Kresy dialects on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Eastern Borderlands ( pl, Kresy Wschodnie) or simply Borderlands ( pl, Kresy, ) was a term coined for the eastern part of the
From peace to war: Germany, Soviet Russia, and the world, 1939–1941.
' Berghahn Books. p. 74. . Soviet territorial annexations during

 The Polish word ("borderlands") is the plural form of the word meaning 'edge'. According to , it is "a medieval borrowing from the German word ", which in the Middle Ages meant ("borderline, delineation or circumscribed territory").
The Polish word ("borderlands") is the plural form of the word meaning 'edge'. According to , it is "a medieval borrowing from the German word ", which in the Middle Ages meant ("borderline, delineation or circumscribed territory").
/ref> Frequently, whole ''Kresy'' villages and towns were deported in a single rail transport to new locations in the west. For instance, the village of Biała, near Chojnów, is still divided into two parts: Lower Biała and Upper Biała. Lower Biała was settled by people who used to live in a Bieszczady village of Polana near
 The proportions of different native languages in each voivodeship in 1931, according to the Polish census of 1931, were as follows:
*
The proportions of different native languages in each voivodeship in 1931, according to the Polish census of 1931, were as follows:
*
 The territory known to Poles as ''Kresy'' is now partitioned off between the states of Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania. Ethnic Poles still live in those areas: in Lithuania, they are the largest ethnic minority in the country (see
The territory known to Poles as ''Kresy'' is now partitioned off between the states of Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania. Ethnic Poles still live in those areas: in Lithuania, they are the largest ethnic minority in the country (see
Kresy.pl - The Biggest Polish Kresy PortalCommonwealth of Diverse Cultures: Poland's HeritageEastern Borderlands of Poland (in English)
* ttp://rzecz-pospolita.com/ Virtual Commonwealth - Eastern Borderlandsbr>Virtual Tour of KresyVolhynia in the Interwar PeriodAn extensive digital collection of Kresy-oriented historic publicationsMojeKresy.pl The newest Polish Kresy Portal
{{Coord missing, Belarus Historical regions in Belarus * Geographic history of Ukraine World War II crimes in Poland Poland in World War II Historical regions in Lithuania Deportation Aftermath of World War II Borders of Poland Polish irredentism Victims of post–World War II forced migrations
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World ...
during the interwar period (1918–1939). Largely agricultural and extensively multi-ethnic, it amounted to nearly half of the territory of pre-war Poland. Historically situated in the eastern Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ...
, following the 18th-century foreign partitions it was annexed by Russia and partly by the Habsburg monarchy (Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
), and ceded to Poland in 1921 after the Peace of Riga
The Peace of Riga, also known as the Treaty of Riga ( pl, Traktat Ryski), was signed in Riga on 18 March 1921, among Poland, Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus) and Soviet Ukraine. The treaty ended the Polish–Soviet War. ...
. As a result of the post-World War II border changes, none of the lands remain in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
today.
The Polish plural term ''Kresy'' corresponds to the Russian ''okrainy'' (), meaning "the border regions". It is also largely co-terminous with the northern areas of the "Pale of Settlement
The Pale of Settlement (russian: Черта́ осе́длости, '; yi, דער תּחום-המושבֿ, '; he, תְּחוּם הַמּוֹשָב, ') was a western region of the Russian Empire with varying borders that existed from 1791 to 19 ...
", a scheme devised by Catherine the Great to limit Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
from settling in the homogenously Christian Orthodox core of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
, such as Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
and Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
. The Pale was established after the Second Partition of Poland
The 1793 Second Partition of Poland was the second of three partitions (or partial annexations) that ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The second partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian ...
and lasted until the 1917 revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of governme ...
, when the Russian Empire ceased to exist. In the aftermath of the Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (Polish–Bolshevik War, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Russian War 1919–1921)
* russian: Советско-польская война (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), Польский фронт (' ...
and the Peace of Riga, both Austrian and Russian sectors of the Kresy were reincorporated into Poland. However, the population already consisted of various religious and ethnic minorities, which exceeded the number of ethnic Poles, for instance Jews in small towns called shtetl
A shtetl or shtetel (; yi, שטעטל, translit=shtetl (singular); שטעטלעך, romanized: ''shtetlekh'' (plural)) is a Yiddish term for the small towns with predominantly Ashkenazi Jewish populations which existed in Eastern Europe before ...
s and Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Or ...
in the region of Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
.
Administratively, the Eastern Borderlands territory was composed of Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukrain ...
, Nowogródek
Novogrudok ( be, Навагрудак, Navahrudak; lt, Naugardukas; pl, Nowogródek; russian: Новогрудок, Novogrudok; yi, נאַוואַראַדאָק, Novhardok, Navaradok) is a town in the Grodno Region, Belarus.
In the Middle A ...
, Polesie
Polesia, Polesie, or Polesye, uk, Полісся (Polissia), pl, Polesie, russian: Полесье (Polesye) is a natural and historical region that starts from the farthest edge of Central Europe and encompasses Eastern Europe, including East ...
, Stanisławów, Tarnopol
Ternópil ( uk, Тернопіль, Ternopil' ; pl, Tarnopol; yi, טאַרנאָפּל, Tarnopl, or ; he, טארנופול (טַרְנוֹפּוֹל), Tarnopol; german: Tarnopol) is a city in the west of Ukraine. Administratively, Ternopi ...
, Wilno
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urba ...
, Wołyń
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
, and Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok Up ...
voivodeship
A voivodeship is the area administered by a voivode (Governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval ...
s (provinces). Today, all these regions are divided between Western Ukraine
Western Ukraine or West Ukraine ( uk, Західна Україна, Zakhidna Ukraina or , ) is the territory of Ukraine linked to the former Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, which was part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Austri ...
, Western Belarus
Western Belorussia or Western Belarus ( be, Заходняя Беларусь, translit=Zachodniaja Bielaruś; pl, Zachodnia Białoruś; russian: Западная Белоруссия, translit=Zapadnaya Belorussiya) is a historical region of mod ...
, and south-eastern Lithuania, with the major cities of Lviv
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukra ...
, Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional u ...
, and Grodno
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish ...
no longer in Poland. During the Second Polish Republic, Eastern Borderlands denoted the lands beyond the Curzon Line
The Curzon Line was a proposed demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and the Soviet Union, two new states emerging after World War I. It was first proposed by The 1st Earl Curzon of Kedleston, the British Foreign Secretary, to th ...
proposed after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
in December 1919 by the British Foreign Office as the eastern border of the re-emerging sovereign Polish Republic, after over a century of partitions. In September 1939, after the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
simultaneously invaded Poland under the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
, all the territories were forcibly incorporated into the Soviet republics of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
and Lithuania, often by means of terror. Bernd Wegner (1997). From peace to war: Germany, Soviet Russia, and the world, 1939–1941.
' Berghahn Books. p. 74. . Soviet territorial annexations during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
were later ratified by the Allies at the Tehran Conference
The Tehran Conference ( codenamed Eureka) was a strategy meeting of Joseph Stalin, Franklin Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill from 28 November to 1 December 1943, after the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran. It was held in the Soviet Union's embass ...
, the Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (codenamed Argonaut), also known as the Crimea Conference, held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the post ...
and at the Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris Pe ...
. At the Dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, Kresy remained within the former Soviet republics as they gained independence. Even though the Eastern Borderlands are no longer part of Poland, the provinces are still home to a Polish minority and the memory of Eastern Borderlands, as a continuation of their centuries-long nationhood, is maintained among many of them.
Etymology

 The Polish word ("borderlands") is the plural form of the word meaning 'edge'. According to , it is "a medieval borrowing from the German word ", which in the Middle Ages meant ("borderline, delineation or circumscribed territory").
The Polish word ("borderlands") is the plural form of the word meaning 'edge'. According to , it is "a medieval borrowing from the German word ", which in the Middle Ages meant ("borderline, delineation or circumscribed territory"). Samuel Linde
Samuel Gottlieb Linde (polonised ''Samuel Bogumił Linde''; 11 or 24 April 1771, in Toruń – 8 August 1847, in Warsaw) was a linguist, librarian, and lexicographer of the Polish language. He was director of the Prussian-founded Warsaw Lyceum d ...
in his ''Dictionary of the Polish Language'' gives a different etymology of the term. According to him, meant the borderline between Poland and the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
, in the region of the lower Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine ...
. The term appeared for the first time in literature in poems, "" (1854) and "". Pol claimed that Kresy was the line between the Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and ...
and Dnieper rivers, neighbouring the Tatar borderland. Coincidentally in relation to Jewish settlement in the macro region, the notion of the ''pale'' is an archaic English term derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
word ', (which in Polish exists as ''pal'' and also means a stake), extended in this instance to mean the area enclosed by a fence or boundary.
At the beginning of the 20th century, the meaning of the term expanded to include the lands of the former eastern provinces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ...
, east of the line. In the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of the First World ...
, equated to historically Polish settled lands to the east of the notional Curzon line
The Curzon Line was a proposed demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and the Soviet Union, two new states emerging after World War I. It was first proposed by The 1st Earl Curzon of Kedleston, the British Foreign Secretary, to th ...
. Currently, the term applies to all the eastern lands of the Second Polish Republic that are no longer within the frontiers of modern Poland, together with lands further east, that had been integral to the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with " republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from th ...
before 1772, and where Polish communities continue to exist.
History
Polish eastern settlements date back to the dawn of Poland as a state. In 1018, KingBolesław I the Brave
Bolesław I the Brave ; cs, Boleslav Chrabrý; la, Boleslaus I rex Poloniae (17 June 1025), less often known as Bolesław the Great, was Duke of Poland from 992 to 1025, and the first King of Poland in 1025. He was also Duke of Bohemia bet ...
invaded Kievan Rus
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas o ...
(see Boleslaw I's intervention in the Kievan succession crisis, 1018), capturing Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
, and annexing Red Strongholds
The Cherven Cities or Cherven Gords ( pl, Grody Czerwieńskie, uk, Червенські городи), often literally translated as Red Cities, Red Forts or Red Boroughs, was a point of dispute between the Kingdom of Poland and Kievan Rus' at th ...
. In 1340, Red Ruthenia
Red Ruthenia or Red Rus' ( la, Ruthenia Rubra; '; uk, Червона Русь, Chervona Rus'; pl, Ruś Czerwona, Ruś Halicka; russian: Червонная Русь, Chervonnaya Rus'; ro, Rutenia Roșie), is a term used since the Middle Ages fo ...
came under Polish control, which intensified defensive Polish settlement and the introduction of Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. After the Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the per ...
1569, more Polish settlers moved into the eastern borderlands of the vast Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ...
. Most of them came from the Polish provinces of Mazovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centuri ...
and Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
. They had moved gradually eastwards settling in sparsely populated areas, inhabited by earlier settlers (Lithuanians
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Ame ...
and Ruthenians
Ruthenian and Ruthene are exonyms of Latin origin, formerly used in Eastern and Central Europe as common ethnonyms for East Slavs, particularly during the late medieval and early modern periods. The Latin term Rutheni was used in medieval sourc ...
). Moreover, the indigenous upper classes of ''Kresy'' accepted Polish religion, culture and language, resulting in their assimilation and Polonization
Polonization (or Polonisation; pl, polonizacja)In Polish historiography, particularly pre-WWII (e.g., L. Wasilewski. As noted in Смалянчук А. Ф. (Smalyanchuk 2001) Паміж краёвасцю і нацыянальнай ідэя� ...
.
The Partitions of Poland
The year 1772 marked the first partition of the Commonwealth of theKingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lit ...
(see Partitions of Poland). By 1795, the whole eastern half of the state had been annexed by the Russian Empire in concert with the Habsburgs and Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
's Hohenzollerns
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenbu ...
. The dramatic westward expansion of the Russian Empire through the annexation of Polish-Lithuanian territory substantially increased the new "Russian" Jewish population. Kresy and the superimposed Pale, in the former Polish and Lithuanian territories, had a Jewish population of over five million, and represented the largest community (40%) of the world Jewish population at that time.
From the Polish perspective, the lands came to be called the " Stolen Lands". Even though Poles were a minority in those areas, owing to forced depopulation, the "Stolen Lands" remained an integral part of Polish national identity, with Polish cultural centres and seats of learning in Wilno University
Vilnius University ( lt, Vilniaus universitetas) is a public research university, oldest in the Baltic states and in Northern Europe outside the United Kingdom (or 6th overall following foundations of Oxford, Cambridge, St. Andrews, Glasgo ...
, Jan Kazimierz University
The University of Lviv ( uk, Львівський університет, Lvivskyi universytet; pl, Uniwersytet Lwowski; german: Universität Lemberg, briefly known as the ''Theresianum'' in the early 19th century), presently the Ivan Franko Na ...
and Liceum Krzemienieckie among many others. Since many local educated inhabitants had actively participated in Polish national insurgencies (November Uprising
The November Uprising (1830–31), also known as the Polish–Russian War 1830–31 or the Cadet Revolution,
was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in ...
, January Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at ...
), the Russian authorities resorted to intensified persecution, confiscations of property and land, penal deportation to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
, and the systematic attempt at Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
of Poles and their traditional culture and institutions.
The Pale of Settlement
From the Russian perspective the "Pale of Settlement" included all ofBelarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
, Lithuania and Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnist ...
, much of present-day Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
, parts of eastern Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, eastern Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
, and some parts of western Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
, generally corresponding to the Kresy macroregion and the modern-day western border of Russia. It extended from the eastern ''pale'', or demarcation line, to the Russian border with the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) constituted the German state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: ...
(later the German Empire) and the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with t ...
. It also comprised about 20% of the territory of European Russia and largely corresponded to historical lands of the former Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ...
, Cossack Hetmanate
The Cossack Hetmanate ( uk, Гетьманщина, Hetmanshchyna; or ''Cossack state''), officially the Zaporizhian Host or Army of Zaporizhia ( uk, Військо Запорозьке, Viisko Zaporozke, links=no; la, Exercitus Zaporoviensis) ...
, and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
(with Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
).
The area included in the Pale, with its large Jewish, Uniate
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also called the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous (''sui iuris'') particular churches of th ...
and Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
populations, was acquired through a series of military conquests and diplomatic manoeuvres, between 1654 and 1815. While the religious nature of the edicts creating the Pale is clear: conversion to Russian Orthodoxy
Russian Orthodoxy (russian: Русское православие) is the body of several churches within the larger communion of Eastern Orthodox Christianity, whose liturgy is or was traditionally conducted in Church Slavonic language. Most C ...
, the state religion, released individuals from the strictures - historians argue that the motivations for its creation and maintenance were primarily economic and nationalist
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
ic in nature.
Economic decline of Kresy
TheRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
had abandoned Kresy to decline as a vast rural backwater after the original Polish landowners had been disposed of in the wake of insurrections and the Abolition of serfdom in Poland in 1864. The devastation of country estates put a halt to large scale economic activity which had depended on agriculture, forestry, brewing and small scale industries. Paradoxically, the Southern Kresy (present-day Ukraine) was famous for its fertile soil and was known as the "bread basket of Europe". Towards the end of the 19th century, the decline was so acute that trade and food supplies became problematic and large scale emigration from towns and villages began as Jewish communities, in particular, began heading West, to Europe and the United States. By the time of a newly resurgent Polish state, the provinces had been additionally disadvantaged by having the lowest literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, hum ...
levels in the country, since education had not been compulsory during Russian rule. The regions had suffered a legacy of decades of neglect and underinvestment so were generally less economically developed than the western parts of interwar Poland.
Between the World Wars
The years 1918–1921 were especially turbulent for ''Kresy'', due to the resurgence of the Polish nation-state and the formation of new borders. At that time, Poland had fought three wars to establish its eastern frontier: with Ukraine (seePolish–Ukrainian War
The Polish–Ukrainian War, from November 1918 to July 1919, was a conflict between the Second Polish Republic and Ukrainian forces (both the West Ukrainian People's Republic and Ukrainian People's Republic). The conflict had its roots in eth ...
), the Soviet Union (see Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (Polish–Bolshevik War, Polish–Soviet War, Polish–Russian War 1919–1921)
* russian: Советско-польская война (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), Польский фронт (' ...
), and with Lithuania (see Polish–Lithuanian War
The Polish–Lithuanian War (in Polish historiography, Polish–Lithuanian Conflict) was an undeclared war between newly-independent Lithuania and Poland following World War I, which happened mainly, but not only, in the Vilnius and Suwałki reg ...
). In all three conflicts Poland emerged victorious, and as a result, it recovered territories that had been previously annexed under Russian conquest and were east of the Curzon line, plus land formerly absorbed into Austrian Eastern Galicia
Eastern Galicia ( uk, Східна Галичина, Skhidna Galychyna, pl, Galicja Wschodnia, german: Ostgalizien) is a geographical region in Western Ukraine (present day oblasts of Lviv, Ivano-Frankivsk and Ternopil), having also essential h ...
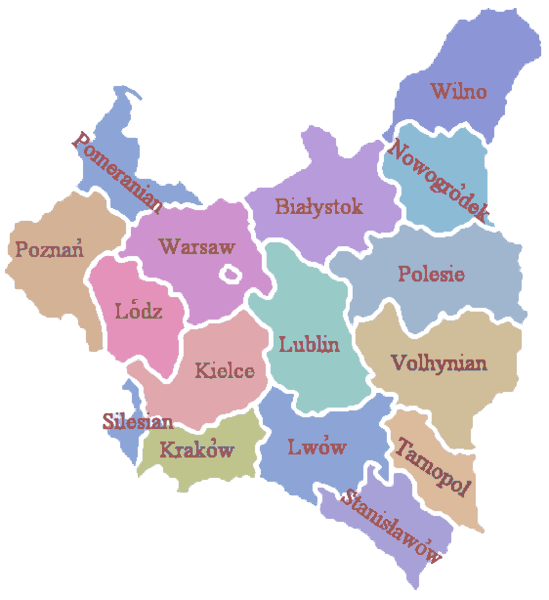
. The region later formed the eastern provinces of the Second Polish Republic. Territories that were included in Kresy during the interbellum period comprised the eastern part of Lwów Voivodeship
Lwów Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo lwowskie) was an administrative unit of interwar Poland (1918–1939). Because of the Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland in accordance with the secret Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, it became occupied by both the Wehr ...
, Nowogródek Voivodeship, Polesie Voivodeship
Polesie Voivodeship ( pl, województwo poleskie) was an administrative unit of interwar Poland (1918–1939), named after the historical region of Polesia. It was created by the Council of Ministers of the Second Polish Republic on February 19, ...
, Stanisławów Voivodeship
Stanisławów Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo stanisławowskie) was an administrative district of the interwar Poland (1920–1939). It was established in December 1920 with an administrative center in Stanisławów. The voivodeship had an area of ...
, Tarnopol Voivodeship
Tarnopol Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo tarnopolskie) was an administrative region of interwar Poland (1918–1939), created on 23 December 1920, with an area of 16,500 km² and provincial capital in Tarnopol (now ''Ternopil'', Ukraine). The voi ...
, Wilno Voivodeship, Wołyń Voivodeship, and the eastern part of Białystok Voivideship. The Polish government undertook an active policy of re-polonization in those territories (see Osadnik
Osadniks ( pl, osadnik/osadnicy, "settler/settlers, colonist/colonists") were veterans of the Polish Army and civilians who were given or sold state land in the ''Kresy'' (current Western Belarus and Western Ukraine) territory ceded to Poland by P ...
). This led to frequent conflicts with Ukrainian nationalists in the southeastern part of the ''Kresy'' region (see Pacification of Ukrainians in Eastern Galicia (1930)).
Numerous Polish communities continued to live beyond the eastern border of the Second Polish Republic, especially around Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative stat ...
, Zhytomir and Berdychev. In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the Soviet authorities created two Polish Autonomous District
Polish National Districts (called in Russian "полрайоны", ''polrajony'', an abbreviation for "польские национальные районы", "Polish national raions") were in the interbellum period possessing some form of a ...
s in Belarus and Ukraine, but during the Polish operation of the NKVD, most of the Poles in those areas were murdered, while those remaining were forcibly resettled in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
(see also Poles in the former Soviet Union).
During and after World War II
As a consequence of theMolotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
, on September 17, 1939, the Kresy territories were annexed by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
(see Soviet invasion of Poland
The Soviet invasion of Poland was a military operation by the Soviet Union without a formal declaration of war. On 17 September 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Poland from the east, 16 days after Nazi Germany invaded Poland from the west. Subs ...
), and a significant part of the ethnic Polish population of ''Kresy'' was deported to other areas of the Soviet Union including Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
and Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
. The new border between Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and the Soviet Union was re-designated by the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty, signed on September 29, 1939. After the elections to the People's Assemblies of Western Ukraine and Western Belarus, communist governments for Western Ukraine and Western Belarus were formed and immediately announced their intention of joining their respective republics to the Soviet Union (see also Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union
Seventeen days after the German invasion of Poland in 1939, which marked the beginning of the Second World War, the Soviet Union entered the eastern regions of Poland (known as the '' Kresy'') and annexed territories totalling with a population ...
). After the German invasion of the USSR, the southeastern part of ''Kresy'' was absorbed into Greater Germany
Pan-Germanism (german: Pangermanismus or '), also occasionally known as Pan-Germanicism, is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanists originally sought to unify all the German-speaking people – and possibly also Germanic-speaking ...
's General Government, whereas the rest was integrated with the Reichskommissariat
''Reichskommissariat'' ( en, Imperial Commissariat) is a German word for a type of administrative entity headed by a government official known as a '' Reichskommissar'' ( en, Imperial Commissioner). Although many offices existed, primarily throu ...
s Ostland and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
. In 1943–1944, units of the Ukrainian Insurgent Army
The Ukrainian Insurgent Army ( uk, Українська повстанська армія, УПА, translit=Ukrayins'ka povstans'ka armiia, abbreviated UPA) was a Ukrainian nationalist paramilitary and later partisan formation. During Worl ...
, with the help of Ukrainian peasants, carried out mass exterminations of Poles living in southeastern ''Kresy'' (see Massacres of Poles in Wołyń
The massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern Galicia ( pl, rzeź wołyńska, lit=Volhynian slaughter; uk, Волинська трагедія, lit=Volyn tragedy, translit=Volynska trahediia), were carried out in German-occupied Poland by the ...
).
In January 1944, Soviet troops had reached the former Polish–Soviet border, and by the end of July 1944, they again re-annexed the whole territory that had been taken by the USSR in September 1939 into their control. During the Tehran Conference
The Tehran Conference ( codenamed Eureka) was a strategy meeting of Joseph Stalin, Franklin Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill from 28 November to 1 December 1943, after the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran. It was held in the Soviet Union's embass ...
in 1943, a new Soviet-Polish border was established, in effect sanctioning most of the Soviet territorial acquisitions of September 1939 (except for some areas around Białystok and Przemyśl), ignoring protests from the Polish government-in-exile in London. The Potsdam Conference, via substantive recognition of the pro-Soviet Polish Committee of National Liberation
The Polish Committee of National Liberation ( Polish: ''Polski Komitet Wyzwolenia Narodowego'', ''PKWN''), also known as the Lublin Committee, was an executive governing authority established by the Soviet-backed communists in Poland at the ...
, implicitly consented to the deportation of Polish people from ''Kresy'' (see Polish population transfers (1944–1946)
The Polish population transfers in 1944–1946 from the eastern half of prewar Poland (also known as the expulsions of Poles from the Kresy macroregion), were the forced migrations of Poles toward the end and in the aftermath of World War I ...
). Most Polish inhabitants of ''Kresy'' were ordered by the Soviets to migrate west to Germany's former eastern provinces, newly emptied of their German population and renamed as the "Recovered Territories
The Recovered Territories or Regained Lands ( pl, Ziemie Odzyskane), also known as Western Borderlands ( pl, Kresy Zachodnie), and previously as Western and Northern Territories ( pl, Ziemie Zachodnie i Północne), Postulated Territories ( pl, Z ...
" of the People's Republic of Poland
The Polish People's Republic ( pl, Polska Rzeczpospolita Ludowa, PRL) was a country in Central Europe that existed from 1947 to 1989 as the predecessor of the modern Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million nea ...
, based on Polish medieval settlement of the areas. Poles from the southern ''Kresy'' (now Ukraine) were forced to settle mainly in Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is spli ...
, while those from the north (Belarus and Lithuania) moved to Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to t ...
and Masuria
Masuria (, german: Masuren, Masurian: ''Mazurÿ'') is a ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the ...
. Polish residents of Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukrain ...
settled not only in Wrocław, but also in Gliwice
Gliwice (; german: Gleiwitz) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. The city is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Kłodnica river (a tributary of the Oder). It lies approximately 25 km west from Katowice, the regional cap ...
and in Bytom
Bytom (Polish pronunciation: ; Silesian: ''Bytōm, Bytōń'', german: Beuthen O.S.) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. Located in the Silesian Voivodeship of Poland, the city is 7 km northwest of Katowice, the regional capital. ...
. Those cities had not been destroyed during the war. They were relatively closer to the new eastern border of Poland, which could become significant in case of a sudden hoped for a return to the East.Gazeta Wyborcza, Kresowianie nie mieli wyboru, musieli jechać na zachód, interview with Professor Grzegorz Hryciuk, 2010-12-20/ref> Frequently, whole ''Kresy'' villages and towns were deported in a single rail transport to new locations in the west. For instance, the village of Biała, near Chojnów, is still divided into two parts: Lower Biała and Upper Biała. Lower Biała was settled by people who used to live in a Bieszczady village of Polana near
Ustrzyki Dolne
Ustrzyki Dolne (; yi, Istrik, uk, Устри́ки-Долі́шні, translit=Ustrýky-Dolíshni) is a town in south-eastern Poland, situated in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship (since 1999) close to the border with Ukraine. It is the capital of B ...
(this area belonged to the Soviet Union until 1951: see 1951 Polish–Soviet territorial exchange), while inhabitants of the village Pyszkowce near Buczacz moved to Upper Biała. Every year in September, Biała is the scene of an annual festival called ''Kresowiana''. In Szczecin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
and Polish West Pomerania, in the immediate postwar period, one-third of Polish settlers were either people from ''Kresy'' or Sybiraks. In 1948, people born in the Eastern Borderlands made up 47.5% of the population of Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opolí''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city lo ...
, 44.7% of Baborów, 47.5% of Wołczyn, 42.1% of Głubczyce
Głubczyce ( cs, Hlubčice or sparsely ''Glubčice'', german: Leobschütz, Silesian German: ''Lischwitz'') is a town in Opole Voivodeship in southern Poland, near the border with the Czech Republic. It is the administrative seat of Głubczyce C ...
, 40.1% of Lewin Brzeski, and 32.6% of Brzeg
Brzeg (; Latin: ''Alta Ripa'', German language, German: ''Brieg'', Silesian German: ''Brigg'', , ) is a town in southwestern Poland with 34,778 inhabitants (December 2021) and the capital of Brzeg County. It is situated in Silesia in the Opole V ...
. In 2011, people with ''Kresy'' background made up 25% of the population of the Opole Voivodeship
Opole Voivodeship, or Opole Province ( pl, województwo opolskie ), is the smallest and least populated voivodeship (province) of Poland. The province's name derives from that of the region's capital and largest city, Opole. It is part of Upper S ...
. The town of Jasień was settled by people from the area of Ternopil
Ternópil ( uk, Тернопіль, Ternopil' ; pl, Tarnopol; yi, טאַרנאָפּל, Tarnopl, or ; he, טארנופול (טַרְנוֹפּוֹל), Tarnopol; german: Tarnopol) is a city in the west of Ukraine. Administratively, Ternopi ...
in late 1945 and early 1946, while Poles from Borschiv moved to Trzcińsko-Zdrój and Chojna
Chojna (german: Königsberg in der Neumark; csb, Czińsbarg; la, Regiomontanus Neomarchicus "King's Mountain in the New March") is a small town in northwestern Poland in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. It lies approximately south of Szcze ...
. The situation was completely different in Wschowa
Wschowa (pronounced , german: Fraustadt) is a town in the Lubusz Voivodeship in western Poland with 13,875 inhabitants (2019). It is the capital of Wschowa County and a significant tourist site containing many important historical monuments.
Hi ...
and its county. In 1945–1948, more than 8,000 people moved there. They came from different areas of the ''Kresy'' — Ashmyany
Ashmyany ( be, Ашмя́ны; Łacinka: ''Ašmiany''; russian: Ошмя́ны; lt, Ašmena; pl, Oszmiana; yi, אָשמענע, ''Oshmene'') is a town in Grodno Region, Belarus, located at 50 km from Vilnius. The town is Ashmyany Distri ...
, Stanislawow, Równe, Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukrain ...
, Brody
Brody ( uk, Броди; russian: Броды, Brodï; pl, Brody; german: Brody; yi, בראָד, Brod) is a city in Zolochiv Raion of Lviv Oblast (province) of western Ukraine. It is located in the valley of the upper Styr River, approximately ...
