|
Polabians
Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic ( West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The approximate territory stretched from the Baltic Sea in the north, the Saale and the '' Limes Saxoniae''Christiansen, 18 in the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes in the south, and medieval Poland in the east. The Polabian Slavs, largely conquered by Saxons and Danes from the 9th century onwards, were included and gradually assimilated within the Holy Roman Empire. The tribes became gradually Germanized and assimilated in the following centuries; the Sorbs are the only descendants of the Polabian Slavs to have retained their identity and culture. The Polabian language is now extinct. However, the two Sorbian languages are spoken by approximately 22,000–30,000 inhabitants of the region. The government of Germany regards Upper and Lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs, also known as Elbe Slavs and more broadly as Wends, is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites, Lechitic (West Slavs, West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The approximate territory stretched from the Baltic Sea in the north, the Saale and the ''Limes Saxoniae''Christiansen, 18 in the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes in the south, and medieval History of Poland (966–1385), Poland in the east. The Polabian Slavs, largely conquered by Saxons and Danish people, Danes from the 9th century onwards, were included and gradually cultural assimilation, assimilated within the Holy Roman Empire. The tribes became gradually Germanization, Germanized and assimilated in the following centuries; the Sorbs are the only descendants of the Polabian Slavs to have retained their identity and culture. The Polabian language is now extinct. However, the two Sorbian languages are spoken by approximate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
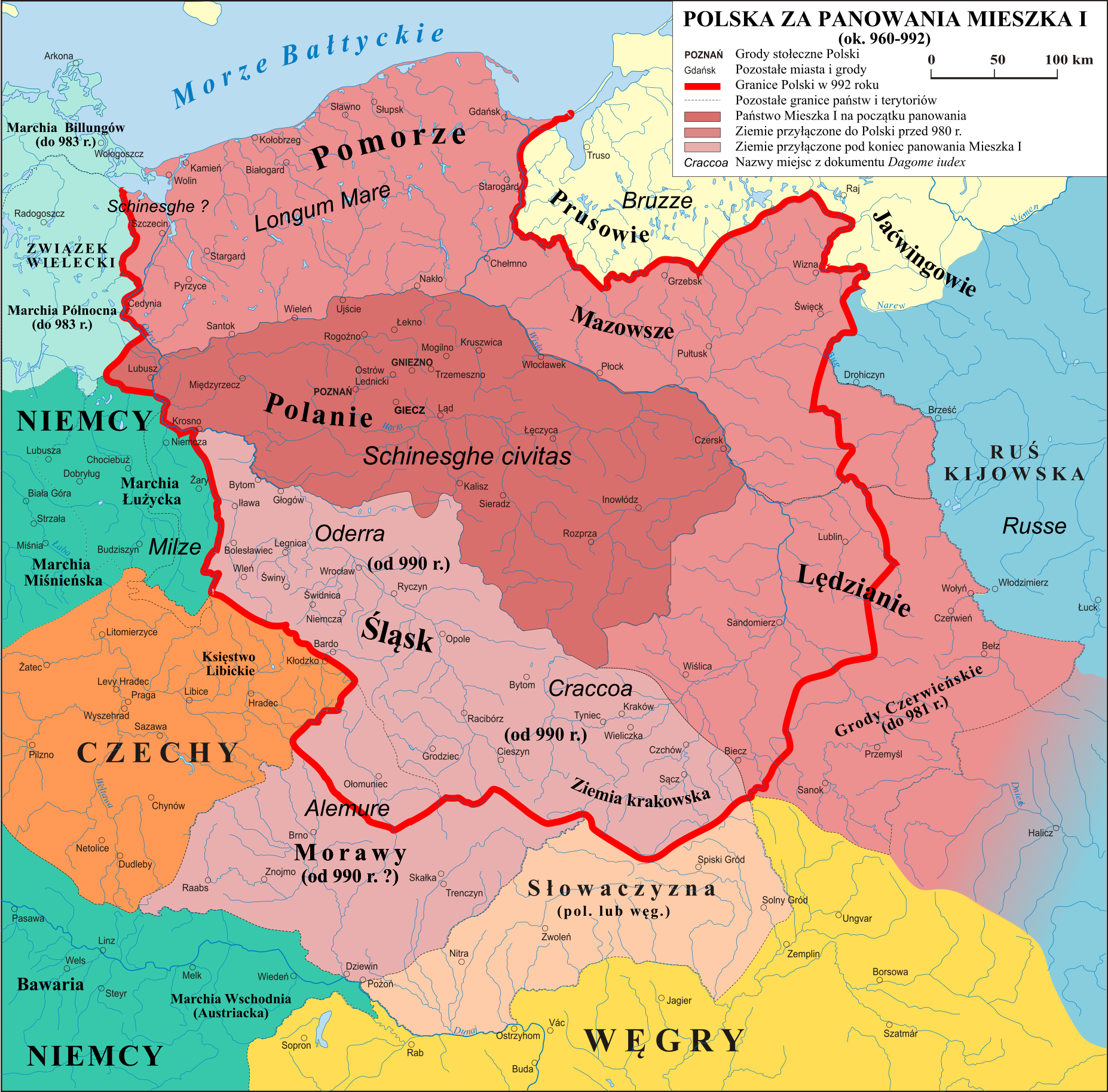
Lechites
Lechites (, ), also known as the Lechitic tribes (, ), is a name given to certain West Slavs, West Slavic tribes who inhabited modern-day Poland and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages. Distinct from the Czech–Slovak languages, Czech–Slovak subgroup, they are the closest ancestors of ethnic Polish people, Poles and of Pomeranians (Slavic tribe), Pomeranians, Lusatians and Polabians. History According to Polish legend, Mieszko I inherited the ducal throne from his father who probably ruled over two-thirds of the territory inhabited by eastern Lechite tribes. He united the Lechites east of the Oder (Polans (western), Polans, Masovians, Pomeranians (Slavic tribe), Pomeranians, Vistulans, Silesians) into a single country of Poland. His son, Bolesław Chrobry, Bolesław I the Brave, founded the bishoprics at Wrocław, Kołobrzeg, and Kraków, and an archbishopric at Gniezno. Bolesław carried out successful wars against Bohemia, Moravia, Kievan Rus' and L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic languages diversified into their historically attested forms over the 10th to 14th centuries. Today, groups which speak West Slavic languages include the Poles, Czechs, Slovaks, Silesians, Kashubians, and Sorbs. From the ninth century onwards, most West Slavs converted to Roman Catholicism, thus coming under the cultural influence of the Latin Church, adopting the Latin alphabet, and tending to be more closely integrated into cultural and intellectual developments in western Europe than the East Slavs, who converted to Eastern Orthodox Christianity and adopted the Cyrillic alphabet. Linguistically, the West Slavic group can be divided into three subgroups: Lechitic, including Polish, Silesian, Kashubian, and the extinct Polabian and Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
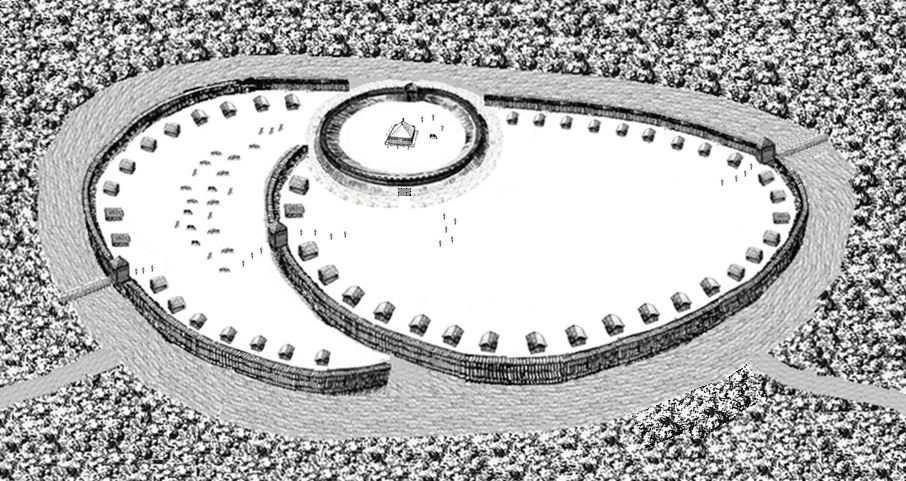
Obotrites
The Obotrites (, ''Abodritorum'', ''Abodritos'') or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany (see Polabian Slavs). For decades, they were allies of Charlemagne in his wars against the Germanic Saxons and the Slavic Veleti. The Obotrites under Prince Thrasco defeated the Saxons in the Battle of Bornhöved (798). The still-Pagan Saxons were dispersed by the emperor, and the part of their former land in Holstein north of Elbe was awarded to the Obotrites in 804, as a reward for their victory. This however was soon reverted through an invasion of the Danes. The Obotrite regnal style was abolished in 1167, when Pribislav was restored to power by Duke Henry the Lion, as Prince of Mecklenburg, thereby founding the Germanized House of Mecklenburg. Obotritic confederation The Bavarian Geographer, an anonymous medieval document compiled in Regensburg in 830, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polabian Language
The Polabian language, also known as Drevanian–Polabian language, Drevanian language, and Lüneburg Wendish language, is a West Slavic language that was spoken by the Polabian Slavs () in present-day northeastern Germany around the Elbe, from which comes the term ''Polabian''. It was spoken approximately until the rise to power of Prussia in the mid-18th century – when it was superseded by Low German – in the areas of Mecklenburg-West Pomerania, central Mittelmark part of Brandenburg and eastern Saxony-Anhalt (Wittenberg originally part of Bela Serbia), as well as in eastern parts of Wendland (Lower Saxony) and Schleswig-Holstein, Ostholstein and Lauenburg). Polabian was also relatively long (until the 16th century) spoken in and around the cities of Lübeck and Oldenburg. The very poorly attested Slavic dialects of Rügen seemed to have had more in common with Polabian than with Pomeranian varieties. In the south, it bordered on the Sorbian language area in Lusati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wends
Wends is a historical name for Slavs who inhabited present-day northeast Germany. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying as Wendish exist in Slovenia, Austria, Lusatia, the United States (such as the Wends of Texas, Texas Wends), and in Australia. In German-speaking Europe during the Middle Ages, the term "Wends" was interpreted as synonymous with "Slavs" and sporadically used in literature to refer to West Slavs and South Slavs living within the Holy Roman Empire. The name has possibly survived in Finnic languages ( ; ; ), denoting modern Russia. Term According to one theory, Germanic peoples first applied this name to the Vistula Veneti, ancient Veneti. For the North Germanic peoples, medieval Scandinavians, the term Wends (''Vender'') meant Slavs living near the southern shore of the Baltic Sea (''Vendland''), and the term was therefore used to refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbian Languages
The Sorbian languages (, ) are the Upper Sorbian language and Lower Sorbian language, two closely related and partially mutually intelligible languages spoken by the Sorbs, a West Slavs, West Slavic ethno-cultural minority in the Lusatia region of Eastern Germany. They are classified under the West Slavic languages, West Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages and are therefore closely related to the other two West Slavic subgroups: Lechitic languages, Lechitic and Czech–Slovak languages, Czech–Slovak.About Sorbian Language by Helmut Faska, University of Leipzig Historically, the languages have also been known as Wendish (named after the Wends, the earliest Slavic people in modern Poland and Germany) or Lusatian. Their collective ISO 639-2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Sorbian Language
Upper Sorbian (), occasionally referred to as Wendish (), is a minority language spoken by Sorbs in the historical province of Upper Lusatia, today part of Saxony, Germany. It is a West Slavic language, along with Lower Sorbian, Czech, Polish, Silesian, Slovak, and Kashubian. It is now spoken by fewer than 10,000 people, mostly in Budyšin and its immediate countryside. History The history of the Upper Sorbian language in Germany began with the Slavic migrations during the 6th century AD. Beginning in the 12th century, there was a massive influx of rural Germanic settlers from Flanders, Saxony, Thuringia and Franconia. This so-called "" (eastern settlement or expansion) led to a slow but steady decline in use of the Sorbian language. In addition, in the Saxony region, the Sorbian language was legally subordinated to the German language. Language prohibitions were later added: In 1293, the Sorbian language was forbidden in Berne castle before the courts; in 1327 it was forb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Sorbian Language
Lower Sorbian () is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic minority language spoken in eastern Germany in the historical province of Lower Lusatia, today part of Brandenburg. Standard Lower Sorbian is one of the two literary Sorbian languages, the other being the more widely spoken Upper Sorbian. The Lower Sorbian literary standard was developed in the 18th century, based on a southern form of the Cottbus dialect. The standard language, standard variety of Lower Sorbian has received structural influence from Upper Sorbian. Lower Sorbian is spoken in and around the city of Cottbus in Brandenburg. Signs in this region are typically bilingual, and Cottbus has a ''Lower Sorbian Gymnasium Cottbus, Lower Sorbian Gymnasium'' where one language of instruction is Lower Sorbian. It is a heavily endangered language. Most native speakers today belong to the older generations. Phonology The phonology of Lower Sorbian has been greatly influenced by language contact, contact with German lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Germany
The official language of Germany is German, with over 95 percent of the country speaking Standard German or a dialect of German as their first language. This figure includes speakers of Northern Low Saxon, a recognized minority or regional language that is not considered separately from Standard German in statistics. Recognized minority languages have official status as well, usually in their respective regions. Language spoken at home Neither the 1987 West German census nor the 2011 census inquired about language. Starting with the 2017 microcensus (a survey with a sampling fraction of 1% of the persons and households in Germany that supplies basic sociodemographic data and facilitates ongoing monitoring of the labor market), a question asking, "Which language is spoken predominantly in your household?" was added, nearly eighty years since the 1939 Census asked for the mother tongue of the population. According to a 2020 Pew Research survey, the most commonly spoken langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe, 919-1125
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object. Central may also refer to: Directions and generalised locations * Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as Middle Africa * Central America, a region in the centre of America continent * Central Asia, a region in the centre of Eurasian continent * Central Australia, a region of the Australian continent * Central Belt, an area in the centre of Scotland * Central Europe, a region of the European continent * Central London, the centre of London * Central Region (other) * Central United States, a region of the United States of America Specific locations Countries * Central African Republic, a country in Africa States and provinces * Blue Nile (state) or Central, a state in Sudan * Central Department, Paraguay * Central Province (Kenya) * Central Province (Papua New Guinea) * Central Province (Solomon Islands) * Central Province, Sri La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarian Geographer
The epithet "Bavarian Geographer" () is the conventional name for the anonymous author of a short Latin medieval text containing a list of the tribes in Central and Eastern Europe, headed . The name "Bavarian Geographer" was first bestowed (in its French form, "") in 1796 by Polish count and scholar Jan Potocki. The term is now also used at times to refer to the document itself. It was the first Latin source to claim that all Slavs originated in the same homeland, called the Zeriuani. Origin The short document, written in Latin, was discovered in 1772 in the Bavarian State Library, Munich by Louis XV's ambassador to the Saxon court, Comte Louis-Gabriel Du Buat-Nançay. It had been acquired by the Wittelsbachs with the collection of the antiquarian Hermann Schädel (1410–85) in 1571. The document was much discussed in the early 19th-century historiography, notably by Nikolai Karamzin and Joachim Lelewel. The provenance of the document is disputed. Although early commen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |