Lausitz on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lusatia (; ; ; ; ; ), otherwise known as Sorbia, is a region in
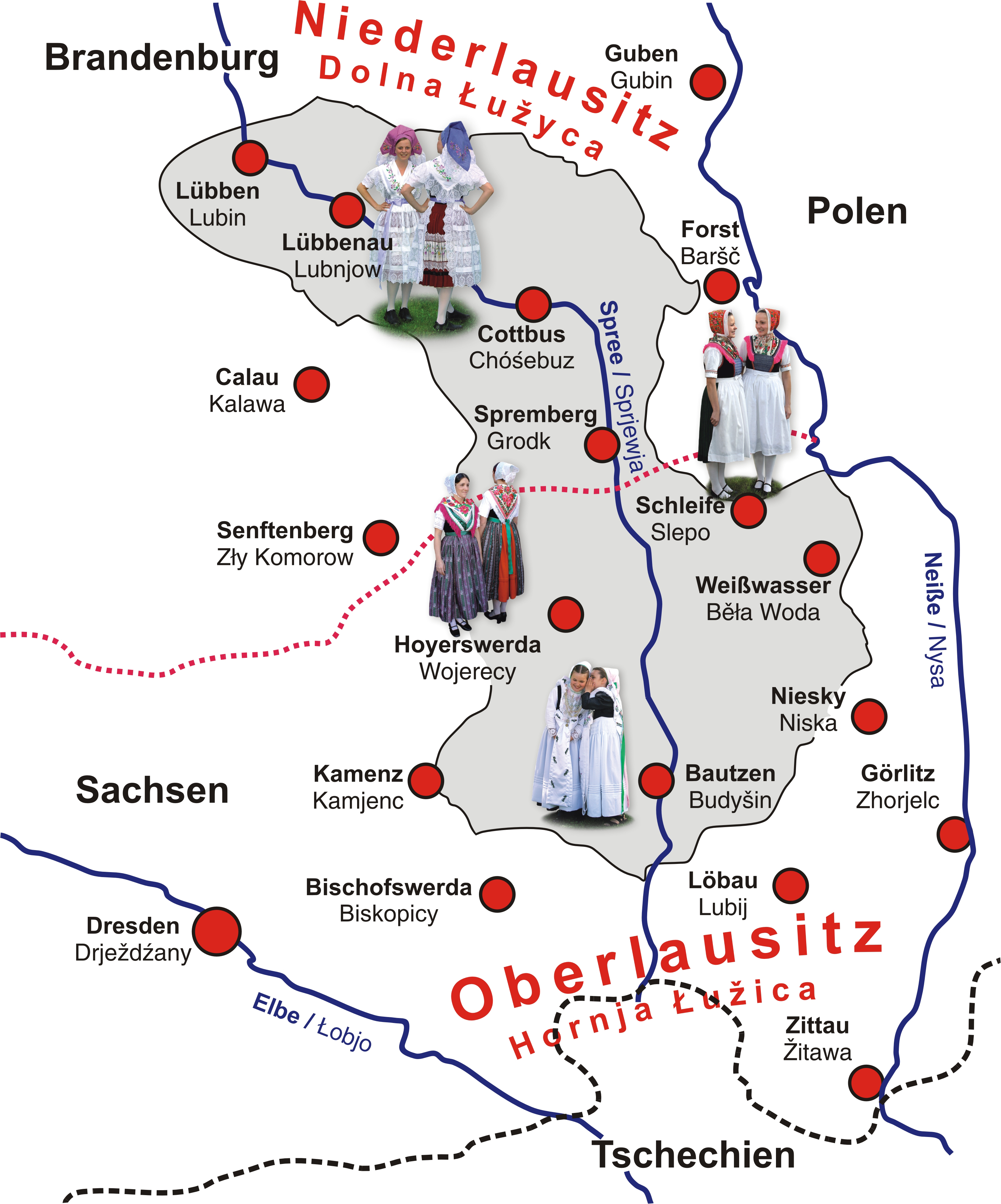
 Lusatia comprises two both scenically and historically different parts: a hilly southern "upper" section and a "lower" region, which belongs to the
Lusatia comprises two both scenically and historically different parts: a hilly southern "upper" section and a "lower" region, which belongs to the
 Upper Lusatia (''Oberlausitz'', ''Łużyce Górne'' or ''Hornja Łužica'') is today part of the German state of Saxony, except for a small part east of the Neisse River around
Upper Lusatia (''Oberlausitz'', ''Łużyce Górne'' or ''Hornja Łužica'') is today part of the German state of Saxony, except for a small part east of the Neisse River around
Bautzen Altstadt 57.jpg,
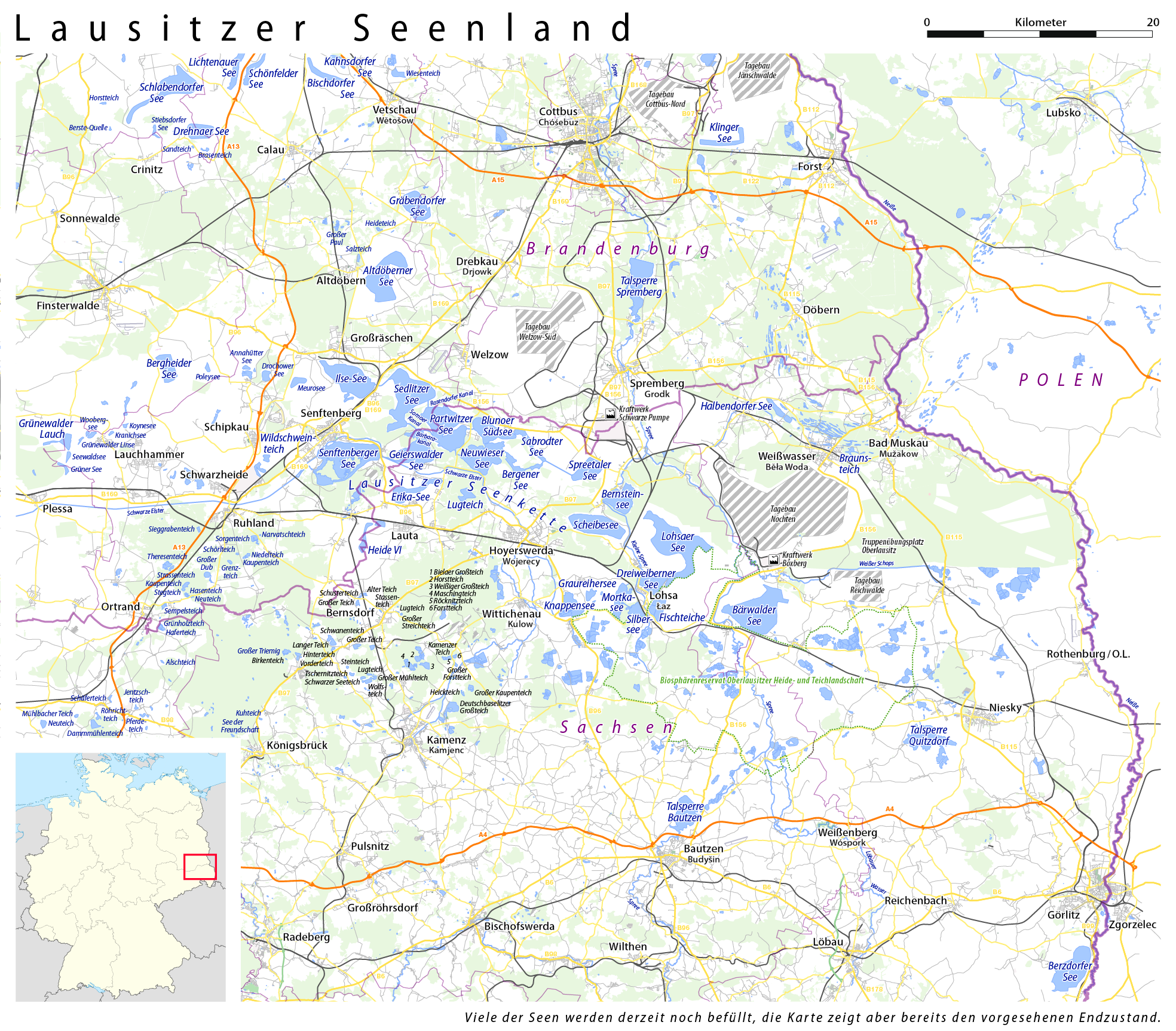 The Lusatian Lake District (German: Lausitzer Seenland, Lower Sorbian: Łužyska jazorina, Upper Sorbian: Łužiska jězorina) is an artificially created lake area. By the end of the 2020s, Europe's largest artificial water landscape and Germany's fourth-largest lake area are to be created by flooding disused brown coal mines in the Lusatian brown coal mining area. Some of the largest lakes are connected to each other as a chain of lakes by navigable canals.
The new lakeland is largely created from remaining holes from former brown coal opencast mines. These are flooded and converted into lakes. Some of the resulting lakes have already reached their final water level, others will not be completely flooded for a few years.
Other lakes are artificially dammed lakes. While the Quitzdorf Dam was created to provide enough process water for the Boxberg Power Station, the Spremberg Dam was primarily planned for flood protection in the lake district, but was also used for process water for power plants. The Bautzen Reservoir was also artificially created in order to be able to continuously supply the Boxberg Power Station with water.
The ponds of the Upper Lusatian Heath and Pond Landscape Biosphere Reserve, which are also located in the Lake District area, were partly created in the Middle Ages, but also during the GDR period for agricultural reasons, as the moor-rich land was restructured and made usable. These very shallow waters are mostly used for fish farming.
The ponds of the Muskau Arch are also located between the large opencast mining holes. They arose from faults in the terminal moraine of glaciers from the Ice Age, and partly through the mining of soil raw materials such as sand, clay and coal even before industrialization. In general, these ponds are not created intentionally by humans, but are filled with water due to a lack of drainage.
The Lusatian Lake District (German: Lausitzer Seenland, Lower Sorbian: Łužyska jazorina, Upper Sorbian: Łužiska jězorina) is an artificially created lake area. By the end of the 2020s, Europe's largest artificial water landscape and Germany's fourth-largest lake area are to be created by flooding disused brown coal mines in the Lusatian brown coal mining area. Some of the largest lakes are connected to each other as a chain of lakes by navigable canals.
The new lakeland is largely created from remaining holes from former brown coal opencast mines. These are flooded and converted into lakes. Some of the resulting lakes have already reached their final water level, others will not be completely flooded for a few years.
Other lakes are artificially dammed lakes. While the Quitzdorf Dam was created to provide enough process water for the Boxberg Power Station, the Spremberg Dam was primarily planned for flood protection in the lake district, but was also used for process water for power plants. The Bautzen Reservoir was also artificially created in order to be able to continuously supply the Boxberg Power Station with water.
The ponds of the Upper Lusatian Heath and Pond Landscape Biosphere Reserve, which are also located in the Lake District area, were partly created in the Middle Ages, but also during the GDR period for agricultural reasons, as the moor-rich land was restructured and made usable. These very shallow waters are mostly used for fish farming.
The ponds of the Muskau Arch are also located between the large opencast mining holes. They arose from faults in the terminal moraine of glaciers from the Ice Age, and partly through the mining of soil raw materials such as sand, clay and coal even before industrialization. In general, these ponds are not created intentionally by humans, but are filled with water due to a lack of drainage.
Elsterheide Geierswalde Aerial Pan.jpg, Geierswalder See (Lejnjanski jězor)
Groß Düben Halbendorfer See Aerial.jpg,
Gablenz Kromlau Faltenbogen Pan.jpg, Gieser landscape between
 At the same time the Polan duke of the later
At the same time the Polan duke of the later
 As Margrave Egbert II of Meissen supported
As Margrave Egbert II of Meissen supported

 According to the 1635 Peace of Prague, most of Lusatia became a province of the
According to the 1635 Peace of Prague, most of Lusatia became a province of the
 During the war, the Poles postulated that after the defeat of Germany, the Sorbs should be allowed free national development either within the borders of Poland or
During the war, the Poles postulated that after the defeat of Germany, the Sorbs should be allowed free national development either within the borders of Poland or

 After World War II according to the
After World War II according to the
 More than 80,000 of the Sorbian
More than 80,000 of the Sorbian
File:Das neue Schloss im Fürst- Pückler-Park.IMG 9438WI.jpg, Schloss Muskau
File:Rakotzbrücke 2021 06.jpg, Rakotz Bridge
File:2023-08 Muskauer Park (24).jpg,
Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
, formerly entirely in Germany and today territorially split between Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and modern-day Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr
The Bóbr (; ; ) is a river which flows through the north of the Czech Republic and the southwest of Poland. It is a left tributary of the Oder. Its Polish name translates directly to ' beaver'.
Course
The Bóbr has a length of (3 in Czech ...
and Kwisa
The Kwisa (, , ) is a river in south-western Poland, a left tributary of the Bóbr, which itself is a left tributary of the Oder river.
It rises in the Jizera Mountains, part of the Western Sudetes range, where it runs along the border with t ...
rivers in the east to the Pulsnitz
Pulsnitz (German, ; Upper Sorbian name: ''Połčnica'', ) is a town in the district of Bautzen, in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. It is situated on the small river Pulsnitz, 11 km southwest of Kamenz, and 24 km northeast ...
and Black Elster
The Black Elster or Schwarze Elster ( German, ; ; ) is a long river in eastern Germany, in the states of Saxony, Brandenburg and Saxony-Anhalt. It is a right tributary of the Elbe. Its source is in the Upper Lusatia region, near Elstra.
The Blac ...
rivers in the west, and is located within the German states of Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
and Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
as well as in the Polish voivodeship
A voivodeship ( ) or voivodate is the area administered by a voivode (governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in ...
s of Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ) is a historical and geographical region mostly located in Poland with small portions in the Czech Republic and Germany. It is the western part of the region of Silesia. Its largest city is Wrocław.
The first ...
and Lubusz. Major rivers of Lusatia are the Spree and the Lusatian Neisse
The Lusatian Neisse (; ; ; Upper Sorbian: ''Łužiska Nysa''; Lower Sorbian: ''Łužyska Nysa''), or Western Neisse, is a river in northern Central Europe.
, which defines the border between Germany and Poland. The Lusatian Mountains
The Lusatian Mountains (; ; ) are a mountain range of the Western Sudetes on the southeastern border of Germany with the Czech Republic. They are a continuation of the Ore Mountains range west of the Elbe valley. The mountains of the northern, G ...
of the Western Sudetes separate Lusatia from Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
(Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, also known as Czechia, and historically known as Bohemia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the south ...
) in the south. Lusatia is traditionally divided into Upper Lusatia
Upper Lusatia (, ; , ; ; or ''Milsko''; ) is a historical region in Germany and Poland. Along with Lower Lusatia to the north, it makes up the region of Lusatia, named after the Polabian Slavs, Slavic ''Lusici'' tribe. Both parts of Lusatia a ...
, the hilly southern part, and Lower Lusatia
Lower Lusatia (; ; ; ; ) is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the Germany, German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the south, Lower Lusa ...
, the flat northern part.
The areas east and west along the Spree in the German part of Lusatia are home to the Slavic
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Peoples
* Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia
** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples
** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples
** West Slav ...
Sorbs
Sorbs (; ; ; ; ; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Germany, states of Saxony and Brandenburg. Sorbs tradi ...
, one of Germany’s four officially recognized indigenous ethnic minorities. The Upper Sorbs inhabit Saxon Upper Lusatia, and the Lower Sorbs Brandenburgian Lower Lusatia. Upper and Lower Sorbian
Lower may refer to:
* ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is sit ...
are spoken in the German parts of Upper and Lower Lusatia respectively, and the signage there is mostly bilingual.
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
states that this entire region was part of ''Germania'' and that in and before the second century was populated by German tribes. From the seventh century Slavs began migrating into this region. Subsequently it has been ruled variously by Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
, and very briefly by Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
.
The Lusatian Lake District
The Lusatian Lake District (, , ) is a chain of artificial lakes under construction in Germany across the north-eastern part of Saxony and the southern part of Brandenburg. Through flooding as a part of an extensive regeneration programme, sever ...
is Europe's largest artificial lake district. The village of Herrnhut
Herrnhut (; ; ; Upper Lusatian: ''Harrnhutt'', ''Harrnutt'') is a town of around 6,000 inhabitants in Upper Lusatia, in the district of Görlitz, in eastern Saxony, Germany. The town is mainly known as the place of origin of the community of t ...
() is the seat of the Moravian Church
The Moravian Church, or the Moravian Brethren ( or ), formally the (Latin: "Unity of the Brethren"), is one of the oldest Protestant denominations in Christianity, dating back to the Bohemian Reformation of the 15th century and the original ...
. Muskau Park
Muskau Park (, officially: ''Fürst-Pückler-Park Bad Muskau''; ) is a landscape park in the Upper Lusatia region of Germany and Poland. It is the largest and one of the most famous English gardens in Central Europe, stretching along both sides ...
in Bad Muskau
Bad Muskau (; formerly ''Muskau'', , , ) is a spa town in the historic Upper Lusatia region in eastern Germany, at the border with Poland. It is part of the Görlitz district in the State of Saxony.
It is located on the banks of the Lusatian Ne ...
() and Łęknica
Łęknica (; , ) is a border town in western Poland, one of the two gminas of Żary County in Lubusz Voivodeship.
Muskau Park (''Park Mużakowski''), a Polish-German World Heritage Site and Historic Monument of Poland, stretches north of the ...
is a UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. The Tropical Islands Resort, a large water park housed in a former airship hangar that is the biggest free-standing hall in the world, is located in the north of Lusatia. The closest international airport to Lusatia is Dresden Airport in Klotzsche ().
The largest Lusatian city is Cottbus
Cottbus () or (;) is a university city and the second-largest city in the German state of Brandenburg after the state capital, Potsdam. With around 100,000 inhabitants, Cottbus is the most populous city in Lusatia. Cottbus lies in the Sorbian ...
(), with nearly 100,000 inhabitants. Other notable towns are the former members of the Lusatian League
The Lusatian League () was a historical alliance of six towns in the region of Upper Lusatia from 1346 until 1815, when the region was controlled first by Bohemia (1346–1635) and later by the Electorate of Saxony (1635–1815). The member towns ...
: the German/Polish twin towns of Görlitz
Görlitz (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, East Lusatian: , , ) is a town in the Germany, German state of Saxony. It is on the river Lusatian Neisse and is the largest town in Upper Lusatia, the second-largest town in the region of Lusatia after ...
() and Zgorzelec
Zgorzelec (, , , , Lower Sorbian: ''Zgórjelc'') is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in southwestern Poland, with 30,374 inhabitants (2019). It is the seat of Zgorzelec County and of Gmina Zgorzelec (although it is not part of the territory ...
, Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
(), Zittau
Zittau (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, Upper Lusatian dialect: ''Sitte''; ) is the southeasternmost city in the Germany, German state of Saxony, and belongs to the Görlitz (district), district of Görlitz, Germany's easternmost Districts of Germ ...
(), Lubań
Lubań (; ), sometimes called Lubań Śląski (; , ); is a town in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship in southwest Poland. It is the administrative seat of Lubań County and also of the smaller Gmina Lubań (although it is not part of the territory ...
, Kamenz
Kamenz () or Kamjenc ( Sorbian, ) is a town (''Große Kreisstadt'') in the district of Bautzen in Saxony, Germany. Until 2008 it was the administrative seat of Kamenz District. The town is known as the birthplace of the philosopher and poet Gotth ...
(), and Löbau
Löbau (; , ) is a city in the east of Saxony, Germany, in the traditional region of Upper Lusatia. It is situated between the slopes of the Löbauer Berg and the fertile hilly area of the Upper Lusatian Mountains. It is the gateway to this volca ...
()), as well as Żary
Żary (, , , ) is a town in western Poland with 37,502 inhabitants (2019), situated in the Lubusz Voivodeship. It is the administrative seat of the Żary County and of the Gmina Żary within the county, though the town is not part of the gmina (c ...
, the German/Polish twin towns of Guben
Guben (Polish language, Polish and Sorbian languages, Sorbian: ''Gubin'') is a town on the Lusatian Neisse river in Lower Lusatia, in the States of Germany, state of Brandenburg, in eastern Germany. Located in the Spree-Neiße Districts of German ...
() and Gubin, Hoyerswerda
Hoyerswerda () or Wojerecy () is a major district town in the district of Bautzen in the German state of Saxony. It is located in the Sorbian settlement area of Upper Lusatia, in which the Upper Sorbian language is spoken in addition to German.
...
(), Senftenberg
Senftenberg ( German, ) or (Lower Sorbian, ) is a town in Lower Lusatia, Brandenburg, in eastern Germany, capital of the Oberspreewald-Lausitz district.
Geography
Senftenberg is located in the southwest of the historic Lower Lusatia region at t ...
(), Eisenhüttenstadt
Eisenhüttenstadt (; ; ) is a town in the Oder-Spree district of the state of Brandenburg, in eastern Germany, on the border with Poland. East Germany founded the city in 1950. It was known as Stalinstadt () between 1953 and 1961.
Geography
Th ...
(), and Spremberg ().
Etymology
The name derives from the Sorbian word ''łužicy'' meaning "swamps" or "water-hole", Germanized as ''Lausitz''. ''Lusatia'' is theLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
ized form which spread in the English and Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
area.
Geography
 Lusatia comprises two both scenically and historically different parts: a hilly southern "upper" section and a "lower" region, which belongs to the
Lusatia comprises two both scenically and historically different parts: a hilly southern "upper" section and a "lower" region, which belongs to the North European Plain
The North European Plain ( – North German Plain; ; – Central European Plain; and ; French: ''Plaine d'Europe du Nord'') is a geomorphological region in Europe that covers all or parts of Belgium, the Netherlands (i.e. the Low Countries), ...
. The border between Upper and Lower Lusatia is roughly marked by the course of the Black Elster river at Senftenberg
Senftenberg ( German, ) or (Lower Sorbian, ) is a town in Lower Lusatia, Brandenburg, in eastern Germany, capital of the Oberspreewald-Lausitz district.
Geography
Senftenberg is located in the southwest of the historic Lower Lusatia region at t ...
and its eastern continuation toward the Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
n town of Przewóz on the Lusatian Neisse. Neighbouring regions were Silesia in the east, Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
in the south, the Margraviate of Meissen
The Margravate or Margraviate of Meissen () was a medieval principality in the area of the modern German state of Saxony. It originally was a frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, created out of the vast ''Marca Geronis'' ( Saxon Eastern March ...
, and the Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg
The Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg () was a medieval duchy of the Holy Roman Empire centered at Wittenberg, which emerged after the dissolution of the stem duchy of Saxony. The Ascanian dukes prevailed in obtaining the Saxon electoral dignity until ...
in the west as well as the Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg () was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that, having electoral status although being quite poor, grew rapidly in importance after inheriting the Duchy of Prussia in 1618 and then came ...
(Mittelmark
The Mittelmark (, ) is a historical region in eastern Germany that was the core territory of the Margrave of Brandenburg between the Oder and Elbe rivers.
The name refers to the location of the territory between the Altmark (Old March) and the N ...
) in the north.
Upper Lusatia
 Upper Lusatia (''Oberlausitz'', ''Łużyce Górne'' or ''Hornja Łužica'') is today part of the German state of Saxony, except for a small part east of the Neisse River around
Upper Lusatia (''Oberlausitz'', ''Łużyce Górne'' or ''Hornja Łužica'') is today part of the German state of Saxony, except for a small part east of the Neisse River around Lubań
Lubań (; ), sometimes called Lubań Śląski (; , ); is a town in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship in southwest Poland. It is the administrative seat of Lubań County and also of the smaller Gmina Lubań (although it is not part of the territory ...
, which now belongs to the Polish Lower Silesian voivodeship. It consists of hilly countryside rising in the South to the Lusatian Highlands
The Lusatian Highlands at www.silvaportal.info. Accessed on 10 July 2011. or Lusatian HillsCzech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus
*Czech (surnam ...
border, and then even higher to form the Zittau Hills, the small northern part of the Lusatian Mountains
The Lusatian Mountains (; ; ) are a mountain range of the Western Sudetes on the southeastern border of Germany with the Czech Republic. They are a continuation of the Ore Mountains range west of the Elbe valley. The mountains of the northern, G ...
(''Lužické hory''/''Lausitzer Gebirge'') in the Czech Republic.
Upper Lusatia is characterized by fertile soil and undulating hills as well as by historic towns and cities such as Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
, Görlitz
Görlitz (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, East Lusatian: , , ) is a town in the Germany, German state of Saxony. It is on the river Lusatian Neisse and is the largest town in Upper Lusatia, the second-largest town in the region of Lusatia after ...
, Zittau
Zittau (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, Upper Lusatian dialect: ''Sitte''; ) is the southeasternmost city in the Germany, German state of Saxony, and belongs to the Görlitz (district), district of Görlitz, Germany's easternmost Districts of Germ ...
, Löbau
Löbau (; , ) is a city in the east of Saxony, Germany, in the traditional region of Upper Lusatia. It is situated between the slopes of the Löbauer Berg and the fertile hilly area of the Upper Lusatian Mountains. It is the gateway to this volca ...
, Kamenz
Kamenz () or Kamjenc ( Sorbian, ) is a town (''Große Kreisstadt'') in the district of Bautzen in Saxony, Germany. Until 2008 it was the administrative seat of Kamenz District. The town is known as the birthplace of the philosopher and poet Gotth ...
, Lubań
Lubań (; ), sometimes called Lubań Śląski (; , ); is a town in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship in southwest Poland. It is the administrative seat of Lubań County and also of the smaller Gmina Lubań (although it is not part of the territory ...
, Bischofswerda
Bischofswerda (; ) is a small town in eastern Germany at the western edge of Upper Lusatia in Saxony.
Geography
The town is located 33 km to the east of Dresden at the edge of the Upper Lusatian mountain country. The town is known as t ...
, Herrnhut
Herrnhut (; ; ; Upper Lusatian: ''Harrnhutt'', ''Harrnutt'') is a town of around 6,000 inhabitants in Upper Lusatia, in the district of Görlitz, in eastern Saxony, Germany. The town is mainly known as the place of origin of the community of t ...
, Hoyerswerda
Hoyerswerda () or Wojerecy () is a major district town in the district of Bautzen in the German state of Saxony. It is located in the Sorbian settlement area of Upper Lusatia, in which the Upper Sorbian language is spoken in addition to German.
...
, and Bad Muskau
Bad Muskau (; formerly ''Muskau'', , , ) is a spa town in the historic Upper Lusatia region in eastern Germany, at the border with Poland. It is part of the Görlitz district in the State of Saxony.
It is located on the banks of the Lusatian Ne ...
. Many villages in the very south of Upper Lusatia contain a typical attraction of the region, the so-called ''Umgebindehäuser'', half-timbered-houses representing a combination of Franconian and Slavic style. Among those villages are Niedercunnersdorf, Obercunnersdorf, Wehrsdorf, Jonsdorf
The community of Jonsdorf is located in the south of the Kreis Görlitz in the southeast of the German federal state of Saxony. It is embedded into a valley of the Zittau Mountains, part of the Lusatian Mountains.
History
In 1539 Jonsdorf was fir ...
, Sohland an der Spree
Sohland an der Spree (German) or Załom (Upper Sorbian, ) is a municipality in the district of Bautzen in Saxony, Germany near the border of the Czech Republic in a region called Lusatia. The river Spree flows through the village. Together with s ...
with Taubenheim, Oppach, Varnsdorf
Varnsdorf (; ) is a town in the Ústí nad Labem Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 15,000 inhabitants. It lies on the border with Germany.
Administrative division
Varnsdorf consists of three municipal parts (in brackets population accordi ...
or Ebersbach.
Lower Lusatia
Most of the area belonging to the German state of Brandenburg today is called Lower Lusatia (''Niederlausitz, Łużyce Dolne'' or ''Dolna Łužyca'') and is characterized by forests and meadows. In the course of much of the 19th and the entire 20th century, it was shaped by the lignite industry and extensive open-pit mining. Important towns includeCottbus
Cottbus () or (;) is a university city and the second-largest city in the German state of Brandenburg after the state capital, Potsdam. With around 100,000 inhabitants, Cottbus is the most populous city in Lusatia. Cottbus lies in the Sorbian ...
, Eisenhüttenstadt
Eisenhüttenstadt (; ; ) is a town in the Oder-Spree district of the state of Brandenburg, in eastern Germany, on the border with Poland. East Germany founded the city in 1950. It was known as Stalinstadt () between 1953 and 1961.
Geography
Th ...
, Lübben, Lübbenau
Lübbenau (, ; officially Lübbenau/Spreewald, Lower Sorbian, L.S. Lubnjow/Błota (meaning ''Lübbenau/Spree Forest'') Polish language, Polish: ''Lubniów'') is a town in the Oberspreewald-Lausitz, Upper Spree Forest-Lusatia District of Brandenbu ...
, Spremberg, Finsterwalde
Finsterwalde (, , ) is a town in the Elbe-Elster district (German: Landkreis), in Lower Lusatia, Brandenburg, Germany.
Overview
It is situated on the Schackebach, a tributary of the Kleine Elster, 28 m. W.S.W of Cottbus by rail. Pop. (2005) 18,8 ...
, Senftenberg
Senftenberg ( German, ) or (Lower Sorbian, ) is a town in Lower Lusatia, Brandenburg, in eastern Germany, capital of the Oberspreewald-Lausitz district.
Geography
Senftenberg is located in the southwest of the historic Lower Lusatia region at t ...
(Zły Komorow), and Żary
Żary (, , , ) is a town in western Poland with 37,502 inhabitants (2019), situated in the Lubusz Voivodeship. It is the administrative seat of the Żary County and of the Gmina Żary within the county, though the town is not part of the gmina (c ...
, which is now considered the capital of Polish Lusatia.
Between Upper and Lower Lusatia is a region called the ''Grenzwall'', literally meaning "border dyke", although it is in fact a morainic
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice she ...
ridge. In the Middle Ages this area had dense forests, so it represented a major obstacle to civilian and military traffic. Some of the region's villages were damaged or destroyed by the open-pit lignite mining industry during the DDR era. Some, now exhausted, former open-pit mines are now being converted into artificial lakes, with the hope of attracting holiday-makers, and the area is now being referred to as the Lusatian Lake District
The Lusatian Lake District (, , ) is a chain of artificial lakes under construction in Germany across the north-eastern part of Saxony and the southern part of Brandenburg. Through flooding as a part of an extensive regeneration programme, sever ...
.
Lusatian capitals
As Lusatia is not, and never has been, a single administrative unit, Upper and Lower Lusatia have different, but in some respects similar, histories. The city ofCottbus
Cottbus () or (;) is a university city and the second-largest city in the German state of Brandenburg after the state capital, Potsdam. With around 100,000 inhabitants, Cottbus is the most populous city in Lusatia. Cottbus lies in the Sorbian ...
is the largest in the region, and though it is recognized as the cultural capital of Lower Lusatia, it was a Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
exclave since 1445. Historically, the administrative centres of Lower Lusatia were at Luckau
Luckau (Lower Sorbian: ''Łuków'') is a city in the district of Dahme-Spreewald in the States of Germany#States, federal state of Brandenburg, in eastern Germany. Known for its beauty, it has been dubbed "the Pearl of Lower Lusatia".
Origin of t ...
and Lübben, while the historical capital of Upper Lusatia is Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
. Since 1945, when a small part of Lusatia east of the Oder–Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line (, ) is an unofficial term for the Germany–Poland border, modern border between Germany and Poland. The line generally follows the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, meeting the Baltic Sea in the north. A small portion ...
was incorporated into Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
, Żary
Żary (, , , ) is a town in western Poland with 37,502 inhabitants (2019), situated in the Lubusz Voivodeship. It is the administrative seat of the Żary County and of the Gmina Żary within the county, though the town is not part of the gmina (c ...
has been touted as the capital of Polish Lusatia.
Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
(Budyšin), capital of Upper Lusatia
Cottbus 07-2017 img23 Altmarkt.jpg, Cottbus
Cottbus () or (;) is a university city and the second-largest city in the German state of Brandenburg after the state capital, Potsdam. With around 100,000 inhabitants, Cottbus is the most populous city in Lusatia. Cottbus lies in the Sorbian ...
(Chóśebuz), capital of Lower Lusatia
Lübben (Spreewald) - Paul-Gerhardt-Kirche.JPG, Lübben (Spreewald)
Lübben (Spreewald) (Lower Sorbian: ''Lubin (Błota)'' , Polish: ''Lubin'') is a town of 14,000 people, capital of the Dahme-Spreewald district in the Lower Lusatia region in Brandenburg, in eastern Germany.
Administrative structure
Districts o ...
(Lubin (Błota)), former capital of Lower Lusatia
Nicolaikirche in Luckau.jpg, Luckau
Luckau (Lower Sorbian: ''Łuków'') is a city in the district of Dahme-Spreewald in the States of Germany#States, federal state of Brandenburg, in eastern Germany. Known for its beauty, it has been dubbed "the Pearl of Lower Lusatia".
Origin of t ...
(Łuków), former capital of Lower Lusatia
Town hall in Zary (5).jpg, Żary
Żary (, , , ) is a town in western Poland with 37,502 inhabitants (2019), situated in the Lubusz Voivodeship. It is the administrative seat of the Żary County and of the Gmina Żary within the county, though the town is not part of the gmina (c ...
, capital of Polish Lusatia
Lusatian Lake District
 The Lusatian Lake District (German: Lausitzer Seenland, Lower Sorbian: Łužyska jazorina, Upper Sorbian: Łužiska jězorina) is an artificially created lake area. By the end of the 2020s, Europe's largest artificial water landscape and Germany's fourth-largest lake area are to be created by flooding disused brown coal mines in the Lusatian brown coal mining area. Some of the largest lakes are connected to each other as a chain of lakes by navigable canals.
The new lakeland is largely created from remaining holes from former brown coal opencast mines. These are flooded and converted into lakes. Some of the resulting lakes have already reached their final water level, others will not be completely flooded for a few years.
Other lakes are artificially dammed lakes. While the Quitzdorf Dam was created to provide enough process water for the Boxberg Power Station, the Spremberg Dam was primarily planned for flood protection in the lake district, but was also used for process water for power plants. The Bautzen Reservoir was also artificially created in order to be able to continuously supply the Boxberg Power Station with water.
The ponds of the Upper Lusatian Heath and Pond Landscape Biosphere Reserve, which are also located in the Lake District area, were partly created in the Middle Ages, but also during the GDR period for agricultural reasons, as the moor-rich land was restructured and made usable. These very shallow waters are mostly used for fish farming.
The ponds of the Muskau Arch are also located between the large opencast mining holes. They arose from faults in the terminal moraine of glaciers from the Ice Age, and partly through the mining of soil raw materials such as sand, clay and coal even before industrialization. In general, these ponds are not created intentionally by humans, but are filled with water due to a lack of drainage.
The Lusatian Lake District (German: Lausitzer Seenland, Lower Sorbian: Łužyska jazorina, Upper Sorbian: Łužiska jězorina) is an artificially created lake area. By the end of the 2020s, Europe's largest artificial water landscape and Germany's fourth-largest lake area are to be created by flooding disused brown coal mines in the Lusatian brown coal mining area. Some of the largest lakes are connected to each other as a chain of lakes by navigable canals.
The new lakeland is largely created from remaining holes from former brown coal opencast mines. These are flooded and converted into lakes. Some of the resulting lakes have already reached their final water level, others will not be completely flooded for a few years.
Other lakes are artificially dammed lakes. While the Quitzdorf Dam was created to provide enough process water for the Boxberg Power Station, the Spremberg Dam was primarily planned for flood protection in the lake district, but was also used for process water for power plants. The Bautzen Reservoir was also artificially created in order to be able to continuously supply the Boxberg Power Station with water.
The ponds of the Upper Lusatian Heath and Pond Landscape Biosphere Reserve, which are also located in the Lake District area, were partly created in the Middle Ages, but also during the GDR period for agricultural reasons, as the moor-rich land was restructured and made usable. These very shallow waters are mostly used for fish farming.
The ponds of the Muskau Arch are also located between the large opencast mining holes. They arose from faults in the terminal moraine of glaciers from the Ice Age, and partly through the mining of soil raw materials such as sand, clay and coal even before industrialization. In general, these ponds are not created intentionally by humans, but are filled with water due to a lack of drainage.
Halbendorfer See
Halbendorfer See is a lake in Saxony, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States o ...
(Brězowski jězor)
File:Sornoer Kanal.jpg, Sornoer Kanal (Žarnowski kanal) linking Geierswalder See to Sedlitzer See (Sedlišćański jazor)
Muskau Morainic Arch
The Muskau Morainic Arch is aterminal moraine
A terminal moraine, also called an end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed by the front e ...
formed during the Elster glaciation
The Elster glaciation (, ''Elster-Glazial'' or ''Elster-Zeit'') or, less commonly, the Elsterian glaciation, in the older and popular scientific literature also called the Elster Ice Age (''Elster-Eiszeit''), is the oldest known ice age that resu ...
, which together with its immediate surroundings forms the "UNESCO Global Geopark
UNESCO Global Geoparks (UGGp) are geoparks certified by the UNESCO Global Geoparks Council as meeting all the requirements for belonging to the Global Geoparks Network (GGN). The GGN is both a network of geoparks and the agency of the United Nati ...
Muskau Morainic Arch" (German: ''Muskauer Faltenbogen'', Sorbian: ''Mužakowski Zahork'', Polish: ''Łuk Mużakowa'').
A glacier on the inland ice that was up to 500 m thick compressed the sand and brown coal layers in front of and below it over a length of more than 40 km to form a small-scale fold arch with a compression terminal moraine up to 180 m high and 700 m wide. The structure is currently preserved as a flat, undulating hill range and is almost unique in the world. The meltwater lake that subsequently emerged within the horseshoe was filled with clays. Ice advances in the following cold periods eroded the higher parts of the terminal moraine. Due to oxidation and the associated loss of volume in the areas near the surface of the brown coal seams, furrows of 3 m to 5 m, a maximum of 20 m deep, 10 m to 30 m wide and up to several kilometers long were formed. Known as "Gieser" (from the Sorbian "jězor" for "lake"), they form long stretches of drainless ditches that are either filled with standing water or often peat-covered.
After already centuries of extraction of clay and sand, brown coal was mined in the area of the Muskau Arch in the 19th and 20th centuries, partly in pillar mining and partly in opencast mining. Due to the location of the mined seams, noticeably elongated lakes formed in the remaining holes north and east of Weißwasser
Weißwasser (, ; ) is a town in Upper Lusatia in eastern Saxony, Germany.
Weißwasser is the third largest town in the Görlitz (district), Görlitz district after Görlitz and Zittau. The town's landmark is its water tower. The town is part o ...
after the end of mining.
Weißwasser
Weißwasser (, ; ) is a town in Upper Lusatia in eastern Saxony, Germany.
Weißwasser is the third largest town in the Görlitz (district), Görlitz district after Görlitz and Zittau. The town's landmark is its water tower. The town is part o ...
and Gablenz
Upper Lusatian Heath and Pond Landscape
The Upper Lusatian Heath and Pond Landscape (German: ''Oberlausitzer Heide- und Teichlandschaft'', Upper Sorbian: ''Hornjołužiska hola a hatowa krajina'') is the region richest in ponds in Germany, and together with the Lower Lusatian Pond Landscape forms the biggest pond landscape in Central Europe.History
Early history
According to the earliest records, the area was settled by culturallyCeltic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
tribes. Later, around 100 BC, the Germanic Semnones
The Semnones were a Germanic and specifically a Suebi people, located between the Elbe and the Oder in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD.
They were described in the late 1st century by Tacitus in his ''Germania'':
"The Semnones give themselves out t ...
settled in that area. The name of the region may be derived from that of the Ligians. From around 600 onwards, West Slavic tribes known as the Milceni
The Milceni or Milzeni (; ; ) were a West Slavic tribe, who settled in the present-day Upper Lusatia region. They were gradually conquered by Germans during the 10th century. They were part of Sorbian tribes. Modern descendants of the Milceni are ...
and Lusici settled permanently in the region.
In the 10th century, the region came under the influence of the Kingdom of Germany
The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom ( 'kingdom of the Germans', 'German kingdom', "kingdom of Germany", ) was the mostly Germanic language-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843. The king was elec ...
, starting with the 928 eastern campaigns of King Henry the Fowler
Henry the Fowler ( or '; ; – 2 July 936) was the duke of Saxony from 912 and the king of East Francia from 919 until his death in 936. As the first non- Frankish king of East Francia, he established the Ottonian dynasty of kings and emper ...
. Until 963 the Lusatian tribes were subdued by the Saxon
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
margrave Gero
Gero I ( 900 – 20 May 965), sometimes called the Great (),Thompson, 486. Also se was a nobleman from East Francia who ruled an initially modest march centred on Merseburg in the south of the present German state of Saxony-Anhalt, which he ...
and upon his death two years later, the March of Lusatia
The March or Margraviate of Lusatia () was an eastern border march of the Holy Roman Empire in the lands settled by Polabian Slavs. It arose in 965 in the course of the partition of the vast ''Marca Geronis''. Ruled by several Saxon margravial dy ...
was established on the territory of today's Lower Lusatia and remained with the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, while the adjacent Northern March
The Northern March or North March (, ) was created out of the division of the vast ''Marca Geronis'' in 965. It initially comprised the northern third of the ''Marca'' (roughly corresponding to the modern state of Brandenburg) and was part of the ...
again got lost in the Slavic uprising of 983. The later Upper Lusatian region of the Milceni lands up to the Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
n border at the Kwisa
The Kwisa (, , ) is a river in south-western Poland, a left tributary of the Bóbr, which itself is a left tributary of the Oder river.
It rises in the Jizera Mountains, part of the Western Sudetes range, where it runs along the border with t ...
river at first was part of the Margraviate of Meissen
The Margravate or Margraviate of Meissen () was a medieval principality in the area of the modern German state of Saxony. It originally was a frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, created out of the vast ''Marca Geronis'' ( Saxon Eastern March ...
under Margrave Eckard I.
 At the same time the Polan duke of the later
At the same time the Polan duke of the later Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland (; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a monarchy in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval period from 1025 until 1385.
Background
The West Slavs, West Slavic tribe of Polans (western), Polans who lived in what i ...
raised claims to the Lusatian lands and upon the death of Emperor Otto III
Otto III (June/July 980 – 23 January 1002) was the Holy Roman emperor and King of Italy from 996 until his death in 1002. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto III was the only son of Emperor Otto II and his wife Theophanu.
Otto III was c ...
in 1002, Margrave Gero II
Gero II (c. 975 – 1 September 1015 at Krosno Odrzańskie) was the eldest son of Thietmar, Margrave of Meissen, and Swanehilde of Saxony, Schwanehilde (Suanhild), daughter of Herman, Duke of Saxony. He was therefore probably a grandson of ...
lost Lusatia to the Polish Duke Boleslaw I the Brave, who took the region in his conquests, acknowledged by Henry II first in the same year in Merseburg and later in the 1018 Peace of Bautzen
The Peace of Bautzen (; ; ) was a treaty concluded on 30 January 1018, between Holy Roman Emperor Henry II and Bolesław I of Poland which ended a series of Polish-German wars over the control of Lusatia and Upper Lusatia (''Milzenerland'' or ...
, Lusatia became part of his territory; however, Germans and Poles continued to struggle over the administration of the region. It was regained in a 1031 campaign by Emperor Conrad II in favour of the Saxon German rulers of the Meissen House of Wettin
The House of Wettin () was a dynasty which included Saxon monarch, kings, Prince Elector, prince-electors, dukes, and counts, who once ruled territories in the present-day German federated states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynas ...
and the Ascanian
The House of Ascania () was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Anhalt.
The Ascanians are named after Ascania (or Ascaria) Castle, known as ''Schloss Askanien'' in ...
margraves of Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
, who purchased the March of (Lower) Lusatia in 1303.
In 1367 the Brandenburg elector Otto V of Wittelsbach finally sold Lower Lusatia to King Karel
Karel may refer to:
People
* Karel (given name)
* Karel (surname)
* Charles Karel Bouley (born 1962), American talk radio personality known on air as Karel
* Christiaan Karel Appel (1921–2006), Dutch painter and sculptor
Business
* Karel Elec ...
of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
, thereby becoming a Bohemian crown land.
Bohemian rule
 As Margrave Egbert II of Meissen supported
As Margrave Egbert II of Meissen supported anti-king
An anti-king, anti king or antiking (; ) is a would-be king who, due to succession disputes or simple political opposition, declares himself king in opposition to a reigning monarch. OED "Anti-, 2" The OED does not give "anti-king" its own entry ...
Rudolf of Rheinfelden
Rudolf of Rheinfelden ( – 15 October 1080) was Duke of Swabia from 1057 to 1079. Initially a follower of his brother-in-law, the Salian emperor Henry IV, his election as German anti-king in 1077 marked the outbreak of the Great Saxon Revolt a ...
during the Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy or Investiture Contest (, , ) was a conflict between church and state in medieval Europe, the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops (investiture), abbots of monasteri ...
, King Henry IV of Germany
Henry IV (; 11 November 1050 – 7 August 1106) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1084 to 1105, King of Germany from 1054 to 1105, King of Italy and Burgundy from 1056 to 1105, and Duke of Bavaria from 1052 to 1054. He was the son of Henry III, Holy R ...
in 1076 awarded the Milceni lands of Upper Lusatia as a fief to the Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
n duke Vratislav II. After Emperor Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (; ), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death in 1190. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aachen on 9 March 115 ...
had elevated Duke Vladislaus II to the rank of a King of Bohemia in 1158, the Upper Lusatian lands around Bautzen evolved into a Bohemian crown land. Around 1200, large numbers of German settlers came to Lusatia in the course of the ''Ostsiedlung
(, ) is the term for the Early Middle Ages, early medieval and High Middle Ages, high medieval migration of Germanic peoples and Germanisation of the areas populated by Slavs, Slavic, Balts, Baltic and Uralic languages, Uralic peoples; the ...
'', settling in the forested areas yet not inhabited by the Slavs. For centuries, from as early as the Middle Ages, trade flourished, and several important trade routes ran through Lusatia, connecting German states in the west, Poland in the east and Bohemia in the south. In 1319, the region was divided between the Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the pr ...
and the Duchy of Jawor
Duchy of Jawor (, ) was one of the duchies of Silesia and medieval Poland established in 1274 as a subdivision of the Duchy of Legnica. It was ruled by the Silesian Piasts, with its capital at Jawor in Lower Silesia.
It was the southwesternmost ...
, the southwesternmost duchy of fragmented Piast
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of King Casimir III the Great.
Branches of ...
-ruled Poland, while northernmost parts also passed to the Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg () was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that, having electoral status although being quite poor, grew rapidly in importance after inheriting the Duchy of Prussia in 1618 and then came ...
in the following years. From 1368, it was entirely part of the Bohemian Crown.
In 1346 six Upper Lusatian cities formed the Lusatian League
The Lusatian League () was a historical alliance of six towns in the region of Upper Lusatia from 1346 until 1815, when the region was controlled first by Bohemia (1346–1635) and later by the Electorate of Saxony (1635–1815). The member towns ...
to resist the constant attacks conducted by robber barons. The association supported King Sigismund Sigismund (variants: Sigmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it ''Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of ...
in the Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, a ...
leading to armed attacks and devastation. The cities were represented in the (Upper) Lusatian ''Landtag
A ''Landtag'' (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence ...
'' assembly, where they met with the fierce opposition of the noble state countries. In 1469 the region passed to Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, and in 1490 it returned to the Bohemian Crown, then under the rule of Polish Prince Vladislaus II.
Following the Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
Reformation, the greater part of Lusatia became Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
except for the area between Bautzen, Kamenz and Hoyerswerda. The Lusatias remained under Bohemian rule – from 1526 onwards under the rule of the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful Dynasty, dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout ...
– until the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
.
Saxon rule

 According to the 1635 Peace of Prague, most of Lusatia became a province of the
According to the 1635 Peace of Prague, most of Lusatia became a province of the Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony ( or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356 to 1806 initially centred on Wittenberg that came to include areas around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz. It was a ...
, except for the region around Cottbus possessed by Brandenburg. After the Saxon elector Augustus the Strong
Augustus II the Strong (12 May 1670 – 1 February 1733), was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1697 to 1706 and from 1709 until his death in 1733. He belonged to the Albertine branch of the ...
was elected king of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
in 1697, Lusatia became strategically important as the elector-kings sought to create a land connection between their Saxon homelands and the Polish territories. Two main routes connecting Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
and Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most p ...
ran through the region in the 18th century and Kings Augustus II the Strong
Augustus II the Strong (12 May 1670 – 1 February 1733), was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1697 to 1706 and from 1709 until his death in 1733. He belonged to the Albertine branch of the H ...
and Augustus III of Poland
Augustus III (; – "the Saxon"; ; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was List of Polish monarchs, King of Poland and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as List of rulers of Saxony, Elector of Saxony i ...
often traveled the routes. Numerous Polish dignitaries also traveled through Lusatia on several occasions, and some Polish nobles owned estates in Lusatia. A distinct remnant of the region's ties to Poland are the 18th-century milepost
A milestone is a numbered marker placed on a route such as a road, railway, railway line, canal or border, boundary. They can indicate the distance to towns, cities, and other places or landmarks like Mileage sign, mileage signs; or they c ...
s decorated with the coat of arms of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth located in various towns in the region. Polish-Sorbian contacts increased in that period. With the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
, the Sorbian national revival began and resistance to Germanization emerged.
Herrnhut
Herrnhut (; ; ; Upper Lusatian: ''Harrnhutt'', ''Harrnutt'') is a town of around 6,000 inhabitants in Upper Lusatia, in the district of Görlitz, in eastern Saxony, Germany. The town is mainly known as the place of origin of the community of t ...
, between Löbau
Löbau (; , ) is a city in the east of Saxony, Germany, in the traditional region of Upper Lusatia. It is situated between the slopes of the Löbauer Berg and the fertile hilly area of the Upper Lusatian Mountains. It is the gateway to this volca ...
and Zittau
Zittau (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, Upper Lusatian dialect: ''Sitte''; ) is the southeasternmost city in the Germany, German state of Saxony, and belongs to the Görlitz (district), district of Görlitz, Germany's easternmost Districts of Germ ...
, founded in 1722 by religious refugees from Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
on the estate of Count Nicolaus Zinzendorf
Nikolaus Ludwig, Reichsgraf
Imperial Count (, ) was a title in the Holy Roman Empire. During the medieval era, it was used exclusively to designate the holder of an imperial county, that is, a fief held directly (Imperial immediacy, immediat ...
became the starting point of the organized Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
missionary
A missionary is a member of a Religious denomination, religious group who is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thoma ...
movement in 1732 and missionaries went out from the Moravian Church
The Moravian Church, or the Moravian Brethren ( or ), formally the (Latin: "Unity of the Brethren"), is one of the oldest Protestant denominations in Christianity, dating back to the Bohemian Reformation of the 15th century and the original ...
in Herrnhut to all corners of the world to share the Gospel.
The newly established Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony () was a German monarchy in Central Europe between 1806 and 1918, the successor of the Electorate of Saxony. It joined the Confederation of the Rhine after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, later joining the German ...
, however, sided with Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
; therefore, at the 1815 Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
, Lusatia was divided, with Lower Lusatia and the northeastern part of Upper Lusatia around Hoyerswerda
Hoyerswerda () or Wojerecy () is a major district town in the district of Bautzen in the German state of Saxony. It is located in the Sorbian settlement area of Upper Lusatia, in which the Upper Sorbian language is spoken in addition to German.
...
, Rothenburg, Görlitz
Görlitz (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, East Lusatian: , , ) is a town in the Germany, German state of Saxony. It is on the river Lusatian Neisse and is the largest town in Upper Lusatia, the second-largest town in the region of Lusatia after ...
, and Lauban awarded to Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
. Only the southwestern part of Upper Lusatia, which included Löbau
Löbau (; , ) is a city in the east of Saxony, Germany, in the traditional region of Upper Lusatia. It is situated between the slopes of the Löbauer Berg and the fertile hilly area of the Upper Lusatian Mountains. It is the gateway to this volca ...
, Kamenz
Kamenz () or Kamjenc ( Sorbian, ) is a town (''Große Kreisstadt'') in the district of Bautzen in Saxony, Germany. Until 2008 it was the administrative seat of Kamenz District. The town is known as the birthplace of the philosopher and poet Gotth ...
, Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
, and Zittau
Zittau (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, Upper Lusatian dialect: ''Sitte''; ) is the southeasternmost city in the Germany, German state of Saxony, and belongs to the Görlitz (district), district of Görlitz, Germany's easternmost Districts of Germ ...
, remained part of Saxony.
Prussian rule
The Lusatians in Prussia demanded that their land become a distinct administrative unit, but Lower Lusatia was incorporated into theProvince of Brandenburg
The Province of Brandenburg () was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1947. Brandenburg was established in 1815 from the Kingdom of Prussia's core territory, comprised the bulk of the historic Margraviate of Brandenburg (excluding Altmark) and ...
, while the Upper Lusatian territories were attached to the Province of Silesia
The Province of Silesia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1919. The Silesia region was part of the Prussian realm since 1742 and established as an official province in 1815, then became part of the German Empire in 1871. In 1919, as ...
instead.
One of the main escape routes for insurgents of the unsuccessful Polish November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31) (), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in Russian Partition, the heartland of Partitions of Poland, partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. ...
from partitioned Poland to the Great Emigration
The Great Emigration () was the emigration of thousands of Poles and Lithuanians, particularly from the political and cultural élites, from 1831 to 1870, after the failure of the November Uprising of 1830–1831 and of other uprisings such as ...
led through Lübben and Luckau
Luckau (Lower Sorbian: ''Łuków'') is a city in the district of Dahme-Spreewald in the States of Germany#States, federal state of Brandenburg, in eastern Germany. Known for its beauty, it has been dubbed "the Pearl of Lower Lusatia".
Origin of t ...
.
The 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed an era of cultural revival for Sorbs. The modern languages of Upper and Lower Lusatian (or Sorbian) emerged, national literature flourished, and many national organizations such as Maćica Serbska Maćica Serbska (Upper Sorbian language, Upper Sorbian name, ; ) is a scientific association of Sorbs. It aims at promoting Sorbian studies and disseminating knowledge about the Sorbs and their culture. It is the oldest Sorbian association that is ...
and Domowina
Domowina () is a political independent league of the Sorbian and Wendish people and umbrella organization of Sorbian societies in Lower and Upper Lusatia, Germany. It represents the interests of Sorbian people and is the continual successor of ...
were founded. There were also notable Polish communities in Lusatia, such as Klettwitz (, ), inhabited in the 1930s by some 550 Poles.
In the interbellum, the German government carried out a massive campaign of changing of place names in Lusatia in order to erase traces of Slavic origin, and while most of the historic names were restored after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, some were retained.
This era came to an end during the Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
regime in Germany, when all Sorbian organizations were abolished and forbidden, newspapers and magazines closed, and any use of the Sorbian languages was prohibited. During World War II, some Sorbian activists were arrested, executed, exiled or sent as political prisoner
A political prisoner is someone imprisoned for their political activity. The political offense is not always the official reason for the prisoner's detention.
There is no internationally recognized legal definition of the concept, although ...
s to concentration camps
A concentration camp is a prison or other facility used for the internment of political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or ethnic minority groups, on the grounds of national security, or for exploit ...
. From 1942 to 1944 the underground Lusatian National Committee was formed and was active in German-occupied Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
.
During the war, the Germans established and operated several prisoner-of-war camps
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a ...
, including Oflag III-C, Oflag IV-D, Oflag 8, Stalag III-B, Stalag IV-A and Stalag VIII-A
Stalag VIII-A was a German World War II prisoner-of-war camp, located just to the south of the town of Görlitz in Lower Silesia, east of the River Neisse. The location of the camp lies in today's Polish town of Zgorzelec, which lies over the r ...
, with multiple forced labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, or violence, including death or other forms of ...
subcamps in the region. Prisoners included Polish POWs and civilians, and French, Belgian, British, Australian, New Zealander, Canadian, South African, Dutch, Italian, Soviet, Serbian, Slovak and American POWs. There were also several Nazi prisons with multiple forced labour subcamps, including in Görlitz
Görlitz (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, East Lusatian: , , ) is a town in the Germany, German state of Saxony. It is on the river Lusatian Neisse and is the largest town in Upper Lusatia, the second-largest town in the region of Lusatia after ...
, Luckau
Luckau (Lower Sorbian: ''Łuków'') is a city in the district of Dahme-Spreewald in the States of Germany#States, federal state of Brandenburg, in eastern Germany. Known for its beauty, it has been dubbed "the Pearl of Lower Lusatia".
Origin of t ...
, Zittau
Zittau (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, Upper Lusatian dialect: ''Sitte''; ) is the southeasternmost city in the Germany, German state of Saxony, and belongs to the Görlitz (district), district of Görlitz, Germany's easternmost Districts of Germ ...
, and a prison solely for women in Cottbus
Cottbus () or (;) is a university city and the second-largest city in the German state of Brandenburg after the state capital, Potsdam. With around 100,000 inhabitants, Cottbus is the most populous city in Lusatia. Cottbus lies in the Sorbian ...
, and multiple subcamps of the Gross-Rosen concentration camp
Gross-Rosen was a network of Nazi concentration camps built and operated by Nazi Germany during World War II. The main camp was located in the German village of Gross-Rosen, now the modern-day Rogoźnica in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Poland, di ...
, the prisoners of which were mostly Jews, Poles and Russians, but also Frenchmen, Italians, Yugoslavs, Czechs, Belgians, etc.
 During the war, the Poles postulated that after the defeat of Germany, the Sorbs should be allowed free national development either within the borders of Poland or
During the war, the Poles postulated that after the defeat of Germany, the Sorbs should be allowed free national development either within the borders of Poland or Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
, or as an independent Sorbian state in alliance with Poland.
The Eastern Front reached Lusatia in early 1945, with Soviet and Polish troops defeating the Germans and capturing the region. In Horka, on April 26, 1945, the Germans carried out a massacre of a field hospital column of the 9th Polish Armored Division, killing some 300 POWs, mostly wounded soldiers and medical personnel (see '' German atrocities committed against Polish prisoners of war'').
Since 1945
 After World War II according to the
After World War II according to the Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement () was the agreement among three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union after the war ended in Europe that was signed on 1 August 1945 and published the following day. A ...
, Lusatia was divided between Allied-occupied Germany
The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II, from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Nazi Germany was stripped of its sov ...
(Soviet occupation zone
The Soviet occupation zone in Germany ( or , ; ) was an area of Germany that was occupied by the Soviet Union as a communist area, established as a result of the Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945. On 7 October 1949 the German Democratic Republ ...
) and the Republic of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
along the Oder–Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line (, ) is an unofficial term for the Germany–Poland border, modern border between Germany and Poland. The line generally follows the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, meeting the Baltic Sea in the north. A small portion ...
. Poland's communist government expelled all remaining Germans and Sorbs from the area east of the Neisse river in 1945 and 1946 in accordance with the Potsdam Agreement. The Lusatian National Committee in Prague claimed the right to self-government and separation from Germany and the creation of a Lusatian Free State or attachment to Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
. The majority of the Sorbian intelligentsia was organized in the Domowina
Domowina () is a political independent league of the Sorbian and Wendish people and umbrella organization of Sorbian societies in Lower and Upper Lusatia, Germany. It represents the interests of Sorbian people and is the continual successor of ...
, though, and did not wish to split from Germany. Claims asserted by the Lusatian National movement were postulates of joining Lusatia to Poland or Czechoslovakia. Between 1945 and 1947 they produced about ten memorials to the United States, Soviet Union, Great Britain, France, Poland, and Czechoslovakia; however, this did not bring any results. On 30 April 1946, the Lusatian National Committee also submitted a petition to the Polish Government, signed by Paweł Cyż – the minister and an official Sorbian delegate in Poland. There was also a project to proclaim a Lusatian Free State, whose Prime Minister was intended to be the Polish archaeologist of Lusatian origin, Wojciech Kóčka.
In 1945, the northeastern part of Upper Lusatia west of the Neisse rejoined Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
and in 1952, when the state was divided into three administrative areas (''Bezirke''), the Upper Lusatian region became part of the Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most p ...
administrative region. After the East German Revolution of 1989, the state of Saxony was reestablished in 1990. Lower Lusatia remained with Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
, from 1952 until 1990 in the ''Bezirk'' of Cottbus
Cottbus () or (;) is a university city and the second-largest city in the German state of Brandenburg after the state capital, Potsdam. With around 100,000 inhabitants, Cottbus is the most populous city in Lusatia. Cottbus lies in the Sorbian ...
.
In 1950, the Sorbs obtained language and cultural autonomy within the then–East German state of Saxony. Lusatian schools and magazines were launched and the Domowina association was revived, although under increasing political control of the ruling Communist Socialist Unity Party of Germany
The Socialist Unity Party of Germany (, ; SED, ) was the founding and ruling party of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) from the country's foundation in 1949 until its dissolution after the Peaceful Revolution in 1989. It was a Mar ...
(SED). At the same time, the large German-speaking majority of the Upper Lusatian population kept up a considerable degree of local, 'Upper Lusatian' patriotism of its own. An attempt to establish a Lusatian ''Land'' within the Federal Republic of Germany failed after German reunification
German reunification () was the process of re-establishing Germany as a single sovereign state, which began on 9 November 1989 and culminated on 3 October 1990 with the dissolution of the East Germany, German Democratic Republic and the int ...
in 1990. The constitutions of Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
and Brandenburg guarantee cultural rights, but not autonomy, to the Sorbs.
Demographics
Sorbs

Slavic
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Peoples
* Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia
** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples
** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples
** West Slav ...
minority continue to live in the region. Historically, their ancestors are West-Slavic-speaking tribes such as the Milceni
The Milceni or Milzeni (; ; ) were a West Slavic tribe, who settled in the present-day Upper Lusatia region. They were gradually conquered by Germans during the 10th century. They were part of Sorbian tribes. Modern descendants of the Milceni are ...
, who settled in the region between the Elbe
The Elbe ( ; ; or ''Elv''; Upper Sorbian, Upper and , ) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Republic), then Ge ...
and the Saale
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale ( ) and Thuringian Saale (), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Fränkische Saale, Franconian Saale, a right-bank tributary of the M ...
. Many still speak their language (though numbers are dwindling and especially Lower Sorbian
Lower may refer to:
* ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is sit ...
is considered endangered), and road signs are usually bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
. However, the number of all the inhabitants of this part of eastern Saxony is declining rapidly – by 20% in the last 10 to 15 years. Sorbs make efforts to protect their traditional culture manifested in the traditional folk costumes and the style of village houses. The coal industry in the region (like the Schwarze Pumpe power station needing vast areas of land) destroyed dozens of Lusatian villages in the past and threatens some of them even now. The Sorbian language is taught at many primary and some secondary schools and at two universities (Leipzig and Prague). Project "Witaj" ("welcome!") is a project of eight preschools where Sorbian is currently the main language for a few hundred Lusatian children.
There is a daily newspaper in the Sorbian language (''Serbske Nowiny''); a Sorbian radio station (Serbski Rozhłós) uses local frequencies of two otherwise German-speaking radio stations for several hours a day. There are very limited programmes on television (once a month) in Sorbian on two regional television stations ( RBB and MDR MDR may refer to:
Biology
* MDR1, an ATP-dependent cellular efflux pump affording multiple drug resistance
* Mammalian diving reflex
* Medical device reporting
* Multiple drug resistance, when a microorganism has become resistant to multiple drugs ...
TV).
In 2020, despite the loss of the Sorbian language in most of Lusatia, there are some Sorbian traditions and habits that still live on to this day. In February, many people (mostly people from villages, regardless of German or Sorbian ancestry) will still engage in the Sorbian tradition of '' Zampern'' (a festive procession)''.'' Some Sorbian dishes like boiled potatoes with linseed oil and curd (German: ''Quark mit Leineöl'') are still prevalent and, today, are eaten in other parts of Germany (like Berlin or western Saxony) too. ''Spreewälder Gurken'' (pickled cucumbers potted by using a special mixture of herbs and spices) are often associated with the Sorbs even though the cucumbers themselves were introduced by Dutch migrants, who started to pickle them for higher durability. Soon Sorbs adopted the pickling and might have changed the recipes slightly over time.
The traditional Sorbian costumes are still to be worn in the Spreewald region even though mainly in the tourism industry. Recently, some women started to revive traditional clothes by using them as wedding dresses, even though this practise differs from original traditions.
Demographics in 1900
Percentage ofSorbs
Sorbs (; ; ; ; ; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Germany, states of Saxony and Brandenburg. Sorbs tradi ...
:
*Cottbus
Cottbus () or (;) is a university city and the second-largest city in the German state of Brandenburg after the state capital, Potsdam. With around 100,000 inhabitants, Cottbus is the most populous city in Lusatia. Cottbus lies in the Sorbian ...
(Chóśebuz) (Province of Brandenburg
The Province of Brandenburg () was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1947. Brandenburg was established in 1815 from the Kingdom of Prussia's core territory, comprised the bulk of the historic Margraviate of Brandenburg (excluding Altmark) and ...
) 55.8%
*Hoyerswerda
Hoyerswerda () or Wojerecy () is a major district town in the district of Bautzen in the German state of Saxony. It is located in the Sorbian settlement area of Upper Lusatia, in which the Upper Sorbian language is spoken in addition to German.
...
(Wojerecy) (Province of Silesia
The Province of Silesia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1919. The Silesia region was part of the Prussian realm since 1742 and established as an official province in 1815, then became part of the German Empire in 1871. In 1919, as ...
) 37.8%
*Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
(Budyšin) (Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony () was a German monarchy in Central Europe between 1806 and 1918, the successor of the Electorate of Saxony. It joined the Confederation of the Rhine after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, later joining the German ...
) 17.7%
*Rothenburg, Oberlausitz
Rothenburg/Oberlausitz (; , ; ) is a small Lusatian town in eastern Saxony, in eastern Germany, on the Neisse river on the Germany–Poland border. It has a population of 4,405 (2020).
History
The town was first mentioned in 1268. In 1319, it be ...
(Rózbork) (Province of Silesia) 17.2%
*Kamenz
Kamenz () or Kamjenc ( Sorbian, ) is a town (''Große Kreisstadt'') in the district of Bautzen in Saxony, Germany. Until 2008 it was the administrative seat of Kamenz District. The town is known as the birthplace of the philosopher and poet Gotth ...
(Kamjenc) (Kingdom of Saxony) 7.1%
Total number: 93,032
The percentage of Serbs (Sorbs) in Lusatia has decreased since the 1900 census due to intermarriage, germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, German people, people, and German culture, culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nati ...
, cultural assimilation related to industrialization and urbanization, Nazi suppression and discrimination, ethnocide
Ethnocide is the extermination or destruction of ethnic identities. Bartolomé Clavero differentiates ethnocide from genocide by stating that "Genocide kills people while ethnocide kills social cultures through the killing of individual souls". ...
and the settlement of expelled Germans after World War II, mainly from Lower Silesia and northern Bohemia.
Largest cities
Culture
Sights
The region is rich in architecture from various reigns, including Czech, Polish, German and Hungarian, whose styles range from Romanesque and Gothic throughRenaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
and Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
to modern architecture.
There are two major Sorbian museums in Cottbus
Cottbus () or (;) is a university city and the second-largest city in the German state of Brandenburg after the state capital, Potsdam. With around 100,000 inhabitants, Cottbus is the most populous city in Lusatia. Cottbus lies in the Sorbian ...
(''Serbski muzej Chóśebuz'') and Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
(''Serbski muzej Budyšin'').
In Poland, notable museums include the ''Muzeum Łużyckie'' ("Lusatian Museum") in Zgorzelec
Zgorzelec (, , , , Lower Sorbian: ''Zgórjelc'') is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in southwestern Poland, with 30,374 inhabitants (2019). It is the seat of Zgorzelec County and of Gmina Zgorzelec (although it is not part of the territory ...
and the ''Muzeum Pogranicza Śląsko-Łużyckiego'' ("Museum of Silesian-Lusatian Borderland") in Żary
Żary (, , , ) is a town in western Poland with 37,502 inhabitants (2019), situated in the Lubusz Voivodeship. It is the administrative seat of the Żary County and of the Gmina Żary within the county, though the town is not part of the gmina (c ...
.
Zgorzelec is home to one of Poland's largest war cemeteries.
The CargoLifter airship hangar that now houses the Tropical Islands Resort is the largest freebearing hall in the world.
The Saurierpark Kleinwelka is Germany's largest dinosaur park.
UNESCO world heritage sites
TheMuskau Park
Muskau Park (, officially: ''Fürst-Pückler-Park Bad Muskau''; ) is a landscape park in the Upper Lusatia region of Germany and Poland. It is the largest and one of the most famous English gardens in Central Europe, stretching along both sides ...
in Bad Muskau
Bad Muskau (; formerly ''Muskau'', , , ) is a spa town in the historic Upper Lusatia region in eastern Germany, at the border with Poland. It is part of the Görlitz district in the State of Saxony.
It is located on the banks of the Lusatian Ne ...
(''Mužakow'') and Łęknica
Łęknica (; , ) is a border town in western Poland, one of the two gminas of Żary County in Lubusz Voivodeship.
Muskau Park (''Park Mużakowski''), a Polish-German World Heritage Site and Historic Monument of Poland, stretches north of the ...
is a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
and Historic Monument of Poland.
Herrnhut
Herrnhut (; ; ; Upper Lusatian: ''Harrnhutt'', ''Harrnutt'') is a town of around 6,000 inhabitants in Upper Lusatia, in the district of Görlitz, in eastern Saxony, Germany. The town is mainly known as the place of origin of the community of t ...
is also a UNESCO world heritage site since 2024.
The Spree Forest as well as the Upper Lusatian Heath and Pond Landscape are UNESCO biosphere reserves.
Gallery
Muskau Park
Muskau Park (, officially: ''Fürst-Pückler-Park Bad Muskau''; ) is a landscape park in the Upper Lusatia region of Germany and Poland. It is the largest and one of the most famous English gardens in Central Europe, stretching along both sides ...
File:20-05-13-Tropical-Islands-0883 1-RalfR.jpg, CargoLifter airship hangar
File:Tropical Islands Draufsicht.JPG, Tropical Islands Resort
File:Im Spreewald 03.jpg, Spree Forest
File:D-SN-Boxberg - Kraftwerk Boxberg.jpg, Findlingspark Nochten (Nochten Glacial Erratic Park)
File:Slawenburg Raddusch (Raduš) 01.JPG, Raddusch Slavic Castle
File:Blick vom Götzen Stein im Zittauer Gebirge...2H1A9275WI.jpg, Olbersdorfer See
File:Zittauer Schmalspurbahn - panoramio.jpg, Zittau–Oybin/Jonsdorf railway
File:Kromlau Asiatische-Brücke Inselteich 20240520 123012.jpg, Kromlau Azalea and Rhododendron Park
The Kromlau Azalea and Rhododendron Park (German: ''Azaleen- und Rhododendronpark Kromlau''; Upper Sorbian: ''Acalejowy a Rododendronowy Park Kromola'') is an landscaped park in the village of Kromlau (Upper Sorbian: Kromola), in the municipal ...
File:Erlebnispark "Teichland" (Naturschutzgebiet bei Peitz).jpg, Teichland tower
File:Cottbus 07-2017 img03 Teichland.jpg, Grove of Slavic Gods
File:Lausitzer Seenland 2022.jpg, Lusatian Lake District
The Lusatian Lake District (, , ) is a chain of artificial lakes under construction in Germany across the north-eastern part of Saxony and the southern part of Brandenburg. Through flooding as a part of an extensive regeneration programme, sever ...
File:Kleiner Schwielochsee 03.JPG, Schwielochsee
File:Bautzen Kleinwelka - Saurierpark 01 ies.jpg, Saurierpark Kleinwelka
File:Oybin (21774610218).jpg, Oybin mountain cemetery
File:Blick auf den Berg Oybin in Zittauer Gebirge..2H1A9122WI.jpg, Oybin castle ruin
See also
*Herrnhut
Herrnhut (; ; ; Upper Lusatian: ''Harrnhutt'', ''Harrnutt'') is a town of around 6,000 inhabitants in Upper Lusatia, in the district of Görlitz, in eastern Saxony, Germany. The town is mainly known as the place of origin of the community of t ...
Moravian Church
The Moravian Church, or the Moravian Brethren ( or ), formally the (Latin: "Unity of the Brethren"), is one of the oldest Protestant denominations in Christianity, dating back to the Bohemian Reformation of the 15th century and the original ...
and Nicolaus Zinzendorf
Nikolaus Ludwig, Reichsgraf
Imperial Count (, ) was a title in the Holy Roman Empire. During the medieval era, it was used exclusively to designate the holder of an imperial county, that is, a fief held directly (Imperial immediacy, immediat ...
* Lusatian League
The Lusatian League () was a historical alliance of six towns in the region of Upper Lusatia from 1346 until 1815, when the region was controlled first by Bohemia (1346–1635) and later by the Electorate of Saxony (1635–1815). The member towns ...
* Milceni
The Milceni or Milzeni (; ; ) were a West Slavic tribe, who settled in the present-day Upper Lusatia region. They were gradually conquered by Germans during the 10th century. They were part of Sorbian tribes. Modern descendants of the Milceni are ...
* Wends
Wends is a historical name for Slavs who inhabited present-day northeast Germany. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying ...
* Obotrites
The Obotrites (, ''Abodritorum'', ''Abodritos'') or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany (see Polabian Slavs). For ...
References
Sources
* Micklitza, Kerstin and André: ''Lausitz – Unterwegs zwischen Spreewald und Zittauer Gebirge''. 5. aktualisierte und erweiterte Aufl. Trescher Verlag, Berlin 2016. . * Brie, André: ''Lausitz – Landschaft mit neuem Gesicht''.Michael Imhof Verlag
Michael Imhof Verlag is a German publishing company in Petersberg, Hesse. They are known especially for publishing books with a local interest, on art, on history, politics, religion, nature, and culture. Besides titles in German
German(s) may r ...
, Petersberg 2011. .
* Micklitza, Kerstin and André: ''HB-Bildatlas Spreewald-Lausitz''. 4. aktualisierte Aufl. HB Verlag, Ostfildern 2008. .
* Jacob, Ulf: ''Zwischen Autobahn und Heide. Das Lausitzbild im Dritten Reich. Eine Studie zur Entstehung, Ideologie und Funktion symbolischer Sinnwelten''. Hrsg. von der Internationalen Bauausstellung Fürst-Pückler-Land, Großräschen (''Zeitmaschine Lausitz''), Verlag der Kunst, Dresden in der Verlagsgruppe Husum, Husum 2004. .
* Freiherr von Vietinghoff-Riesch, Arnold: ''Der Oberlausitzer Wald – seine Geschichte und seine Struktur bis 1945'' eprint
In academic publishing, an eprint or e-print is a digital version of a research document (usually a journal article, but could also be a thesis, conference paper, book chapter, or a book) that is accessible online, usually as green open access, ...
Oberlausitzer Verlag, Spitzkunnersdorf 2004. .
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * *External links
* * {{Authority control Geography of Brandenburg Regions of Saxony Historical regions in Germany Historical regions in Poland Former duchies of the Kingdom of Bohemia