, Dziatłava district
Dzyatlava District ( be, Дзятлаўскі раён) is a district (rajon) in Grodno Region of Belarus.
The administrative center is Dzyatlava.
Notable residents
* Viačasłaŭ Adamčyk
Viačasłaŭ Uładzimieravič Adamčyk ( be, Вяча ...
, and Tarnopol
Ternópil ( uk, Тернопіль, Ternopil' ; pl, Tarnopol; yi, טאַרנאָפּל, Tarnopl, or ; he, טארנופול (טַרְנוֹפּוֹל), Tarnopol; german: Tarnopol) is a city in the west of Ukraine. Administratively, Ternopi ...
.
Altogether, between 1944 and 1946, more than a million Poles from the ''Kresy'' were moved to the Recovered Territories
The Recovered Territories or Regained Lands ( pl, Ziemie Odzyskane), also known as Western Borderlands ( pl, Kresy Zachodnie), and previously as Western and Northern Territories ( pl, Ziemie Zachodnie i Północne), Postulated Territories ( pl, Z ...
, including 150,000 from the area of Wilno, 226,300 from Polesie
Polesia, Polesie, or Polesye, uk, Полісся (Polissia), pl, Polesie, russian: Полесье (Polesye) is a natural and historical region that starts from the farthest edge of Central Europe and encompasses Eastern Europe, including East ...
, 133,900 from Wołyń
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
, 5,000 from Northern Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter Berge ...
, and 618,200 from Eastern Galicia. The so-called First Repatriation of Poles (1944–1946) was carried out in a chaotic, disorganized way. People had to spend weeks, even months at railroad stations, waiting for transport. During that time, they were robbed of their belongings by either locals, Soviet soldiers or Soviet rail workers. For lack of railroad cars, in Lithuania at some point the "one-suitcase policy" was introduced, which meant that Poles had to leave behind all their belongings. They travelled in freight or open wagon
Open wagons (trucks in the UK) form a large group of railway goods wagons designed primarily for the transportation of bulk goods that are not moisture-retentive and can usually be tipped, dumped or shovelled. The International Union of R ...
s, and the journeys were long and dangerous, as there was no protection from the military or the police. In the years 1955–1959, the second mass repatriation of Poles from Kresy (Easter Borderlands) took place. As a result, in the years 1945–1960, over 2 million Polish people left Kresy. About 1-2 million more remained in the Kresy after 1960 (especially in the territories of the Lithuanian SSR
The Lithuanian Soviet Socialist Republic (Lithuanian SSR; lt, Lietuvos Tarybų Socialistinė Respublika; russian: Литовская Советская Социалистическая Республика, Litovskaya Sovetskaya Sotsialistiche ...
and the Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, Беларуская Савецкая Сацыялістычная Рэспубліка, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyčnaja Respublika; russian: Белор� ...
). Even today, Poles constitute the majority of inhabitants in many regions in the Grodno and Vilnius regions.
In the immediate postwar period, Polish Communists, who ceded the Eastern Borderlands to the Soviet Union, were universally regarded as traitors, and Władysław Gomułka
Władysław Gomułka (; 6 February 1905 – 1 September 1982) was a Polish communist politician. He was the ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized ...
, First Secretary of the Polish Workers' Party, was fully aware of it. People who moved from the East to the Recovered Territories talked amongst themselves about their return to Lwów and other eastern locations, and the German return to Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is spli ...
, as a result of World War III
World War III or the Third World War, often abbreviated as WWIII or WW3, are names given to a hypothetical worldwide large-scale military conflict subsequent to World War I and World War II. The term has been in use since at ...
, in which Western Allies would defeat the Soviets. One of the adages of the postwar period was: "Just one atom bomb, and we will be back in Lwów again.
Just second one is small but strong and we will be back in Wilno again." ("Jedna bomba atomowa i wrócimy znów do Lwowa. Druga mała, ale silna i wrócimy znów do Wilna"). Polish settlers in former German areas were insecure about their future there until the 1970s (see Warschauer Kniefall). Eastern settlers did not feel at home in Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the ...
, and as a result, they did not care about the machinery, households and farms abandoned by Germans. Lubomierz
Lubomierz (german: Liebenthal) is a town in Lwówek Śląski County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivo ...
in 1945 was in good condition, but in the following years, Polish settlers from the area of Czortków in Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-central ...
let it run down and become a ruin. The Germans were aware of it. In 1959, German sources wrote that Lower Silesia had been ruined by the Poles. Zdzisław Mach, a sociologist from the Jagiellonian University, explains that when Poles were forced to resettle in the West, which they resented, they had to leave the land they considered sacred and move to areas inhabited by the enemy. In addition, Communist authorities did not initially invest in the Recovered Territories because, like the settlers, for a long time they were unsure about the future of these lands. As Mach says, people in Western Poland for years lived "on their suitcases", with all their belongings packed in case of return to the East.
Interwar population
The population of ''Kresy'' was multi-ethnic, primarily comprising Poles, Jews, Ukrainians and Belarusians. According to official Polish statistics from the interwar period, Poles formed the largest linguistic group in these regions, and were demographically the largest ethnic group in the cities. Other national minorities includedLithuanians
Lithuanians ( lt, lietuviai) are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another million or two make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Ame ...
and Karaites
Karaite or Qaraite may refer to:
*Karaite Judaism, a Jewish religious movement that rejects the Talmud
**Crimean Karaites, an ethnic group derived from Turkic-speaking adherents of Karaite Judaism in Eastern Europe
***Karaim language, Turkic lan ...
(in the north), Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
(scattered in cities and towns across the area), Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, ...
and Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
(in Wołyń and East Galicia), Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
and Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ural ...
(in Lwów) and also Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
and Tartars.
 The proportions of different native languages in each voivodeship in 1931, according to the Polish census of 1931, were as follows:
*
The proportions of different native languages in each voivodeship in 1931, according to the Polish census of 1931, were as follows:
*Lwów Voivodeship
Lwów Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo lwowskie) was an administrative unit of interwar Poland (1918–1939). Because of the Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland in accordance with the secret Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, it became occupied by both the Wehr ...
; 58% Polish, 34% Ukrainian, 8% Yiddish
* Nowogródek Voivodeship; 53% Polish, 39% Belarusian, 7% Yiddish, 1% Russian
*Polesie Voivodeship
Polesie Voivodeship ( pl, województwo poleskie) was an administrative unit of interwar Poland (1918–1939), named after the historical region of Polesia. It was created by the Council of Ministers of the Second Polish Republic on February 19, ...
; 63% "Other" or Tutejsi, 14% Polish, 10% Yiddish, 6% Belarusian, 5% Ukrainian
*Stanisławów Voivodeship
Stanisławów Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo stanisławowskie) was an administrative district of the interwar Poland (1920–1939). It was established in December 1920 with an administrative center in Stanisławów. The voivodeship had an area of ...
; 69% Ukrainian, 23% Polish, 7% Yiddish, 1% German
*Tarnopol Voivodeship
Tarnopol Voivodeship ( pl, Województwo tarnopolskie) was an administrative region of interwar Poland (1918–1939), created on 23 December 1920, with an area of 16,500 km² and provincial capital in Tarnopol (now ''Ternopil'', Ukraine). The voi ...
; 50% Polish, 45% Ukrainian, 5% Yiddish
* Wilno Voivodeship; 60% Polish, 23% Belarusian, 8% Yiddish, 3% Russian, 8% Other (including Lithuanian)
* Volhynia Voivodeship; 68% Ukrainian, 17% Polish, 10% Yiddish, 2% German, 1% Russian, 2% Other
* Białystok Voivodeship; 71% Polish, 13% Belarusian, 11% Yiddish, 3% Russian, 2% Other
In addition to ethnic Poles in former eastern Poland, there were also large Polish communities in the USSR and in the Baltic states. Polish population east of the Curzon Line before World War II can be estimated by adding together figures for Former Eastern Poland and for pre-1939 Soviet Union:
Largest cities and towns
In 1931, according to the Polish National Census, the ten largest cities in Polish Eastern Borderlands were:Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukrain ...
(pop. 312,200), Wilno
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urba ...
(pop. 195,100), Stanisławów (pop. 60,000), Grodno
Grodno (russian: Гродно, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, Гродна ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish ...
(pop. 49,700), Brześć nad Bugiem (pop. 48,400), Borysław (pop. 41,500), Równe (pop. 40,600), Tarnopol
Ternópil ( uk, Тернопіль, Ternopil' ; pl, Tarnopol; yi, טאַרנאָפּל, Tarnopl, or ; he, טארנופול (טַרְנוֹפּוֹל), Tarnopol; german: Tarnopol) is a city in the west of Ukraine. Administratively, Ternopi ...
(pop. 35,600), Łuck
Lutsk ( uk, Луцьк, translit=Lutsk}, ; pl, Łuck ; yi, לוצק, Lutzk) is a city on the Styr River in northwestern Ukraine. It is the administrative center of the Volyn Oblast (province) and the administrative center of the surrounding Lut ...
(pop. 35,600) and Kołomyja (pop. 33,800).
In addition, Daugavpils
Daugavpils (; russian: Двинск; ltg, Daugpiļs ; german: Dünaburg, ; pl, Dyneburg; see other names) is a state city in south-eastern Latvia, located on the banks of the Daugava River, from which the city gets its name. The parts of the c ...
(pop. 43,200 in 1930) in inter-war Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
was also a major Polish community with 21% ethnic Polish inhabitants.
Polish minority after World War II
Despite the expulsion of most of ethnic Poles from the Soviet Union between 1944 and 1958, the Soviet census of 1959 still counted around 1.5 million ethnic Poles remaining in the USSR: According to a more recent census, there were about 295,000 Poles in Belarus in 2009 (3.1% of the Belarus population).Notable people
A number of influential figures in Polish history were born in the area of ''kresy'' (note: the redirected list does not include Poles born in the cities of Lwów (Lviv), and Wilno (Vilnius) - see List of Leopolitans,List of Vilnius-related people
The following is a list of notable people from Lithuania's capital city of Vilnius (historically known by the names of Vilna/Wilna/Wilno). It includes people who were born or resided there.
A
* Neringa Aidietytė (born 1983), athlete
* Frantsis ...
). The family of former President of Poland, Bronisław Komorowski
Bronisław Maria Komorowski (; born 4 June 1952) is a Polish politician and historian who served as President of Poland from 2010 to 2015.
Komorowski served as Minister of Defence from 2000 to 2001. As Marshal of the Sejm, Komorowski exercis ...
, allegedly hails from northern Lithuania. The mother of Bogdan Zdrojewski, Minister of Culture and National Heritage is from Boryslav
Boryslav ( uk, Борислав; pl, Borysław) is a city located on the Tysmenytsia (a tributary of the Dniester), in Drohobych Raion, Lviv Oblast (region) of western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Boryslav urban hromada, one of the ...
, and the father of former First Lady Jolanta Kwaśniewska
Jolanta Kwaśniewska (Polish: , née Konty, ; born 3 June 1955) is a Polish lawyer and charity activist who was First Lady of Poland between 1995 and 2005, as the wife of the then President Aleksander Kwaśniewski.
Biography
She was a graduat ...
was born in Wołyń
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
, where his sister was murdered in 1943 by the Ukrainian nationalists.
Cradle of Polish culture
Since some of the most distinguished names of Polish literature and music were born in ''Kresy'', e.g. Mikołaj Rej,Adam Mickiewicz
Adam Bernard Mickiewicz (; 24 December 179826 November 1855) was a Polish poet, dramatist, essayist, publicist, translator and political activist. He is regarded as national poet in Poland, Lithuania and Belarus. A principal figure in Polish ...
, Juliusz Słowacki
Juliusz Słowacki (; french: Jules Slowacki; 4 September 1809 – 3 April 1849) was a Polish Romantic poet. He is considered one of the " Three Bards" of Polish literature — a major figure in the Polish Romantic period, and the father of m ...
, Karol Szymanowski
Karol Maciej Szymanowski (; 6 October 188229 March 1937) was a Polish composer and pianist. He was a member of the modernist Young Poland movement that flourished in the late 19th and early 20th century.
Szymanowski's early works show the in ...
or Czesław Miłosz
Czesław Miłosz (, also , ; 30 June 1911 – 14 August 2004) was a Polish-American poet, prose writer, translator, and diplomat. Regarded as one of the great poets of the 20th century, he won the 1980 Nobel Prize in Literature. In its citation, ...
, ''Eastern Borderlands'' have featured repeatedly in the Polish Literary canon
The term canon derives from the Greek (), meaning "rule", and thence via Latin and Old French into English. The concept in English usage is very broad: in a general sense it refers to being one (adjectival) or a group (noun) of official, authent ...
. Mickiewicz's Pan Tadeusz
''Pan Tadeusz'' (full title: ''Mister Thaddeus, or the Last Foray in Lithuania: A Nobility's Tale of the Years 1811–1812, in Twelve Books of Verse'') is an epic poem by the Polish poet, writer, translator and philosopher Adam Mickiewicz. The ...
begins with the Polish language invocation, "O Lithuania, my fatherland, thou art like good health...." Other notable works located in ''Kresy'', are Nad Niemnem, Sanatorium Under the Sign of the Hourglass, With Fire and Sword
''With Fire and Sword'' ( pl, Ogniem i mieczem, links=no) is a historical novel by the Polish author Henryk Sienkiewicz, published in 1884. It is the first volume of a series known to Poles as The Trilogy, followed by ''The Deluge'' (''Potop'', ...
, Fire in the Steppe. In Communist Poland, all ''Kresy''-related topics, such as Poland's eastern centuries old heritage, including ecclesiastical architecture, country houses and stately homes down to the Massacres of Poles in Wołyń
The massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern Galicia ( pl, rzeź wołyńska, lit=Volhynian slaughter; uk, Волинська трагедія, lit=Volyn tragedy, translit=Volynska trahediia), were carried out in German-occupied Poland by the ...
were banned from publication for Soviet propaganda reasons, because these lands now belonged to the Soviet Union. In official documents, people born in the Eastern Borderlands were declared as born in the Soviet Union, and very few ''Kresy''-themed books or films were passed by the state censor at that time. One of the exceptions was the immensely popular comedy trilogy by Sylwester Chęciński ('' Sami swoi'' from 1967, ''Nie ma mocnych'' from 1974, and ''Kochaj albo rzuć'' from 1977). The trilogy tells the story of two quarreling families, who after the end of the Second World War were resettled from current Western Ukraine to Lower Silesia, after Poland was shifted westwards.
After the collapse of the Communist system, the old ''Kresy'' returned as a Polish cultural theme in the form of historical polemics. Numerous books and albums were published about the Eastern Borderlands, frequently with original photos from the prewar era. Examples of such publications include:
* Roman Aftanazy. ''Dzieje rezydencji na dawnych kresach Rzeczypospolitej''. Wrocław: Wydawnictwo Ossolineum, 1991–1997. ''History of Residences in Poland's Former Eastern Borderlands'', (1991–1997), listing and describing in a monumental eleven volume work the cultural heritage contained in the myriad estates and grand residences in the once Polish Kresy and Inflanty regions.
* ''Kresy in Photos of Henryk Poddębski'', published in May 2010 in Lublin, with a foreword by people with a ''Kresy'' background - Anna Seniuk, Krzesimir Dębski
Krzesimir Marcin Dębski (; born 26 October 1953 in Wałbrzych) is a Polish composer, conductor and jazz violinist. His music career as a musician has been that of a performer as well as composer of classical music, opera, television and featur ...
and Maciej Płażyński
Maciej Płażyński (; 10 February 1958 – 10 April 2010) was a Polish liberal-conservative politician.
Biography
Płażyński was born in Młynary. He began his political career in 1980 / 1981 as one of the leaders of the Students' Solidar ...
* ''The World of Kresy'', with numerous photos, postcards and maps
* ''Sentimental Journeys. Travel across Kresy with Andrzej Wajda
Andrzej Witold Wajda (; 6 March 1926 – 9 October 2016) was a Polish film and theatre director. Recipient of an Honorary Oscar, the Palme d'Or, as well as Honorary Golden Lion and Honorary Golden Bear Awards, he was a prominent member of th ...
and Daniel Olbrychski
Daniel Marcel Olbrychski (; born 27 February 1945) is a Polish film and theatre actor who is widely considered one of the greatest Polish actors of his generation. He appeared in 180 films and TV productions and is best known for leading roles ...
''
* ''The Encyclopedia of Kresy'', with 3600 articles, and foreword by another famous person from ''Kresy'', Stanisław Lem
Stanisław Herman Lem (; 12 September 1921 – 27 March 2006) was a Polish writer of science fiction and essays on various subjects, including philosophy, futurology, and literary criticism. Many of his science fiction stories are of satirica ...
. Articles about the Eastern Borderlands frequently appear in Polish newspapers and magazines. The local office of ''Gazeta Wyborcza
''Gazeta Wyborcza'' (; ''The Electoral Gazette'' in English) is a Polish daily newspaper based in Warsaw, Poland. It is the first Polish daily newspaper after the era of " real socialism" and one of Poland's newspapers of record, covering the ...
'' in Wrocław in late 2010 began a ''Kresy Family Album'', stories and photos of those who were forced to move from the East.
In the first half of 2011, ''Rzeczpospolita
() is the official name of Poland and a traditional name for some of its predecessor states. It is a compound of "thing, matter" and "common", a calque of Latin ''rés pública'' ( "thing" + "public, common"), i.e. '' republic'', in Engl ...
'' daily published a series called "The Book of Eastern Borderlands" (''Księga kresów wschodnich''). The July 2012 issue of the Uważam Rze Historia magazine was dedicated to the Eastern Borderlands and their importance in Polish history and culture.
Present day
 The territory known to Poles as ''Kresy'' is now partitioned off between the states of Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania. Ethnic Poles still live in those areas: in Lithuania, they are the largest ethnic minority in the country (see
The territory known to Poles as ''Kresy'' is now partitioned off between the states of Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania. Ethnic Poles still live in those areas: in Lithuania, they are the largest ethnic minority in the country (see Poles in Lithuania
The Poles in Lithuania ( pl, Polacy na Litwie, lt, Lietuvos lenkai), estimated at 183,000 people in the Lithuanian census of 2021 or 6.5% of Lithuania's total population, are the country's largest ethnic minority.
During the Polish–Lithuania ...
), in Belarus, they are the second largest ethnic minority in the country after Russians (see Poles in Belarus
The Polish minority in Belarus numbers officially 288,000 according to 2019 census.. Listing total population of Belarus with population by age and sex, marital status, education, nationality, language and livelihood ("Общая численн ...
), and in Ukraine, they officially number 144,130, but some Polish organizations claim that the number of Poles in Ukraine may be as many as 2 million, most of them assimilated. (see Poles in Ukraine
The Polish minority in Ukraine officially numbers about 144,130 (according to the 2001 census),
). Furthermore, there is a 50,000 Polish minority in Latvia. In Lithuania and Belarus, Poles are more numerous than in Ukraine. This is the result of the Polish population transfers (1944–1946)
The Polish population transfers in 1944–1946 from the eastern half of prewar Poland (also known as the expulsions of Poles from the Kresy macroregion), were the forced migrations of Poles toward the end and in the aftermath of World War I ...
as well as Massacres of Poles in Wołyń Voivodeship
The massacres of Poles in Volhynia and Eastern Galicia ( pl, rzeź wołyńska, lit=Volhynian slaughter; uk, Волинська трагедія, lit=Volyn tragedy, translit=Volynska trahediia), were carried out in German-occupied Poland by th ...
. Those Poles who survived the slaughter begged for the opportunity to emigrate.
Many Polish organizations are active in the former Eastern Borderlands, such as the Association of Poles in Ukraine, Association of Polish Culture of the Lviv Land, the Federation of Polish Organizations in Ukraine, Union of Poles in Belarus, and the Association of Poles in Lithuania. There are Polish sports clubs ( Pogoń Lwów, FK Polonia Vilnius
Klub Sportowy Polonia ( lt, FK Polonija Vilnius) was a football club based in Vilnius, Lithuania. KS Polonia was formed on 18 March 1990 by Poles from Vilnius.
History
The Club was founded on March 18, 1990, under the name Poles Club of Lithu ...
), newspapers ( Gazeta Lwowska, Kurier Wileński), radio stations (in Lviv and Vilnius), many theatres, schools, choirs and folk ensembles. Poles living in ''Kresy'' are helped by a government-sponsored organization Fundacja Pomoc Polakom na Wschodzie Fundacja Pomoc Polakom na Wschodzie (''The Foundation Aid to Poles in the East'') is a foundation created by Polish government (State Treasury) in order to facilitate the cooperation between Polish government and Polonia in the East (primarily, fo ...
, and by other organizations, such as the Association of Help of Poles in the East Kresy (see also Karta Polaka). Money is frequently collected to help those Poles who live in ''Kresy'', and there are several annual events, such as "Christmas Package for a Polish Veteran in Kresy", and "Summer with Poland", sponsored by Association "Polish Community", in which Polish children from ''Kresy'' are invited to visit Poland. Polish language handbooks and films, as well as medicines and clothes are collected and sent to ''Kresy''. Books are most often sent to Polish schools which exist there — for example, in December 2010, University of Wrocław organized an event called "Become a Polish Santa Claus and Give a Book to a Polish Child in Kresy". Polish churches and cemeteries (such as Cemetery of the Defenders of Lwów) are renovated with money from Poland. For example, in Nysa, money is collected to renovate the Roman Catholic church in Łopatyn near Lviv, while residents of Oława
Oława (pronounced , , szl, Oława) is a historic town in south-western Poland with 33,029 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (from 1975–1998 it was in the former Wrocław Voivodeship), within the Wrocław ...
collect funds to renovate the church in Sasiv, also in the area of Lviv. Also, physicians from Kraków's organization Doctors of Hope regularly visit Eastern Borderlands, and the Polish Ministry of Education runs a special program, which sends Polish teachers to the former Soviet Union. In 2007, more than 700 teachers worked in the East, most of them in ''Kresy''. Studio East of Polish TV Wrocław organizes an event called "Save your grandfather's tomb from oblivion" (''Mogiłę pradziada ocal od zapomnienia''), during which students from Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( pl, Dolny Śląsk; cz, Dolní Slezsko; german: Niederschlesien; szl, Dolny Ślōnsk; hsb, Delnja Šleska; dsb, Dolna Šlazyńska; Silesian German: ''Niederschläsing''; la, Silesia Inferior) is the northwestern part of the ...
visit Western Ukraine, to clean Polish cemeteries there. In July 2011, about 150 students cleaned 16 cemeteries in the areas of Lviv, Ternopil
Ternópil ( uk, Тернопіль, Ternopil' ; pl, Tarnopol; yi, טאַרנאָפּל, Tarnopl, or ; he, טארנופול (טַרְנוֹפּוֹל), Tarnopol; german: Tarnopol) is a city in the west of Ukraine. Administratively, Ternopi ...
, Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-central ...
and Pokuttya
Pokuttia, also known as Pokuttya or Pokutia ( uk, Покуття, Pokuttya; pl, Pokucie; german: Pokutien; ro, Pocuția), is a historical area of East-Central Europe, situated between the Dniester and Cheremosh rivers and the Carpathian Mounta ...
.
Despite wars and ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population trans ...
many treasures of Polish culture still remain in the East. In Vilnius, there is the Wróblewski Library, with 160,000 volumes and 30,000 manuscripts, which now belong to the Lithuanian Academy of Sciences
The Lithuanian Academy of Sciences or LMA ( lt, Lietuvos mokslų akademija) is a state-funded independent organization in Lithuania dedicated for science and research. Its mission is to mobilize prominent scientists and initiate activities that ...
. In Lviv, there is the Ossolineum, one of the most important Polish culture centres. Adolf Juzwenko, current president of Wrocław's office of the Ossolineum, says that in 1945, there was a mass public campaign in Poland, aimed at transporting the whole Ossolineum to Wrocław. It succeeded in recovering only 200,000 volumes, as the Soviets decided that the bulk of the library had to remain in Lviv.
In contemporary Poland
Even though Poland lost its Eastern Borderlands in the aftermath of World War II, Poles connected with the Kresy still have some affection for those lands. Since Poles from current Western Ukraine mostly moved toSilesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is spli ...
, the city of Wrocław
Wrocław (; , . german: Breslau, , also known by other names) is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly ...
is regarded as ''miasto lwowskie'' (city of Lwów affinity), while Toruń
)''
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_flag = POL Toruń flag.svg
, image_shield = POL Toruń COA.svg
, nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town
, pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pom ...
, Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
and Olsztyn
Olsztyn ( , ; german: Allenstein ; Old Prussian: ''Alnāsteini''
* Latin: ''Allenstenium'', ''Holstin'') is a city on the Łyna River in northern Poland. It is the capital of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, and is a city with county right ...
are regarded as ''miasta wileńskie'' (cities of Wilno affinity). Lwów's Ossolineum Foundation, its collections and famous library are now located in Wrocław. Polish academics from Lwów established the Polish University of Wrocław
, ''Schlesische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität zu Breslau'' (before 1945)
, free_label = Specialty programs
, free =
, colors = Blue
, website uni.wroc.pl
The University of Wrocław ( pl, Uniwersytet Wrocławski, U ...
(taking over from the old German University of Breslau) and Silesian University of Technology
The Silesian University of Technology ( Polish name: Politechnika Śląska; ) is a university located in the Polish province of Silesia, with most of its facilities in the city of Gliwice. It was founded in 1945 by Polish professors of the Lwow P ...
. At the same time, Polish academics from Vilnius founded Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń
Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń or NCU ( pl, Uniwersytet Mikołaja Kopernika w Toruniu, UMK) is located in Toruń, Poland. It is named after Nicolaus Copernicus, who was born in Toruń in 1473.Bytom
Bytom (Polish pronunciation: ; Silesian: ''Bytōm, Bytōń'', german: Beuthen O.S.) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. Located in the Silesian Voivodeship of Poland, the city is 7 km northwest of Katowice, the regional capital. ...
, and branches scattered across Poland, and abroad. The Congress organizes annual World Convention and Pilgrimage of Kresy Inhabitants to Jasna Góra Monastery
The Jasna Góra Monastery ( pl, Jasna Góra , ''Luminous Mount'', hu, Fényes Hegy, lat, Clarus Mons) in Częstochowa, Poland, is a shrine dedicated to the Virgin Mary and one of the country's places of pilgrimage. The image of the Black Mado ...
.
Other important ''Kresy'' organizations, active in contemporary Poland, include:
* ''Polskie Towarzystwo Miłośników Miasta Krzemieńca i Ziemi Krzemienieckiej'' (Polish Association of Lovers of Krzemieniec and Krzemieniec Land) from Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
.
* ''Stowarzyszenie Kresowe "Podkamień"'' (Kresy Association "Podkamien") from Wołów
Wołów (german: Wohlau, cz, Volov) is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in south-western Poland. It is the seat of Wołów County and Gmina Wołów. It lies approximately north-west of the regional capital Wrocław. , the town has a popula ...
,
* ''Stowarzyszenie Odra-Niemen'' (Association Odra - Niemen
The Neman, Nioman, Nemunas or MemelTo bankside nations of the present: Lithuanian: be, Нёман, , ; russian: Неман, ''Neman''; past: ger, Memel (where touching Prussia only, otherwise Nieman); lv, Nemuna; et, Neemen; pl, Niemen; ; ...
) from Wrocław,
* ''Stowarzyszenie Przyjaciół Ziemi Drohobyckiej'' (Association of Friends of Drohobycz
Drohobych ( uk, Дрого́бич, ; pl, Drohobycz; yi, דראָהאָביטש;) is a city of regional significance in Lviv Oblast, Ukraine. It is the administrative center of Drohobych Raion and hosts the administration of Drohobych urban hr ...
Land) from Legnica
Legnica (Polish: ; german: Liegnitz, szl, Lignica, cz, Lehnice, la, Lignitium) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River (left tributary of the Oder) and the Czarna Woda. Between 1 June 19 ...
,
* ''Stowarzyszenie Rodzin Osadników Wojskowych i Cywilnych Kresów Wschodnich'' (Association of Families of Osadnik
Osadniks ( pl, osadnik/osadnicy, "settler/settlers, colonist/colonists") were veterans of the Polish Army and civilians who were given or sold state land in the ''Kresy'' (current Western Belarus and Western Ukraine) territory ceded to Poland by P ...
s of Eastern Borderlands) from Warsaw,
* ''Towarzystwo Miłośników Kultury Kresowej'' (Association of Friends of Kresy Culture) from Wrocław,
* ''Towarzystwo Miłośników Wołynia i Polesia'' (Association of Lovers of Wołyn and Polesie) from Warsaw,
* ''Towarzystwo Miłośników Lwowa i Kresów Południowo-Wschodnich'' (Association of Lovers of Lwów and Southeastern Kresy) from Wrocław
Wrocław (; , . german: Breslau, , also known by other names) is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, roughly ...
, with branches in Brzeg, Bydgoszcz, Bytom, Chełm, Gdańsk, Jelenia Góra, Kłodzko, Kraków, Leszno, Lublin, Poznań, Szczecinek, Świdwin, Warszawa, Węgliniec and Zabrze,
* ''Towarzystwo Przyjaciół Grodna i Wilna'' (Association of Friends of Grodno and Wilno), with branches in Białystok, Ełk, Gdańsk, Giżycko, Lublin, Łódź, Ostrołęka, Stargard Szczeciński, Warszawa, Węgorzewo, Wrocław,
* ''Związek Sybirakow'' (Association of Sybiraks) from Warsaw, with branches scattered across Poland and abroad.
Every year, in the Masuria
Masuria (, german: Masuren, Masurian: ''Mazurÿ'') is a ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the ...
n town of Mrągowo, there is a ''Festiwal Kultury Kresowej'' (Festival of Kresy Culture), sponsored among others by the Senate of the Republic of Poland and the Minister of Culture, with the patronage of the First Lady. The Festival is broadcast by TVP2
TVP 2 (TVP Dwa, ''Program II Telewizji Polskiej'', ''"Dwójka"'') is a Polish public mainstream TV channel operated by TVP. Launched in October 1970, its varied line-up contains a variety of programming (documentary, history, talk-shows, game-sh ...
and TVP Polonia
TVP Polonia (formerly known as TV Polonia) is the international channel of the Telewizja Polska (TVP). The channel is co-funded by the TVP and the Polish Ministry for Foreign Affairs and broadcasts from the TVP headquarters in Warsaw.
TVP Pol ...
, and in 2011 it was organized for the 17th time. Among participants of the 2011 Festival, there were such artists, as Folk Ensemble Mozyrzanka from Mozyr, Children and Youth Band Tęcza from Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative stat ...
, Folk Band Kresowianka from Ivyanets
Ivyanets ( be, Iвяне́ц, ; russian: Ивенец; pl, Iwieniec), also known as Ivianec, is a town in the Valozhyn District of Minsk Region, Belarus. It is located west of Minsk, and has a population of 4,206 (2017).
Ivyanets is best known ...
, Polish Academic Choir Zgoda from Brest, Instrumental Band Biedronki from Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative stat ...
, Vocal Duo Wspólna wędrówka from Minsk, Children's Polonia Ensemble Dolinianka from Stara Huta (Ukraine), Ensemble Fujareczka from Sambir
Sambir ( uk, Самбір, pl, Sambor, yi, סאמבאָר, Sambor) is a city in Sambir Raion, Lviv Oblast, Ukraine. It serves as the administrative center of Sambir Raion (district) and is located close to the border with Poland. Sambir hosts t ...
, Ensemble Boryslawiacy from Boryslav
Boryslav ( uk, Борислав; pl, Borysław) is a city located on the Tysmenytsia (a tributary of the Dniester), in Drohobych Raion, Lviv Oblast (region) of western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Boryslav urban hromada, one of the ...
, Ensemble Niebo do Wynajecia from Stralhivci (Ukraine), Polish Dance and Song Ensemble Wilenka from Vilnius, Dance and Song Band Troczenie from Trakai
Trakai (; see names section for alternative and historic names) is a historic town and lake resort in Lithuania. It lies west of Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. Because of its proximity to Vilnius, Trakai is a popular tourist destination. ...
, Band Wesołe Wilno from Vilnius, Song and Dance Ensemble Kotwica from Kaunas
Kaunas (; ; also see other names) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Tra ...
, and Folk and Polish Folklore Dance and Song Ensemble Syberyjski Krakowiak from Abakan
Abakan (russian: Абака́н, p=ɐbɐˈkan; Khakas: , ''Ağban''/, ''Abaxan'') is the capital city of the Republic of Khakassia, Russia, located in the central part of Minusinsk Depression, at the confluence of the Yenisei and Abakan Rive ...
in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
.
Other notable Kresy-oriented festivals are:
* ''Dzień Kresowiaka'' (Kresy Inhabitant Day) in the village of Lagiewniki near Malbork
Malbork; ;
* la, Mariaeburgum, ''Mariae castrum'', ''Marianopolis'', ''Civitas Beatae Virginis''
* Kashubian: ''Malbórg''
* Old Prussian: ''Algemin'' is a town in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland. It is the seat of Malbork County and has a p ...
,
* ''Dzień Kresowy'' (Kresy Day) in Wschowa
Wschowa (pronounced , german: Fraustadt) is a town in the Lubusz Voivodeship in western Poland with 13,875 inhabitants (2019). It is the capital of Wschowa County and a significant tourist site containing many important historical monuments.
Hi ...
,
* ''Dzień Kultury Kresowej'' (Day of Kresy Culture) in Kędzierzyn-Koźle
Kędzierzyn-Koźle (german: Kandrzin-Cosel, szl, Kandrzin-Koźle) is a city in southern Poland, the administrative center of Kędzierzyn-Koźle County. With 58,899 inhabitants as of 2021, it is the second most-populous city in the Opole Voivode ...
,
* ''Dni Kultury Kresowej'' (Days of Kresy Culture) in Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok Up ...
,
* ''Dni Kultury Kresowej'' (Days of Kresy Culture) in Brzeg
Brzeg (; Latin: ''Alta Ripa'', German language, German: ''Brieg'', Silesian German: ''Brigg'', , ) is a town in southwestern Poland with 34,778 inhabitants (December 2021) and the capital of Brzeg County. It is situated in Silesia in the Opole V ...
,
* ''Dni Kultury Kresowej'' (Days of Kresy Culture) in Prochowice
Prochowice (german: Parchwitz) is a town in Legnica County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It is the seat of the administrative district (gmina) called Gmina Prochowice.
It lies approximately north-east of Legnica, and we ...
,
* ''Kaziuki'' (''Kaziuko mugė
Kaziuko mugė or Saint Casimir's Fair is a large annual folk arts and crafts fair in Vilnius, Lithuania, dating to the beginning of the 17th century. The fair is traditionally held in city's markets and streets on the Sunday nearest to 4 March (Fe ...
''), an annual folk arts and crafts fair, which takes place in Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional u ...
, is organized in several Polish cities (Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
, Olsztyn
Olsztyn ( , ; german: Allenstein ; Old Prussian: ''Alnāsteini''
* Latin: ''Allenstenium'', ''Holstin'') is a city on the Łyna River in northern Poland. It is the capital of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, and is a city with county right ...
, Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
, Suwałki
Suwałki ( lt, Suvalkai; yi, סואוואַלק) is a city in northeastern Poland with a population of 69,206 (2021). It is the capital of Suwałki County and one of the most important centers of commerce in the Podlaskie Voivodeship. Suwałki ...
, Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is official ...
), on initiative of Poles resettled from Vilnius,
* ''Kresowy Festiwal Polonijny Młodzieży Szkolnej'' (Kresy Festival of Polonia Schoolchildren) in Zamość
Zamość (; yi, זאמאשטש, Zamoshtsh; la, Zamoscia) is a historical city in southeastern Poland. It is situated in the southern part of Lublin Voivodeship, about from Lublin, from Warsaw. In 2021, the population of Zamość was 62,021.
...
,
* ''Legnickie Dni Kultury Kresowej'' (Legnica Days of Kresy Culture) in Legnica
Legnica (Polish: ; german: Liegnitz, szl, Lignica, cz, Lehnice, la, Lignitium) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River (left tributary of the Oder) and the Czarna Woda. Between 1 June 19 ...
, Lubin
Lubin (; german: Lüben, szl, Lubin) is a city in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in south-western Poland. It is the administrative seat of Lubin County, and also of the rural district called Gmina Lubin, although it is not part of the territory of ...
, Jawor
Jawor (german: Jauer) is a town in south-western Poland with 22,890 inhabitants (2019). It is situated in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship (from 1975 to 1998 it was in the former Legnica Voivodeship). It is the seat of Jawor County, and lies appr ...
, Chojnów,
* ''Lipcowy Festiwal Kresowy (July Kresy Festival) in Rejowiec,
* ''Międzynarodowy Festiwal Kultury Kresowej'' (International Festival of Kresy Culture) in Jarosław
Jarosław (; uk, Ярослав, Yaroslav, ; yi, יאַרעסלאָוו, Yareslov; german: Jaroslau) is a town in south-eastern Poland, with 38,970 inhabitants, as of 30 June 2014. Situated in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship (since 1999), previ ...
,
* ''Prezentacja Kultury Polaków z Kresów Wschodnich i Bukowiny'' (Show of Culture of Poles from Eastern Borderlands and Bucovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter BergerT ...
) in Zielona Góra
Zielona Góra is the largest city in Lubusz Voivodeship, located in western Poland, with 140,403 inhabitants (2021). Zielona Góra has a favourable geographical position, being close to the Polish-German border and on several international road ...
, Szprotawa
Szprotawa (german: Sprottau) is a town in western Poland, in Żagań County, Lubusz Voivodeship. It has 11,820 inhabitants (2019).
History
The region was part of Poland after the emergence of the Piast monarchy in the 10th century. The first m ...
, Nowa Sól
Nowa Sól is a city on the Oder River in Lubusz Voivodeship, western Poland. It is the capital of Nowa Sól County and had a population of 38,763 (2019).
History
The first settlement in the region of modern Nowa Sól dates to the 14th century, ...
, Kożuchów
Kożuchów (; german: Freystadt in Schlesien) is a town in Lubusz Voivodeship, Poland.
History
The town was founded in the 12th century, when it was part of the Kingdom of Poland. It was granted town rights in 1273 in the process of Ostdieslung. ...
, Żagań
Żagań (French and german: Sagan, hsb, Zahań , la, Saganum) is a town in western Poland, on the Bóbr river, with 25,731 inhabitants (2019). The town is the capital of Żagań County in the historic region of Silesia. Previously in the Ziel ...
* ''Świdnicki Dzień Kultury Kresowej i Lwowa'' (Świdnica Day of Kresy and Lwów Culture) in Świdnica
Świdnica (; german: Schweidnitz; cs, Svídnice; szl, Świdńica) is a city in south-western Poland in the region of Silesia. As of 2019, it has a population of 57,014 inhabitants. It lies in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, being the seventh larges ...
.
In Lubaczów
Lubaczów ( uk, Любачів ''Liubachiv'') is a town in southeastern Poland, close to the border with Ukraine, with 12,567 inhabitants
Situated in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship (since 1999), it is the capital of Lubaczów County and is locate ...
is a Museum of Kresy, and there is a project, supported by local government, to create a Museum of Eastern Borderlands in Wrocław, the city where a number of Poles from Kresy settled after World War II. Numerous photo albums and books, depicting cities, towns and landscapes of ''Kresy'' are published every year in Poland. In Chełm
Chełm (; uk, Холм, Kholm; german: Cholm; yi, כעלם, Khelm) is a city in southeastern Poland with 60,231 inhabitants as of December 2021. It is located to the south-east of Lublin, north of Zamość and south of Biała Podlaska, some ...
, there is Kresy Bicycle Marathon, Polish Radio Białystok every week broadcasts ''Kresy Magazine'', dedicated to the history and present times of the Eastern Borderlands. Every Sunday, Polish Radio Katowice broadcasts a program based on famous prewar Lwów's Merry Wave, every Tuesday, Polish Radio Rzeszów broadcasts a program ''Kresy Landscapes''. In Wrocław, the Association of Remembrance of Victims of Ukrainian Nationalists publishes ''Na Rubieży'' (''On the Border'') magazine. Among best known ''Kresy'' activists of contemporary Poland are Father Tadeusz Isakowicz-Zaleski, and Dr. Tadeusz Kukiz, father of popular singer Paweł Kukiz
Paweł Piotr Kukiz (born 24 June 1963) is a Polish politician, singer and actor. He is the leader of Kukiz'15, a non-partisan political alliance campaigning for single-member districts, and was a candidate in the 2015 presidential election, in wh ...
. Since 2007, annual medals Heritage of Eastern Borderlands are awarded in Wrocław. The 2011 recipient was emeritus Archbishop of Wrocław, Henryk Gulbinowicz. Participants of annual Katyń Motorcycle Raid (''Motocyklowy Rajd Katyński'') always visit Polish centers in ''Kresy'', giving presents to children, and meeting local Poles.
The program of 2011 Days of Kresy Culture (October 22–23) in Brzeg
Brzeg (; Latin: ''Alta Ripa'', German language, German: ''Brieg'', Silesian German: ''Brigg'', , ) is a town in southwestern Poland with 34,778 inhabitants (December 2021) and the capital of Brzeg County. It is situated in Silesia in the Opole V ...
covered such events, as: ''Kresy'' themed cabaret, promotion of ''Kresy'' books, Eastern Borderlands cuisine, mass in a local church, meetings with ''Kresy'' activists and scholars, and theatre shows of Brzeg's Garrison Club as well as Lwów Eaglets Middle School number 3 in Brzeg. Organizers of the festival assured that for the two days Brzeg would turn into the "capital of interwar Polish Kresy".
In January, February and March 2012, Centre for Public Opinion Research did a survey, asking Poles about their ties to Kresy. It turned out that almost 15% of the population of Poland (4,3 - 4,6 million people) declared that they either were born in the Kresy, or have a parent or a grandparent from that region. The number of ''Kresowiacy'' is high in northern and western Poland – as many as 51% of inhabitants of Lubusz Voivodeship
Lubusz Voivodeship, or Lubuskie Province ( pl, województwo lubuskie ), is a voivodeship (province) in western Poland.
It was created on January 1, 1999, out of the former Gorzów Wielkopolski and Zielona Góra Voivodeships, pursuant to the Pol ...
, and 47% of inhabitants of Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Lower Silesian Voivodeship, or Lower Silesia Province, in southwestern Poland, is one of the 16 voivodeships (provinces) into which Poland is divided. The voivodeship was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Wrocław, Legnica, Wałb ...
stated that their family has ties to the Kresy. Furthermore, ''Kresowiacy'' now make 30% of the population of Opole Voivodeship
Opole Voivodeship, or Opole Province ( pl, województwo opolskie ), is the smallest and least populated voivodeship (province) of Poland. The province's name derives from that of the region's capital and largest city, Opole. It is part of Upper S ...
, 25% of the population of West Pomeranian Voivodeship
The West Pomeranian Voivodeship, also known as the West Pomerania Province, is a voivodeship (province) in northwestern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Szczecin. Its area equals 22 892.48 km² (8,838.84 sq mi), and in 2021, it was ...
, and 18% of the population of Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship
Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship or Warmia-Masuria Province or Warmia-Mazury Province (in pl, Województwo warmińsko-mazurskie, is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Olsztyn. The voivodeship has an ar ...
.
Polish regional dialects
Since Poles have lived in Kresy for hundreds of years, two groups of Kresy Polish dialects emerged: the northern (''dialekt północnokresowy''), and the southern (''dialekt południowokresowy''). Both dialects have been influenced either byUkrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* Som ...
, Belarusian or by Lithuanian. To Polish speakers in Poland, Kresy dialects are easy to distinguish, as their pronunciation and intonation are markedly different from standard Polish. Before World War II, the Kresy provinces were part of Poland, and both dialects were in common usage, spoken by millions of ethnic Poles. After the war and Soviet annexation of Kresy, however, the majority of ethnic Poles were deported
Deportation is the expulsion of a person or group of people from a place or country. The term ''expulsion'' is often used as a synonym for deportation, though expulsion is more often used in the context of international law, while deportation ...
westward, resulting in a severe decline in the number of native speakers. The northern Kresy dialect is still used along the Lithuanian-Belarusian border, where Poles still live in large numbers, but the southern Kresy dialect is endangered, as Poles in western Ukraine do not form a majority of the population in any district. Particularly notable among the Kresy dialects is the Lwów dialect
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukrain ...
which emerged early in the 19th century and was spoken in the city gaining much recognition in the 1920s and 1930s, partly due to the countrywide popularity of numerous Kresy-born and trained actors and comedians whose native speech it was (see also: Dialects of the Polish language).
See also
* Bug River land * Lithuanian and Belarusian Self-Defence * Lwów Eaglets *Peace of Riga
The Peace of Riga, also known as the Treaty of Riga ( pl, Traktat Ryski), was signed in Riga on 18 March 1921, among Poland, Soviet Russia (acting also on behalf of Soviet Belarus) and Soviet Ukraine. The treaty ended the Polish–Soviet War. ...
* Poles in the former Soviet Union
* Polish historical regions
* Polish National-Territorial Region
* Polonia
*Republic of Central Lithuania
The Republic of Central Lithuania ( pl, Republika Litwy Środkowej, ), commonly known as the Central Lithuania, and the Middle Lithuania ( pl, Litwa Środkowa, , be, Сярэдняя Літва, translit=Siaredniaja Litva), was an unrecognize ...
*Repatriation of Poles (1955–1959)
Repatriation of Polish population in the years of 1955–1959 (also known as the ''second repatriation'', to distinguish it from the ''first repatriation'' in the years 1944-1946) was the second wave of forced repatriation (in fact, deportation) ...
* Soviet repressions of Polish citizens (1939–1946)
* Suwałki Agreement
*Territories of Poland annexed by the Soviet Union
Seventeen days after the German invasion of Poland in 1939, which marked the beginning of the Second World War, the Soviet Union entered the eastern regions of Poland (known as the '' Kresy'') and annexed territories totalling with a population ...
*Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russia's ...
*Treaty of Warsaw (1920)
, uk, Варшавський договір
, image =
, image_width = 234px
, caption =
, type = Bilateral political treaty (Military alliance)
, date_drafted =
, date_signed ...
*Vilnius Region
Vilnius Region is the territory in present-day Lithuania and Belarus that was originally inhabited by ethnic Baltic tribes and was a part of Lithuania proper, but came under East Slavic and Polish cultural influences over time.
The territory ...
*Volhynia Experiment The Volhynia Experiment was a cultural and political program by the interwar Polish government in the province of Volhynia whose purpose was to create a Ukrainian identity that was also loyal to the Polish state. It was hoped that this program would ...
* Wanda Wasilewska
*West Ukrainian People's Republic
The West Ukrainian People's Republic (WUPR) or West Ukrainian National Republic (WUNR), known for part of its existence as the Western Oblast of the Ukrainian People's Republic, was a short-lived polity that controlled most of Eastern Galic ...
* Zakerzonia
*Żeligowski's Mutiny
Żeligowski's Mutiny ( pl, bunt Żeligowskiego, also ''żeligiada'', lt, Želigovskio maištas) was a Polish false flag operation led by General Lucjan Żeligowski in October 1920, which resulted in the creation of the Republic of Central Lithuani ...
References
Bibliography
* Beauvois, Daniel ''Trójkąt ukraiński, szlachta, carat i lud na Wołyniu, Podolu i Kijowszczyźnie 1793–1914'', University of Maria Curie-Sklodowska,Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
, 2005, 2011 and 2016 (in Polish)
* Mały rocznik statystyczny 1939, Central Statistical Office of Poland, Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is official ...
1939 (in Polish)
External links
Kresy.pl - The Biggest Polish Kresy Portal
* ttp://rzecz-pospolita.com/ Virtual Commonwealth - Eastern Borderlandsbr>Virtual Tour of Kresy
{{Coord missing, Belarus Historical regions in Belarus * Geographic history of Ukraine World War II crimes in Poland Poland in World War II Historical regions in Lithuania Deportation Aftermath of World War II Borders of Poland Polish irredentism Victims of post–World War II forced migrations