|
Fourche Maline Culture
The Fourche Maline culture (pronounced foosh-ma-lean) was a Woodland Period Native American culture that existed from 300 BCE to 800 CE,"The McCutcheon-McLaughlin Site." Oklahoma Archeological Survey. November 15, 2016. in what are now defined as southeastern , southwestern , northwestern , and northeastern . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fourche Maline And Mill Creek Cultures Map HRoe 2010
Fourche ( ) is a town in Perry County, Arkansas, United States. The population was 59 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Little Rock–North Little Rock–Conway Metropolitan Statistical Area. Geography Fourche is located at (34.993192, -92.618974). According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of , all land. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 59 people, 23 households, and 16 families residing in the town. The population density was . There were 25 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the town was 94.92% White and 5.08% Black or African American. There were 23 households, out of which 52.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 60.9% were married couples living together, 8.7% had a female householder with no husband present, and 26.1% were non-families. 21.7% of all households were made up of individuals, and 8.7% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Woodland Period
In the classification of :category:Archaeological cultures of North America, archaeological cultures of North America, the Woodland period of North American pre-Columbian cultures spanned a period from roughly 1000 BC to European contact in the eastern part of North America, with some archaeologists distinguishing the Mississippian period, from 1000 AD to European contact as a separate period. The term "Woodland Period" was introduced in the 1930s as a generic term for prehistoric, prehistoric sites falling between the Archaic period in the Americas, Archaic hunter-gatherers and the agriculturalist Mississippian cultures. The Eastern Woodlands cultural region covers what is now eastern Canada south of the Subarctic region, the Eastern United States, along to the Gulf of Mexico. This period is variously considered a developmental stage, a time period, a suite of technological adaptations or "traits", and a "family tree" of cultures related to earlier Archaic cultures. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
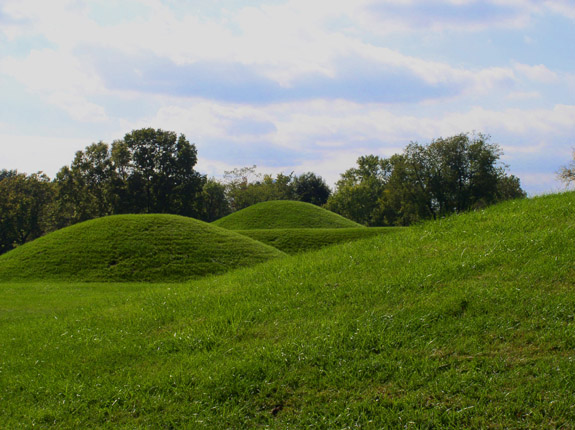
Burial Mound
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objects in it, and covering it over. A funeral is a ceremony that accompanies the final disposition. Evidence suggests that some archaic and early modern humans buried their dead. Burial is often seen as indicating respect for the dead. It has been used to prevent the odor of decay, to give family members closure and prevent them from witnessing the decomposition of their loved ones, and in many cultures it has been seen as a necessary step for the deceased to enter the afterlife or to give back to the cycle of life. Methods of burial may be heavily ritualized and can include natural burial (sometimes called "green burial"); embalming or mummification; and the use of containers for the dead, such as shrouds, coffins, grave liners, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle (mollusc), mantle) of a living Exoskeleton, shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carbonate (mainly aragonite or a mixture of aragonite and calcite) in minute crystalline form, which has deposited in concentric layers. More commercially valuable pearls are perfectly round and smooth, but many other shapes, known as baroque pearls, can occur. The finest quality of natural pearls have been highly valued as gemstones and objects of beauty for many centuries. Because of this, ''pearl'' has become a metaphor for something rare, fine, admirable, and valuable. The most valuable pearls occur spontaneously in the wild but are extremely rare. These wild pearls are referred to as ''natural'' pearls. ''Cultured'' or ''farmed'' pearls from Pinctada, pearl oysters and freshwater mussels make up the majority o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
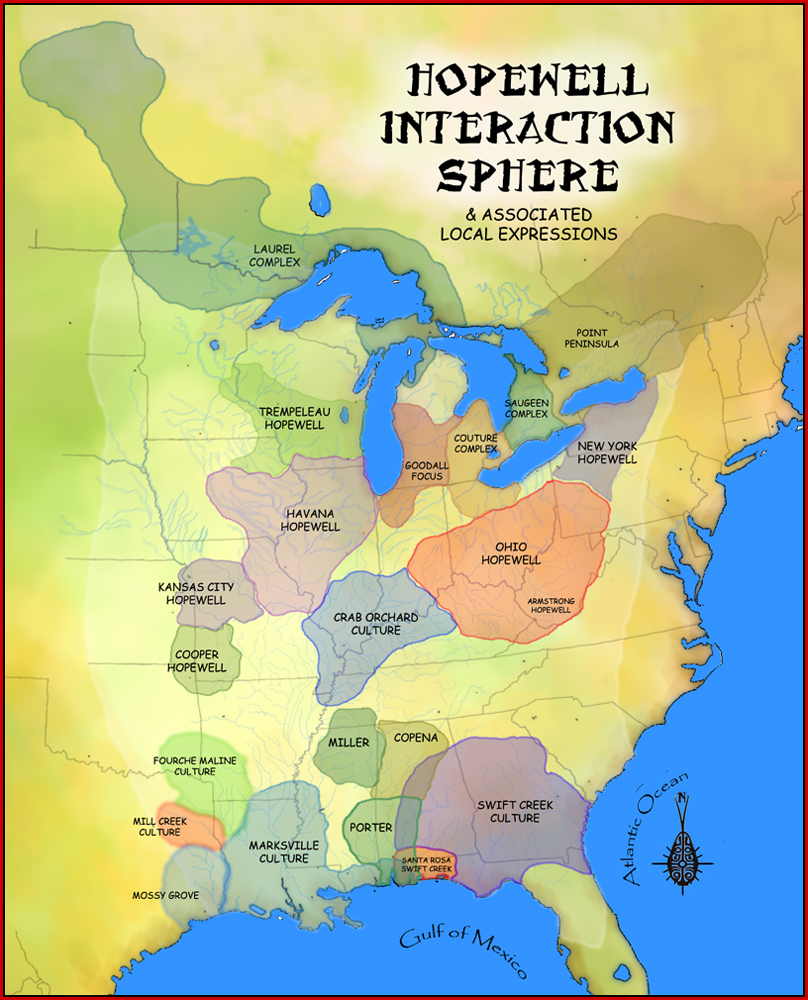
Hopewell Tradition
The Hopewell tradition, also called the Hopewell culture and Hopewellian exchange, describes a network of precontact Native American cultures that flourished in settlements along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern Eastern Woodlands from 100 BCE to 500 CE, in the Middle Woodland period. The Hopewell tradition was not a single culture or society but a widely dispersed set of populations connected by a common network of trade routes. At its greatest extent, the Hopewell exchange system ran from the northern shores of Lake Ontario south to the Crystal River Indian Mounds in modern-day Florida. Within this area, societies exchanged goods and ideas, with the highest amount of activity along waterways, which were the main transportation routes. Peoples within the Hopewell exchange system received materials from all over the territory of what now comprises the mainland United States. Most of the items traded were exotic materials; they were delivered to peoples living in the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marksville Culture
The Marksville culture was an archaeological culture in the lower Lower Mississippi valley, Yazoo valley, and Tensas valley areas of present-day Louisiana, Mississippi, Arkansas, and extended eastward along the Gulf Coast to the Mobile Bay area, from 100 BCE to 400 CE. This culture takes its name from the Marksville Prehistoric Indian Site in Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana. Marksville Culture was contemporaneous with the Hopewell cultures within present-day Ohio and Illinois. It evolved from the earlier Tchefuncte culture and into the Baytown and Troyville cultures, and later the Coles Creek and Plum Bayou cultures. It is considered ancestral to the historic Natchez and Taensa peoples. Description The Hopewell tradition was a widely dispersed set of related populations, which were connected by a common network of trade routes, known as the Hopewell Exchange System. The Marksville culture was a southern manifestation of this network. Settlements were large and usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arrow
An arrow is a fin-stabilized projectile launched by a bow. A typical arrow usually consists of a long, stiff, straight shaft with a weighty (and usually sharp and pointed) arrowhead attached to the front end, multiple fin-like stabilizers called fletchings mounted near the rear, and a slot at the rear end called a nock for engaging the bowstring. A container or bag carrying additional arrows for convenient reloading is called a quiver. The use of bows and arrows by humans predates recorded history and is common to most cultures. A craftsman who makes arrows is a fletcher, and one who makes arrowheads is an arrowsmith.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 56 History The oldest evidence of likely arrowheads, dating to years ago, were found in Sibudu Cave, current South Africa.Backwell L, d'Errico F, Wadley L.(2008). Middle Stone Age bone tools from the Howiesons Poort layers, Sibudu Cave, South Africa. Journal of Archaeological Science, 35:1566–1580. Backwell L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bow (weapon)
The bow and arrow is a ranged weapon system consisting of an elastic launching device (bow) and long-shafted projectiles (arrows). Humans used bows and arrows for hunting and aggression long before recorded history, and the practice was common to many prehistoric cultures. They were important weapons of war from ancient history until the early modern period, when they were rendered increasingly obsolete by the development of the more powerful and accurate firearms. Today, bows and arrows are mostly used for hunting and sports. Archery is the art, practice, or skill of using bows to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 A person who shoots arrows with a bow is called a bowman or an archer. Someone who makes bows is known as a bowyer,Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 31 someone who makes arrows is a fletcher,Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 56 and someone who manufactures metal arrowheads is an arrowsmith.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maize
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago from wild teosinte. Native Americans planted it alongside beans and squashes in the Three Sisters polyculture. The leafy stalk of the plant gives rise to male inflorescences or tassels which produce pollen, and female inflorescences called ears. The ears yield grain, known as kernels or seeds. In modern commercial varieties, these are usually yellow or white; other varieties can be of many colors. Maize relies on humans for its propagation. Since the Columbian exchange, it has become a staple food in many parts of the world, with the total production of maize surpassing that of wheat and rice. Much maize is used for animal feed, whether as grain or as the whole plant, which can either be baled or made into the more palatable silage. Sugar-rich varieties called sw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eastern Agricultural Complex
The Eastern Agricultural Complex in the woodlands of eastern North America was one of about 10 independent centers of plant domestication in the pre-historic world. Incipient agriculture dates back to about 5300 BCE. By about 1800 BCE the Native Americans of the woodlands were cultivating several species of food plants, thus beginning a transition from a hunter-gatherer economy to agriculture. After 200 BCE when maize from Mexico was introduced to the Eastern Woodlands, the Native Americans of the eastern United States and adjacent Canada slowly changed from growing local indigenous plants to a maize-based agricultural economy. The cultivation of local indigenous plants other than squash and sunflower declined and was eventually abandoned. The formerly domesticated plants returned to their wild forms. The first four plants known to have been domesticated at the Riverton Site in Illinois in 1800 BCE were goosefoot (''Chenopodium berlandieri''), sunflower (''Helianthus annuus var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in the cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the 20th century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output. , small farms produce about one-third of the world's food, but large farms are prevalent. The largest 1% of farms in the world are greater than and operate more than 70% of the world's farmland. Nearly 40% of agricultural land is found on farms larger than . However, five of every six farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |