Lechitic Tribes on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lechites (, german: Lechiten), also known as the Lechitic tribes (, german: Lechitische Stämme), is a name given to certain West Slavic
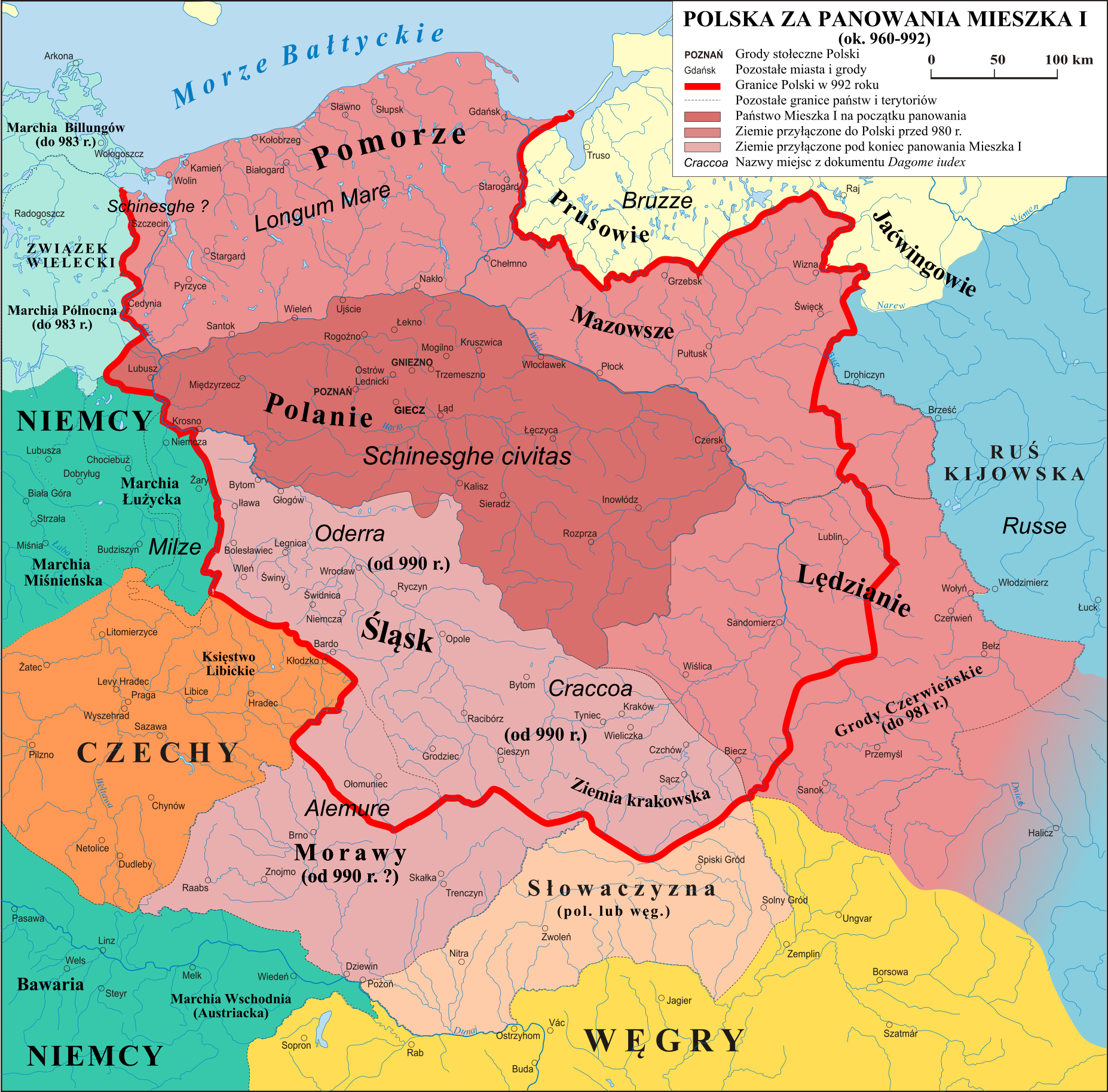
 According to Polish legend,
According to Polish legend,
 The name
The name
tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confl ...
who inhabited modern-day Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages
The Lechitic (or Lekhitic) languages are a language subgroup consisting of Polish and several other languages and dialects that were once spoken in the area that is now Poland and eastern Germany. It is one of the branches of the larger West Sl ...
