Leukoderma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vitiligo is a disorder that causes the skin to lose its color. Specific causes are unknown but studies suggest a link to immune system changes.
File:Vitiligo03.jpg, Vitiligo on lighter skin
File:Vitiligo1.JPG, Non-segmental vitiligo on dark skin, hand facing up
File:Eyelid vitiligo 06.jpg, Non-segmental vitiligo of the eyelids

 An
An
, by Rabbi Ken Spiro, Aish.com. Retrieved 2010-08-19.) described a group of skin diseases associated with white spots, and a subsequent translation to Greek led to continued conflation of those with vitiligo with
 The change in appearance caused by vitiligo can affect a person's emotional and psychological well-being and may create difficulty in becoming or remaining employed, particularly if vitiligo develops on visible areas of the body, such as the face, hands or arms. Participating in a vitiligo support group may improve social coping skills and emotional resilience.
Notable cases include US pop singer
The change in appearance caused by vitiligo can affect a person's emotional and psychological well-being and may create difficulty in becoming or remaining employed, particularly if vitiligo develops on visible areas of the body, such as the face, hands or arms. Participating in a vitiligo support group may improve social coping skills and emotional resilience.
Notable cases include US pop singer
Questions and Answers about Vitiligo
nbsp;– US National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases {{Authority control Autoimmune diseases Disturbances of human pigmentation Genetic disorders by system Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
Signs and symptoms
The only sign of vitiligo is the presence of pale patchy areas of depigmented skin which tend to occur on the extremities. Some people may experience itching before a new patch occurs. The patches are initially small, but often grow and change shape. When skinlesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by disease or trauma. ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin "injury". Lesions may occur in plants as well as animals.
Types
There is no designated classif ...
s occur, they are most prominent on the face, hands and wrists. The loss of skin pigmentation is particularly noticeable around body orifices, such as the mouth, eyes, nostril
A nostril (or naris , plural ''nares'' ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called t ...
s, genitalia
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, ...
and umbilicus. Some lesions have increased skin pigment around the edges. Those affected by vitiligo who are stigmatized
Social stigma is the disapproval of, or discrimination against, an individual or group based on perceived characteristics that serve to distinguish them from other members of a society. Social stigmas are commonly related to culture, gender, r ...
for their condition may experience depression and similar mood disorder
A mood disorder, also known as an affective disorder, is any of a group of conditions of mental and behavioral disorder where a disturbance in the person's mood is the main underlying feature. The classification is in the '' Diagnostic and Stati ...
s.
Causes
Although multiple hypotheses have been suggested as potential triggers that cause vitiligo, studies strongly imply that changes in theimmune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells and objects such ...
are responsible for the condition. Vitiligo has been proposed to be a multifactorial disease with genetic susceptibility and environmental factors both thought to play a role.
The National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U ...
states that some believe that sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that i ...
s can cause or exacerbate the condition, but that this idea is not well-supported by good evidence.
Immune
Melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amin ...
is the pigment that gives skin its color; it is produced by skin cells called melanocytes
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea),
the inner ear,
vaginal epithelium, meninges,
bones,
and heart.
...
.
Variations in genes that are part of the immune system or part of melanocytes have both been associated with vitiligo. It is also thought to be caused by the immune system attacking and destroying the melanocytes of the skin. A genome wide association study found approximately 36 independent susceptibility loci
Locus (plural loci) is Latin for "place". It may refer to:
Entertainment
* Locus (comics), a Marvel Comics mutant villainess, a member of the Mutant Liberation Front
* ''Locus'' (magazine), science fiction and fantasy magazine
** '' Locus Award ...
for generalized vitiligo.
The TYR gene encodes the protein tyrosinase
Tyrosinase is an oxidase that is the rate-limiting enzyme for controlling the production of melanin. The enzyme is mainly involved in two distinct reactions of melanin synthesis otherwise known as the Raper Mason pathway. Firstly, the hydroxyl ...
, which is not a component of the immune system, but is an enzyme of the melanocyte that catalyzes melanin biosynthesis, and a major autoantigen
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease". ...
in generalized vitiligo.
Autoimmune associations
Vitiligo is sometimes associated withautoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
and inflammatory disease
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
s such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over time, the thyroid may enlar ...
, scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas o ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and ...
, type 1 diabetes mellitus
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that originates when cells that make insulin (beta cells) are destroyed by the immune system. Insulin is a hormone required for the cells to use blood sugar for ...
, psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complet ...
, Addison's disease
Addison's disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare long-term endocrine disorder characterized by inadequate production of the steroid hormones cortisol and aldosterone by the two outer layers of the cells of the adrena ...
, pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia is a type of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, a disease in which not enough red blood cells are produced due to the malabsorption of vitamin B12. Malabsorption in pernicious anemia results from the lack or loss of intrinsic fac ...
, alopecia areata
Alopecia areata, also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. Often, it results in a few bald spots on the scalp, each about the size of a coin. Psychological stress and illness are po ...
, systemic lupus erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Comm ...
, and celiac disease
Coeliac disease ( British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and ba ...
.
Among the inflammatory products of NALP1 are caspase 1
Caspase-1/Interleukin-1 converting enzyme (ICE) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that proteolytically cleaves other proteins, such as the precursors of the inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β and interleukin 18 as well as the pyroptos ...
and caspase 7
Caspase-7, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase, also known as CASP7, is a human protein encoded by the ''CASP7'' gene.
''CASP7'' orthologs have been identified in nearly all mammals for which complete genome data are available. Unique orthologs ...
, which activate the inflammatory cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in a ...
interleukin-1β. Interleukin-1β and interleukin-18 are expressed at high levels in people with vitiligo. In one of the mutations, the amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
leucine in the NALP1 protein was replaced by histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the ...
(Leu155 → His). The original protein and sequence is highly conserved in evolution, and is found in humans, chimpanzee, rhesus monkey
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies that are split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally b ...
, and the bush baby. Addison's disease
Addison's disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare long-term endocrine disorder characterized by inadequate production of the steroid hormones cortisol and aldosterone by the two outer layers of the cells of the adrena ...
(typically an autoimmune destruction of the adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex w ...
s) may also be seen in individuals with vitiligo.
Diagnosis

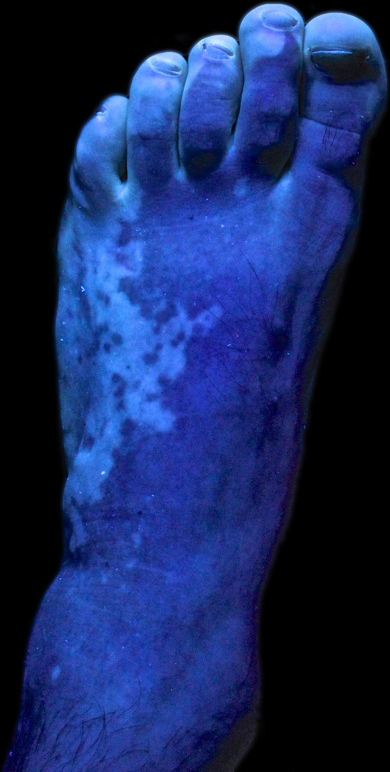
 An
An ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiati ...
can be used in the early phase of this disease for identification and to determine the effectiveness of treatment. Using a Wood's light, skin will change colour (fluoresce
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, tha ...
) when it is affected by certain bacteria, fungi, and changes to pigmentation of the skin.
Classification
Classification attempts to quantify vitiligo have been analyzed as being somewhat inconsistent, while recent consensus have agreed to a system of segmental vitiligo (SV) and non-segmental vitiligo (NSV). NSV is the most common type of vitiligo.Non-segmental
In non-segmental vitiligo (NSV), there is usually some form of symmetry in the location of the patches of depigmentation. New patches also appear over time and can be generalized over large portions of the body or localized to a particular area. Extreme cases of vitiligo, to the extent that little pigmented skin remains, are referred to as ''vitiligo universalis''. NSV can come about at any age (unlike segmental vitiligo, which is far more prevalent in teenage years). Classes of non-segmental vitiligo include the following: * Generalized vitiligo: the most common pattern, wide and randomly distributed areas of depigmentation * Universal vitiligo: depigmentation encompasses most of the body * Focal vitiligo: one or a few scattered macules in one area, most common in children * Acrofacial vitiligo: fingers and periorificial areas * Mucosal vitiligo: depigmentation of only the mucous membranesSegmental
Segmental vitiligo (SV) differs in appearance, cause, and frequency of associated illnesses. Its treatment is different from that of NSV. It tends to affect areas of skin that are associated withdorsal root
The dorsal root of spinal nerve (or posterior root of spinal nerve or sensory root) is one of two "roots" which emerge from the spinal cord. It emerges directly from the spinal cord, and travels to the dorsal root ganglion. Nerve fibres with the ve ...
s from the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spin ...
and is most often unilateral. It is much more stable/static in course and its association with autoimmune diseases appears to be weaker than that of generalized vitiligo. SV does not improve with topical therapies or UV light, however surgical treatments such as cellular grafting can be effective.
Differential diagnosis
Chemical leukoderma is a similar condition due to multiple exposures to chemicals. Vitiligo however is a risk factor. Triggers may include inflammatory skin conditions, burns, intralesional steroid injections and abrasions. Other conditions with similar symptoms include the following: *Albinism
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albino.
Varied use and interpretation of the term ...
* Halo nevus
Halo nevus (also known as "Leukoderma acquisitum centrifugum," "Perinevoid vitiligo," and "Sutton nevus") is a mole that is surrounded by a depigmented ring or 'halo'.
Presentation
Halo nevi are also known as Sutton's nevi, or leukoderma acquisi ...
* Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis is characterised by multiple small whitish flat spots. They are typically irregular, well defined and frequently appear on the arms, legs and face of older people.
It occurs in up to 80% of over 70-year olds. F ...
(white sunspots)
* Piebaldism
Piebaldism refers to the absence of mature melanin-forming cells (melanocytes) in certain areas of the skin and hair. It is a rare autosomal dominant disorder of melanocyte development.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews ...
* Pityriasis alba
Pityriasis alba is a skin condition, a type of dermatitis, commonly seen in children and young adults as dry, fine-scaled, pale patches on the face. It is self-limiting and usually only requires use of moisturizer creams.
The condition is so name ...
* Postinflammatory hypopigmentation
* Primary adrenal insufficiency
Addison's disease, also known as primary adrenal insufficiency, is a rare long-term endocrine disorder characterized by inadequate production of the steroid hormones cortisol and aldosterone by the two outer layers of the cells of the adrenal ...
* Progressive macular hypomelanosis
Progressive macular hypomelanosis is a common skin condition, a disorder, observed more frequently in young women with darkly pigmented skin who originate from or reside in tropical climates.
An interesting property of the skin condition is that i ...
* Tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor (also pityriasis versicolor) is a condition characterized by a skin eruption on the trunk and proximal extremities. The majority of tinea versicolor is caused by the fungus ''Malassezia globosa'', although ''Malassezia furfur'' is ...
* Tuberculoid leprosy
Treatment
There is no cure for vitiligo but several treatment options are available. The best evidence is for appliedsteroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and ...
s and the combination of ultraviolet light
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiati ...
in combination with creams. Due to the higher risks of skin cancer, the United Kingdom's National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
suggests phototherapy be used only if primary treatments are ineffective. Lesions located on the hands, feet, and joints are the most difficult to repigment; those on the face are easiest to return to the natural skin color as the skin is thinner in nature.
Immune mediators
Topical preparations of immune suppressing medications includingglucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every verte ...
