Lehman Caves on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Great Basin National Park is an American
Great Basin National Park is an American
 The oldest non clonal organism ever discovered, a
The oldest non clonal organism ever discovered, a
 The Bonneville cutthroat trout is the only fish native to Great Basin National Park. It arrived in the mountain waters naturally and was eventually isolated by changing climatic conditions. Other trout species, such as Lahontan cutthroat trout,
The Bonneville cutthroat trout is the only fish native to Great Basin National Park. It arrived in the mountain waters naturally and was eventually isolated by changing climatic conditions. Other trout species, such as Lahontan cutthroat trout,
 Many of the rocks formed during the
Many of the rocks formed during the  Both continuous and intermittent fault movements also occurred, with individual fault surfaces on both sides of the Snake Range thinning and stretching.
;Glaciation
Both continuous and intermittent fault movements also occurred, with individual fault surfaces on both sides of the Snake Range thinning and stretching.
;Glaciation
 The Lehman Caves were originally protected as a
The Lehman Caves were originally protected as a
 According to the
According to the
Park photo gallery
–
Johnson Lake Mine
– National Park Service *
Winchester Model 1873 Rifle Recovered in Great Basin National Park
– National Park Service, official press release {{authority control National parks in Nevada Natural history museums in Nevada Protected areas of White Pine County, Nevada Protected areas established in 1987 Great Basin National Heritage Area Cambrian volcanism Caves of Nevada Landforms of White Pine County, Nevada Museums in White Pine County, Nevada
 Great Basin National Park is an American
Great Basin National Park is an American national park
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
located in White Pine County in east-central Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
, near the Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its ...
border, established in 1986. The park is most commonly entered by way of Nevada State Route 488, which is connected to U.S. Routes 6 and 50 by Nevada State Route 487 via the small town of Baker
A baker is a tradesperson who bakes and sometimes sells breads and other products made of flour by using an oven or other concentrated heat source. The place where a baker works is called a bakery.
History
Ancient history
Since grains ...
, the closest settlement.
The park derives its name from the Great Basin, the dry and mountainous region between the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
and the Wasatch Mountains
The Wasatch Range ( ) or Wasatch Mountains is a mountain range in the western United States that runs about from the Utah-Idaho border south to central Utah. It is the western edge of the greater Rocky Mountains, and the eastern edge of the ...
. Topographically, this area is known as the Basin and Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternatin ...
. The park is located about north of Las Vegas
Las Vegas (; Spanish language, Spanish for "The Meadows"), often known simply as Vegas, is the List of United States cities by population, 25th-most populous city in the United States, the most populous city in the U.S. state, state of Neva ...
and protects .
The park is notable for its groves of ancient bristlecone pines
The term bristlecone pine covers three species of pine tree (family Pinaceae, genus '' Pinus'', subsection ''Balfourianae''). All three species are long-lived and highly resilient to harsh weather and bad soils. One of the three species, ''Pin ...
, the oldest known living non-clonal organisms; Lehman Caves; Wheeler Peak Glacier
Wheeler Peak Glacier is a glacier situated at the base of Wheeler Peak within Great Basin National Park in the U.S. state of Nevada. It is the only glacier in the state, and one of the southernmost glaciers in the United States. At a height o ...
, below Wheeler Peak; and some of the darkest night skies in the contiguous United States.
President Warren G. Harding created Lehman Caves National Monument by presidential proclamation on January 24, 1922. The monument and its surroundings was designated a national park on October 27, 1986, following the advocacy of Congressman Harry Reid
Harry Mason Reid Jr. (; December 2, 1939 – December 28, 2021) was an American lawyer and politician who served as a United States senator from Nevada from 1987 to 2017. He led the Senate Democratic Caucus from 2005 to 2017 and was the Sena ...
.
A number of developed campsites are within the park, as well as backcountry camping opportunities. The Highland Ridge Wilderness lies adjacent to Great Basin National Park. These two protected areas provide contiguous wildlife habitat and protection to of eastern Nevada's basin lands.
Natural history
Flora
Eleven species of conifer trees and over 800 species of plants are found in Great Basin National Park and the neighboring valleys. The area around the Visitor Center is dominated by plants such assagebrush
Sagebrush is the common name of several woody and herbaceous species of plants in the genus '' Artemisia''. The best known sagebrush is the shrub '' Artemisia tridentata''. Sagebrushes are native to the North American west.
Following is an al ...
, saltbush Saltbush is a vernacular plant name that most often refers to '' Atriplex'', a genus of about 250 plants distributed worldwide from subtropical to subarctic regions. ''Atriplex'' species are native to Australia, North and South America, and Eurasia. ...
, single-leaf pinyon
''Pinus monophylla'', the single-leaf pinyon, (alternatively spelled piñon) is a pine in the pinyon pine group, native to North America. The range is in southernmost Idaho, western Utah, Arizona, southwest New Mexico, Nevada, eastern and south ...
, and Utah juniper
''Juniperus osteosperma'' (Utah juniper; syn. ''J. utahensis'') is a shrub or small tree native to the southwestern United States.
Description
The plant reaches , rarely to 9 m, tall. The shoots are fairly thick compared to most junipers, i ...
. Higher elevations are home to mountain meadows, white fir
''Abies concolor'', the white fir, is a coniferous tree in the pine family Pinaceae. This tree is native to the mountains of western North America, including the Cascade Range and southern Rocky Mountains, and into the isolated mountain ranges ...
, quaking aspen
''Populus tremuloides'' is a deciduous tree native to cooler areas of North America, one of several species referred to by the common name aspen. It is commonly called quaking aspen, trembling aspen, American aspen, mountain or golden aspen, t ...
, Engelmann spruce
''Picea engelmannii'', with the common names Engelmann spruce, white spruce, mountain spruce, and silver spruce, is a species of spruce native to western North America. It is mostly a high-altitude mountain tree but also appears in watered canyon ...
, and large Ponderosa pine
''Pinus ponderosa'', commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is t ...
. At treeline is an alpine area of low, delicate plants and rocky outcroppings.
There are several endemic species of plants that are found in the park, some of which include Mt. Wheeler sandwort and Holgrem's buckwheat.
 The oldest non clonal organism ever discovered, a
The oldest non clonal organism ever discovered, a Great Basin bristlecone pine
''Pinus longaeva'' (commonly referred to as the Great Basin bristlecone pine, intermountain bristlecone pine, or western bristlecone pine) is a long-living species of bristlecone pine tree found in the higher mountains of California, Nevada, and ...
tree at least 5,000 years old, grew at the treeline near Wheeler Peak in the national park. It was cut down in 1964 by a graduate student and U.S. Forest Service personnel for research purposes. It was given the nickname Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titan god of fire. Prometheus is best known for defying the gods by stealing fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technology, know ...
, after the mythological figure who stole fire from the gods and gave it to man.
Fauna
Sixty-one species of mammals, 18 species of reptiles, 238 species of birds, two species of amphibians, and eight species of fish are in Great Basin National Park and the neighboring valleys. ;Mammals An abundance of wildlife has taken advantage of the habitat zones in Great Basin National Park.Jackrabbit
Hares and jackrabbits are mammals belonging to the genus ''Lepus''. They are herbivores, and live solitarily or in pairs. They nest in slight depressions called forms, and their young are able to fend for themselves shortly after birth. The gen ...
s, pygmy rabbits, mountain cottontails, ground squirrel
Ground squirrels are members of the squirrel family of rodents (Sciuridae), which generally live on or in the ground, rather than trees. The term is most often used for the medium-sized ground squirrels, as the larger ones are more commonly known ...
s, chipmunk
Chipmunks are small, striped rodents of the family Sciuridae. Chipmunks are found in North America, with the exception of the Siberian chipmunk which is found primarily in Asia.
Taxonomy and systematics
Chipmunks may be classified either as ...
s, and various mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
live in the low-elevation sagebrush desert. Pronghorn
The pronghorn (, ) (''Antilocapra americana'') is a species of artiodactyl (even-toed, hoofed) mammal indigenous to interior western and central North America. Though not an antelope, it is known colloquially in North America as the American ant ...
s, coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecological ni ...
s, kit foxes, and badger
Badgers are short-legged omnivores in the family Mustelidae (which also includes the otters, wolverines, martens, minks, polecats, weasels, and ferrets). Badgers are a polyphyletic rather than a natural taxonomic grouping, being united ...
s are less common inhabitants.
In the more rugged areas on the slopes of mountains and in the valley areas nearby, cougar
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') is a large cat native to the Americas. Its range spans from the Canadian Yukon to the southern Andes in South America and is the most widespread of any large wild terrestrial mammal in the Western Hemisphere. I ...
s, bobcat
The bobcat (''Lynx rufus''), also known as the red lynx, is a medium-sized cat native to North America. It ranges from southern Canada through most of the contiguous United States to Oaxaca in Mexico. It is listed as Least Concern on the IU ...
s, marmot
Marmots are large ground squirrels in the genus ''Marmota'', with 15 species living in Asia, Europe, and North America. These herbivores are active during the summer, when they can often be found in groups, but are not seen during the winter, w ...
s, rock squirrel
The rock squirrel (''Otospermophilus variegatus'') is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae and is native to Mexico and the Southwestern United States, including southern Nevada, Utah, Colorado, Arizona, New Mexico, West Texas, and the panh ...
s, and bighorn sheep
The bighorn sheep (''Ovis canadensis'') is a species of sheep native to North America. It is named for its large horns. A pair of horns might weigh up to ; the sheep typically weigh up to . Recent genetic testing indicates three distinct subspe ...
can occasionally be seen throughout this park. Other animals that can be found here include elk, mule deer
The mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') is a deer indigenous to western North America; it is named for its ears, which are large like those of the mule. Two subspecies of mule deer are grouped into the black-tailed deer.
Unlike the related whit ...
, spotted skunks, shrew
Shrews (family Soricidae) are small mole-like mammals classified in the order Eulipotyphla. True shrews are not to be confused with treeshrews, otter shrews, elephant shrews, West Indies shrews, or marsupial shrews, which belong to diffe ...
s, ringtail cat
The ringtail (''Bassariscus astutus'') is a mammal of the raccoon family native to arid regions of North America. It is widely distributed and well adapted to disturbed areas. It has been legally trapped for its fur. It is listed as Least Conc ...
s, and ermine.
;Fish
 The Bonneville cutthroat trout is the only fish native to Great Basin National Park. It arrived in the mountain waters naturally and was eventually isolated by changing climatic conditions. Other trout species, such as Lahontan cutthroat trout,
The Bonneville cutthroat trout is the only fish native to Great Basin National Park. It arrived in the mountain waters naturally and was eventually isolated by changing climatic conditions. Other trout species, such as Lahontan cutthroat trout, rainbow
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection, refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. Rainbows ...
, brook
A brook is a small river or natural stream of fresh water. It may also refer to:
Computing
*Brook, a programming language for GPU programming based on C
*Brook+, an explicit data-parallel C compiler
* BrookGPU, a framework for GPGPU programm ...
, and brown trout
The brown trout (''Salmo trutta'') is a European species of salmonid fish that has been widely introduced into suitable environments globally. It includes purely freshwater populations, referred to as the riverine ecotype, ''Salmo trutta'' morp ...
, were stocked in the lakes and streams of the South Snake Range until the park's incorporation in 1986.
;Birds
Many species of birds can be found in Great Basin National Park, including Canada geese
The Canada goose (''Branta canadensis''), or Canadian goose, is a large wild goose with a black head and neck, white cheeks, white under its chin, and a brown body. It is native to the arctic and temperate regions of North America, and it is ...
, hawk
Hawks are birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are widely distributed and are found on all continents except Antarctica.
* The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks and others. This subfa ...
s, sparrow
Sparrow may refer to:
Birds
* Old World sparrows, family Passeridae
* New World sparrows, family Passerellidae
* two species in the Passerine family Estrildidae:
** Java sparrow
** Timor sparrow
* Hedge sparrow, also known as the dunnock or hedg ...
s, bald eagle
The bald eagle (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus'') is a bird of prey found in North America. A sea eagle, it has two known subspecies and forms a species pair with the white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), which occupies the same nich ...
s, tundra swan
The tundra swan (''Cygnus columbianus'') is a small swan of the Holarctic. The two taxa within it are usually regarded as conspecific, but are also sometimes split into two species: Bewick's swan (''Cygnus bewickii'') of the Palaearctic and the w ...
s, barn owl
The barn owl (''Tyto alba'') is the most widely distributed species of owl in the world and one of the most widespread of all species of birds, being found almost everywhere except for the polar and desert regions, Asia north of the Himala ...
s, snow geese, killdeer
The killdeer (''Charadrius vociferus'') is a large plover found in the Americas. It was described and given its current scientific name in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus in the 10th edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. Three subspecies are described. Th ...
, golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds ...
s, woodpecker
Woodpeckers are part of the bird family Picidae, which also includes the piculets, wrynecks, and sapsuckers. Members of this family are found worldwide, except for Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, Madagascar, and the extreme polar region ...
s, mallard
The mallard () or wild duck (''Anas platyrhynchos'') is a dabbling duck that breeds throughout the temperate and subtropical Americas, Eurasia, and North Africa, and has been introduced to New Zealand, Australia, Peru, Brazil, Uruguay, Arge ...
s, wren
Wrens are a family of brown passerine birds in the predominantly New World family Troglodytidae. The family includes 88 species divided into 19 genera. Only the Eurasian wren occurs in the Old World, where, in Anglophone regions, it is commonl ...
s, greater roadrunner
The greater roadrunner (''Geococcyx californianus'') is a long-legged bird in the cuckoo family, Cuculidae, from the Aridoamerica region in the Southwestern United States and Mexico. The scientific name means "Californian earth-cuckoo". Along ...
s, chickadee
The chickadees are a group of North American birds in the tit family included in the genus '' Poecile''. Species found in North America are referred to as chickadees, while other species in the genus are called tits.
They are small-sized bird ...
s, great horned owl
The great horned owl (''Bubo virginianus''), also known as the tiger owl (originally derived from early naturalists' description as the "winged tiger" or "tiger of the air"), or the hoot owl, is a large owl native to the Americas. It is an extr ...
s, raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigned ...
s, magpie
Magpies are birds of the Corvidae family. Like other members of their family, they are widely considered to be intelligent creatures. The Eurasian magpie, for instance, is thought to rank among the world's most intelligent creatures, and is on ...
s, and swallow
The swallows, martins, and saw-wings, or Hirundinidae, are a family of passerine songbirds found around the world on all continents, including occasionally in Antarctica. Highly adapted to aerial feeding, they have a distinctive appearance. The ...
s.
;Amphibians
Only two species of amphibians have been positively identified in the southern Snake Range
The Snake Range is a mountain range in White Pine County, Nevada, United States. The south-central portion of the range is included within Great Basin National Park, with most of the remainder included within the Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forest ...
and adjacent portions of Snake
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more j ...
and Spring Valleys: the western spadefoot toad ''(Spea hammondii)'' and the leopard frog
Leopard frog is a generic name used to refer to various species in the true frog genus Lithobates. They all have similar coloration: brown or green with spots that form a leopard pattern. They are distinguished by their distribution and behaviora ...
''(Rana pipiens)''.
Geology
 Many of the rocks formed during the
Many of the rocks formed during the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ag ...
, when the region lay at the edge of a continental landmass called Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
. These rocks include the Cambrian strata. As the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
era progressed, several intensified geologic events occurred, including repeated episodes of faulting
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectoni ...
, and in turn, orogenies which involved upward lifting of a metamorphic core complex, creating mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks includ ...
and rhyolitic
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained ( aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals ( phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The miner ...
dikes and sills.
Extensive volcanism also occurred during the middle to late Cambrian, contributing further to the uplift of the area. This also contributed to a second round of block faulting, in which conglomerates, ash flows, and tuffs accumulated in the Snake Range.National Park Service, "Great Basin Geology". Web. http://www.nps.gov/grba/planyourvisit/upload/geology.pdfHarris, Ann G., et al. Geology of National Parks, Kendall/Hunt: Iowa, 2005. Print. 663-673.
 Both continuous and intermittent fault movements also occurred, with individual fault surfaces on both sides of the Snake Range thinning and stretching.
;Glaciation
Both continuous and intermittent fault movements also occurred, with individual fault surfaces on both sides of the Snake Range thinning and stretching.
;Glaciation
Glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate bet ...
, mostly during a series of ice ages in the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the '' Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed ...
, heavily eroded the peaks of the Snake Range, leaving canyon walls, U-shaped valleys, cirques
A (; from the Latin word ') is an amphitheatre-like valley formed by glacial erosion. Alternative names for this landform are corrie (from Scottish Gaelic , meaning a pot or cauldron) and (; ). A cirque may also be a similarly shaped landf ...
, and moraines
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice she ...
throughout the range.
;Lehman Caves
The Lehman Cave system began forming around 550 million years ago (during the Cambrian), while it was still submerged in a relatively warm, shallow ocean. The caves are made up of a marble and limestone solution, for the most part, that forms the many cave decorations throughout the caverns.
The cave system became much deeper during the Pleistocene, when a prolonged and increased flow of water eroded through the cave's fracturing bedrock. Eventually, the water level dropped, leaving glare rooms and cavities in the rock, creating the depths of the Lehman Caves system.
Scenic features
The park's scenic features include Lexington Arch, the Lehman Orchard and Aqueduct, Rhodes Cabin, Stella andTeresa Lake
Teresa Lake is a glacial tarn in the Snake Range of White Pine County, Nevada, United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in No ...
s, and Wheeler Peak Glacier
Wheeler Peak Glacier is a glacier situated at the base of Wheeler Peak within Great Basin National Park in the U.S. state of Nevada. It is the only glacier in the state, and one of the southernmost glaciers in the United States. At a height o ...
.
Lehman Caves
 The Lehman Caves were originally protected as a
The Lehman Caves were originally protected as a national monument
A national monument is a monument constructed in order to commemorate something of importance to national heritage, such as a country's founding, independence, war, or the life and death of a historical figure.
The term may also refer to a sp ...
in 1922, which was combined with the national park in 1986.
The cave had been known to indigenous peoples long before the arrival of Europeans. In 1885, Absalom Lehman, a rancher in the area, began guiding tours into the cave. Visitors' inscriptions in the cave from the era before it became a National Monument note its use and popularity among recent settlers to the region.
Several species occupy the Lehman Caves. Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
are the most common. Crickets
Crickets are orthopteran insects which are related to bush crickets, and, more distantly, to grasshoppers. In older literature, such as Imms,Imms AD, rev. Richards OW & Davies RG (1970) ''A General Textbook of Entomology'' 9th Ed. Methuen 88 ...
, spiders
Spiders (order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight legs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and rank seventh in total species di ...
, pseudoscorpions
Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida.
Pseudoscorpions are generally beneficial to humans sin ...
, mites
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evi ...
, and springtails
Springtails (Collembola) form the largest of the three lineages of modern hexapods that are no longer considered insects (the other two are the Protura and Diplura). Although the three orders are sometimes grouped together in a class called Ento ...
may live their full lifecycles in the cave. They are dependent on organic material packed in by other animals or washed in from the surface.
Other animals use the cave, but must leave to forage for food. These include chipmunk
Chipmunks are small, striped rodents of the family Sciuridae. Chipmunks are found in North America, with the exception of the Siberian chipmunk which is found primarily in Asia.
Taxonomy and systematics
Chipmunks may be classified either as ...
s, mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
, pack rat
A pack rat or packrat, also called a woodrat or trade rat, are any species in the North and Central American rodent genus ''Neotoma''. Pack rats have a rat-like appearance, with long tails, large ears, and large, black eyes. Pack rats are notice ...
s, and several species of bats. Only insectivorous
A robber fly eating a hoverfly
An insectivore is a carnivorous animal or plant that eats insects. An alternative term is entomophage, which can also refer to the human practice of eating insects.
The first vertebrate insectivores were ...
bats occur in the Great Basin. At least 10 species of bats have been found in the vicinity of Great Basin National Park, including the Townsend's big-eared bat
Townsend's big-eared bat (''Corynorhinus townsendii'') is a species of vesper bat.
Description
Townsend's big-eared bat is a medium-sized bat (7-12 g)
.
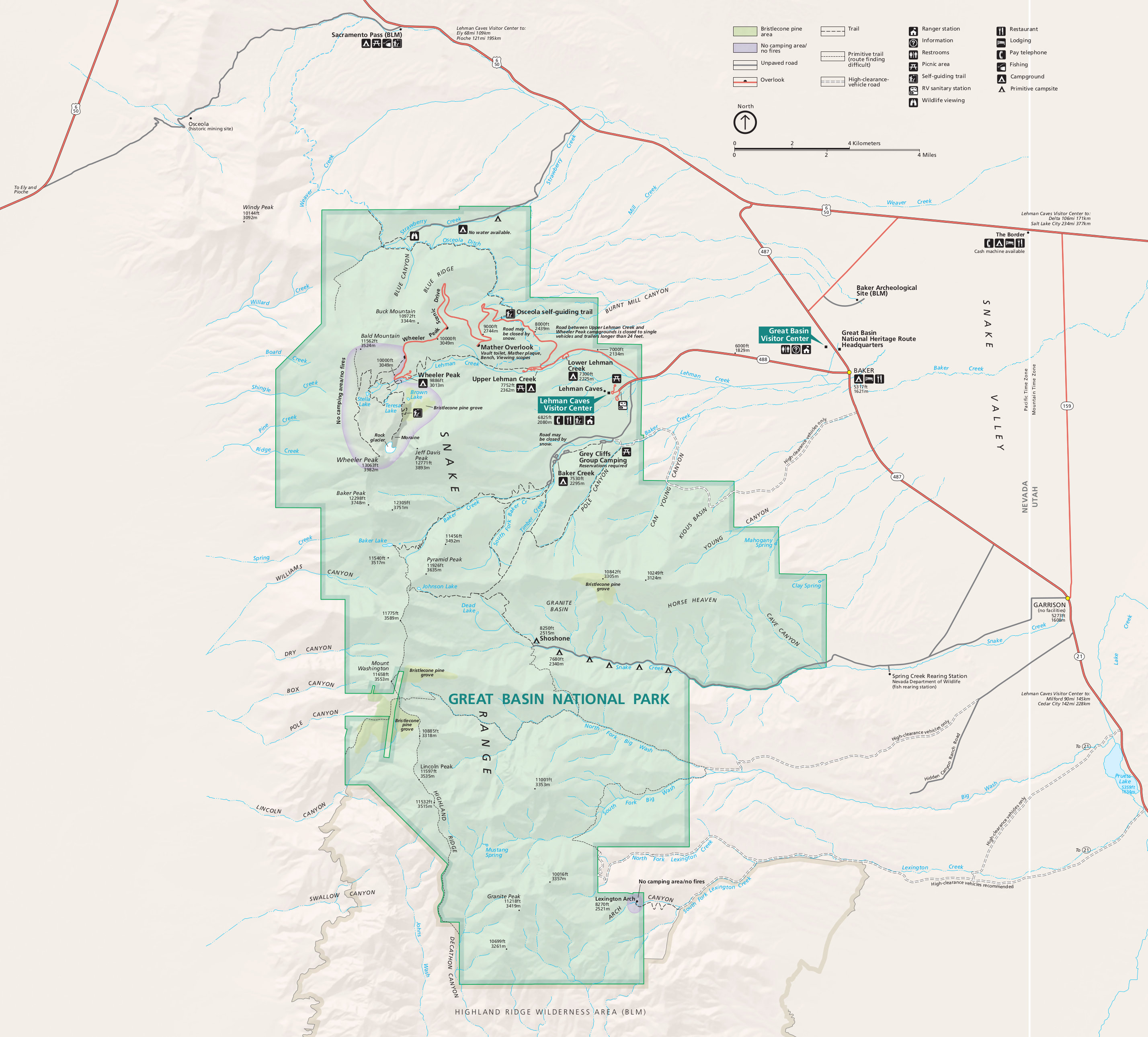
Trails
The park has 12 trails ranging from . Trails range from short nature trails at (Mountain View Nature Trail), to the Wheeler summit trail starting at . The Wheeler Summit trail is quite strenuous, and the altitude presents significant hazards for unprepared or inexperienced hikers. Backcountry routes are occasionally maintained throughout the more remote southern portion of the park. A number of these trailheads are accessible by the road that terminates at the primitive Shoshone campground.Visitor centers
The Great Basin visitor center is located on Nevada State Route 487 in the town of Baker. The Lehman Caves visitor center is located on Nevada State Route 488, about from Baker, inside the park boundary. The Forgotten Winchester, a rifle manufactured in 1882 that was found leaning against a juniper tree in the park in 2014, is on display inside the Great Basin visitor center. Both centers feature exhibits about the park's geology and natural and cultural history, as well as theaters with orientation films.Climate
 According to the
According to the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
system, Great Basin National Park has a warm-summer humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(''Dfb''). The plant hardiness zone at Lehman Caves Visitor Center is 6b with an average annual extreme minimum temperature of .
The park lies in an arid region and receives very little rainfall during most of the year. Most precipitation is winter snow or summer thunderstorms. All precipitation in this region evaporates, sinks underground, or flows into lakes — i.e., it is ''endorheic''. No water reaches the ocean.
Winters are cool and summers are mild to hot. Weather can change quickly, especially in the back country or on Wheeler Peak at high elevations.
Lehman Caves maintain a fairly constant temperature of with 90% humidity year round.
The climate varies throughout the park, depending on elevation and location. The following data are for the Lehman Caves Visitor Center only. Higher elevations are cooler and receive more precipitation, whereas lower elevations are hotter and drier.
See also
* Great Basin National Heritage Area * List of national parks of the United StatesReferences
External links
*Park photo gallery
–
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an List of federal agencies in the United States, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government within the United States Department of the Interior, U.S. Department of ...
on Flickr
Flickr ( ; ) is an American image hosting and video hosting service, as well as an online community, founded in Canada and headquartered in the United States. It was created by Ludicorp in 2004 and was a popular way for amateur and professiona ...
Johnson Lake Mine
– National Park Service *
Winchester Model 1873 Rifle Recovered in Great Basin National Park
– National Park Service, official press release {{authority control National parks in Nevada Natural history museums in Nevada Protected areas of White Pine County, Nevada Protected areas established in 1987 Great Basin National Heritage Area Cambrian volcanism Caves of Nevada Landforms of White Pine County, Nevada Museums in White Pine County, Nevada