, most lithium is used to make lithium-ion batteries for electric cars and mobile devices.Ceramics and glass
Lithium oxide is widely used as a Flux (metallurgy), flux for processing silica, reducing themelting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state of matter, state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase (matter), phase exist in Thermodynamic equilib ...
and viscosity of the material and leading to ceramic glaze, glazes with improved physical properties including low coefficients of thermal expansion. Worldwide, this is one of the largest use for lithium compounds. Glazes containing lithium oxides are used for ovenware. Lithium carbonate (Li2CO3) is generally used in this application because it converts to the oxide upon heating.
Electrical and electronic
Late in the 20th century, lithium became an important component of battery electrolytes and electrodes, because of its high electrode potential. Because of its low atomic mass, it has a high charge- and power-to-weight ratio. A typical lithium-ion battery can generate approximately 3 volts per cell, compared with 2.1 volts for lead–acid battery, lead-acid and 1.5 volts for zinc-carbon cell, zinc-carbon. Lithium-ion batteries, which are rechargeable and have a high energy density, differ from lithium metal batteries, which are disposable (primary cell, primary) Battery (electricity), batteries with lithium or its compounds as the anode. Other rechargeable batteries that use lithium include the lithium-ion polymer battery, lithium iron phosphate battery, and the nanowire battery. Over the years opinions have been differing about potential growth. A 2008 study concluded that "realistically achievable lithium carbonate production would be sufficient for only a small fraction of future PHEV and electric vehicle, EV global market requirements", that "demand from the portable electronics sector will absorb much of the planned production increases in the next decade", and that "mass production of lithium carbonate is not environmentally sound, it will cause irreparable ecological damage to ecosystems that should be protected and that LiIon propulsion is incompatible with the notion of the 'Green Car'".Lubricating greases
The third most common use of lithium is in greases. Lithium hydroxide is a strong base (chemistry), base, and when heated with a fat, it produces a soap, such as lithium stearate from stearic acid. Lithium soap has the ability to thickening agent, thicken oils, and it is used to manufacture all-purpose, high-temperature grease (lubricant), lubricating greases.Metallurgy
Lithium (e.g. as lithium carbonate) is used as an additive to continuous casting mould flux slags where it increases fluidity, a use which accounts for 5% of global lithium use (2011). Lithium compounds are also used as additives (fluxes) to foundry sand for iron casting to reduce veining. Lithium (as lithium fluoride) is used as an additive to aluminium smelters (Hall–Héroult process), reducing melting temperature and increasing electrical resistance, a use which accounts for 3% of production (2011). When used as a flux (metallurgy), flux for welding or soldering, metallic lithium promotes the fusing of metals during the process and eliminates the formation of oxides by absorbing impurities. Alloys of the metal with aluminium, cadmium, copper and manganese are used to make high-performance, low density aircraft parts (see also Al-Li, Lithium-aluminium alloys).Silicon nano-welding
Lithium has been found effective in assisting the perfection of silicon nano-welds in electronic components for electric batteries and other devices.Pyrotechnics
Lithium compounds are used as pyrotechnic colorants and oxidizers in red fireworks and Flare (pyrotechnic), flares.Air purification
Lithium chloride and lithium bromide are hygroscopic and are used as desiccants for gas streams. Lithium hydroxide and lithium peroxide are the salts most commonly used in confined areas, such as aboard spacecraft and submarines, for carbon dioxide removal and air purification. Lithium hydroxide absorbs carbon dioxide from the air by forming lithium carbonate, and is preferred over other alkaline hydroxides for its low weight. Lithium peroxide (Li2O2) in presence of moisture not only reacts with carbon dioxide to form lithium carbonate, but also releases oxygen. The reaction is as follows: :2 Li2O2 + 2 CO2 → 2 Li2CO3 + O2 Some of the aforementioned compounds, as well as lithium perchlorate, are used in Chemical oxygen generator#Oxygen candle, oxygen candles that supply submarines with oxygen. These can also include small amounts of boron,magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 ...
, aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, silicon, titanium, manganese, and iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
.