(such as 0.05% clobetasol or 0.10% betamethasone) and calcineurin inhibitor
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system.
Classification
Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified int ...
s (such as tacrolimus
Tacrolimus, sold under the brand name Prograf among others, is an immunosuppressive drug. After allogeneic organ transplant, the risk of organ rejection is moderate. To lower the risk of organ rejection, tacrolimus is given. The drug can als ...
or pimecrolimus
Pimecrolimus is an immunomodulating agent of the calcineurin inhibitor class used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema). It is available as a topical cream, once marketed by Novartis (however, Galderma has been promoting the compound in ...
) are considered to be first-line vitiligo treatments.
In July 2022, ruxolitinib
Ruxolitinib, sold under the brand names Jakafi and Jakavi, is a medication used for the treatment of intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis, a type of myeloproliferative disorder that affects the bone marrow; polycythemia vera (PCV), when ther ...
cream (sold under the brand name Opzelura) was approved for medical use in the United States for the treatment of vitiligo.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy is considered a second-line treatment for vitiligo. Exposing the skin to light from UVB lamps is the most common treatment for vitiligo. The treatments can be done at home with an UVB lamp or in a clinic. The exposure time is managed so that the skin does not suffer overexposure. Treatment can take a few weeks if the spots are on the neck and face and if they existed not more than 3 years. If the spots are on the hands and legs and have been there for more than 3 years, it can take a few months. Phototherapy sessions are done 2–3 times a week. Spots on a large area of the body may require full body treatment in a clinic or hospital. UVB broadband and narrowband lamps can be used, but narrowband ultraviolet peaked around 311 nm is the choice. It has been constitutively reported that a combination of UVB phototherapy with other topical treatments improves re-pigmentation. However, some people with vitiligo may not see any changes to skin or re-pigmentation occurring. A serious potential side effect involves the risk of developing skin cancer, the same risk as an overexposure to natural sunlight. Ultraviolet light ( UVA) treatments are normally carried out in a hospital clinic.Psoralen
Psoralen (also called psoralene) is the parent compound in a family of naturally occurring organic compounds known as the linear furanocoumarins. It is structurally related to coumarin by the addition of a fused furan ring, and may be considered ...
and ultraviolet A light (PUVA
PUVA ( psoralen and UVA) is an ultraviolet light therapy treatment for skin diseases: eczema, psoriasis, graft-versus-host disease, vitiligo, mycosis fungoides, large plaque parapsoriasis, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, using the sensitizin ...
) treatment involves taking a drug that increases the skin's sensitivity to ultraviolet light, then exposing the skin to high doses of UVA light. Treatment is required twice a week for 6–12 months or longer. Because of the high doses of UVA and psoralen, PUVA may cause side effects such as sunburn-type reactions or skin freckling.
Narrowband ultraviolet B (NBUVB) phototherapy lacks the side-effects caused by psoralens and is as effective as PUVA. As with PUVA, treatment is carried out twice weekly in a clinic or every day at home, and there is no need to use psoralen. Longer treatment is often recommended, and at least 6 months may be required for effects to phototherapy. NBUVB phototherapy appears better than PUVA therapy with the most effective response on the face and neck.
With respect to improved repigmentation: topical calcineurin inhibitors plus phototherapy are better than phototherapy alone, hydrocortisone
Hydrocortisone is the name for the hormone cortisol when supplied as a medication. Uses include conditions such as adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenogenital syndrome, high blood calcium, thyroiditis, rheumatoid arthritis, dermatitis, a ...
plus laser light is better than laser light alone, gingko biloba
''Ginkgo biloba'', commonly known as ginkgo or gingko ( ), also known as the maidenhair tree, is a species of tree native to China. It is the last living species in the order Ginkgoales, which first appeared over 290 million years ago. Fossils ...
is better than placebo
A placebo ( ) is a substance or treatment which is designed to have no therapeutic value. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like Saline (medicine), saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
In general ...
, and oral mini-pulse of prednisolone
Prednisolone is a steroid medication used to treat certain types of allergies, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders, and cancers. Some of these conditions include adrenocortical insufficiency, high blood calcium, rheumatoid arthrit ...
(OMP) plus NB-UVB is better than OMP alone.
Skin camouflage
In mild cases, vitiligo patches can be hidden with makeup or other cosmetic camouflage solutions. If the affected person is pale-skinned, the patches can be made less visible by avoidingtanning
Tanning may refer to:
* Tanning (leather), treating animal skins to produce leather
* Sun tanning, using the sun to darken pale skin
** Indoor tanning, the use of artificial light in place of the sun
** Sunless tanning, application of a stain or d ...
of unaffected skin.
De-pigmenting
In cases of extensive vitiligo the option to de-pigment the unaffected skin with topical drugs likemonobenzone
Monobenzone, also called 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol and monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone (MBEH) is an organic chemical in the phenol family with chemical formula C6H5CH2OC6H4OH. It is used as a topical drug for medical depigmentation. It is a colourle ...
, mequinol, or hydroquinone
Hydroquinone, also known as benzene-1,4-diol or quinol, is an aromatic organic compound that is a type of phenol, a derivative of benzene, having the chemical formula C6H4(OH)2. It has two hydroxyl groups bonded to a benzene ring in a ''para'' ...
may be considered to render the skin an even color. The removal of all the skin pigment with monobenzone
Monobenzone, also called 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol and monobenzyl ether of hydroquinone (MBEH) is an organic chemical in the phenol family with chemical formula C6H5CH2OC6H4OH. It is used as a topical drug for medical depigmentation. It is a colourle ...
is permanent and vigorous. Sun-safety must be adhered to for life to avoid severe sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that i ...
and melanomas. Depigmentation takes about a year to complete.
History
Descriptions of a disease believed to be vitiligo date back to a passage in the medical text Ebers Papyrus in ancientEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
. Also, the Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
word "Tzaraath
''Tzaraath'' (Hebrew צָרַעַת ''ṣāraʿaṯ''), variously transcribed into English and frequently mistranslated as leprosy, describes various ritually unclean disfigurative conditions of the skin, hair of the beard and head, clothing ma ...
" from the Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
book of Leviticus dating to 1280 BC (or 1312 BCHistory Crash Course #36: Timeline: From Abraham to Destruction of the Temple, by Rabbi Ken Spiro, Aish.com. Retrieved 2010-08-19.) described a group of skin diseases associated with white spots, and a subsequent translation to Greek led to continued conflation of those with vitiligo with
leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria '' Mycobacterium leprae'' or '' Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve da ...
and spiritual uncleanliness.
Medical sources in the ancient world such as Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
often did not differentiate between vitiligo and leprosy, often grouping these diseases together. The name "vitiligo" was first used by the Roman physician Aulus Cornelius Celsus
Aulus Cornelius Celsus ( 25 BC 50 AD) was a Roman encyclopaedist, known for his extant medical work, '' De Medicina'', which is believed to be the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia. The ''De Medicina'' is a primary source o ...
in his classic medical text ''De Medicina
''De Medicina'' is a 1st-century medical treatise by Aulus Cornelius Celsus, a Roman encyclopedist and possibly (but not likely) a practicing physician. It is the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia; only small parts still survi ...
''.
The etymology of the term "vitiligo" is believed to be derived from "vitium", meaning "defect" or "blemish".
Society and culture
 The change in appearance caused by vitiligo can affect a person's emotional and psychological well-being and may create difficulty in becoming or remaining employed, particularly if vitiligo develops on visible areas of the body, such as the face, hands or arms. Participating in a vitiligo support group may improve social coping skills and emotional resilience.
Notable cases include US pop singer
The change in appearance caused by vitiligo can affect a person's emotional and psychological well-being and may create difficulty in becoming or remaining employed, particularly if vitiligo develops on visible areas of the body, such as the face, hands or arms. Participating in a vitiligo support group may improve social coping skills and emotional resilience.
Notable cases include US pop singer Michael Jackson
Michael Joseph Jackson (August 29, 1958 – June 25, 2009) was an American singer, songwriter, dancer, and philanthropist. Dubbed the "King of Pop", he is regarded as one of the most significant cultural figures of the 20th century. Over a ...
, Canadian fashion model Winnie Harlow
Chantelle Whitney Brown-Young (born July 27, 1994), known professionally as Winnie Harlow, is a Canadian fashion model and public spokesperson on the skin condition vitiligo. She gained prominence in 2014 as a contestant on the 21st cycle of th ...
, New Zealand singer-songwriter Kimbra
Kimbra Lee Johnson (born 27 March 1990), known mononymously as Kimbra, is a New Zealand singer and songwriter. Known for mixing pop with R&B, jazz and rock musical elements, her accolades include four ARIA Music Awards, two Grammy Awards and ...
, US actor David Dastmalchian
David Dastmalchian (; born July 21, 1975) is an American film and stage actor. He has had supporting roles in a number of superhero franchises; he portrayed Thomas Schiff in '' The Dark Knight'', Kurt in the first two Marvel Cinematic Universe ...
and Argentine musician Charly García
Charly García (born Carlos Alberto García, October 23, 1951) is an Argentine singer-songwriter, musician and record producer. He formed and headlined two of the most popular bands in Argentina's rock history: Sui Generis in the 1970s and ...
. French actor Michaël Youn
Michaël Benayoun (; born 1973), known professionally as Michaël Youn, is a French actor, singer, comedian and television personality.
Life and career
Youn was born Michaël Benayoun in Suresnes, France, to a family of Hungarian, Italian, ...
is also affected, as is former French Prime Minister Édouard Philippe
Édouard Charles Philippe (; born 28 November 1970) is a French politician serving as Mayor of Le Havre since 2020, previously holding the office from 2010 to 2017. He was Prime Minister of France from 15 May 2017 to 3 July 2020 under Presiden ...
, the TV host, model and former Miss Colombia 2007, Taliana Vargas
Research
,afamelanotide
Afamelanotide, sold under the brand name Scenesse, is a synthetic peptide and analogue of α-melanocyte stimulating hormone. It has been used to prevent skin damage from the sun in people with erythropoietic protoporphyria in the European U ...
is in phase II and III clinical trials for vitiligo and other skin diseases.
A medication for rheumatoid arthritis, tofacitinib
Tofacitinib, sold under the brand Xeljanz among others, is a medication used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ulcerative colitis.
Common side effects include diarrhea, headache, and high blood pressure. Serious side eff ...
, has been tested for the treatment of vitiligo.
In October 1992, a scientific report was published of successfully transplanting melanocyte
Melanocytes are melanin-producing neural crest-derived cells located in the bottom layer (the stratum basale) of the skin's epidermis, the middle layer of the eye (the uvea),
the inner ear,
vaginal epithelium, meninges,
bones,
and hear ...
s to vitiligo-affected areas, effectively re-pigmenting the region. The procedure involved taking a thin layer of pigmented skin from the person's gluteal region. Melanocytes were then separated out to a cellular suspension that was expanded in culture. The area to be treated was then denuded with a dermabrader and the melanocytes graft
Graft or grafting may refer to:
*Graft (politics), a form of political corruption
* Graft, Netherlands, a village in the municipality of Graft-De Rijp
Science and technology
*Graft (surgery), a surgical procedure
*Grafting, the joining of plant t ...
applied. Between 70 and 85 percent of people with vitiligo experienced nearly complete repigmentation of their skin. The longevity of the repigmentation differed from person to person.
References
External links
*Questions and Answers about Vitiligo
nbsp;– US National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases {{Authority control Autoimmune diseases Disturbances of human pigmentation Genetic disorders by system Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate