Endosperm on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
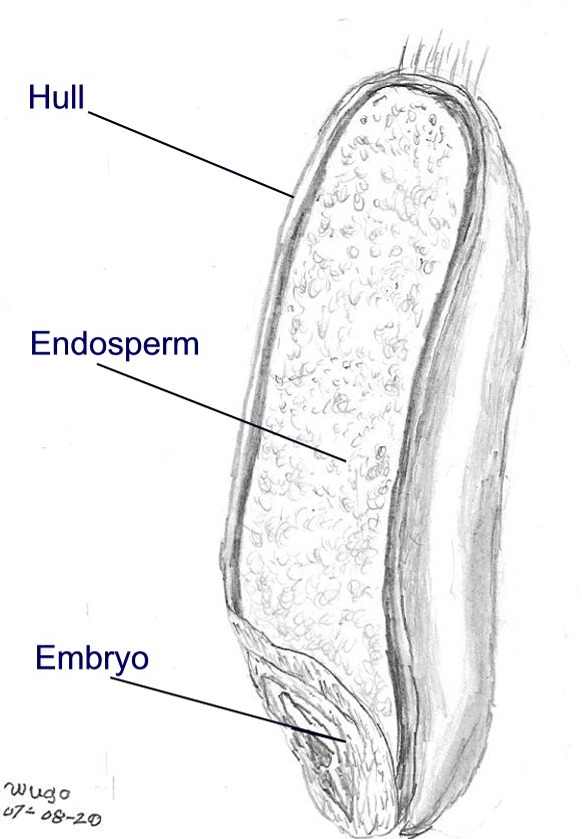 The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the
Endosperm: the pivot of the sexual conflict in flowering plants
at Earthling Nature {{Authority control Plant morphology Plant physiology
 The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the
The endosperm is a tissue produced inside the seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
s of most of the flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s following double fertilization. It is triploid (meaning three chromosome sets per nucleus) in most species, which may be auxin-driven. It surrounds the embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
and provides nutrition in the form of starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
, though it can also contain oils and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
. This can make endosperm a source of nutrition in animal diet. For example, wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
endosperm is ground into flour for bread
Bread is a baked food product made from water, flour, and often yeast. It is a staple food across the world, particularly in Europe and the Middle East. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cu ...
(the rest of the grain is included as well in whole wheat flour), while barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
endosperm is the main source of sugars for beer
Beer is an alcoholic beverage produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches from cereal grain—most commonly malted barley, although wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. The grain is mashed to convert starch in the ...
production. Other examples of endosperm that forms the bulk of the edible portion are coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
"meat" and coconut "water", and corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
. Some plants, such as certain orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Eart ...
s, lack endosperm in their seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
s.
Ancestral flowering plants have seeds with small embryos and abundant endosperm. In some modern flowering plants the embryo occupies most of the seed and the endosperm is non-developed or consumed before the seed matures. In other flowering plant taxa, the Poaceae
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivate ...
for example, the endosperm is greatly developed.
Double fertilization
An endosperm is formed after the twosperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
nuclei inside a pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
grain reach the interior of a female gametophyte or megagametophyte, also called the embryonic sac. One sperm nucleus fertilizes the egg cell
The egg cell or ovum (: ova) is the female Reproduction, reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female game ...
, forming a zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
, while the other sperm nucleus usually fuses with the binucleate central cell, forming a primary endosperm cell (its nucleus is often called the ''triple fusion nucleus''). That cell created in the process of double fertilization develops into the endosperm. Because it is formed by a separate fertilization event, the endosperm is a separate entity from the developing embryo, and some consider it to be a separate organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
.
About 70% of angiosperm species have endosperm cells that are polyploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the biological cell, cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of (Homologous chromosome, homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have Cell nucleus, nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning ...
. These are typically triploid (containing three sets of chromosomes), but can vary widely from diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
(2n) to 15n.
One flowering plant, '' Nuphar polysepala'', has diploid endosperm, resulting from the fusion of a pollen nucleus with one, rather than two, maternal nuclei. The same is supposed for some other basal angiosperms. It is believed that early in the development of angiosperm lineages, there was a duplication in this mode of reproduction, producing seven-celled/eight-nucleate female gametophytes, and triploid endosperms with a 2:1 maternal to paternal genome ratio.
Double fertilisation is a characteristic feature of angiosperms.
Endosperm development
There are three types of endosperm development: Nuclear endosperm development – where repeated free-nuclear divisions take place; if a cell wall is formed it will form after free-nuclear divisions. Commonly referred to as liquid endosperm. Coconut water is an example of this. Cellular endosperm development – where a cell-wall formation is coincident with nuclear divisions. Coconut meat is cellular endosperm. Acoraceae has cellular endosperm development while other monocots are helobial. Helobial endosperm development – where a cell wall is laid down between the first two nuclei, after which one half develops endosperm along the cellular pattern and the other half along the nuclear pattern.Evolutionary origins
The evolutionary origins of double fertilization and endosperm are unclear, attracting researcher attention for over a century. There are the two major hypotheses: * The double fertilization initially used to produce two identical, independent embryos ("twins"). Later these embryos acquired different roles, one growing into the mature organism, and another merely supporting it. Thus, the early endosperm was probably diploid, like the embryo. Somegymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( ; ) are a group of woody, perennial Seed plant, seed-producing plants, typically lacking the protective outer covering which surrounds the seeds in flowering plants, that include Pinophyta, conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetoph ...
s, such as '' Ephedra'', may produce twin embryos by double fertilization. Either of these two embryos is capable of filling in the seed, but normally only one develops further (the other eventually aborts). Also, most basal angiosperms still contain the four-cell embryo sac and produce diploid endosperms.
* Endosperm is the evolutionary remnant of the actual gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternating multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the se ...
, similar to the complex multicellular gametophytes found in gymnosperms. In this case, acquisition of the additional nucleus from the sperm cell is a later evolutionary step. This nucleus may provide the parental (not only maternal) organism with some control over endosperm development. Becoming triploid or polyploid are later evolutionary steps of this "primary gametophyte". Nonflowering seed plants (conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', ''Ephedra'') form a large homozygous female gametophyte to nourish the embryo within a seed.
The triploid transition - and the production of antipodal cells - may have occurred due to a shift in gametophyte development which produced a new interaction with an auxin-dependent mechanism originating in the earliest angiosperms.
Role in seed development
In some groups (e.g. grains of the familyPoaceae
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivate ...
), the endosperm persists to the mature seed stage as a storage tissue, in which case the seeds are called "albuminous" or "endospermous", and in others it is absorbed during embryo development (e.g., most members of the family Fabaceae
Fabaceae () or Leguminosae,International Code of Nomen ...
, including the common bean
''Phaseolus vulgaris'', the common bean,, is a herbaceous annual plant grown worldwide for its edible dry seeds or green bean, green, unripe pods. Its leaf is also occasionally used as a Leaf vegetable, vegetable and the straw as fodder. Its Pla ...
, ''Phaseolus vulgaris''), in which case the seeds are called "exalbuminous" or "cotyledonous" and the function of storage tissue is performed by enlarged cotyledons ("seed leaves"). In certain species (e.g. corn, ''Zea mays''); the storage function is distributed between both endosperm and the embryo. Some mature endosperm tissue stores fats (e.g. castor bean, ''Ricinus communis'') and others (including grains, such as wheat and corn) store mainly starches.
The dust-like seeds of orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Eart ...
s have no endosperm. Orchid seedlings are mycoheterotrophic in their early development. In some other species, such as coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
, the endosperm also does not develop. Instead, the nucellus produces a nutritive tissue termed "perisperm". The endosperm of some species is responsible for seed dormancy. Endosperm tissue also mediates the transfer of nutrients from the mother plant to the embryo, it acts as a location for gene imprinting, and is responsible for aborting seeds produced from genetically mismatched parents. In angiosperms, the endosperm contain hormones such as cytokinin
Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant hormones that promote cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots and shoots. They are involved primarily in Cell (biology), cell growth and cellular differentiation, differentiation, but also affect apical ...
s, which regulate cellular differentiation and embryonic organ formation.
Cereal grains
Cereal
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize ( Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, ...
crops are grown for their edible fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
(grains or caryopses), which are primarily endosperm. In the caryopsis, the thin fruit wall is fused to the seed coat. Therefore, the nutritious part of the grain is the seed and its endosperm. In some cases (e.g. wheat, rice) the endosperm is selectively retained in food processing (commonly called white flour), and the embryo ( germ) and seed coat (bran
Bran, also known as miller's bran, is the component of a Cereal, cereal grain consisting of the hard layersthe combined aleurone and Fruit anatomy#Pericarp layers, pericarpsurrounding the endosperm. Maize, Corn (maize) bran also includes the p ...
) removed. The processed grain has a lower quality of nutrition. Endosperm thus has an important role within the human diet worldwide.
The aleurone is the outer layer of endosperm cells, present in all small grains and retained in many dicots with transient endosperm. The cereal aleurone functions for both storage and digestion. During germination, it secretes the amylase
An amylase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyses the hydrolysis of starch (Latin ') into sugars. Amylase is present in the saliva of humans and some other mammals, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Foods that contain large ...
enzyme that breaks down endosperm starch into sugars to nourish the growing seedling.
See also
*Ovule
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the sporangium, megasporangium), ...
References
External links
*Endosperm: the pivot of the sexual conflict in flowering plants
at Earthling Nature {{Authority control Plant morphology Plant physiology