Late Woodland period on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the classification of archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of
 The beginning of the Middle Woodland saw a shift of settlement to the Interior. As the Woodland period progressed, local and inter-regional trade of exotic materials greatly increased to the point where a trade network covered most of the
The beginning of the Middle Woodland saw a shift of settlement to the Interior. As the Woodland period progressed, local and inter-regional trade of exotic materials greatly increased to the point where a trade network covered most of the
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
n pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era, also known as the pre-contact era, or as the pre-Cabraline era specifically in Brazil, spans from the initial peopling of the Americas in the Upper Paleolithic to the onset of European col ...
cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BC to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 AD to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s and the agriculturalist Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building la ...
s. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of hemiboreal regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Fennoscandia, Northwestern Russia, Siberia, and the Cair ...
region, the Eastern United States
The Eastern United States, often abbreviated as simply the East, is a macroregion of the United States located to the east of the Mississippi River. It includes 17–26 states and Washington, D.C., the national capital.
As of 2011, the Eastern ...
, along to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
.
This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. It can be characterized as a chronological and cultural manifestation without any massive changes in a short time but instead having a continuous development in stone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
and bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
tool
A tool is an Physical object, object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many Tool use by animals, animals use simple tools, only human bei ...
s, leather crafting
Leather crafting or simply leathercraft is the practice of making leather into craft objects or works of art, using shaping techniques, coloring techniques or both.
Techniques
Dyeing
The application of pigments carried by solvents or water i ...
, textile manufacture, cultivation, and shelter construction. Many Woodland peoples used spear
A spear is a polearm consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with Fire hardening, fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable materia ...
s and atlatl
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever, or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Classical Nahuatl, Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in Dart (missile), dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a Plain bearing, b ...
s until the end of the period, when they were replaced by bows and arrows; however, Southeastern Woodland peoples also used blowgun
A blowgun (also called a blowpipe or blow tube) is a simple ranged weapon consisting of a long narrow tube for shooting light projectiles such as darts. It operates by having the projectile placed inside the pipe and using the force created by ...
s.
The most cited technological distinction of this period was the widespread use of pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
(although pottery manufacture had arisen during the Archaic period in some places), and the diversification of pottery forms, decorations, and manufacturing practices. The increasing use of horticulture and the development of the Eastern Agricultural Complex
The Eastern Agricultural Complex in the woodlands of eastern North America was one of about 10 independent centers of plant domestication in the pre-historic world. Incipient agriculture dates back to about 5300 BCE. By about 1800 BCE the Native ...
, consisting of weedy seed plants as well as gourd cultivation, also meant that groups became less mobile over time and, in some times and places, people lived in permanently occupied villages and cities. Intensive agriculture characterizes the Mississippian period from –1400 AD and may have continued up to European contact, around 500 years ago.
Early Woodland period (1000–200 BCE)
The Early Woodland period continued many trends begun during the Late and Terminal Archaic periods, including extensive mound-building, regional distinctive burial complexes, the trade of exotic goods across a large area of North America as part of interaction spheres, the reliance on both wild and domesticated plant foods, and a mobile subsistence strategy in which small groups took advantage of seasonally available resources such as nuts, fish, shellfish, and wild plants. Pottery, which had been manufactured during the Archaic period in limited amounts, was now widespread across the Eastern Interior, the Southeast, and the Northeast. The Far Northeast, the Sub-Arctic, and the Northwest/Plains regions widely adopted pottery somewhat later, about 200 BCE.Interaction
TheAdena culture
The Adena culture was a pre-Columbian Native American culture that existed from 500 BCE to 100 CE, in a time known as the Early Woodland period. The Adena culture refers to what were probably a number of related Native American societies sharin ...
built conical mounds in which single- or multiple-event burials, often cremated, were interred along with rich grave goods including copper bracelets, beads, and gorget
A gorget ( ; ) was a band of linen wrapped around a woman's neck and head in the English medieval clothing, medieval period or the lower part of a simple chaperon (headgear), chaperon hood. The term later described a steel or leather Collar (c ...
s, art objects made from mica, novaculite, hematite, banded slate, and other kinds of stone, shell beads and cups, and leaf-shaped "cache blades". This culture is believed to have been core to the Meadowood Interaction Sphere, in which cultures in the Great Lakes region, the St. Lawrence region, the Far Northeast, and the Atlantic region interacted. The large area of interaction is indicated by the presence of Adena-style mounds, the presence of exotic goods from other parts of the interaction spheres, and the participation in the "Early Woodland Burial Complex" defined by William Ritchie
Pottery
Pottery was widely manufactured and sometimes traded, particularly in the Eastern Interior region. Clay for pottery was typically tempered (mixed with non-clay additives) with grit (crushed rock) or limestone. Pots were usually made in a conoidal or conical jar with rounded shoulders, slightly constricted necks, and flaring rims. Pottery was most often decorated with a variety of linear or paddle stamps that created "dentate" (tooth-like) impressions, wavy line impressions, checked surfaces, or fabric-impressed surfaces, but some pots were incised with herringbone and other geometric patterns or, more rarely, with pictorial imagery such as faces. Pots were coiled and paddled entirely by hand without the use of fast rotation such as a pottery wheel. Some were slipped or brushed with red ochre. Pottery, agriculture, and permanent settlements have often been thought of the three defining characteristics of the Woodland period. However, it has become evident that, in some areas of North America, prehistoric cultural groups with a clearly Archaic cultural assemblage were making pottery without any evidence of the cultivation of domesticated crops. In fact, it appears that hunting and gathering continued as the basic subsistenceeconomy
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
and that subsistence horticulture/agriculture did not occur in much of the Southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A ''compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, ...
for a couple of thousand years after the introduction of pottery, and in parts of the Northeast, horticulture was never practiced. This research indicated that a fiber-tempered horizon of ceramics greatly predates 1000 BCE, first appearing about 2500 BCE in parts of Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
with the Orange culture
The Orange period or Orange culture was a late- Archaic archaeological culture along the eastern side of the Florida peninsula, from about 4,000 years ago to about 2,500 or 3,000 years ago. The Orange period is largely defined by the presence of Or ...
and in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
with the Stallings culture. Nevertheless, these early sites were typical Archaic settlements, differing only in the use of basic ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
technology. As such, researchers are now redefining the period to begin with not only pottery, but the appearance of permanent settlements, elaborate burial practices, intensive collection and/or horticulture
Horticulture (from ) is the art and science of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, trees, shrubs and ornamental plants. Horticulture is commonly associated with the more professional and technical aspects of plant cultivation on a smaller and mo ...
of starchy seed plants (see Eastern Agricultural Complex
The Eastern Agricultural Complex in the woodlands of eastern North America was one of about 10 independent centers of plant domestication in the pre-historic world. Incipient agriculture dates back to about 5300 BCE. By about 1800 BCE the Native ...
), differentiation in social organization, and specialized activities, among other factors. Most of these are evident in the Southeastern Woodlands
Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an Ethnography, ethnographic classification for Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now ...
by 1000 BCE.
In some areas, like South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
and coastal Georgia, Deptford culture pottery manufacture ceased after .
Subsistence strategies
In coastal regions, many settlements were near the coast, often near salt marshes, which were habitats rich in food resources. People tended to settle along rivers and lakes in both coastal and interior regions for maximum access to food resources. Nuts were processed in large amounts, includinghickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes 19 species accepted by ''Plants of the World Online''.
Seven species are native to southeast Asia in China, Indochina, and northeastern India (Assam), and twelve ...
and acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
s, and many wild berries, including palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
** List of Arecaceae genera
**Palm oil
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music ...
berries, blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' with the genus ''Vaccinium''. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) ...
, raspberries
The raspberry is the edible fruit of several plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the Rosaceae, rose family, most of which are in the subgenus ''Rubus#Modern classification, Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Ras ...
, and strawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid plant cultivated worldwide for its fruit. The genus ''Fragaria'', the strawberries, is in the rose family, Rosaceae. The fruit is appreciated f ...
, were eaten, as well as wild grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
s and persimmon
The persimmon () is the edible fruit of a number of species of trees in the genus '' Diospyros''. The most widely cultivated of these is the Chinese and Japanese kaki persimmon, ''Diospyros kaki''. In 2022, China produced 77% of the world's p ...
. Most groups relied heavily on white-tailed deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known Common name, commonly as the whitetail and the Virginia deer, is a medium-sized species of deer native to North America, North, Central America, Central and South America. It is the ...
, but a variety of other small and large mammals were hunted also, including beaver
Beavers (genus ''Castor'') are large, semiaquatic rodents of the Northern Hemisphere. There are two existing species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers are the second-large ...
, raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the North American, northern or common raccoon (also spelled racoon) to distinguish it from Procyonina, other species of raccoon, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest ...
, and bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family (biology), family Ursidae (). They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats ...
. Shellfish
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries usage, are exoskeleton-bearing Aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrates used as Human food, food, including various species of Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish ...
formed an important part of the diet, attested to by numerous shell middens along the coast and interior rivers.
Coastal peoples practiced seasonal mobility, moving to the coast during the summer to take advantage of numerous marine resources such as sea mammals and shellfish, then moved to interior locations during the winter where access to deer, bear, and anadromous fish such as salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
could see them through the winter. Seasonal foraging also characterized the strategies of many interior populations, with groups moving strategically among dense resource areas.
Recently evidence has accumulated a greater reliance on woodland peoples on cultivation in this period, at least in some localities, than has historically been recognized. This is especially true for the middle woodland period and perhaps beyond. C. Margaret Scarry states "in the Woodland periods, people diversified their use of plant foods ... heyincreased their consumption of starchy foods. They did so, however, by cultivating starchy seeds rather than by gathering more acorns." Smith and Yarnell refer to an "indigenous crop complex" as early as 3800 B.P. in parts of the region.
Middle Woodland period (200 BCE – 500 CE)
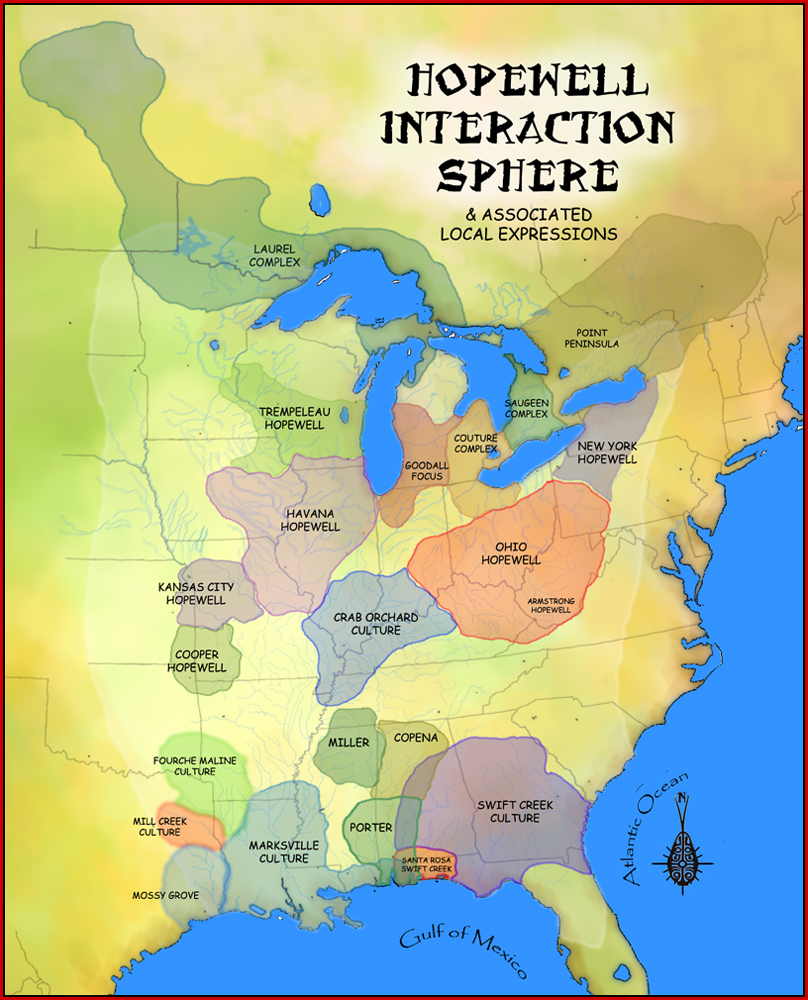
 The beginning of the Middle Woodland saw a shift of settlement to the Interior. As the Woodland period progressed, local and inter-regional trade of exotic materials greatly increased to the point where a trade network covered most of the
The beginning of the Middle Woodland saw a shift of settlement to the Interior. As the Woodland period progressed, local and inter-regional trade of exotic materials greatly increased to the point where a trade network covered most of the Eastern Woodlands
The Eastern Woodlands is a cultural region of the Indigenous people of North America. The Eastern Woodlands extended roughly from the Atlantic Ocean to the eastern Great Plains, and from the Great Lakes region to the Gulf of Mexico, which is now ...
. Throughout the Southeast and north of the Ohio River
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its river mouth, mouth on the Mississippi Riv ...
, burial mound
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
s of important people were very elaborate and contained a variety of mortuary
A morgue or mortuary (in a hospital or elsewhere) is a place used for the storage of human corpses awaiting identification (ID), removal for autopsy, respectful burial, cremation or other methods of disposal. In modern times, corpses have cus ...
gifts, many of which were not local. Among the traded materials were copper from the Lake Superior deposits; silver from Lake Superior and especially Ontario; galena from Missouri and Illinois; mica from the southern Appalachians; chert from various places including Ohio, Indiana, and Illinois; pipestone from Ohio and Illinois; alligator teeth from the lower Mississippi Valley eastward to Florida; marine shells, especially whelks, from the south Atlantic and Gulf coasts; Knife River chalcedony from North Dakota; and obsidian from Yellowstone in Wyoming.
The most archaeologically certifiable sites of burial during this time were in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
and Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
. These have come to be known as the Hopewell tradition
The Hopewell tradition, also called the Hopewell culture and Hopewellian exchange, describes a network of precontact Native American cultures that flourished in settlements along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern Eastern Woodlands from 1 ...
. Due to the similarity of earthworks and burial goods, researchers assume a common body of religious practice and cultural interaction existed throughout the entire region (referred to as the "Hopewellian Interaction Sphere"). Such similarities could also be the result of reciprocal trade, obligations, or both between local clans that controlled specific territories. Access to food or resources outside a clan's territory would be made possible through formal agreements with neighbors. Clan heads would be buried along with goods received from their trading partners to symbolize the relationships they had established. Under this scenario, permanent settlements would be likely to develop, leading to increased agricultural production and a population increase.
Ceramics during this time were thinner and better quality than earlier times. Examples show pottery also was more decorated than Early Woodland. One style was the Trempealeau phase, which could have been seen by the Hopewell in Indiana. This type included a round body, and lines of decoration with cross-etching on rim. The Havana style found in Illinois had a decorated neck. One of the major tools unique to this era was Snyders Points. These were quite large and corner-notched. They were made by soft-hammering percussion, and finished by pressure flaking.Behm, Jeffrey (2007 March) ''Middle Woodland''. Oshkosh, WI: University of Wisconsin-Oshkosh
Although many of the Middle Woodland cultures are called "Hopewellian", and groups shared ceremonial practices, archeologists have identified the development of distinctly separate cultures during the Middle Woodland period. Examples include the Armstrong culture, Copena culture, Crab Orchard culture, Fourche Maline culture, the Goodall Focus
The Goodall focus was a Hopewellian culture from the Middle Woodland period peoples that occupied Western Michigan and northern Indiana from around 200 BCE to 500 CE. Extensive trade networks existed at this time, particularly among the many local ...
, the Havana Hopewell culture, the Kansas City Hopewell
The Kansas City Hopewell were the farthest west regional variation of the Hopewell tradition of the Middle Woodland period (100 BCE – 700 CE). Sites were located in Kansas and Missouri around the mouth of the Kansas River where it enters the Mi ...
, the Marksville culture, and the Swift Creek culture.
The Center for American Archeology specializes in Middle Woodland culture.
Late Woodland period (500–1000 CE)
The late Woodland period was a time of apparent population dispersal, although populations do not appear to have decreased. In most areas, the construction of burial mounds decreased markedly, as did the long-distance trade in exotic materials. At the same time, bow and arrow technology gradually overtook the use of the spear andatlatl
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever, or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Classical Nahuatl, Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in Dart (missile), dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a Plain bearing, b ...
. Agricultural production of the " Three Sisters" (maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native American ...
, bean
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are traditi ...
s, and squash) was introduced. While full-scale intensive agriculture did not begin until the following Mississippian period, the beginning of serious cultivation greatly supplemented the traditional gathering of plants.
Late Woodland settlements became more numerous, but the size of each one (with exceptions) was smaller than their Middle Woodland counterparts. The reasons for this are unknown, but it has been theorized that populations increased so much that trade alone could no longer support the communities. Some clans resorted to raiding others for resources. Alternatively, the efficiency of bows and arrows in hunting may have decimated the large game animals, forcing the tribes to break apart into smaller clans to use local resources better, thus limiting the trade potential of each group. A third possibility is that a colder climate may have affected food yields, possibly affected by the volcanic winter of 536
The volcanic winter of 536 was among the most severe and protracted episodes of climatic cooling in the Northern Hemisphere in the last 2,000 years. The volcanic winter was caused by at least three simultaneous eruptions of uncertain origin, wit ...
in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
, and also limited trade possibilities. Lastly, it may be that agricultural technology became sophisticated enough that crop variation between clans lessened, thereby decreasing the need for trade.
As communities became more isolated, they began to develop in their own unique ways, giving rise to small-scale cultures that were distinctive to their regional areas. Examples include the Baytown, Troyville and Coles Creek cultures of Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
; the Alachua and Weeden Island cultures of Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
; and the Plum Bayou culture of Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
and Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
.
Although the 1000 CE ending of the Late Woodland period is traditional, in practice, many regions of the Eastern Woodlands adopted the Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a collection of Native American societies that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building la ...
much later than that. Some groups in the north and northeast of the current United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, such as the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( ), also known as the Five Nations, and later as the Six Nations from 1722 onwards; alternatively referred to by the Endonym and exonym, endonym Haudenosaunee ( ; ) are an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Ind ...
, retained a way of life that was technologically identical to the Late Woodland until the arrival of Europeans. Despite the widespread adoption of the bow and arrow during this time, the peoples of a few areas appear never to have made the change. During Hernando de Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1497 – 21 May 1542) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, ...
's travels through the Southeastern Woodlands around 1543, for instance, his expedition noted the groups living at the mouth of the Mississippi who still preferentially used the spear.
See also
* Rock Eagle * Rock Hawk * Old Stone Fort (Tennessee) * Pinson Mounds * Cane Island Site * Crystal River Archaeological State Park *Mound Builders
Many pre-Columbian cultures in North America were collectively termed "Mound Builders", but the term has no formal meaning. It does not refer to specific people or archaeological culture but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks that in ...
* Glenwood culture
*Cherokee
The Cherokee (; , or ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern ...
Notes
References
* * *Further reading
*External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Woodland Period 1930s neologisms Archaeological cultures of North America Pre-Columbian cultures Late Prehistoric period of North America Prehistoric cultures in Nebraska