|
Rudolf Of Rheinfelden
Rudolf of Rheinfelden ( – 15 October 1080) was Duke of Swabia from 1057 to 1079. Initially a follower of his brother-in-law, the Salian emperor Henry IV, his election as German anti-king in 1077 marked the outbreak of the Great Saxon Revolt and the first phase of open conflict in the Investiture Controversy between Emperor and Pope, Papacy. After a series of armed conflicts, Rudolf succumbed to his injuries after his forces defeated Henry's in the Battle on the Elster. Life Rudolf was the son of the Duchy of Swabia, Swabian count (''Graf'') Kuno of Rheinfelden (Aargau), Rheinfelden. He was first mentioned in a 1048 deed issued by the Salian emperor Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry III as a count in the Swabian Sisgau on the High Rhine (in present-day Northwestern Switzerland), an estate then held by the Prince-Bishopric of Basel. Rudolf's family had large possessions up to Sankt Blasien Abbey in the Black Forest and down to the Aargau beyond the border with the Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Swabia
The Dukes of Swabia were the rulers of the Duchy of Swabia during the Middle Ages. Swabia was one of the five stem duchy, stem duchies of the medieval German kingdom, and its dukes were thus among the most powerful magnates of Germany. The most notable family to rule Swabia was the Hohenstaufen family, who held it, with a brief interruption, from 1079 until 1268. For much of that period, the Hohenstaufen were also Holy Roman Emperors. With the death of Conradin, the last Duke of Hohenstaufen, the duchy itself disintegrated although King Rudolph I of Germany, Rudolf I attempted to revive it for his Habsburg family in the late 13th century. Dukes of Swabia (909–1268) Early dukes * Burchard I Hunfriding (d. 911), mentioned as ''marchio'' (margrave) in 903 and ''dux'' (duke) in 909 * Erchanger, Duke of Swabia, Erchanger Ahalolfing, dominant count in Alemannia after the execution of Burchard I, declared duke in 915, exiled September 916, executed January 917. * Burchard II, Duke of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle On The Elster
Battle on the Elster () was the third and last battle between the Salian king Henry IV of Germany and anti-king Rudolf of Rheinfelden, fought on October 14, 1080 near Hohenmölsen on the White Elster river. Rudolf's forces were victorious; however, he was mortally wounded and succumbed to his injuries the next day. Background In February 1076, Pope Gregory VII had excommunicated Henry over the Investiture Controversy. In turn, the rebellious German princes met at Trebur in October and resolved upon his deposition, if he would not be able to obtain the revocation of the ban within a year. By his Walk to Canossa in January 1077, the king received absolution, nevertheless the princes elected Rudolf of Rheinfelden anti-king on March 15. Henry placed Rudolf under imperial ban and marched against him. Their forces first met in the Battle of Mellrichstadt on 7 August 1078 and again in the Battle of Flarchheim on 27 January 1080. Both encounters remained inconclusive. Prelude Henry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottonian Dynasty
The Ottonian dynasty () was a Saxons, Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman emperors, especially Otto the Great. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German stem duchy of Duchy of Saxony, Saxony. The family itself is also sometimes known as the Liudolfings (), after its earliest known member Count Liudolf, Duke of Saxony, Liudolf (d. 866) and one of its most common given names. The Ottonian rulers were successors of Conrad I of Germany, Conrad I, who was the only German king to rule in East Francia after the Carolingian dynasty. The Ottonians are associated with the notable military success that transformed the political situation in contemporary Western Europe: "It was the success of the Ottonians in molding the raw materials bequeathed to them into a formidable military machine that made possible the establishment of Germany as the preeminent kingdom in Europe from the tenth through the mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorraine (duchy)
The Duchy of Lorraine was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire which existed from the 10th century until 1766 when it was annexed by the kingdom of France. It gave its name to the larger present-day region of Lorraine in northeastern France. Its capital was Nancy. It was founded in 959 following the division of Lotharingia into two separate duchies: Upper and Lower Lorraine, the westernmost parts of the Holy Roman Empire. The Lower duchy was quickly dismantled, while Upper Lorraine came to be known as simply the Duchy of Lorraine. The Duchy of Lorraine was coveted and briefly occupied by the dukes of Burgundy and the kings of France, but was ruled by the dukes of the House of Lorraine after 1473. In 1737, the duchy was given to Stanisław Leszczyński, the former king of Poland, who had lost his throne as a result of the War of the Polish Succession, with the understanding that it would fall to the French crown on his death. When Stanisław died on 23 February 1766, Lorrai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph II Of Burgundy
Rudolph II (/885 – 12 or 13 July 937) was King of Upper Burgundy from 912 until 933, and then King of the united Kingdom of Burgundy (the polity later known as the Kingdom of Arles) from 933 until his death in 937. He was also King of Italy from 922 to 926. He initially succeeded his father, king Rudolph I, in Upper Burgundy. In 933, Rudolph II acquired the Kingdom of Lower Burgundy (Provence) from King Hugh of Italy in exchange for the waiver of his claims to the Italian crown, thereby establishing the united Kingdom of Burgundy. Life A member of the Elder House of Welf, Rudolph was the son of the Upper Burgundian king Rudolph I, and his wife Guilla of Provence. Following his ascent to the throne in 912, Rudolph II entered into a border conflict with the neighbouring dukes of Swabia and campaigned the Thurgau and Zürich estates. Duke Burchard II of Swabia finally defeated him in the 919 Battle of Winterthur; both rulers made peace and Rudolph married Burchard's da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Burgundy-Arles
The Kingdom of Burgundy, known from the 12th century as the Kingdom of Arles, was a realm established in 933 by the merger of the kingdoms of Upper and Lower Burgundy under King Rudolf II. It was incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire in 1033 and from then on was one of the empire's three constituent realms, together with the Kingdom of Germany and the Kingdom of Italy. By the mid-13th century at the latest, however, it had lost its concrete political relevance. Its territory stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the High Rhine River in the north, roughly corresponding to the present-day French regions of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, Rhône-Alpes and Franche-Comté, as well as western Switzerland. Until 1032 it was ruled by independent kings of the Elder House of Welf.''The New Columbia Encyclopedia'' 1975, 150 Carolingian Burgundy Since the conquest of the Ancient Kingdom of Burgundy by the Franks in 534, its territory had been ruled within the Merovingian state, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
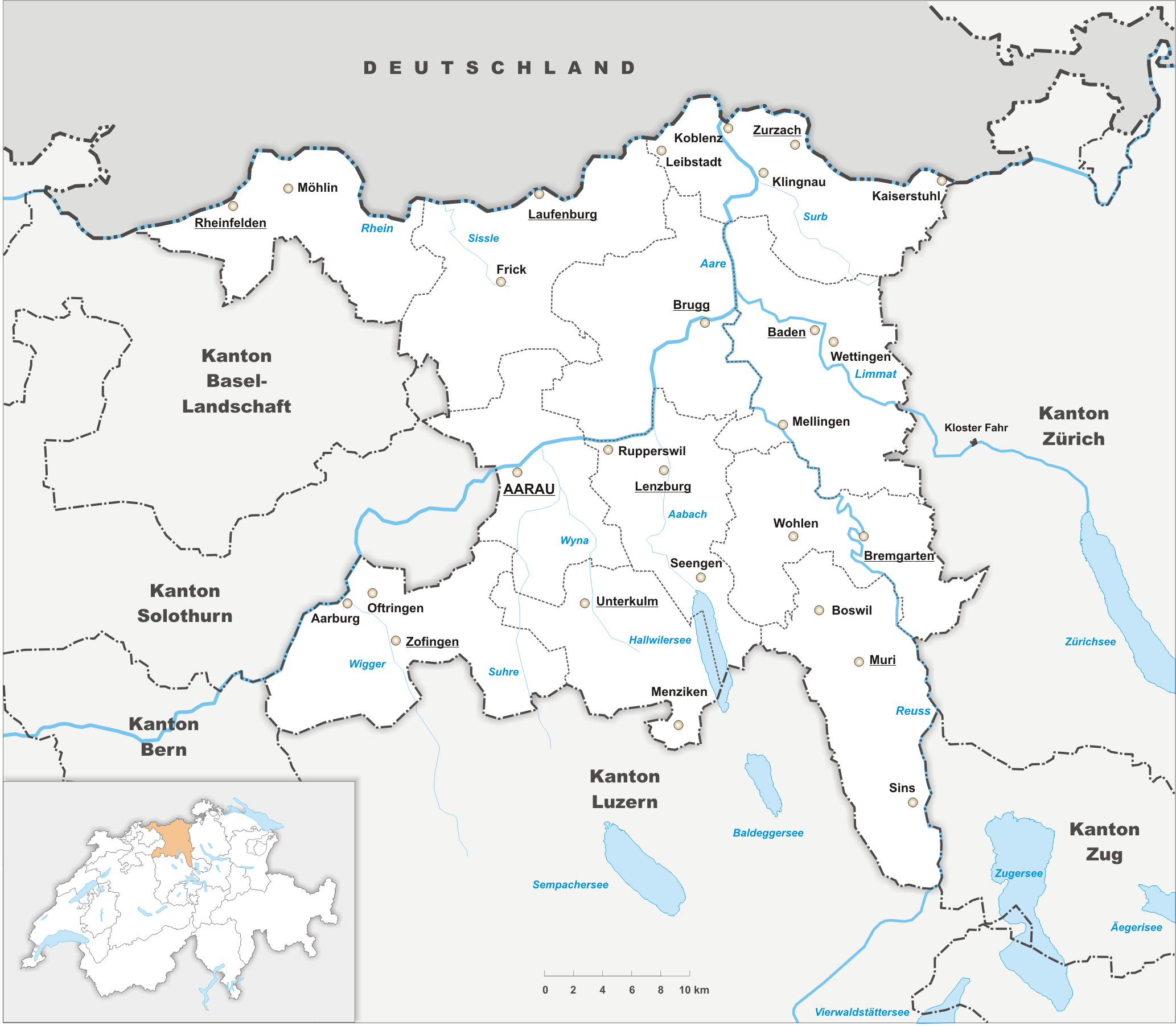
Aargau
Aargau ( ; ), more formally the Canton of Aargau (; ; ; ), is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau. Aargau is one of the most northerly cantons of Switzerland, by the lower course of the Aare River, which is why it is called ''Aar-Gau (country subdivision), gau'' ("Aare province"). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland. History Early history The area of Aargau and the surrounding areas were controlled by the Helvetians, a tribe of Celts, as far back as 200 BC. It was eventually occupied by the Roman Empire, Romans and then by the 6th century, the Franks. The Romans built a major settlement called Vindonissa, near the present location of Brugg. Medieval Aargau The reconstructed Old High German name of Aargau is ''Argowe'', first unambiguously attested (in the spelling ''Argue'') in 795. The term described a territory only loosely eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sankt Blasien Abbey In The Black Forest
Saint Blaise Abbey () was a Benedictine monastery in the village of St. Blasien in the Black Forest in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History 9th–12th centuries The early history of the abbey is obscure. Its predecessor in the 9th century is supposed to have been a cell of Rheinau Abbey, known as ''cella alba'' (the "white cell"), but the line of development between that and the confirmed existence of St Blaise's Abbey in the 11th century is unclear. At some point the new foundation would have had to become independent of Rheinau, in which process the shadowy Reginbert of Seldenbüren (died about 962), traditionally named as the founder, may have played some role. The first definite abbot of St Blaise however was Werner I (1045?–1069). On 8 June 1065 the abbey received a grant of immunity from Emperor Henry IV, although it had connections to the family of the anti-king Rudolf of Rheinfelden. Between 1070 and 1073 there seem to have been contacts between St. Blaise and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-Bishopric Of Basel
The Prince-Bishopric of Basel () was an ecclesiastical principality within the Holy Roman Empire, ruled from 1032 by prince-bishops with their seat at Basel, and from 1528 until 1792 at Porrentruy, and thereafter at Schliengen. As an imperial estate, the prince-bishop had a seat and voting rights at the Imperial Diet. The final dissolution of the state occurred in 1803 as part of the German Mediatisation. The Prince-Bishopric comprised territories now in the Swiss cantons of Basel-Landschaft, Jura, Solothurn and Bern, besides minor territories in nearby portions of southern Germany and eastern France. The city of Basel ceased to be part of the Prince-Bishopric after it joined the Swiss Confederacy in 1501. History The Bishopric of Basel was established by the Carolingians, either by Pepin the Short or by Charlemagne himself. The first recorded bishop of Basel is one Walaus, the first entry in the list of bishops preserved in Munster Abbey. He is listed as ''archiepisco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwestern Switzerland
Northwestern Switzerland (, , ), is a subdivision of Switzerland as defined by the Federal Statistical Office for statistical purposes. It is classified as a Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics, NUTS-2 statistical NUTS:CH, region of Switzerland, and encompasses the Cantons of Switzerland, cantons of Basel-Stadt, Basel-Landschaft, and Aargau. It is different from the traditional region of the same name (:de:Nordwestschweiz, Nordwestschweiz in German language, German), which also includes Basel-Stadt and Basel-Landschaft, certain northern parts of the canton of Solothurn, Solothurn and only parts of the canton of Aargau. Sub-division The country of Switzerland is federally organized into 26 Cantons of Switzerland, cantons, which are the primary Subdivisions of Switzerland, sub-divisions of the country. For statistical purposes, the Federal Statistical Office organizes the country into broader level sub-divisions based on cardinal directions. These are classified as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Rhine
High Rhine (, ; kilometres 0 to 167 of the Rhine) is the section of the Rhine between Lake Constance () and the city of Basel, flowing in a general east-to-west direction and forming mostly the Germany–Switzerland border. It is the first of four named sections of the Rhine (High Rhine, Upper Rhine, Middle Rhine, Lower Rhine) between Lake Constance and the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, river delta at the North Sea. Name The term ''High Rhine'' was introduced by scientists in the 19th century. Above all geologists tried to differentiate the High Rhine () linguistically from the Upper Rhine (, ). Until the 19th century, it was also known as the 'Badisch-Swiss Rhine'. It lends its name to the High Rhine Railway line, which to a great extend follows the river to the north of it. Geography Course The High Rhine begins at the outflow of the Rhine from the ''Untersee (Lake Constance), Untersee'' (Lower Lake Constance) in Stein am Rhein and turns into the Upper Rhine at the Rhine knee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry III (, 28 October 1016 – 5 October 1056), called the Black () or the Pious, was Holy Roman Emperor from 1046 until his death in 1056. A member of the Salian dynasty, he was the eldest son of Conrad II and Gisela of Swabia. Henry was raised by his father, who made him Duke of Duchy of Bavaria, Bavaria in 1026, appointed him co-ruler in 1028 and bestowed him with the duchy of Swabia and the Kingdom of Burgundy ten years later in 1038. The emperor's death the following year ended a remarkably smooth and harmonious transition process towards Henry's sovereign rule, that was rather uncharacteristic for the Ottonian dynasty, Ottonian and Salian dynasty, Salian monarchs. Henry succeeded Conrad II as Duke of Carinthia and King of Italy and continued to pursue his father's political course on the basis of ''virtus et probitas'' (courage and honesty), which led to an unprecedented sacral exaltation of the kingship. In 1046 Henry ended the History of the papacy (1048–1257), papal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |