|
Single-leaf Pinyon
''Pinus monophylla'', the single-leaf pinyon, (alternatively spelled piñon) is a pine in the pinyon pine group, native to North America. The range is in southernmost Idaho, western Utah, Arizona, southwest New Mexico, Nevada, eastern and southern California and northern Baja California. It occurs at moderate altitudes from , rarely as low as and as high as . It is widespread and often abundant in this region, forming extensive open woodlands, often mixed with junipers in the Pinyon-juniper woodland plant community. Single-leaf pinyon is the world's only one-needled pine.Gerry Moore et al. 2008 Description ''Pinus monophylla'' is a small to medium size tree, reaching tall and with a trunk diameter of up to rarely more. The bark is irregularly furrowed and scaly. The leaves ('needles') are, uniquely for a pine, usually single (not two or more in a fascicle, though trees with needles in pairs are found occasionally), stout, long, and grey-green to strongly glaucous blue-green, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Torrey
John Torrey (August 15, 1796 – March 10, 1873) was an American botany, botanist, chemist, and physician. Throughout much of his career, he was a teacher of chemistry, often at multiple universities, while he also pursued botanical work, focusing on the flora of North America. His most renowned works include studies of the New York flora, the Mexican Boundary, the Pacific railroad surveys, and the uncompleted ''Flora of North America''. Biography Torrey was born in New York City in 1796, the second child of Capt. William and Margaret (née Nichols) Torrey.Robbins, C. C. (1968). John Torrey (1796–1873), His Life & Times. ''Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club''. Vol. 95, No. Nov. 6–Dec. 1968, 515–645. Torrey Botanical Club, New York. He showed a fondness for mechanics, and at one time planned to become a machinist. When he was 15 or 16, his father received an appointment to the state prison at Greenwich Village, New York, where he was tutored by Amos Eaton, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomata
In botany, a stoma (: stomata, from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth"), also called a stomate (: stomates), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange between the internal air spaces of the leaf and the atmosphere. The pore is bordered by a pair of specialized parenchyma cells known as guard cells that regulate the size of the stomatal opening. The term is usually used collectively to refer to the entire stomatal complex, consisting of the paired guard cells and the pore itself, which is referred to as the stomatal aperture. Air, containing oxygen, which is used in respiration, and carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis, passes through stomata by gaseous diffusion. Water vapour diffuses through the stomata into the atmosphere as part of a process called transpiration. Stomata are present in the sporophyte generation of the vast majority of land plants, with the exception of liverworts, as well as so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid (biology)
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different varieties, subspecies, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Generally, it means that each cell has genetic material from two different organisms, whereas an individual where some cells are derived from a different organism is called a chimera. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents such as in blending inheritance (a now discredited theory in modern genetics by particulate inheritance), but can show hybrid vigor, sometimes growing larger or taller than either parent. The concept of a hybrid is interpreted differently in animal and plant breeding, where there is interest in the individual parentage. In genetics, attention is focused on the numbers of chromosomes. In taxonomy, a key question is how closely related the parent species are. Species are reproductively isolated by strong barriers to hybridization, which include genetic and morph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado Pinyon
''Pinus edulis'', the Colorado pinyon, two-needle piñon, pinyon pine, or simply piñon, is a pine in the pinyon pine group native to the Southwestern United States, used for its edible pine nuts. Description The piñon pine (''Pinus edulis'') is a small to medium size tree, reaching tall and with a trunk diameter of up to , rarely more. Its growth is "at an almost inconceivably slow rate" growing only 1.8 meters (6 ft) in one hundred years under good conditions. for an average growth of 18 millimeters (0.72 in) per year. The bark is irregularly furrowed and scaly. The leaves ('needles') are in pairs, moderately stout, long, and green, with stomata on both inner and outer surfaces but distinctly more on the inner surface forming a whitish band. The cones are globose, long and broad when closed, green at first, ripening yellow-buff when 18–20 months old, with only a small number of thick scales, with typically 5–10 fertile scales. The cones open to broad when mature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver City, New Mexico
Silver City is a town in Grant County, New Mexico, United States. It is the county seat and the home of Western New Mexico University. As of the 2010 census the population was 10,315. As of the 2020 census, the population was 9,704. History The valley that is now the site of Silver City once served as an Apache campsite. With the arrival of the Spaniards, the area became known for its copper mining. The Apaches occupied areas in the vicinity of Silver City beginning in the late 1500s to early 1600s, based on archaeological evidence. Founding of town After the American Civil War, a settlement developed and became known as "La Ciénega de San Vicente" (the Oasis of St. Vincent). With a wave of American prospectors, the pace of change increased, and Silver City was founded in the summer of 1870. The founding of the town occurred shortly after the discovery of silver ore deposits at Chloride Flat, on the hill just west of the farm of Captain John M. Bullard and his brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mogollon Rim
The Mogollon Rim ( or or ) is a topography, topographical and geological feature cutting across Northern Arizona, the northern half of the U.S. state of Arizona. It extends approximately , starting in northern Yavapai County, Arizona, Yavapai County and running eastward, ending near the border with New Mexico.The Mogollon Rim is not to be confused with the Mogollon Mountains in New Mexico located somewhat east of the eastern end of the Rim. The official estimate of the eastern end is near Show Low, AZ, Show Low, although some sources extend it farther east. See It forms the southern edge of the Colorado Plateau in Arizona. Description The Rim is an escarpment defining the southwestern edge of the Colorado Plateau. Its central and most spectacular portions are characterized by high cliffs of limestone and sandstone, namely the Kaibab Limestone and Coconino Sandstone cliffs. The escarpment was created by erosion and geologic fault, faulting, creating canyons such as Fossil Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hualapai Mountains
The Hualapai Mountains are a mountain range located in Mohave County, Arizona, Mohave County, east of Kingman, Arizona, Kingman, Arizona. Rising up to 8,417 feet at its highest peak, the higher elevations of the Hualapai Mountains support Madrean Sky Islands, Madrean Sky Island habitats, and are host to a plethora of unique flora and fauna in a wide range of microclimates, high above the surrounding Mojave Desert. Etymology Pronounced: "wah-lah-pie" Meaning of "Hualapai" in Hualapai language: "People of the tall Pines". English spelling: Walapai Spanish spelling: Hualapai Most used spelling: Hualapai, though both are acceptable Other names for Hualapai Mountain: Mojave language: ''Amat 'Avii Kahuwaaly'' Geography The Hualapai Mountain range is located in the central portion of the Basin and Range Province of the southwestern United States, and along the western-most extension of the Arizona transition zone, Arizona Transition Zone (or "Central Highlands" of Arizona). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado River (U
The Colorado River () is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and in northern Mexico. The river, the 5th longest in the United States, drains an expansive, arid watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. states and two Mexican states. The name Colorado derives from the Spanish language for "colored reddish" due to its heavy silt load. Starting in the central Rocky Mountains of Colorado, it flows generally southwest across the Colorado Plateau and through the Grand Canyon before reaching Lake Mead on the Arizona–Nevada border, where it turns south toward the international border. After entering Mexico, the Colorado approaches the mostly dry Colorado River Delta at the tip of the Gulf of California between Baja California and Sonora. Known for its dramatic canyons, whitewater rapids, and eleven U.S. National Parks, the Colorado River and its tributaries are a vital source of water for 40 million people. An extensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Jacinto Mountains
The San Jacinto Mountains ()Munro, P., et al. ''A Mojave Dictionary''. Los Angeles: UCLA. 1992. are a mountain range in Riverside County, California, Riverside County, located east of Los Angeles, California, Los Angeles in southern California in the United States. The mountains are named for one of the first Dominican Order, Black Friars, Hyacinth of Poland, Saint Hyacinth (), who is a popular patron in Latin America. Geography The range extends for approximately from the San Bernardino Mountains southeast to the Santa Rosa Mountains (California), Santa Rosa Mountains. The San Jacinto Mountains are the northernmost of the Peninsular Ranges, which run from Southern California to the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula. The highest peak in the range is San Jacinto Peak (3,302 m; 10,834 ft), and the range is also a Great Basin Divide landform for the Salton Sea, Salton Watershed to the east. The hills east of Live Oak Canyon Road, in San Bernardino County, are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyon Jay
The pinyon jay (''Gymnorhinus cyanocephalus'') is a species of jay, and is the only member of the genus ''Gymnorhinus''. Native to Western North America, the species ranges from central Oregon to northern Baja California, and eastward as far as western Oklahoma, though wanderers are often sighted beyond this range. It is typically found within foothills, especially where pinyon pines ('' Pinus edulis'' and '' Pinus monophylla'') occur. Description The pinyon jay is a bluish-grey coloured bird with deeper head colouring and whitish throat with black bill, legs and feet. Roughly intermediate between the blue jay and the Eurasian jay in size, its overall proportions are similar to Clark's nutcracker (''Nucifraga columbiana'') and this can be seen as convergent evolution, as both birds fill similar ecological niches. They were once known as "blue crows". Taxonomy The pinyon jay was first collected, recorded, and first described as a species from a specimen shot along the Maria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
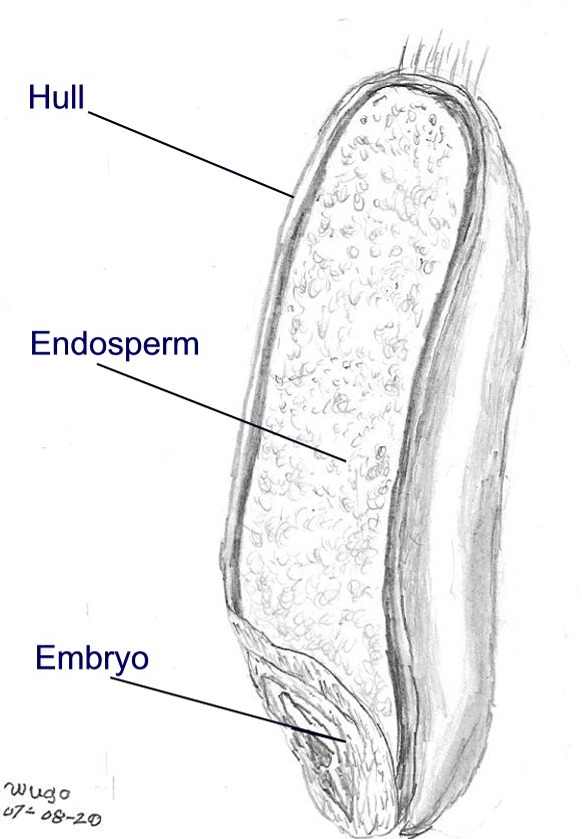
Endosperm
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seeds of most of the flowering plants following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the Embryo#Plant embryos, embryo and provides nutrition in the form of starch, though it can also contain Vegetable oil, oils and protein. This can make endosperm a source of nutrition in animal diet. For example, wheat endosperm is ground into flour for bread (the rest of the grain is included as well in whole wheat flour), while barley endosperm is the main source of sugars for beer production. Other examples of endosperm that forms the bulk of the edible portion are coconut "meat" and coconut "water", and Maize, corn. Some plants, such as certain orchids, lack endosperm in their seeds. Ancestral flowering plants have seeds with small embryos and abundant endosperm. In some modern flowering plants the embryo occupies most of the seed and the endosperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after the embryo sac is fertilization, fertilized by Pollen, sperm from pollen, forming a zygote. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted. The formation of the seed is the defining part of the process of reproduction in seed plants (spermatophytes). Other plants such as ferns, mosses and marchantiophyta, liverworts, do not have seeds and use water-dependent means to propagate themselves. Seed plants now dominate biological Ecological niche, niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates. In the flowering plants, the ovary ripens into a fruit which contains the seed and serves to disseminate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |