Lavo (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Known as "Lavo" during most of its history, Lopburi Province is one of the most important cities in the
Known as "Lavo" during most of its history, Lopburi Province is one of the most important cities in the
 This city is in the Chao Phraya River basin where historical, archaeological, and cultural evidence has been discovered that prehistoric humans lived here about 3,500 – 4,000 years ago or in the
This city is in the Chao Phraya River basin where historical, archaeological, and cultural evidence has been discovered that prehistoric humans lived here about 3,500 – 4,000 years ago or in the 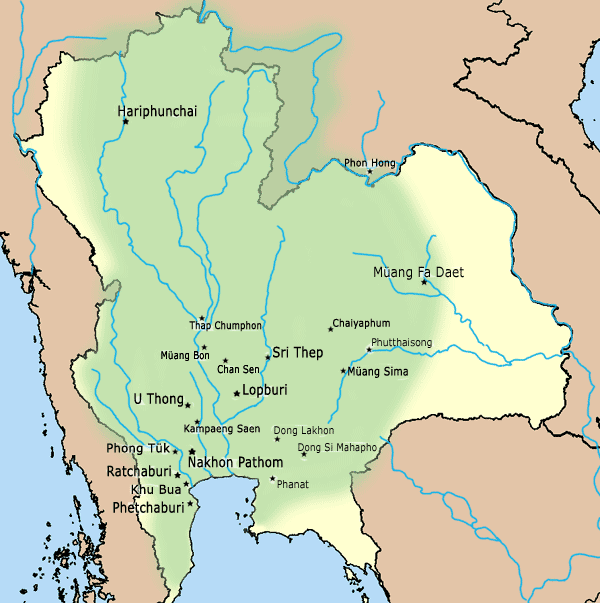 According to the ''Northern Chronicles,'' Lavo (Lopburi) was founded by King Kalavarnadishraj, who came from Takkasila in 648 CE. According to Thai records, King Kakabatr from Takkasila (it is assumed that the city was Tak or Nakhon Chai Si) set the new era,
According to the ''Northern Chronicles,'' Lavo (Lopburi) was founded by King Kalavarnadishraj, who came from Takkasila in 648 CE. According to Thai records, King Kakabatr from Takkasila (it is assumed that the city was Tak or Nakhon Chai Si) set the new era,
 In the 6th century, Lavo sent tribute to the Chinese emperor during the
In the 6th century, Lavo sent tribute to the Chinese emperor during the
 In the 10th century, when it was known as Lavodayapura (
In the 10th century, when it was known as Lavodayapura (
 In 1350, the
In 1350, the
history
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ...
of Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
. The city has a long history, dating back into the prehistory period since the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
of more than 3,500 years ago.
Later, it was influenced by the art and culture of India in the 11th century when it entered the historical era. This first period under the influence of Indian culture was called the Dvaravati Period. Since that time, Lavo has been ruled by the Khmer, coming under the influence of their art and culture, in the 15th century, a time commonly called the Lopburi Period in Thai art
Thai art refers to a diverse range of art forms created in Thailand from prehistoric times to the present day, including architecture, sculpture, painting, textiles, decorative arts, crafts, ceramics, and more. While Buddhism has played a signifi ...
history.
Eventually, when the Ayutthaya empire was established, Lavo decreased in importance until the reign of King Narai
King Narai the Great (, , ) or Ramathibodi III ( ) was the 27th monarch of Ayutthaya Kingdom, the 4th and last monarch of the Prasat Thong dynasty. He was the king of Ayutthaya Kingdom from 1656 to 1688 and arguably the most famous king of the ...
. He had a palace built in Lavo, and each year spent most of his time there. After the time of King Narai, Lavo had been abandoned, until the 19th centuries, King Mongkut
Mongkut (18 October 18041 October 1868) was the fourth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama IV. He reigned from 1851 until his death in 1868.
The reign of Mongkut was marked by significant modernization ini ...
(Rama IV) had it restored to be used as an inland royal city.
Later, in the 20th century, Prime Minister Marshal P. Piboolsongkhram developed Lopburi as a national military center.
Location
Lavo is in central Thailand on a river which descends from the mountains "Sam-Yod" (Khao Sam Yod) above the city, and runs into theLopburi River
The Lopburi River (, , ) is a tributary of the Chao Phraya River in central Thailand. It splits from the Chao Phraya river at Tambon Bang Phutsa, Singburi. Passing through Tha Wung district and the town of Lopburi, it enters the Chao Phraya tog ...
west of the city. This river runs into Chao Phraya
The Chao Phraya River is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.
Etymology
Written evidence of the river being referred to by the ...
River in Singburi Province
Sing Buri (, ) is one of the central provinces (''changwat'') of Thailand. Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise) Nakhon Sawan, Lopburi, Ang Thong, Suphan Buri, and Chai Nat.
Toponymy
The word ''sing'' originates from Sanskrit ''sing ...
.
