La Rioja (autonomous Community) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
La Rioja () is an
File:Façade of Santa María de la Redonda in Logroño.jpg, Santa María de la Redonda Co-cathedral, Logroño.
Image:Valle-de-San-Millán.jpg, Monasterios de San Millán de Yuso
Image:Iglesia de San Servando y San Germán en Arnedillo.jpg, Arnedillo
 During the
During the
Website of UNIR - International University of La Rioja.
Retrieved 15 May 2017. See also Spanish Wikipedia article.
 La Rioja has connections by air via the Logroño-Agoncillo Airport.
Rail journeys to Madrid, Zaragoza, Barcelona, Valladolid, Oviedo, Bilbao, La Coruña, Vigo are possible, since the Castejón-Miranda line crosses the region from east to west. The main railway station is that at Logroño.
Roads between La Rioja and neighboring regions are primarily through the AP-68. Additional highways have been built, such as the Autovía A-12 which connects
La Rioja has connections by air via the Logroño-Agoncillo Airport.
Rail journeys to Madrid, Zaragoza, Barcelona, Valladolid, Oviedo, Bilbao, La Coruña, Vigo are possible, since the Castejón-Miranda line crosses the region from east to west. The main railway station is that at Logroño.
Roads between La Rioja and neighboring regions are primarily through the AP-68. Additional highways have been built, such as the Autovía A-12 which connects
File:Monasterio de Suso (2).jpg, Monasteries of San Millán de la Cogolla
File:Logroño - Iglesia de San Bartolome 01.jpg, Portal of Church of San Bartolomé (Logroño)
File:Calahorra - Catedral 07.jpg, Calahorra Cathedral
 * Ángel Iturriaga Barco
* Celso Morga Iruzubieta
*
* Ángel Iturriaga Barco
* Celso Morga Iruzubieta
*
Government of La Rioja
Tourism in La Rioja
{{Authority control Autonomous communities of Spain NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1982 hr:La Rioja
autonomous community
The autonomous communities () are the first-level administrative divisions of Spain, created in accordance with the Spanish Constitution of 1978, with the aim of guaranteeing limited autonomy to the nationalities and regions that make up Sp ...
and province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
in Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, in the north of the Iberian Peninsula. Its capital is Logroño
Logroño ( , , ) is the capital of the autonomous community of La Rioja (Spain), La Rioja, Spain. Located in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, primarily in the right (South) bank of the Ebro River, Logroño has historically been a place of pa ...
. Other cities and towns in the province include Calahorra, Arnedo, Alfaro, Haro, Santo Domingo de la Calzada, and Nájera. It has an estimated population of 315,675 inhabitants (INE 2018), making it the least populated autonomous community of Spain.
It covers part of the Ebro
The Ebro (Spanish and Basque ; , , ) is a river of the north and northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, in Spain. It rises in Cantabria and flows , almost entirely in an east-southeast direction. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea, forming a de ...
valley towards its north and the Iberian Range in the south. The community is a single province, so there is no provincial deputation, and it is organized into 174 municipalities. It borders the Basque Country (province of Álava) to the north, Navarre to the northeast, Aragón to the southeast ( province of Zaragoza), and Castilla y León
Castile, Castille or Castilla may refer to:
Places Spain
* Castile (historical region), a vaguely defined historical region of Spain covering most of Castile and León, all of the Community of Madrid and most of Castilla–La Mancha
* Kingdom o ...
to the west and south (provinces of Burgos and Soria).
The area was once occupied by pre-Roman Berones, Pellendones and Vascones. After partial recapture from the Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s in the early tenth century, the region became part of the Kingdom of Pamplona, later being incorporated into Castile after a century and a half of disputes. From the eighteenth century the Rioja region remained divided between the provinces of Burgos and Soria, until in 1833 the province of Logroño was created, changing the name of the province to La Rioja in 1980 as a prelude to its constitution under a single provincial autonomous community in 1982. The name "Rioja" (from Río Oja) is first attested in 1099.
The region is well known for its wines under the brand '' Denominación de Origen Calificada Rioja''.
Etymology
Theetymology
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
of the toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''wikt:toponym, toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage, and types. ''Toponym'' is the general term for ...
Rioja is complex and has been much discussed. The main theories point to different origins: the traditional popular one that makes it correspond to the river Oja, the one that points to the term ''Rivalia'' that would be translated as "land of streams", the one that points as germ a nominal tautology in the term ''rivo Ohia'' that would mean "river of fluvial bed"; and the very diverse ones that indicate that it would have its origins in the Basque language
Basque ( ; ) is a language spoken by Basques and other residents of the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country, a region that straddles the westernmost Pyrenees in adjacent parts of northern Spain and southwestern France. Basque ...
, for example as union of the words ''herria'' and ''ogia'' being translated as "land of bread".
Numerous authors from different periods have proposed different theories about it, such as the friar Mateo Anguiano in the 18th century, Ángel Casimiro de Govantes in the 19th century, Menéndez Pidal or Merino Urrutia in the 20th century, or in the 21st century, the researcher Eduardo Aznar Martínez. In addition, there are texts by older authors such as Florián de Ocampo in the 16th century or Rodrigo Méndez Silva in the 17th century, which give an account of the popular etymology of the toponym.
The first written appearances of this toponym as ''Rioga'' or ''Riogam'' date back to the 11th century, and it can also be found with different spellings such as ''Rioxa, Riogia, Rivo de Oia, Rivogio'' or in its definitive form ''Rioja'' in texts of later centuries. On the other hand, the oldest document found in which its demonym
A demonym (; ) or 'gentilic' () is a word that identifies a group of people ( inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place ( hamlet, village, town, city, region, ...
appears dates from the 13th century, with the spellings ''riogeñ'' and ''riogensi'', that is, Riojan ('' Spanish: riojano'').
In the first written appearances of this toponym in the 11th century, the westernmost area of the present-day Spanish region is designated under the same name; therefore, the primitive Rioja was the territory around the basins of the rivers Tirón and Oja, with some divergences in its exact location by different authors. Gradually and as a result of various historical events, the toponym was extended from the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, to name a larger region, consisting of seven river valleys, located between the Tirón in the west and the Alhama in the east, which flow into the Ebro
The Ebro (Spanish and Basque ; , , ) is a river of the north and northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, in Spain. It rises in Cantabria and flows , almost entirely in an east-southeast direction. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea, forming a de ...
, namely La Rioja today.
History
Roman and Muslim periods
In Roman times, the territory of La Rioja was inhabited by the tribes of the Berones (central country), Autrigones (upper country, extending also north and west of it) and the Vascones (lower country, extending also north and east of it). It was part of the province ofHispania Tarraconensis
Hispania Tarraconensis was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. It encompassed much of the northern, eastern and central territories of modern Spain along with modern North Region, Portugal, northern Portugal. Southern Spain, the region now ...
.
In medieval times, La Rioja was often a disputed territory. The Visigoths
The Visigoths (; ) were a Germanic people united under the rule of a king and living within the Roman Empire during late antiquity. The Visigoths first appeared in the Balkans, as a Roman-allied Barbarian kingdoms, barbarian military group unite ...
created the Duchy of Cantabria that probably included most of La Rioja, as a border march
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 2 ...
against the Vascones. After the Muslim invasion of AD 711, La Rioja fell into the Muslim domains of Al Andalus.
Medieval period
Most of the territory was reconquered in 923 by Sancho I of Pamplona, acting for the Kingdom of Pamplona together with the Kingdom of León and the Counts of Castile, feudal lords of the Leonese King. The lower region around Arnedo came under control of his allies the Banu Qasi of Tudela. The territory to the east of the Leza River remained under Muslim control. Later, there was a dispute between Count Fernán González of Castile and the kings of Pamplona-Navarra, involving great battles. It was decided in favour of the Navarrese after the imprisonment of the Count's family in Cirueña, in 960. La Rioja briefly formed the independent Kingdom of Viguera from 970 to about 1005, at which point it became a part of the Kingdom of Pamplona. Sancho Garcés moved the capital of the Kingdom of Pamplona to Nájera (La Rioja), creating the so-called kingdom of Nájera-Pamplona which was, due to its large size, the first Spanish Empire. After the independence of Castile in 1035, this new kingdom fiercely fought against Pamplona for the possession of Bureba, La Rioja and other territories. In 1076, after the murder of Sancho IV, Navarre was divided among Castile and Aragon. Castile obtained La Rioja, together with other Navarrese lands. The name "La Rioja" first appears in written records in the Miranda de Ebro charter of 1099. The territory was centred on the fortified site of Logroño: the 12th-century church Iglesia de Santa Maria de Palacio recalls its origin as a chapel of the administrative palace. Logroño was a borderland disputed between the kings of Navarre and the kings of Castile from the 10th century; From 1134 the Navarrese under García Ramírez ("the Restorer") and his son Sancho VI ("the Wise") fought bitterly with Castile for the recovery of the former Pamplonese domains. The region was awarded to Castile in a judgement by Henry II of England and annexed in 1177. Its importance lay in part in the pilgrimage route toSantiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela, simply Santiago, or Compostela, in the province of Province of A Coruña, A Coruña, is the capital of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Galicia (Spain), Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city ...
, the '' Camino de Santiago'', which crossed the River Ebro on the stone bridge, the ''Puente de Piedra''.
Province of Logroño
In the 18th century, the territory remained divided between the intendences of Burgos and Soria. The region was taken by Napoleonic forces in thePeninsular War
The Peninsular War (1808–1814) was fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal, Spain and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French ...
and remained solidly in French hands until 1814. In the 1810 project of Llorente it was to be a part of the prefecture
A prefecture (from the Latin word, "''praefectura"'') is an administrative jurisdiction traditionally governed by an appointed prefect. This can be a regional or local government subdivision in various countries, or a subdivision in certain inter ...
of Arlanzón with its capital in Burgos. The Cortes of Cádiz declared La Rioja an independent province at the time of the Liberal Constitution of 1812, and during the Liberal Triennium in January 1822 the province of Logroño was created by royal decree as part of the administrative reform of Riego, taking in the whole of the historical territory of La Rioja. However, Ferdinand VII soon annulled these decisions and restored most of the previous territorial divisions. In the 1833 reorganization, a province of Logroño was again formed within the region of Castilla la Vieja. The province increased its territory temporarily in 1841.
Autonomous community
In 1980 the province changed its name to La Rioja, and following the adoption of the Estatuto de San Millán in 1982, during the reorganization following theSpanish transition to democracy
The Spanish transition to democracy, known in Spain as (; ) or (), is a period of History of Spain, modern Spanish history encompassing the regime change that moved from the Francoist dictatorship to the consolidation of a parliamentary system ...
, it was constituted as a uni-provincial autonomous community
The autonomous communities () are the first-level administrative divisions of Spain, created in accordance with the Spanish Constitution of 1978, with the aim of guaranteeing limited autonomy to the nationalities and regions that make up Sp ...
. It is the second-smallest autonomous community in Spain and has the smallest population; half of its 174 municipalities have populations under 200. Nearly half of its citizens live in the capital.
Geography
La Rioja is bordered by the Basque Country (province of Álava), Navarre, Aragón (province ofZaragoza
Zaragoza (), traditionally known in English as Saragossa ( ), is the capital city of the province of Zaragoza and of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tributaries, the ...
), and Castile and León
Castile and León is an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in northwestern Spain. Castile and León is the largest autonomous community in Spain by area, covering 94,222 km2. It is, however, sparsely populated, with a pop ...
(provinces of Soria and Burgos). The river Ebro
The Ebro (Spanish and Basque ; , , ) is a river of the north and northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, in Spain. It rises in Cantabria and flows , almost entirely in an east-southeast direction. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea, forming a de ...
flows through this region, as does the river Oja, after which it is named.
The Ebro runs through the north of the community. The entire right bank (which is to the south) belongs to La Rioja. There are only three municipalities, Briñas, San Vicente de la Sonsierra and Ábalos on the left bank (known as the Riojan Sonsierra), although Logroño, Agoncillo, Alcanadre, Rincón de Soto and Alfaro also have parts of their respective municipal territories on that bank. Because of their proximity, the Álava area between the Ebro and the Sierra de Cantabria is called Rioja Alavesa.
Major cities
Climate
The climate is mainly continental. The Rioja Alta comarca receives more precipitation than Rioja Baja. The average temperature ranges from and the precipitation ranges between as an annual average. The wind called '' Cierzo'' is very frequent around La Rioja during the winter.Mountains and mountain ranges
The mountains in La Rioja are part of the Iberian System. This mountain range extends to the south of the Ebro river, parallel to it at a distance of about , with altitudes ranging between . From the mountain range the Sierra de la Demanda runs northwards, into the heart of La Rioja, incorporating Monte San Lorenzo which, at , is the highest peak in the province. Other mountains include Sierra de Camero Viejo, Sierra de Camero Nuevo, Sierra de Cebollera, and Picos de Urbión.
Hydrography
TheEbro
The Ebro (Spanish and Basque ; , , ) is a river of the north and northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, in Spain. It rises in Cantabria and flows , almost entirely in an east-southeast direction. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea, forming a de ...
is the main river passing through the community. Emerging from the narrow channel between the rocks of the Conchas de Haro, it reaches La Rioja, through which it runs for , before continuing its journey to the Mediterranean. In the Conchas de Haro the altitude of the river is and when it leaves the community, in the Sotos del Ebro Natural Reserve in Alfaro, it is high. The river therefore flows very quickly through La Rioja.
Seven rivers descend rapidly towards the Ebro from the mountain range, which is why La Rioja is sometimes called: "Zone of the seven valleys". They are, from east to west, Alhama, Cidacos, Leza, Iregua, Najerilla, Oja and Tirón, although the headwaters of the Alhama and Cidacos originate in Soria and those of Najerilla-Neila and Tirón are from Burgos. Sometimes Linares (a tributary of Alhama) is added, grouping Tirón with its tributary, the Oja.
All the rivers of these valleys form tributaries that go on to form many valleys in their own right, such as those of Linares, Ocon, Jubera, Tuerto, Brieva, Viniegras and San Millán. There is an almost unlimited number of grandiose canyons, quite splendid in nature, such as Aguas Buenas, Nieva, Manzanares, Ardancha, Navajún, Valderresa, Ollora, Tobia, San Martín and others.
Flora and fauna
In the highlands, oaks, beech andpine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
are grown. There are also thickets of juniper, boxwood, sloes, holly
''Ilex'' () or holly is a genus of over 570 species of flowering plants in the family Aquifoliaceae, and the only living genus in that family. ''Ilex'' has the most species of any woody dioecious angiosperm genus. The species are evergreen o ...
and cistus. Thyme
Thyme () is a culinary herb consisting of the dried aerial parts of some members of the genus ''Thymus (plant), Thymus'' of flowering plants in the mint family Lamiaceae. Thymes are native to Eurasia and north Africa. Thymes have culinary, medici ...
, rosemary, common juniper, and holm oak are present. There are grand hillsides with fine pasture for livestock, cattle and sheep. In the lower areas there are oaks, olive and almond trees. Near the Ebro, in the plains, the land is used for cereal, sugar beet and potatoes, while the hills are covered with vast vineyards of the wine that has brought worldwide fame to this region.
All Riojan rivers, including the Ebro, have a row of poplars and cottonwood. About the Riojan Alamos Ana Maria Matute has written: "... see them on the edge of the water, turning the landscape, like spears magical pointing towards the unreal and mysterious country of the riverbed."
Natural resources
Gypsum andsilica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
are mined. Arnedillo is a spa town
A spa town is a resort town based on a mineral spa (a developed mineral spring). Patrons visit spas to "take the waters" for their purported health benefits.
Thomas Guidott set up a medical practice in the English town of Bath, Somerset, Ba ...
.
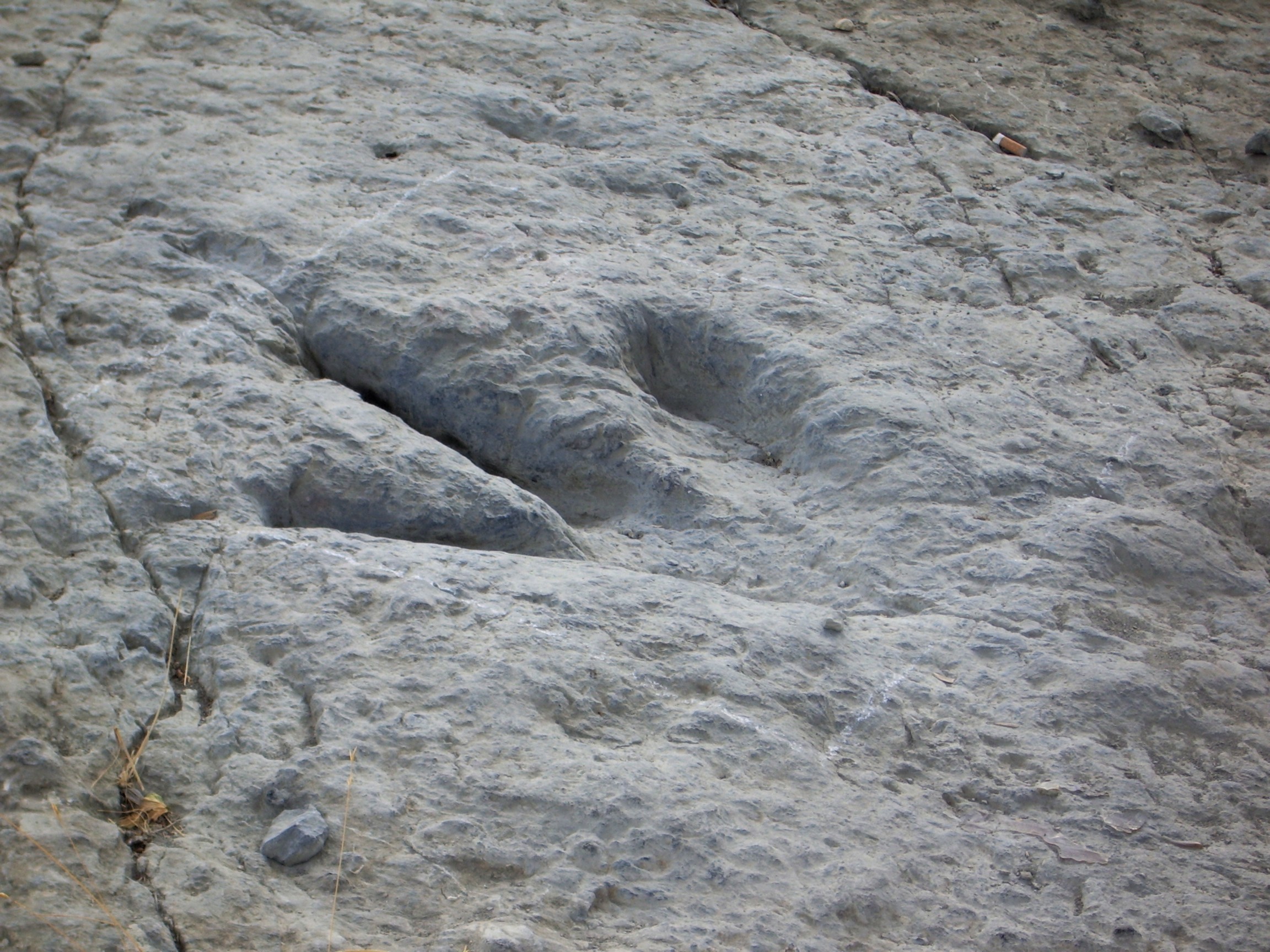
Dinosaur footprints
 During the
During the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
period, the geographical area of Cameros was part of a flooded plain that drained periodically, leaving behind muddy areas where dinosaur tracks marked the path. Eventually they were dried and covered with new sediment layers whose weight pressed down on the lower layers, causing them to solidify into rocks over millions of years. Erosion has been wearing down the upper layers making many of these rock formations visible, bringing into view the fossilized footprints. La Rioja is notable for the number and conservation of these sites, in addition to those found in the north of Soria, such as Yanguas, Santa Cruz de Yanguas and other highland locations.
Comarcas
Geographical comarcas: * Rioja Alta ** Comarca de Anguiano ** Comarca de Ezcaray ** Comarca de Haro ** Comarca de Nájera ** Comarca de Santo Domingo de la Calzada * Rioja Media ** Tierra de Cameros *** Camero Nuevo *** Camero Viejo ** Comarca de Logroño * Rioja Baja ** Comarca de Cervera ** Comarca de Alfaro ** Comarca de Arnedo ** Comarca de CalahorraEconomy
TheGross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
(GDP) of the autonomous community was 8.5 billion euros in 2018, accounting for 0.7% of Spanish economic output. GDP per capita adjusted for purchasing power was 29,200 euros or 97% of the EU27 average in the same year. The GDP per employee was 102% of the EU average.La Rioja is known for its production of Rioja DOCa wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented fruit. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the fruit and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Wine is most often made f ...
s (although the Rioja viticultural region extends slightly into the neighboring administrative regions of Álava and Navarra).
Agriculture
There is dryland farming ofwheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
and grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
; irrigated cultivation of asparagus
Asparagus (''Asparagus officinalis'') is a perennial flowering plant species in the genus ''Asparagus (genus), Asparagus'' native to Eurasia. Widely cultivated as a vegetable crop, its young shoots are used as a spring vegetable.
Description ...
, capsicum
''Capsicum'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the Solanum, nightshade family Solanaceae, native to the Americas, cultivated worldwide for their edible fruit, which are generally known as "peppers" or "capsicum". Chili peppers grow on five s ...
and other crops; and animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, animal fiber, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, management, production, nutrition, selective breeding, and the raising ...
of sheep.
Industry
Types of industry include wine production and conserves (in Logroño, Cenicero, Haro and Calahorra); textiles and footwear (in Logroño, Arnedo, Cervera del Río Alhama and Ezcaray); furniture manufacturing (in Ezcaray, Logroño and Nájera); rubber, plastics, chemical products and transport machinery; and chorizo, made in Casalarreina. Exports are directed mostly towards theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
.
La Rioja hosts the annual Battle of Wine festival in the village of Haro. Another famous local festival is the Toro de fuego, where a metal frame in the shape of a bull is carried among festival goers, which also takes place in Haro.
Demographics
According to the INE the population of La Rioja (as at 2018) is 315,675 inhabitants, with 155,758 men and 159,917 women. Its population density is 62.57 people per km2. It is the least populous autonomous community in Spain. Its capital, Logroño, with approximately 151,113 inhabitants, is its most populous city. La Rioja has 174 municipalities. According to the same INE data, there are more men than women in 150 of them, in two the numbers are the same and in 22 there are more females than males. In the latter set, the differences are small, except in the capital where there are 4,868 more women than men.Education
According to the 2007 PISA report, education in La Rioja is of the highest quality in Spain, close to that of other European countries with better overall educational levels in terms of student knowledge. In the Ministry of Education's 2009 report La Rioja was in first position among the autonomous communities as it relates to general aspects of primary and secondary education. It is placed above the Spanish average in the list of communities with the lowest levels of school failure, with 85% of students being able to obtain the ESO title, despite its schools having the highest proportion of enrolled immigrants. 6,208 euros are spent per pupil, making it the tenth ranked community in this regard. The majority of educational institutions in the community are public, followed by subsidized and private schools, the latter of which are very scarce at the primary and secondary levels. The bachillerato is free in public schools and at a cost in charter schools. In La Rioja the portion of the population with higher education is 30.6%, with two institutions offering studies at this level: the University of La Rioja and an online university, the International University of La Rioja.Retrieved 15 May 2017. See also Spanish Wikipedia article.
Transportation
Pamplona
Pamplona (; ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Navarre, Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain.
Lying at near above sea level, the city (and the wider Cuenca de Pamplona) is located on the flood pl ...
to Logroño since 2006, and in the future will reach Burgos. Other major road routes include:
* N-111
* N-232
* N-120
* Autopista AP-69 (proposed)
* Piqueras Tunnel
* Puerto de Oncala
* Puerto de Piqueras
Government and politics
The current President of La Rioja is Gonzalo Capellán of PP. The autonomous community has its ownParliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
. Other organs include the ''Consejo de Gobierno'' (council of government) and the ''Tribunal Superior de Justicia'' (high court of justice).
Monuments
* Monastery of Santa María la Real of Najera * Concatedral de Santa María de la Redonda * Catedral de Santo Domingo de la Calzada * Iglesia de Santo Tomás * Abbey of Santa María de San Salvador of CañasNotable people
 * Ángel Iturriaga Barco
* Celso Morga Iruzubieta
*
* Ángel Iturriaga Barco
* Celso Morga Iruzubieta
* Dani Aranzubia
Daniel Aranzubia Aguado (born 18 September 1979) is a Spanish former professional Association football, footballer who played as a Goalkeeper (association football), goalkeeper. He is the current goalkeeper coach of SD Amorebieta, Amorebieta.
H ...
* Domingo de Silos
* Fausto Elhuyar
* Fortunato Pablo Urcey
* Francisco Javier de Lizana y Beaumont
* Gonzalo de Berceo
* Gustavo Bueno
* José Ortiz-Echagüe
José Ortiz-Echagüe (2 August 1886 in Guadalajara – 7 September 1980 in Madrid) was a Spanish entrepreneur, industrial and military engineer, pilot and photographer, founder of Construcciones Aeronáuticas SA (CASA) and Honorary lifetime Presi ...
* Juan José Elhuyar
* Manuel Bretón de los Herreros
* Martín Fernández de Navarrete
* Práxedes Mateo Sagasta
See also
* Caparrones, one of the most important dishes in Riojan cooking. * Dulzaina, a popular musical instrument from La Rioja. * History of Rioja wine * Jota (music), a popular dance practiced in some comarcas of La Rioja. * List of presidents of the Parliament of La RiojaReferences
External links
Government of La Rioja
Tourism in La Rioja
{{Authority control Autonomous communities of Spain NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union States and territories established in 1982 hr:La Rioja