. Distinct from the Czech–Slovak subgroup, they are the closest ancestors of ethnic Poles and the Pomeranians, Lusatians
Lusatia (german: Lausitz, pl, Łużyce, hsb, Łužica, dsb, Łužyca, cs, Lužice, la, Lusatia, rarely also referred to as Sorbia) is a historical region in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland. Lusatia stretches from the B� ...
and Polabians
Polabian Slavs ( dsb, Połobske słowjany, pl, Słowianie połabscy, cz, Polabští slované) is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic ( West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germa ...
.
History

 According to Polish legend,
According to Polish legend, Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and a ...
inherited the ducal throne from his father who probably ruled over two-thirds of the territory inhabited by eastern Lechite tribes. He united the Lechites east of the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech language, Czech, Lower Sorbian language, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder ri ...
( Polans, Masovians
Masovians, also spelled as Mazovians, and historically known as Masurians, is an ethnographic group of Polish people that originate from the region of Masovia, located mostly within borders of the Masovian Voivodeship, Poland. They speak the Mas ...
, Pomeranians, Vistulans, Silesians
Silesians ( szl, Ślōnzŏki or Ślůnzoki; Silesian German: ''Schläsinger'' ''or'' ''Schläsier''; german: Schlesier; pl, Ślązacy; cz, Slezané) is a geographical term for the inhabitants of Silesia, a historical region in Central Eur ...
) into a single country of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
. His son, Bolesław I the Brave
Bolesław I the Brave ; cs, Boleslav Chrabrý; la, Boleslaus I rex Poloniae (17 June 1025), less often known as Bolesław the Great, was Duke of Poland from 992 to 1025, and the first King of Poland in 1025. He was also Duke of Bohemia bet ...
, founded the bishoprics at Wrocław
Wrocław (; , . german: Breslau, , also known by other names) is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly ...
, Kołobrzeg
Kołobrzeg ( ; csb, Kòlbrzég; german: Kolberg, ), ; csb, Kòlbrzég , is a port city in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in north-western Poland with about 47,000 inhabitants (). Kołobrzeg is located on the Parsęta River on the south coast o ...
, and Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 159 ...
, and an archbishopric at Gniezno
Gniezno (; german: Gnesen; la, Gnesna) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. One of the Piast dynasty's chief cities, ...
. Bolesław carried out successful wars against Bohemia, Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
Th ...
, Kievan Rus'
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of ...
and Lusatia
Lusatia (german: Lausitz, pl, Łużyce, hsb, Łužica, dsb, Łužyca, cs, Lužice, la, Lusatia, rarely also referred to as Sorbia) is a historical region in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr ...
, and forced the western Pomeranians to pay Poland a tribute. Shortly before his death Bolesław became the first King of Poland in 1025.
Lechitic group
* Poles and Polans *Masovians
Masovians, also spelled as Mazovians, and historically known as Masurians, is an ethnographic group of Polish people that originate from the region of Masovia, located mostly within borders of the Masovian Voivodeship, Poland. They speak the Mas ...
* Vistulans
* Goplans The Goplans or Goplanes ( la, Glopeani, pl, Goplanie) was an early West Slavic tribe that inhabited the central parts of the Kujawy region, with their probable seat at Kruszwica. They might have been named after the Lake Gopło; Kmietowicz believ ...
* Lendians
The Lendians ( pl, Lędzianie) were a Lechitic tribe who lived in the area of East Lesser Poland and Cherven Cities between the 7th and 11th centuries. Since they were documented primarily by foreign authors whose knowledge of Central and East Eu ...
* Silesian tribes The Silesian tribes ( pl, plemiona śląskie) is a term used to refer to tribes, or groups of West Slavs that lived in the territories of Silesia in the Early Middle Ages. The territory they lived on became part of Great Moravia in 875 (now mostly i ...
** Bieżuńczanie
** Bobrzanie
** Dziadoszanie
** Golęszyce
** Lubuszanie
** Opolanie
** Ślężanie
** Trzebowianie
* Pomeranians
** Kashubians
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in no ...
** Slovincians (†)
** Pyrzyczanie The Prissani or Pyritzans ( pl, Pyrzyczanie) were a medieval tribe in Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Prissani" with 70 civitas by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845.Johannes Hoops, Herbert Jankuhn, Heinrich Beck, Reallexikon der germanische ...
(†)
** Wolinianie
The Wolinians ( la, Velunzani, Uelunzani, pl, Wolinianie) were a Lechitic tribe in Early Middle Age Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Velunzani" with 70 ''civitates'' by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845.Johannes Hoops, Herbert Jankuhn, He ...
(†)
* Polabians
Polabian Slavs ( dsb, Połobske słowjany, pl, Słowianie połabscy, cz, Polabští slované) is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic ( West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germa ...
(†)
* Radimichs
The Radimichs (also Radimichi) ( be, Радзiмiчы, russian: Радимичи, uk, Радимичі and pl, Radymicze) were an East Slavic tribe of the last several centuries of the 1st millennium, which inhabited upper east parts of the ...
Henryk Paszkiewicz. ''The making of the Russian nation''. Greenwood Press. 1977. p. 353. (†)
* Vyatichi
The Vyatichs or more properly Vyatichi or Viatichi (russian: вя́тичи) were a native tribe of Early East Slavs who inhabited regions around the Oka, Moskva and Don rivers.
The Vyatichi had for a long time no princes, but the social struc ...
(†)
* Obodrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ( ...
/Abodrites (†)
** Obotrites proper
** Wagrians
The Wagri, Wagiri, or Wagrians were a tribe of Polabian Slavs inhabiting Wagria, or eastern Holstein in northern Germany, from the ninth to twelfth centuries. They were a constituent tribe of the Obodrite confederacy.
In the Slavic uprisings of ...
** Warnower
** Polabians proper
** Linonen
* Wenden
** Travnjane
** Drevani
The Drevani (german: Draväno-Polaben or ''Drevanen'') were a tribe of Polabian Slavs settling on the Elbe river in the area of the present-day Lüchow-Dannenberg district of Lower Saxony, Germany.
They were a constituent tribe of the Obodrit ...
* Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Bran ...
* Venedi
* Luzyczanie
* Veleti (Wilzi) (†)
** Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
(Liutici)
*** Kissini The Kessinians, also known as Kessini, Chizzini, ''Kcynianie'' and ''Chyżanie'', were a medieval West Slavic tribe in what is now northeastern Germany. They inhabited the territory between the Warnow and Recknitz rivers, today split between the di ...
(''Kessiner'', ''Chizzinen'', ''Kyzziner'')
*** Circipani
Circipania (german: Circipanien, Zirzipanien) was a medieval territory in what is now northeastern Germany. The name derives from Latin ''circum'' (around) and ''Pane'' (the Peene River). The region was enclosed roughly by the upper Recknitz, Tre ...
(''Zirzipanen'')
*** Tollensians The Tollensians ( la, Tholenzi, pl, Dołężanie, Tolężanie, Dolency, Doleczanie) were a West Slavic tribe inhabiting the shores of the lower and middle Tollense (Dołęża) river, after which they were named. They were part of the Veleti/Lutici ...
*** Redarians
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
** Ucri
The Intransigent Radical Civic Union ( es, Unión Cívica Radical Intransigente, UCRI) was a political party of Argentina.
The UCRI developed from the centrist Radical Civic Union in 1956, following a split at the party's convention in Tucumán.
...
(''Ukr(an)i, Ukranen'')
** Rani (Rujani)
** Hevelli
The Hevelli or Hevellians/ Navellasîni (sometimes ''Havolane''; german: Heveller or ''Stodoranen''; pl, Hawelanie or ''Stodoranie''; cs, Havolané or ''Stodorané'') were a tribe of the Polabian Slavs, who settled around the middle Havel river ...