Prehistorical era
 This city is in the Chao Phraya River basin where historical, archaeological, and cultural evidence has been discovered that prehistoric humans lived here about 3,500 – 4,000 years ago or in the
This city is in the Chao Phraya River basin where historical, archaeological, and cultural evidence has been discovered that prehistoric humans lived here about 3,500 – 4,000 years ago or in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
. Abandoned ancient cities with many pre-historic instruments and human skeletons has been found in several parts of the modern-day province.
 According to the ''Northern Chronicles,'' Lavo (Lopburi) was founded by King Kalavarnadishraj, who came from Takkasila in 648 CE. According to Thai records, King Kakabatr from Takkasila (it is assumed that the city was Tak or Nakhon Chai Si) set the new era,
According to the ''Northern Chronicles,'' Lavo (Lopburi) was founded by King Kalavarnadishraj, who came from Takkasila in 648 CE. According to Thai records, King Kakabatr from Takkasila (it is assumed that the city was Tak or Nakhon Chai Si) set the new era, Chula Sakarat
Chula Sakarat or Chulasakarat (; , ; , ; , , , abbrv. จ.ศ. ''Choso'') is a lunisolar calendar derived from the Burmese calendar, whose variants were in use by most mainland Southeast Asian kingdoms down to the late 19th century. The calendar is ...
in 638 CE. His son, King Kalavarnadishraj founded the city a decade later. And several years later he assigned Jamadevi
Camadevi (also spelled Jamadevi; IPA: ʃaːmaˈdeːʋiː Pali: Cāmadevī; , , Mon: စာမ္မာဒေဝဳ, ; 7th-century – 8th-century) was the first monarch and Queen of Hariphunchai (Pali: Haribhuñjaya), which was an ancient Kingdo ...
to reign on the throne of the Haribhunjaya kingdom in the northern Thailand.
These kingdoms adopted Indian culture together with Theravada Buddhism and grew up under post-Indian (the local technology that adapt from Indian) and Mon influence in the 11th to 12th centuries, as it entered into the historical era. This first period under the influence of Indian culture was called the Dvaravati
Dvaravati () was a medieval Mon political principality from the 6th century to the 11th century, located in the region now known as central Thailand, and was speculated to be a succeeding state of Lang-chia or Lang-ya-hsiu (). It was describe ...
period. For the time being this kingdom was known as Saruka Lavo (Mon language
The Mon language, formerly known as Peguan and Talaing, is an Austroasiatic language spoken by the Mon people. Mon, like the related Khmer language, but unlike most languages in mainland Southeast Asia, is not tonal. The Mon language is a recogn ...
). Although the inscription stones found in this area are the Mon language, there is not clear evidence to prove if the population of Lavo were actually of Mon ethnicity.
In 2018-2019 The Italian-Thai "Lopburi Regional Archaeological Project", co-directed by Dr Roberto Ciarla (ISMEO - International Association of Mediterranean and Oriental Studies) and Dr Pakpadee Yukongdee (Thai Fine Arts Department, Bangkok), discovered several hundreds of stone and shell adzes, remains of shell industry waste, terracotta artifacts, clay pots of different style, animal and human remains dating back to the Neolithic Period as well as to the Iron Age in the Lop Buri River basin at Khok Phutsa few kilometers north of the Lop Buri City. C14 dates, DNA analysis and full study of the artifacts are still in progress.
Lavo in Chinese records
 In the 6th century, Lavo sent tribute to the Chinese emperor during the
In the 6th century, Lavo sent tribute to the Chinese emperor during the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
(618–907), and another during the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
(960–1279). The Tang Chronicles refer to Lavo and Dvaravati as Tou-ho-lo. The diary of the monk Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mokṣadeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making ...
, dating from the same period (629–645), also mentions the region, referring to it as Tou-lo-po-ti.
Lavo sent tributes to Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
twice, in 1115 and 1155. The Song Chronicles mention Lavo at that time as Lo Hu.
Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
's writings also refer to Lavo, as Locak.Robert J. King, "Finding Marco Polo’s Locach", ''Terrae Incognitae'', vol.50, no.1, April 2018, pp. 1–18. It was described as being in the hinterland of the Chao Phraya basin, a place too far to be subject to attack by the Kublai Khan
Kublai Khan (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder and first emperor of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China. He proclaimed the ...
's army of Yuan (1271–1368).
Khmer era
 In the 10th century, when it was known as Lavodayapura (
In the 10th century, when it was known as Lavodayapura (Khmer language
Khmer ( ; , Romanization of Khmer#UNGEGN, UNGEGN: ) is an Austroasiatic language spoken natively by the Khmer people. This language is an official language and national language of Cambodia. The language is also widely spoken by Khmer people i ...
), Lavo was subordinate to the Khmer empire
The Khmer Empire was an empire in Southeast Asia, centered on Hydraulic empire, hydraulic cities in what is now northern Cambodia. Known as Kambuja (; ) by its inhabitants, it grew out of the former civilization of Chenla and lasted from 802 t ...
came with the influence of their art and culture, in the 10th to 16th centuries. New construction used the stones of ruined Dvaravati holy places that were built originally without mortar. Thus, the oldest ruins that can now be found in Lopburi are always Khmer-style on a Dvaravati foundation.
The Khmers were present since the tenth century, but Lavo "became detached from Cambodia" at the end of the thirteenth century, sending embassies to China from 1289 to 1299.
Ayutthaya era
 In 1350, the
In 1350, the Ayutthaya kingdom
The Ayutthaya Kingdom or the Empire of Ayutthaya was a Thai people, Thai kingdom that existed in Southeast Asia from 1351 to 1767, centered around the city of Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya (city), Ayutthaya, in Siam, or present-day Thailand. Europe ...
was founded by King Ramathibodi I
King U-thongThe Royal Institute.'List of monarchs Ayutthaya''. (; ) or King Ramathibodi I (; ; , 1314–1369) was the first king of the kingdom Ayutthaya (now part of Thailand), reigning from 1351 to 1369.
Origins and Reign
He was known as P ...
, which merged Lavo with the kingdom ruled from Suphanburi
Suphan Buri () is a town ('' thesaban mueang'') in central Thailand. It covers ''tambon'' Tha Philiang and parts of ''tambons'' Rua Yai and Tha Rahat, all within the Mueang Suphan Buri District. As of 2006 it had a population of 26,656. The tow ...
called ''Subharnabhumi'' or ''Pan Pum'', which according to the common Thai history to be identical with the Suvarnabhumi kingdom. This event had been recorded in the Chinese texts that called Thai as ''Xian-lo-guo'' or Siam-Lavo country.
At that time Lavo became a "Mueang
Mueang ( Ahom: 𑜉𑜢𑜤𑜂𑜫; ''mɯ̄ang'', ), Muang ( ''mɯ́ang'', ), Möng ( Tai Nuea: ᥛᥫᥒᥰ ''möeng''; ''móeng'', ), Meng ( zh, c=猛 or 勐) or Mường (Vietnamese) were pre-modern semi-independent city-states or princip ...
Luk Luang", an important city ruled by a crown prince for several years in the beginning of Ayutthaya period. There were not any evidences the prosperity of Lavo was transferred from Lavo to Ayutthaya, but with time Lavo decreased in importance to become only a border town to the north of Ayutthaya.
In the reign of King Narai the Great, the 26th king of Ayutthaya, in the mid-17th century Lavo become an important city again. He commanded to reconstruct the palace at the same place of King Ramesuan's Palace as a summer palace, King Narai's Palace in 1666. Lavo thus served as a second capital, next to Ayutthaya, the king stayed here for about eight months a year.
Rattanakosin era
After the time of King Narai, Lavo had been abandoned, until KingMongkut
Mongkut (18 October 18041 October 1868) was the fourth Monarchy of Thailand, king of Siam from the Chakri dynasty, titled Rama IV. He reigned from 1851 until his death in 1868.
The reign of Mongkut was marked by significant modernization ini ...
(Rama IV) of Rattanakosin kingdom had it restored to be used as an inland royal city.
Lavo had also been renamed to Lopburi
Lopburi (, , ) is the capital city of Lopburi Province in Thailand. It is about northeast of Bangkok. It has a population of 58,000. The town ('' thesaban mueang'') covers the whole ''tambon'' Tha Hin and parts of Thale Chup Son of Muea ...
in this period.
Later, in 1937, Prime Minister Field Marshal Plaek Phibunsongkhram
Plaek Phibunsongkhram; 14 July 1897 – 11 June 1964) was a Thai military officer and politician who served as the third prime minister of Thailand from 1938 to 1944 and again from 1948 to 1957. He rose to power as a leading member of the Kh ...
desired to set up Lopburi as the military center of Thailand. Therefore, the city had been expanded. He laid out Lopburi city, with its modern center about 4 km. east of the historical center. His building style, Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920 ...
, is apparent along Narai Maharat Road. The improvements he made to the city are apparent to the present day.
Archeological researches
* several flaked stone tools were discovered in Ban Mi district dated back to thePaleolithic Age
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
by Karl Friedrich Sarasin in 1931.
* a number of tools, human burial sites and bronze accessories belong to Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
were found in Lop Buri river Basin in 1964.
* Bracelets and beads dated back 2700–3500 years were revealed at Ban Khok Charoen under the leadership of Helmut Loofs-Wissowa, prof. Chin You-di and William Watson in 1966–1970.
* Prehistoric human skeletons and clay jugs were found in Ban Tha Kae in 1979.
* A Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
source was discovered in Khao Wong Phrachan in 1986-1994 by archaeologists from the Fine Arts Department
The Fine Arts Department (, ) is a government department of Thailand, under the Ministry of Culture. Its mission is managing the country's cultural heritage.
History
The department was originally established by King Vajiravudh in 1912, split o ...
and the University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (Penn or UPenn) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. One of nine colonial colleges, it was chartered in 1755 through the efforts of f ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:History of Lopburi Lopburi province