Optics
Lithium fluoride, artificially grown as crystal, is clear and transparent and often used in specialist optics for infrared, IR, ultraviolet, UV and VUV (vacuum UV) applications. It has one of the lowest refractive index, refractive indices and the furthest transmission range in the deep UV of most common materials. Finely divided lithium fluoride powder has been used for Thermoluminescent Dosimeter, thermoluminescent radiation dosimetry (TLD): when a sample of such is exposed to radiation, it accumulates crystal defects which, when heated, resolve via a release of bluish light whose intensity is proportional to the absorbed dose, thus allowing this to be quantified. Lithium fluoride is sometimes used in focal lenses of telescopes. The high non-linearity of lithium niobate also makes it useful in nonlinear optics, non-linear optics applications. It is used extensively in telecommunication products such as mobile phones and optical modulators, for such components as crystal oscillator, resonant crystals. Lithium applications are used in more than 60% of mobile phones.Organic and polymer chemistry
Organolithium compounds are widely used in the production of polymer and fine-chemicals. In the polymer industry, which is the dominant consumer of these reagents, alkyl lithium compounds are catalysts/radical initiator, initiators in Anionic addition polymerization, anionic polymerization of functional group, unfunctionalized olefins. For the production of fine chemicals, organolithium compounds function as strong bases and as reagents for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds. Organolithium compounds are prepared from lithium metal and alkyl halides. Many other lithium compounds are used as reagents to prepare organic compounds. Some popular compounds include lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4), lithium triethylborohydride, N-Butyllithium, ''n''-butyllithium and Tert-Butyllithium, ''tert''-butyllithium.Military
Metallic lithium and its complex hydrides, such as lithium aluminium hydride (LiAlH4), are used as high-energy additives to rocket propellants. LiAlH4 can also be used by itself as a solid fuel. The Mark 50 torpedo stored chemical energy propulsion system (SCEPS) uses a small tank of sulfur hexafluoride, which is sprayed over a block of solid lithium. The reaction generates heat, creating steam to propel the torpedo in a closed Rankine cycle. Lithium hydride containing lithium-6 is used in thermonuclear weapons, where it serves as fuel for the fusion stage of the bomb.Nuclear
Lithium-6 is valued as a source material for tritium production and as a neutron absorber in nuclear fusion. Natural lithium contains about 7.5% lithium-6 from which large amounts of lithium-6 have been produced by isotope separation for use in nuclear weapons. Lithium-7 gained interest for use in nuclear reactorcoolant
A coolant is a substance, typically liquid, that is used to reduce or regulate the temperature of a system. An ideal coolant has high thermal capacity, low viscosity, is low-cost, non-toxic, chemically inert and neither causes nor promotes corr ...
s.
 Lithium deuteride was the nuclear fusion, fusion fuel of choice in early versions of the Nuclear weapon, hydrogen bomb. When bombarded by neutrons, both 6Li and 7Li produce tritium — this reaction, which was not fully understood when Teller-Ulam design, hydrogen bombs were first tested, was responsible for the runaway yield of the Castle Bravo nuclear test. Tritium fuses with
Lithium deuteride was the nuclear fusion, fusion fuel of choice in early versions of the Nuclear weapon, hydrogen bomb. When bombarded by neutrons, both 6Li and 7Li produce tritium — this reaction, which was not fully understood when Teller-Ulam design, hydrogen bombs were first tested, was responsible for the runaway yield of the Castle Bravo nuclear test. Tritium fuses with deuterium
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more c ...
in a Nuclear fusion, fusion reaction that is relatively easy to achieve. Although details remain secret, lithium-6 deuteride apparently still plays a role in modern nuclear weapons as a fusion material.
Lithium fluoride, when highly enriched in the lithium-7 isotope, forms the basic constituent of the fluoride salt mixture LiF-beryllium fluoride, BeF2 used in molten salt reactor, liquid fluoride nuclear reactors. Lithium fluoride is exceptionally chemically stable and LiF-BeF2 mixtures have low melting points. In addition, 7Li, Be, and F are among the few nuclide
Nuclides (or nucleides, from nucleus, also known as nuclear species) are a class of atoms characterized by their number of protons, ''Z'', their number of neutrons, ''N'', and their nuclear energy state.
The word ''nuclide'' was coined by the A ...
s with low enough neutron cross-section, thermal neutron capture cross-sections not to poison the fission reactions inside a nuclear fission reactor.Beryllium and fluorine occur only as one isotope, 9Be and 19F respectively. These two, together with 7Li, as well as deuterium, 2H, 11B, 15N, 209Bi, and the stable isotopes of C, and O, are the only nuclides with low enough thermal neutron capture cross sections aside from actinides to serve as major constituents of a molten salt breeder reactor fuel.
In conceptualized (hypothetical) nuclear fusion power plants, lithium will be used to produce tritium in Magnetic confinement fusion, magnetically confined reactors using deuterium
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more c ...
and tritium as the fuel. Naturally occurring tritium is extremely rare and must be synthetically produced by surrounding the reacting Plasma (physics), plasma with a 'blanket' containing lithium, where neutrons from the deuterium-tritium reaction in the plasma will fission the lithium to produce more tritium:
:6Li + n → 4He + 3H.
Lithium is also used as a source for alpha particles, or helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
nuclei. When 7Li is bombarded by accelerated proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
s 8beryllium, Be is formed, which almost immediately undergoes fission to form two alpha particles. This feat, called "splitting the atom" at the time, was the first fully human-made nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is a process in which two atomic nucleus, nuclei, or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle, collide to produce one or more new nuclides. Thus, a nuclear reaction must cause a t ...
. It was produced by John Douglas Cockcroft, Cockroft and Ernest Walton, Walton in 1932. Injection of lithium powders is used in fusion reactors to manipulate plasma-material interactions and dissipate energy in the hot thermo-nuclear fusion plasma boundary.
In 2013, the US Government Accountability Office said a shortage of lithium-7 critical to the operation of 65 out of 100 American nuclear reactors "places their ability to continue to provide electricity at some risk." The problem stems from the decline of US nuclear infrastructure. The equipment needed to separate lithium-6 from lithium-7 is mostly a cold war leftover. The US shut down most of this machinery in 1963, when it had a huge surplus of separated lithium, mostly consumed during the twentieth century. The report said it would take five years and $10 million to $12 million to reestablish the ability to separate lithium-6 from lithium-7.
Reactors that use lithium-7 heat water under high pressure and transfer heat through heat exchangers that are prone to corrosion. The reactors use lithium to counteract the corrosive effects of boric acid, which is added to the water to absorb excess neutrons.
Medicine
Lithium is useful in the treatment ofbipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder (BD), previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that each last from days to weeks, and in ...
. Lithium salts may also be helpful for related diagnoses, such as schizoaffective disorder and cyclic major depressive disorder. The active part of these salts is the lithium ion Li+. Lithium may increase the risk of developing Ebstein's anomaly, Ebstein's cardiac anomaly in infants born to women who take lithium during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Precautions
Lithium metal is corrosive and requires special handling to avoid skin contact. Breathing lithium dust or lithium compounds (which are often alkaline) initially irritation, irritate the human nose, nose and throat, while higher exposure can cause a buildup of fluid in the lungs, leading to pulmonary edema. The metal itself is a handling hazard because contact with moisture produces the Corrosive substance, caustic lithium hydroxide. Lithium is safely stored in non-reactive compounds such as naphtha.See also
* Cosmological lithium problem * Dilithium * Halo nucleus * Isotopes of lithium * List of countries by lithium production * Lithia water * Lithium–air battery * Lithium burning * :Lithium compounds, Lithium compounds (category) * Lithium-ion battery * Lithium Tokamak ExperimentNotes
References
External links
McKinsey review of 2018
(PDF)
at ''The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
International Lithium Alliance
(archived, August 2009)
USGS: Lithium Statistics and Information
Lithium Supply & Markets 2009 IM Conference 2009 Sustainable lithium supplies through 2020 in the face of sustainable market growth
University of Southampton, Mountbatten Centre for International Studies, Nuclear History Working Paper No5.
(PDF) (archived February 26 February 2008)
Lithium reserves by Country
at investingnews.com {{Authority control Lithium, Chemical elements Alkali metals Reducing agents Chemical elements with body-centered cubic structure