(''Stodorani'')
** Volinians (Velunzani)
** Pyritzans The Prissani or Pyritzans ( pl, Pyrzyczanie) were a medieval tribe in Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Prissani" with 70 civitas by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845.Johannes Hoops, Herbert Jankuhn, Heinrich Beck, Reallexikon der germanisch ...
(Prissani)
Lechitic languages
TheWest Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic la ...
included the ancestors of the peoples known later as Poles, Pomeranians, Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, ...
, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 ...
, Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Bran ...
and Polabians
Polabian Slavs ( dsb, Połobske słowjany, pl, Słowianie połabscy, cz, Polabští slované) is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic ( West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germa ...
. The northern so-called Lechitic group includes, along with Polish, endangered Pomeranian and Polabian, a dead language; Silesian Silesian as an adjective can mean anything from or related to Silesia. As a noun, it refers to an article, item, or person of or from Silesia.
Silesian may also refer to:
People and languages
* Silesians, inhabitants of Silesia, either a West S ...
, which is variously considered a Polish dialect or a language in its own right, is also part of this group. The Sorbian languages
The Sorbian languages ( hsb, serbska rěč, dsb, serbska rěc) are the Upper Sorbian language and Lower Sorbian language, two closely related and partially mutually intelligible languages spoken by the Sorbs, a West Slavic ethno-cultural mi ...
of the southern part of the Polabian area, preserved as relics today in Upper and Lower Lusatia
Lower Lusatia (; ; ; szl, Dolnŏ Łużyca; ; ) is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the ...
, occupy a place between the Lechitic and Czech-Slovak groups.
The name ''Lech''
 The name
The name Lech
Lech may refer to:
People
* Lech (name), a name of Polish origin
* Lech, the legendary founder of Poland
* Lech (Bohemian prince)
Products and organizations
* Lech (beer), Polish beer produced by Kompania Piwowarska, in Poznań
* Lech Poznań ...
or Leszek
Leszek () is a Slavic Polish male given name, originally ''Lestko'', ''Leszko'' or ''Lestek'', related to ''Lech'', ''Lechosław'' and Czech ''Lstimir''.
Individuals named Leszek celebrate their name day on June 3.
Notable people
* Lestko
* L ...
, Lestko, Leszko, Lestek, and Lechosław is a very popular name in Poland. Lech was a popular male name among members of Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branc ...
like Lestko, Leszek I the White
Leszek the White ( pl, Leszek Biały; c. 1184/85 – 24 November 1227) was Prince of Sandomierz and High Duke of Poland in the years 1194–1198, 1199, 1206–1210, and 1211–1227. During the early stages of his reign, his uncle Duke Mieszk ...
, Leszek II the Black
Leszek II the Black (c. 1241 – 30 September 1288), was a Polish prince of the House of Piast, Duke of Sieradz since 1261, Duke of Łęczyca since 1267, Duke of Inowrocław in the years 1273-1278, Duke of Sandomierz and High Duke of Poland from 1 ...
, Leszek, Duke of Masovia
Leszek of Masovia ( pl, Leszek, also ''Lestek'') (b. ca. 1162 - d. 1186) was a Polish prince from the Piast dynasty, the Duke of Masovia from 1173 until his death. He was the only son of Bolesław IV the Curly, Duke of Masovia and High Prince of ...
, Leszek of Racibórz
Leszek of Racibórz ( 1292 – 1336) was a Duke of Racibórz since 1306 and Duke of Koźle from 1334 until his death.
He was the eldest child and only son of Duke Przemysław of Racibórz by his wife Anna, daughter of Duke Konrad II of Masovia ...
.
The oldest part of Gniezno
Gniezno (; german: Gnesen; la, Gnesna) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. One of the Piast dynasty's chief cities, ...
, in the center of Great Poland, is known as ' ("Lech's Hill") as well as ' ("Royal Hill").
Lestko (also Lestek, Leszek), mentioned in the '' Gesta principum Polonorum'', completed between 1112 and 1118 by Gallus Anonymus
''Gallus Anonymus'' ( Polonized variant: ''Gall '') is the name traditionally given to the anonymous author of '' Gesta principum Polonorum'' (Deeds of the Princes of the Poles), composed in Latin between 1112 and 1118.
''Gallus'' is generally reg ...
, was the second legend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived, both by teller and listeners, to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess ...
ary duke of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
and the son of Siemowit
Siemowit (Polish pronunciation: �ɛˈmɔvit also Ziemowit �ɛˈmɔvit was, according to the chronicles of Gallus Anonymus, the son of Piast the Wheelwright and Rzepicha. He is considered to be the first ruler of the Piast dynasty.K. Jasiński ...
, born ca. 870–880. The '' Res gestae saxonicae sive annalium libri tres'' chronicle of 10th-century Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
, written by Widukind of Corvey
Widukind of Corvey (c. 925after 973) was a medieval Saxon chronicler. His three-volume '' Res gestae Saxonicae sive annalium libri tres'' is an important chronicle of 10th-century Germany during the rule of the Ottonian dynasty.
Life
In view of ...
, noted that Mieszko I
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and a ...
(son of Siemomysł
Siemomysł or Ziemomysł (died ) was the third duke of Polans of the Piast dynasty, and the father of Poland's first Christian ruler, Mieszko I. He was listed by Gallus Anonymous in his '' Gesta principum Polonorum'' and was the son of Lestek ...
and grandchild of Lestek), ruled over the tribe called the ''Licicaviki'', who lived in what is now Poland and were known as "Lestkowici" - the tribe of Lestek identified by the historians with the Lendians
The Lendians ( pl, Lędzianie) were a Lechitic tribe who lived in the area of East Lesser Poland and Cherven Cities between the 7th and 11th centuries. Since they were documented primarily by foreign authors whose knowledge of Central and East Eu ...
.
Wincenty Kadłubek
Wincenty Kadłubek ( 1150 – 8 March 1223) was a Polish Catholic prelate and professed Cistercian who served as the Bishop of Kraków from 1208 until his resignation in 1218. His episcopal mission was to reform the diocesan priests to ensure ...
in ''Chronica seu originale regum et principum Poloniae
200px, ''Historia Polonica'', Vincenti Kadłubkonis Episcopi Cracoviensis, 1612
''Chronica seu originale regum et principum Poloniae'', short name ''Chronica Polonorum'', is a Latin history of Poland written by Wincenty Kadłubek between 1190 a ...
'' (Chronicles of the Kings and Princes of Poland), written between 1190 and 1208, used the names ''Lechitae'' (Lechites), ''lechiticus'' (lechitic) and ''Lechia'' many times to describe all of medieval Poland. '' Chronicle of Greater Poland'' 1273 described Casimir I the Restorer
Casimir I the Restorer (; 25 July 1016 – 28 November 1058), a member of the Piast dynasty, was the duke of Poland from 1040 until his death. Casimir was the son of Mieszko II Lambert and Richeza of Lotharingia. He is known as the Restorer bec ...
as "king of Poles means Lechites"."Kronika wielkopolska" ("Greater Poland Chronicle"), Kazimierz Abgarowicz, Brygida Kürbisówna, PWN, Warszawa 1965, second edition Kraków 2010, Both the names "Poles" and "Lechites" were used in medieval Poland as adequate terms. "Laesir is the Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and t ...
term for the Ljachar, a people near the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in t ...
in Poland". Different forms of the name ''Lechia'' to designate the Polish state persist in several European languages
Most languages of Europe belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. Within Indo-European, the three largest phyla are Ro ...
and in some languages of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
and the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
: "Lehia" in Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
*** Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditiona ...
, "Lahestân/لهستان" in Persian (and via borrowing from Persian: "Lehastan" in Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
, and "Lehistan" in the Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish ( ota, لِسانِ عُثمانى, Lisân-ı Osmânî, ; tr, Osmanlı Türkçesi) was the standardized register of the Turkish language used by the citizens of the Ottoman Empire (14th to 20th centuries CE). It borrowed exten ...
).
Legends
In Polish literatureLech
Lech may refer to:
People
* Lech (name), a name of Polish origin
* Lech, the legendary founder of Poland
* Lech (Bohemian prince)
Products and organizations
* Lech (beer), Polish beer produced by Kompania Piwowarska, in Poznań
* Lech Poznań ...
was also the name of the legendary founder of Poland. The legend describes three brothers, Lech, Čech, and Rus – who founded three Slavic nations: Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
(also known as ''Lechia
The ethnonyms for the Poles (people) and Poland (their country) include endonyms (the way Polish people refer to themselves and their country) and exonyms (the way other peoples refer to the Poles and their country). Endonyms and most exonym ...
''), Bohemia (''Čechy'', now known as the Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. Th ...
), and Rus ('' Ruthenia''). In this legend Lech was the founder of Gniezno
Gniezno (; german: Gnesen; la, Gnesna) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. One of the Piast dynasty's chief cities, ...
.
''Three brothers Lech, Czech and Rus were exploring the wilderness to find a place to settle. Suddenly they saw a hill with an old oak and an eagle on top. Lech said: this white eagle I will adopt as an emblem of my people, and around this oak I will build my stronghold, and because of the eagle nest (Polish: ''gniazdo'') I will call it Gniezdno (modern:A variant of this legend, involving only two brothers Lech and Čech, was first written down byGniezno Gniezno (; german: Gnesen; la, Gnesna) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. One of the Piast dynasty's chief cities, ...). The other brothers went further on to find a place for their people. Czech went to the South'' (to found theCzech Lands The Czech lands or the Bohemian lands ( cs, České země ) are the three historical regions of Bohemia, Moravia, and Czech Silesia. Together the three have formed the Czech part of Czechoslovakia since 1918, the Czech Socialist Republic sinc ...) ''and Rus went to the East'' (to create Rus').
Cosmas of Prague
Cosmas of Prague ( cs, Kosmas Pražský; la, Cosmas Decanus; – October 21, 1125) was a priest, writer and historian.
Life
Between 1075 and 1081, he studied in Liège. After his return to Bohemia, he married Božetěcha, with whom he had a so ...
of Bohemia. The legend was described by ''Kronika wielkopolska'' ("Greater Poland Chronicle"), written in 1273 in Latin, and Chronicle of Dalimil
The ''Chronicle of Dalimil'' ( cs, Dalimilova kronika; Kronika tak řečeného Dalimila) is the first chronicle written in the Old Czech language. It was composed in verse by an unknown author at the beginning of the 14th century. The Chronicle c ...
, written in Czech in 1314.Die alttschechische Reimchronik des sogenannten Dalimil, Munich: Sagner, 1981
See also
*Lech (disambiguation)
Lech may refer to:
People
* Lech (name), a name of Polish origin
* Lech, the legendary founder of Poland
* Lech (Bohemian prince)
Products and organizations
* Lech (beer), Polish beer produced by Kompania Piwowarska, in Poznań
* Lech Poznań ...
*Lechia
The ethnonyms for the Poles (people) and Poland (their country) include endonyms (the way Polish people refer to themselves and their country) and exonyms (the way other peoples refer to the Poles and their country). Endonyms and most exonym ...
*Lendians
The Lendians ( pl, Lędzianie) were a Lechitic tribe who lived in the area of East Lesser Poland and Cherven Cities between the 7th and 11th centuries. Since they were documented primarily by foreign authors whose knowledge of Central and East Eu ...
*Polish tribes
"Polish tribes" is a term used sometimes to describe the tribes of West Slavic Lechites that lived from around the mid-6th century in the territories that became Polish with the creation of the Polish state by the Piast dynasty. The territory o ...
* Sorbian people
*Lechitic languages
The Lechitic (or Lekhitic) languages are a language subgroup consisting of Polish and several other languages and dialects that were once spoken in the area that is now Poland and eastern Germany. It is one of the branches of the larger West Sl ...
References
{{Reflist People from Pomerania West Slavic tribes