Konkani, (
Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
: ,
Romi: ,
Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
: ,
Koleluttu
Koleḻuttŭ () was a syllabic script historically employed in Kerala, south India, for writing the Malayalam language
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadw ...
: ,
Nastaliq
''Nastaliq'' (; ; ), also Romanization of Persian, romanized as ''Nastaʿlīq'' or ''Nastaleeq'' (), is one of the main book hand, calligraphic hands used to write Arabic script and is used for some Indo-Iranian languages, predominantly Persi ...
: ;
IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Brahmic family, Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that ...
: , ) formerly Concani or Concanese, is an
Indo-Aryan language
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east of the Indus river in Ba ...
spoken by the
Konkani people
The Konkani people are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group native to the Konkan region of the Indian subcontinent. They speak various dialects of the Konkani language. Following the Konkani language agitation, Konkani becam ...
, primarily in the
Konkan
The Konkan is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, bound by the river Daman Ganga at Damaon in the north, to Anjediva Island next to Karwar town in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau to the eas ...
region, along the western
coast of India. It is one of the 22
scheduled languages mentioned in the
Indian Constitution
The Constitution of India is the supreme legal document of India, and the longest written national constitution in the world. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and ...
, and the official language of the Indian state of
Goa
Goa (; ; ) is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north, and Karnataka to the ...
. It is also spoken in
Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
,
Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
,
Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
,
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
as well as
Damaon, Diu & Silvassa.
Konkani is a member of the
Southern Indo-Aryan language group. It retains elements of
Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed ...
structures and shows similarities with both
Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and
Eastern Indo-Aryan languages
The Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Māgadhan languages, are spoken throughout the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, which includes Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Bengal region, Tripura, Assam, and Odisha; alongside othe ...
. The first Konkani inscription is dated 1187 AD.
There are many Konkani dialects spoken along and beyond the Konkan region, from
Damaon
Daman district () (formerly Distrito de Damão) is one of three districts of the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. It is located on the west coast of India and is surrounded by the Valsad district of Gujarat to ...
in the north to
Karwar
Karwar is a coastal City and the administrative headquarters of Uttara Kannada district, formerly part of the Bombay Presidency, located at the mouth of the Kali River (Karnataka), Kali river along the Konkan Coast in the present-day state of Ka ...
in the south; most of which are only partially mutually intelligible with one another due to a lack of linguistic contact and exchanges with the standard and principal forms of Konkani. It is also spoken by migrants outside of the Konkan proper; in
Nagpore,
Surat
Surat (Gujarati Language, Gujarati: ) is a city in the western Indian States and territories of India, state of Gujarat. The word Surat directly translates to ''face'' in Urdu, Gujarati language, Gujarati and Hindi. Located on the banks of t ...
,
Cochin
Kochi ( , ), formerly known as Cochin ( ), is a major port city along the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of Kerala. The city is also commonly referred to as Ernaku ...
,
Mangalore
Mangaluru (), formerly called Mangalore ( ), is a major industrial port city in the Indian state of Karnataka and on the west coast of India. It is located between the Laccadive Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bengaluru, the st ...
,
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ), also spelled Amdavad (), is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 ...
,
Karachi
Karachi is the capital city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Sindh, Pakistan. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, largest city in Pakistan and 12th List of largest cities, largest in the world, with a popul ...
,
New Delhi
New Delhi (; ) is the Capital city, capital of India and a part of the Delhi, National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the Government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Parliament ...
etc. Dialects such as
Malvani Malvani may refer to:
*Malvani people, people from the Malvan region of Maharashtra, on the Konkan coast of western India
* Malvani language, a dialect of Konkani, with heavy influence from Marathi
*Malvani cuisine Malvani may refer to:
*Malvani peo ...
, Chitpavani, Damani,
Koli
Koli may refer to:
People
* Koli people, Indian caste group
* Koli Christians, a Christian subgroup
* Muslim Kolis, Muslim community
* Koli (surname), Indian surname
* Koli Sewabu (born 1975), Fijian rugby union footballer
Places
* Koli, Fin ...
&
Aagri
Agri or Aagri () is a dialect of Maharashtri Konkani which is written in Devanagari script and is spoken by members of the Agri (caste). Although it is commonly seen in comedy shows, it is not merely the language of humour but also the distinct d ...
in Maharashtra; are threatened by
language assimilation into the linguistic majority of non-Konkani
states and territories of India
India is a federalism, federal union comprising 28 federated state, states and 8 union territory, union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 List of districts ...
.
Classification
Konkani belongs to the
Indo-Aryan language
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east of the Indus river in Ba ...
branch. It is part of the
Marathi-Konkani group of the southern Indo-Aryan languages. It is inflexive, and less distant from
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
as compared to other modern
Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east ...
. Linguists describe Konkani as a fusion of a variety of
Prakrit
Prakrit ( ) is a group of vernacular classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 5th century BCE to the 12th century CE. The term Prakrit is usually applied to the middle period of Middle Ind ...
vernacular languages. This could be attributed to the confluence of immigrants that the Konkan coast has witnessed over the years.
Names and their etymology
It is quite possible that Old Konkani was just referred to as ''Prakrit'' by its speakers.
Reference to the name ''Konkani'' is not found in literature prior to the 13th century. The first reference of the name ''Konkani'' is in "
Abhanga 263" of the 13th century
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
Marathi saint poet,
Namadeva (1270–1350).
Konkani has been known by a variety of names: ''Canarim, Concanim, Gomantaki, Bramana,'' and ''Goani''. Learned Marathi speakers tend to call it ''Gomantaki''.
Konkani was commonly referred to as ''Língua Canarim'' by the Portuguese
and ''Língua Brahmana'' by Catholic missionaries.
The Portuguese later started referring to Konkani as ''Língua Concanim''.
The name ''Canarim'' or ''Língua Canarim'', which is how the 16th century European
Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
Thomas Stephens refers to it in the title of his famous work ''
Arte da lingoa Canarim'' has always been intriguing. It is possible that the term is derived from the Persian word for coast, ''kinara''; if so, it would mean "the language of the coast". The problem is that this term overlaps with ''Kanarese'' or
Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
. All the European authors, however, recognised two forms of the language in Goa: the
plebeian
In ancient Rome, the plebeians or plebs were the general body of free Roman citizens who were not patricians, as determined by the census, or in other words "commoners". Both classes were hereditary.
Etymology
The precise origins of the gro ...
, called ''Canarim'', and the more regular (used by the educated classes), called ''Língua Canarim Brâmana'' or simply ''Brâmana de Goa''. The latter was the preferred choice of the Europeans, and also of other castes, for writing, sermons, and religious purposes.
There are different views as to the origin of the word Konkan and hence Konkani:
* V. P. Chavan states that the etymology of Konkan and hence Konkani is derived from the Kannada word ''konku'' meaning '
''uneven ground''
'. The Kannada origin suggests that Konkana might have included Kannada territory and '
''uneven ground''
' suggests the hilly nature of the territory. ''Konku'' in Kannada also means that which is '
''not straight'
'' and is '
''crooked.
* The word Konkan comes from the Kukkana (
Kokna
Kokni, Kokna, Kukna is an Indian Adivasi tribal community found in Sahyadri- Satpura Ranges of Maharashtra (mostly residing in Nandurbar and Dhule districts – Sakri, Navapur talukas) and in Gujarat (mostly residing in Ahwa- Dang, Navsari ...
) tribe, who were the original inhabitants of the land where Konkani originated.
* According to some texts of
s,
Parashurama
Parashurama (), also referred to as Rama Jamadagnya, Rama Bhargava and Virarama, is the sixth avatar among the Dashavatara of the preserver god Vishnu in Hinduism. Hindu tradition holds him to be the destroyer of the evil on Earth. According t ...
shot his arrow into the sea and commanded the Sea God to recede up to the point where his arrow landed. The new piece of land thus recovered came to be known as
Konkan
The Konkan is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, bound by the river Daman Ganga at Damaon in the north, to Anjediva Island next to Karwar town in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau to the eas ...
meaning ''piece of earth'' or ''corner of earth'', ''kōṇa'' (corner) + ''kaṇa'' (piece). This legend is mentioned in
Sahyadrikhanda ''Sahyādri-khaṇḍa'' is a Sanskrit-language text, notable for containing the founding myths of several Brahmin communities of south-western India. The text claims to be a part of the ''Skanda Purana''. It is actually a collection of disparate te ...
of the
Skanda Purana
The ''Skanda Purana'' ( IAST: Skanda Purāṇa) is the largest '' Mukhyapurāṇa'', a genre of eighteen Hindu religious texts. The text contains over 81,000 verses, and is of Shaivite literature, titled after Skanda, a son of Shiva and Parv ...
.
History
Proposed substrate influences
The
substratum
Substrata, plural of substratum, may refer to:
*Earth's substrata, the geologic layering of the Earth
*''Hypokeimenon'', sometimes translated as ''substratum'', a concept in metaphysics
*Substrata (album), a 1997 ambient music album by Biosphere
* ...
of the Konkani language lies in the speech of
Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages ( ) are a large language family spoken throughout Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia and East Asia. These languages are natively spoken by the majority of the population in Vietnam and Cambodia, and by minority popu ...
tribes that may have once inhabited the region.
According to the
Indian Anthropological Society
Indian Anthropological Association (IAA) is the representative body of the professional anthropologists in India. Established in 1969, its headquarters are situated within the Department of Anthropology, University of Delhi and associated with W ...
, these Australoid tribes speaking Austro-Asiatic or Munda languages who once inhabited Konkan, migrated to Northern India (
Chota Nagpur Plateau
The Chota Nagpur Plateau () is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Bihar. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and th ...
,
Mirzapur
Mirzapur () is a city in Uttar Pradesh, India. It is known for its carpets and brassware industries, and the tradition of kajari and birha music. Straddled by the Kaimur extension of Vindhya mountains, it served as the headquarters of t ...
) and are not found in Konkan any more.
Olivinho Gomes in his essay "Medieval Konkani Literature" also mentions the
Mundari substratum.
Goan Indologist Anant Shenvi Dhume identified many Austro-Asiatic
Munda words in Konkani, like ''mund'', ''mundkar'', ''dhumak'', ''goem-bab''.
This substratum is very prominent in Konkani.
The grammatical impact of the Dravidian languages on the structure and syntax of Indo-Aryan languages is difficult to fathom. Some linguists explain this anomaly by arguing that Middle Indo-Aryan and New Indo-Aryan were built on a Dravidian
substratum
Substrata, plural of substratum, may refer to:
*Earth's substrata, the geologic layering of the Earth
*''Hypokeimenon'', sometimes translated as ''substratum'', a concept in metaphysics
*Substrata (album), a 1997 ambient music album by Biosphere
* ...
.
Some examples of Konkani words of Dravidian origin are: ''naall'' (
coconut
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
), ''madval'' (washerman), ''choru'' (cooked rice) and ''mulo'' (
radish
The radish (''Raphanus sativus'') is a flowering plant in the mustard family, Brassicaceae. Its large taproot is commonly used as a root vegetable, although the entire plant is edible and its leaves are sometimes used as a leaf vegetable. Origina ...
). Linguists also suggest that the substratum of Marathi and Konkani is more closely related to Dravidian Kannada.
Prehistory and early development
Migrations of Indo-Aryan vernacular speakers have occurred throughout the history of the Indian west coast. Around 1100-700 BC the first wave of Indo-Aryans dialect speakers might have occurred, with the second wave appearing around 700-500 BC.
Many spoke
old Indo-Aryan
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east of the Indus river in Ba ...
vernacular languages, which may be loosely related to
Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit, also simply referred as the Vedic language, is the most ancient known precursor to Sanskrit, a language in the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan subgroup of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is atteste ...
; others still spoke Dravidian and Desi dialects. Thus the ancient Konkani Prakrit was born as a confluence of the Indo-Aryan dialects while accepting many words from Dravidian speech. Some linguists assume
Shauraseni to be its progenitor whereas some call it
Paisaci
Paishachi or Paisaci () is a largely unattested literary language of the middle kingdoms of India mentioned in Prakrit and Sanskrit grammars of antiquity. It is generally grouped with the Prakrits, with which it shares some linguistic similari ...
. The influence of Paisachi over Konkani can be proved in the findings of Taraporewala, who in his book ''Elements of Science of Languages'' (Calcutta University) ascertained that Konkani showed many
Dardic
The Dardic languages (also Dardu or Pisaca), or Hindu-Kush Indo-Aryan languages, are a group of several Indo-Aryan languages spoken in northern Pakistan, northwestern India and parts of northeastern Afghanistan. This region has sometimes been re ...
features that are found in present-day
Kashmiri.
[ Thus, the archaic form of old Konkani is referred to as Paishachi by some linguists.]Dnyaneshwari
The ''Dnyaneshwari'' () (IAST: Jñānēśvarī), also referred to as ''Jnanesvari'', ''Jnaneshwari'' or ''Bhavartha Deepika'', is a commentary on the ''Bhagavad Gita'' written by the Marathi saint and poet Sant Dnyaneshwar in 1290 CE. Dnyane ...
'', and ''Leela Charitra''.)Dravidians
The Dravidian peoples, Dravidian-speakers or Dravidians, are a collection of ethnolinguistic groups native to South Asia who speak Dravidian languages. There are around 250 million native speakers of Dravidian languages. Telugus form the la ...
from the Deccan plateau.Bhoja
Bhoja was the Paramara dynasty, Paramara king of Malwa from 1010 until his death in 1055. He ruled from Dhara (city), Dhara (modern Dhar), and Military career of Bhoja, fought wars with nearly all his neighbours in attempts to extend his king ...
s; as a result, numerous migrations occurred from north, east and western India. Immigrants spoke various vernacular languages, which led to a mixture of features of Eastern and Western Prakrit. It was later substantially influenced by Magadhi Prakrit.Pali
Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...
Eastern Indo-Aryan languages
The Eastern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Māgadhan languages, are spoken throughout the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, which includes Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, Bengal region, Tripura, Assam, and Odisha; alongside othe ...
like Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
and Oriya, which have their roots in Magadhi.Maharashtri Prakrit
Maharashtri or Maharashtri Prakrit (') is a Prakrit language of ancient as well as medieval India.
Maharashtri Prakrit was commonly spoken until 875 CEV.Rajwade, ''Maharashtrache prachin rajyakarte'' is the ancestor of Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
**Marathi people (Uttar Pradesh), the Marathi people in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Mar ...
and Konkani, it was the official language of the Satavahana Empire that ruled Goa and Konkan in the early centuries of the Common Era. Under the patronage of the Satavahana Empire, Maharashtri became the most widespread Prakrit of its time. Studying early Maharashtri compilations, many linguists have called Konkani "the first-born daughter of Maharashtri".Maharashtri
Maharashtri or Maharashtri Prakrit (') is a Prakrit language of ancient as well as medieval India.
Maharashtri Prakrit was commonly spoken until 875 CEV.Rajwade, ''Maharashtrache prachin rajyakarte'' Prakrit), was commonly spoken until 875 AD, and at its later phase ultimately developed into Apabhramsha, which could be called a predecessor of old Konkani.Kadambas
The Kadamba dynasty were an ancient royal family from modern Karnataka, India, that ruled northern Karnataka and the Konkan from Banavasi in present-day Uttara Kannada, Uttara Kannada district in India. The kingdom was founded by Mayurash ...
, who ruled Goa for a long period, had their roots in Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
. Konkani was never used for official purposes.Lothal
Lothal () was one of the southernmost sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilization, Indus Valley civilisation, located in the Bhal region of the Indian state of Gujarat. Construction of the city is believed to have begun around 2200 BCE.
Di ...
migrants all settled in Goa during the pre-historic period and later. ''Chavada'', a tribe of warriors (now known as ''Chaddi'' or ''Chaddo''), migrated to Goa from Saurashtra
Saurashtra, Sourashtra, or variants may refer to:
** Kathiawar, also called Saurashtra Peninsula, a peninsula in western India
** Saurashtra (state), alias United State of Kathiawar, a former Indian state, merged into Bombay State and since its d ...
, during the 7th and 8th century AD, after their kingdom was destroyed by the Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
s in 740.
Early
An inscription at the foot of the colossal Jain monolith Bahubali
Bahubali (, ) was the son of Rishabhanatha (the first ''tirthankara'' of Jainism) and the brother of the ''Chakravarti (Sanskrit term), chakravartin'' Bharata (Jainism), Bharata. He is a revered figure in Jainism. He is said to have meditated ...
(The word ''gomateshvara'' apparently comes from Konkani ' which means "beautiful" or "handsome" and ''īśvara'' "lord".Shravanabelagola
Shravanabelagola (pronunciation: ) is a town located near Channarayapatna of Hassan district in the Indian state of Karnataka and is from Bengaluru. The Gommateshwara Bahubali statue at Shravanabelagola is one of the most important tirthas ...
of 981 CE reads, in a variant of Nāgarī: The language of these lines is Konkani according to S.B. Kulkarni (former head of Department of Marathi, Nagpur University
Rashtrasant Tukadoji Maharaj Nagpur University (RTMNU), formerly Nagpur University, is a public state university located in Nagpur, Maharashtra. It is one of India's oldest universities, as well as the second-oldest in Maharashtra. It is named ...
) and Jose Pereira (former professor, Fordham University
Fordham University is a Private university, private Society of Jesus, Jesuit research university in New York City, United States. Established in 1841, it is named after the Fordham, Bronx, Fordham neighborhood of the Bronx in which its origina ...
, USA).
Another inscription in Nāgarī, of Shilahara
Shilahara was a royal dynasty that established itself in northern and southern Konkan in 8th century CE, present-day Mumbai and Southern Maharashtra ( Kolhapur) during the Rashtrakuta period. The founder of the Shilahara dynasty, Sanaphulla, ...
King Aparaditya II of the year 1187 AD in Parel
Parel (ISO 15919, ISO: Paraḷ, pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, əɾəɭ is a neighbourhood in the south of Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. Originally one of the Seven Islands of Bombay, Parel became an industrial center after the unificatio ...
reportedly contains Konkani words, but this has not been reliably verified.
Many stone and copper-plate inscriptions found in Goa and Konkan are written in Konkani. The grammar and the base of such texts is in Konkani, whereas very few verbs are in Marathi.Goykanadi
or Kandavī is a Brahmic script that was once used in the territory of Goa to write Konkani and sometimes Marathi in the Konkan coast. Similarly, it was used by the trading Saraswat and Daivajna families along with the Modi script to maint ...
. A piece of hymn dedicated to Lord
A piece of hymn dedicated to Lord Narayana
Narayana (, ) is one of the forms and epithets of Vishnu. In this form, the deity is depicted in yogic slumber under the celestial waters, symbolising the masculine principle and associated with his role of creation. He is also known as Pu ...
attributed to the 12th century AD says: A hymn from the later 16th century goes
Early Konkani was marked by the use of pronouns like ''dzo'', ''jī'', and ''jẽ''. These are replaced in contemporary Konkani by ''koṇa''. The conjunctions ''yedō'' and ''tedō'' ("when" and "then") which were used in early Konkani are no longer in use.
Medieval
This era was marked by several invasions of Goa and subsequent exodus of some Konkani families to Canara (today's coastal Karnataka), and Cochin.
* Exodus (between 1312 and 1327) when General Malik Kafur
Malik Kafur (died February 1316), also known as Taj al-Din Izz al-Dawla, was a prominent general of the Delhi Sultanate ruler Alauddin Khalji. He was captured by Alauddin's general Nusrat Khan Jalesari, Nusrat Khan during the Alauddin Khalji's co ...
of the Delhi Sultans
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, Alauddin Khalji
Alauddin Khalji (; ), born Ali Gurshasp, was a ruler from the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrative changes in the Delhi Sultanate, related to revenue ...
, and Muhammed bin Tughlaq destroyed Govepuri and the Kadambas
The Kadamba dynasty were an ancient royal family from modern Karnataka, India, that ruled northern Karnataka and the Konkan from Banavasi in present-day Uttara Kannada, Uttara Kannada district in India. The kingdom was founded by Mayurash ...
* Exodus subsequent to 1470 when the Bahmani kingdom captured Goa, and subsequent capture in 1492 by Sultan Yusuf Adil Shah
Yusuf Adil Shah (1450 – 5 December 1510), referred as Yusuf Adil Khan or Hidalcão by the Portuguese, was the founder of the Adil Shahi dynasty that ruled the Sultanate of Bijapur for nearly two centuries. As the founder of the Adil Shahi dyna ...
of Bijapur
Bijapur (officially Vijayapura) is the district headquarters of Bijapur district of the Karnataka state of India. It is also the headquarters for Bijapur Taluk. Bijapur city is well known for its historical monuments of architectural importa ...
* Exodus of converted Muslims to Bijapur-held territory due to the Portuguese conquest of Goa
The Portuguese conquest of Goa occurred when the governor Afonso de Albuquerque captured the city in 1510 from the Sultanate of Bijapur. Old Goa became the capital of Portuguese India, which included territories such as Fort Manuel of Cochin, ...
in 1510
* Migration of Hindu converts to Canara in South India after the Christianisation of Goa
The indigenous population of the erstwhile Portuguese colony of Goa, Daman and Diu was Christianized following the Portuguese conquest of Goa in 1510 and the subsequent establishment of the Goan Inquisition. The converts in the ''Velhas Conquist ...
, the subsequent Goa Inquisition
The Goa Inquisition (, ) was an extension of the Portuguese Inquisition in Portuguese India. Its objective was to enforce Catholic orthodoxy and allegiance to the Apostolic See of the Pontifex.
The inquisition primarily focused on the New Chr ...
, and the Sackings of Goa and Bombay-Bassein.
These events caused the Konkani language to develop into multiple dialects with multiple scripts. The exodus to coastal Karnataka and Kerala required Konkani speakers in these regions to learn the local languages. This caused penetration of local words into the dialects of Konkani spoken by these speakers. Examples include ''dār'' (door) giving way to the word ''bāgil''. Also, the phoneme "a" in the Salcette dialect was replaced by the phoneme "o".
Other Konkani communities came into being with their own dialects of Konkani. The Konkani Muslim communities of Ratnagiri
Ratnagiri (IAST:Ratnāgirī ; �ət̪n̪aːɡiɾiː is a port city on the Arabian Sea coast in Ratnagiri District in southwestern Maharashtra, India. The district is part of Konkan division of Maharashtra. The city is known for the Hapus or ...
and Coastal Karnataka
Kanara or Canara, also known as Karāvali, is the historically significant stretch of land situated by the southwestern Konkan coast of India, alongside the Arabian Sea in the present-day Indian state of Karnataka.
The subregion comprises thr ...
came about due to a mixture of intermarriages of Arab seafarers, Middle East businessman, Britishes and locals as well as conversions of Hindus to Islam. Another migrant community that picked up Konkani are the Siddis
The Siddi (), also known as the Sheedi, Sidi, or Siddhi, are an ethno-religious group living mostly in Pakistan. Some Siddis also live in India. They are primarily descended from the Bantu peoples of the Zanj coast in Southeast Africa, most ...
, who are descended from Bantu peoples
The Bantu peoples are an Indigenous peoples of Africa, indigenous ethnolinguistic grouping of approximately 400 distinct native Demographics of Africa, African List of ethnic groups of Africa, ethnic groups who speak Bantu languages. The language ...
from South East Africa that were brought to the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
as slaves.
Contemporary
Contemporary Konkani is written in Devanagari, Kannada, Malayalam, Persian, and Roman scripts. It is written by speakers in their native dialects. The Goan Antruz dialect in the Devanagari script has been promulgated as Standard Konkani.
Revitalisation
Konkani language was in decline, due to the use of Portuguese as the official and social language among the Christians, the predominance of Marathi over Konkani among Hindus, and the Konkani Christian-Hindu divide. Seeing this, Vaman Raghunath Varde Valaulikar set about on a mission to unite all Konkanis, Hindus as well as Christians, regardless of caste or religion. He saw this movement not just as a nationalistic movement against Portuguese rule, but also against the pre-eminence of Marathi over Konkani. Almost single-handedly he crusaded, writing a number of works in Konkani. He is regarded as the pioneer of modern Konkani literature and affectionately remembered as Shenoi Goembab.
Post-independence period
Following India's independence and its subsequent annexation of Goa in 1961, Goa was absorbed into the Indian Union as a Union Territory, directly under central administration.
However, with the reorganisation of states along linguistic lines, and growing calls from Maharashtra, as well as Marathis in Goa for the merger of Goa into Maharashtra, an intense debate was started in Goa. The main issues discussed were the status of Konkani as an independent language and Goa's future as a part of Maharashtra or as an independent state. The Goa Opinion Poll, a plebiscite, retained Goa as an independent state in 1967.
Recognition as an independent language
With the continued insistence of some Marathis that Konkani was a dialect of Marathi and not an independent language, the matter was finally placed before the Sahitya Akademi
The Sahitya Akademi, India's National Academy of Letters, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of literature in the languages of India. Founded on 12 March 1954, it is supported by, though independent of the Indian government. Its off ...
. Suniti Kumar Chatterji
Suniti Kumar Chatterji (26 November 1890 – 29 May 1977) was an Indian linguist, educationist and litterateur. He was a recipient of the second highest Indian civilian honour of Padma Vibhushan.
Life Childhood
Chatterji was born on 26 Novem ...
, the president of the Akademi appointed a committee of linguistic experts to settle the dispute. On 26 February 1975, the committee came to the conclusion that Konkani was indeed an independent and literary language, classified as an Indo-European language, which in its present state was heavily influenced by the Portuguese language.
Official language status
All this did not change anything in Goa. Finally, fed up with the delay, Konkani activists launched an agitation in 1986, demanding official status for Konkani. The agitation turned violent in various places, resulting in the death of six agitators from the Catholic community: Floriano Vaz from Gogol Margao, Aldrin Fernandes, Mathew Faria, C. J. Dias, John Fernandes, and Joaquim Pereira, all from Agaçaim
Agaçaim (pronounced ''Aagshi'') or Agassaim, is a village on the northern banks of the Zuari River in Tiswadi, Goa, surrounded by Panjim to the north, Margão to the south, Vasco da Gama to the west and Ponda to the east, thus making it a m ...
. Finally, on 4 February 1987, the Goa Legislative Assembly
The Goa Legislative Assembly is the unicameral legislature of the state of Goa in India. The Assembly meets at the Goa State Legislative Assembly Complex in Porvorim, Bardez. The Eighth Goa Legislative Assembly consists of 40 members. The assem ...
passed the Official Language Bill, making Konkani the official language of Goa.Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India
The Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India lists the languages officially recognized by the Government of India. , 22 languages have been classified under the schedule.
Definition
As per the Constitution of India, the provisions belongi ...
as per the Seventy-First Amendment on 20 August 1992, adding it to the list of official languages.
Geographical distribution
 The Konkani language originated and is spoken widely in the western coastal region of India known as
The Konkani language originated and is spoken widely in the western coastal region of India known as Konkan
The Konkan is a stretch of land by the western coast of India, bound by the river Daman Ganga at Damaon in the north, to Anjediva Island next to Karwar town in the south; with the Arabian Sea to the west and the Deccan plateau to the eas ...
. The native lands historically inhabited by Konkani people include the Konkan division
Konkan division is one of the six administrative divisions of Maharashtra state in India. It comprises the central portions of the Konkani region, excluding Goa and Damaon, which were absorbed into Maharashtra owing to the States Reorganisat ...
of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, the state of Goa
Goa (; ; ) is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north, and Karnataka to the ...
and the territory of Daman, the Uttara Kannada
Uttara Kannada is a fifth largest district in the Indian state of Karnataka, It is bordered by the state of Goa and Belagavi districts to the north, Dharwad District and Haveri District to the east, Shivamogga District, and Udupi District to ...
, Udupi
Udupi () also known as 'Odipu' () is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the administrative headquarters of Udupi district, and one of the fastest-growing cities in Karnataka. Udupi is one of the top tourist attractions in Karnataka an ...
& Dakshina Kannada
Dakshina Kannada district is located in the states and territories of India, state of Karnataka in India, with its headquarters in the coastal city of Mangaluru. The district covers an area nestled in between the Western Ghats to its east and the ...
districts of Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
, belagavi
Belgaum (Kannada ISO 15919, ISO: ''Bēḷagāma'', ), officially known as Belagavi (also Belgaon), is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka located near its northern western border in the Western Ghats. It is the administrative headquarters ...
, Mysore
Mysore ( ), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Mysore district and Mysore division. As the traditional seat of the Wadiyar dynasty, the city functioned as the capital of the ...
, and Bengaluru
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Kar ...
along with many districts in Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
such as Kasaragod
Kasaragod () is a municipal town and the administrative headquarters of the Kasaragod district in the state of Kerala, India. Established in 1966, Kasaragod was the first municipal town in the district. It is the northernmost district of Kera ...
, Kochi
Kochi ( , ), List of renamed Indian cities and states#Kerala, formerly known as Cochin ( ), is a major port city along the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea. It is part of the Ernakulam district, district of Ernakulam in the ...
, Alappuzha
Alappuzha (, आलप्पुळ) or Alleppey is a municipality and town on the Laccadive Sea in the southern Indian state of Kerala. It is the district headquarters of the district, and is located about north of the state capital Thiruvana ...
, Thiruvananthapuram
Thiruvananthapuram ( ), also known as Trivandrum, is the Capital city, capital city of the Indian state of Kerala. As of 2011, the Thiruvananthapuram Municipal Corporation had a population of 957,730 over an area of 214.86 sq. km, making it the ...
and Kottayam
Kottayam () is a city in the Kottayam district of Kerala, India. It is the district headquarters of the district and is located about north of the state capital Thiruvananthapuram. As per the 2011 Indian census, Kottayam has a population of ...
. All of the regions and areas have developed distinct dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardize ...
s, pronunciation
Pronunciation is the way in which a word or a language is spoken. To
This may refer to generally agreed-upon sequences of sounds used in speaking a given word or all language in a specific dialect—"correct" or "standard" pronunciation—or si ...
and prose
Prose is language that follows the natural flow or rhythm of speech, ordinary grammatical structures, or, in writing, typical conventions and formatting. Thus, prose ranges from informal speaking to formal academic writing. Prose differs most n ...
styles, vocabulary, tone, and sometimes, significant differences in grammar.Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
, 964,305 in Goa
Goa (; ; ) is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north, and Karnataka to the ...
,Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, and 69,449 in Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
. It ranks 19th on the List of Scheduled Languages by strength. The number of Konkani speakers in India fell by 9.34% in the decade 2001–2011. It is the only scheduled language apart from Urdu to have a negative growth rate in the decade. A very large number of Konkanis live outside India, either as expatriates ( NRIs) with work visa
A work permit or work visa is the permission to take a job within a foreign country. The foreign country where someone seeks to obtain a work permit for is also known as the "country of work", as opposed to the "country of origin" where someone h ...
s or as naturalised citizens and permanent residents of other host countries (immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short- ...
). Determining their numbers is difficult since Konkani is a minority language
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) and ...
that is very often not recognised by censuses and surveys of various government agencies and NGOs catering to Indians abroad.
During the days of Portuguese Goa
The State of India, also known as the Portuguese State of India or Portuguese India, was a state of the Portuguese Empire founded seven years after the discovery of the sea route to the Indian subcontinent by Vasco da Gama, a subject of the ...
and British rule
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
* or dire ...
in Pre-Partition India many Goans and non-Goan Konkani people went to foreign countries as economic migrants to the colonies of Portuguese and British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
respectively, and also to the Pakistan of Pre-Partition India. The migratory trend has continued well into the post-colonial era and a significant number of Konkani people are found in Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
, Uganda
Uganda, officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, the Persian Gulf countries, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, and the British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
and the rest of the Anglosphere
The Anglosphere, also known as the Anglo-American world, is a Western-led sphere of influence among the Anglophone countries. The core group of this sphere of influence comprises five developed countries that maintain close social, cultura ...
. Many families still continue to speak different Konkani dialects that their ancestors spoke, which are now highly influenced by the languages of the dominant majority.
Status and issues
The Konkani language has been in danger of dying out over the years for many of the following reasons:
# The fragmentation of Konkani into various, sometimes mutually unintelligible, dialects.
# The dominance of Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
**Marathi people (Uttar Pradesh), the Marathi people in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Mar ...
and the large degree of bilingualism of Konkani Hindus in Goa state
Goa (; ; ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan Plateau, Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian sta ...
, the union territory of Damaon
Daman district () (formerly Distrito de Damão) is one of three districts of the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. It is located on the west coast of India and is surrounded by the Valsad district of Gujarat to ...
and the Konkan division
Konkan division is one of the six administrative divisions of Maharashtra state in India. It comprises the central portions of the Konkani region, excluding Goa and Damaon, which were absorbed into Maharashtra owing to the States Reorganisat ...
of Maharashtra.
# Progressive inroads made by Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
into the Konkani Muslim community.
# Mutual animosity among various religious sects and caste groups; including a secondary status of Konkani culture to religion.
# The migration of Konkanis to various parts of India and around the world.
# The lack of opportunities to study Konkani in schools and colleges. Even until recently there were few Konkani schools in Goa. Populations outside the native Konkani areas have absolutely no access to Konkani language studies, literature and media.
# The preference among Konkani parents to speak to their children in ''potaachi bhaas'' (language of the stomach) over ''maai bhaas'' (mother tongue
A first language (L1), native language, native tongue, or mother tongue is the first language a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongue'' refers ...
). They sometimes speak primarily in English to help their children gain a grip on English in schools.UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger
The UNESCO ''Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger'' was an online publication containing a comprehensive list of the world's endangered languages. It originally replaced the ''Red Book of Endangered Languages'' as a title in print after ...
since 2009.
Efforts have been made to stop this downward trend of usage of Konkani, starting with Shenoi Goembab's efforts to revive Konkani. The recognition granted by Sahitya Akademi
The Sahitya Akademi, India's National Academy of Letters, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of literature in the languages of India. Founded on 12 March 1954, it is supported by, though independent of the Indian government. Its off ...
to Konkani and the institution of an annual award for Konkani literature has helped to a certain extent.
Some organisations, such as the Konkan Daiz Yatra organised by Konkani Bhasha Mandal, World Konkani Centre and the newer Vishwa Konkani Parishad have laid great stress on uniting all factions of Konkanis.
Opposition
Marathi dispute
José Pereira, in his 1971 work ''Konkani – A Language: A History of the Konkani Marathi Controversy'', pointed to an essay on Indian languages written by John Leyden in 1807, wherein Konkani is called a "dialect of Maharashtra" as an origin of the language controversy.Sahitya Akademi
The Sahitya Akademi, India's National Academy of Letters, is an organisation dedicated to the promotion of literature in the languages of India. Founded on 12 March 1954, it is supported by, though independent of the Indian government. Its off ...
(a prominent literary organisation in India) recognised it as an independent language in 1975, and subsequently Konkani (in Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
script) was made the official language of Goa in 1987.
Karnataka
MLC Ivan D'Souza attempted to speak in Konkani at the Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
state's Legislative Council, but was urged not to by the Chairman D H Shankaramurthy as most of the audience did not know Konkani. Even though Mr D'Souza pleaded that Konkani was amongst the 22 official languages recognised by the Indian Constitution, he was not given permission to continue in Konkani.Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
"activists". Konkani Holy Masses has been held in the Sabbhavana and Saccidananda chapels of the Carmelite and Capuchin Fathers respectively, in Yeswanthpur and Rajajinagar
Rajajinagara (formerly Rajajinagar) is a luxury neighborhood and business hub in the west of Bangalore. It is one of the zones of BBMP. It is bordered by Basaveshwaranagara, Malleshwara, Mahalakshmipura alias West of Chord road second stage ...
, Bangalore. These services are under threat from Kannada groups who do not want church service
A church service (or a worship service) is a formalized period of Christian communal Christian worship, worship, often held in a Church (building), church building. Most Christian denominations hold church services on the Lord's Day (offering Su ...
s to be held in any language other than Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
, even though Kannada Catholics constitute only 30% of the Catholic population in the Archdiocese. Konkani activists and associations have been demanding Konkani language mass and services for a long time.
Multilingualism
According to the Census Department of India, Konkani speakers show a very high degree of multilingualism
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
. In the 1991 census, as compared to the national average of 19.44% for bilingualism and 7.26% for trilingualism, Konkani speakers scored 74.20% and 44.68% respectively. This makes the Konkans the most multilingual community of India.
This has been due to the fact that in most areas where Konkans have settled, they seldom form a majority of the population and have to interact with others in the local tongue. Another reason for bilingualism has been the lack of schools teaching Konkani as a primary or secondary language.
The bilingualism of Konkanis with Marathi in Daman Goa and Maharashtra has been a source of great discontent because it has led to the belief that Konkani is a dialect of Marathi
Scripts and dialects
The problems posed by multiple scripts and varying dialects have come as an impediment in the efforts to unite Konkani people. The Goa state's decision to use Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
as the official script and the Antruz dialect has been met with opposition both within Goa and outside it.Romi Konkani
Konkani in the Roman script, commonly known as Roman Konkani or ''Romi Konknni'' () refers to the writing of the Konkani language in the Roman script. While Konkani is written in five different scripts altogether, Roman Konkani is widely used. ...
in Goa or Konkani in the Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
script.
Outside India
Emigration has also brought the Konkani language to foreign countries, such as Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
and Kenya
Kenya, officially the Republic of Kenya, is a country located in East Africa. With an estimated population of more than 52.4 million as of mid-2024, Kenya is the 27th-most-populous country in the world and the 7th most populous in Africa. ...
.
Phonology
The Konkani language has 16 basic vowels (excluding an equal number of long vowels), 36 consonants, 5 semi-vowels, 3 sibilants, 1 aspirate, and many diphthong
A diphthong ( ), also known as a gliding vowel or a vowel glide, is a combination of two adjacent vowel sounds within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: that is, the tongue (and/or other parts of ...
s. Like the other Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east ...
, it has both long and short vowels and syllables with long vowels may appear to be stressed. Different types of nasal vowels are a special feature of the Konkani language.
* The palatal
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sepa ...
and alveolar
Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* M ...
stops are affricate
An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pai ...
s. The palatal glides are truly palatal but otherwise the consonants in the palatal column are alveopalatal.sonorants
In phonetics and phonology, a sonorant or resonant is a speech sound that is produced with continuous, non-turbulent airflow in the vocal tract; these are the manners of articulation that are most often voiced in the world's languages. Vowels are ...
are all voiced.aspirates
In phonetics, aspiration is a strong burst of breath that accompanies either the release or, in the case of preaspiration, the closure of some obstruents. In English, aspirated consonants are allophones in complementary distribution with their ...
and fricative
A fricative is a consonant produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate in ...
s. Many speakers substitute unaspirated consonants for aspirates.obstruent
An obstruent ( ) is a speech sound such as , , or that is formed by ''obstructing'' airflow. Obstruents contrast with sonorants, which have no such obstruction and so resonate. All obstruents are consonants, but sonorants include vowels as well ...
s, except for palatal and alveolars. Where a palatalised alveolar is expected, a palatal is found instead. In the case of sonorants, only unaspirated consonants show this contrast, and among the glides only labeo-velar glides exhibit this. Vowels show a contrast between oral and nasal ones
Vowels
One of the most distinguishing features of Konkani phonology is the use of , the close-mid central vowel, instead of the schwa found in Hindustani and Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
**Marathi people (Uttar Pradesh), the Marathi people in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Mar ...
.
Whereas many Indian languages use only one of the three front vowels, represented by the Devanagari grapheme ए, Konkani uses three: , and .
Nasalizations exist for all vowels except for .
Consonants
The consonants in Konkani are similar to those in Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
**Marathi people (Uttar Pradesh), the Marathi people in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Mar ...
.
Grammar
Konkani grammar is similar to other Indo-Aryan languages. Notably, Konkani grammar is also influenced by Dravidian languages. It cannot be described as a stress-timed language
Isochrony is a linguistic analysis or hypothesis assuming that any spoken language's utterances are divisible into equal rhythmic portions of some kind. Under this assumption, languages are proposed to broadly fall into one of two categories based ...
, nor as a tonal language
Tone is the use of pitch in language to distinguish lexical or grammatical meaning—that is, to distinguish or to inflect words. All oral languages use pitch to express emotional and other para-linguistic information and to convey emphasi ...
.noun
In grammar, a noun is a word that represents a concrete or abstract thing, like living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, and ideas. A noun may serve as an Object (grammar), object or Subject (grammar), subject within a p ...
)
# ''sarvanaam'' (pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but so ...
)
# ''visheshan'' (adjective
An adjective (abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that describes or defines a noun or noun phrase. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Traditionally, adjectives are considered one of the main part of speech, parts of ...
)
# ''kriyapad'' (verb
A verb is a word that generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic f ...
)
# ''kriyavisheshana'' (adverb An adverb is a word or an expression that generally modifies a verb, an adjective, another adverb, a determiner, a clause, a preposition, or a sentence. Adverbs typically express manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or level of certainty by ...
)
# ''ubhayanvayi avyaya''
# ''shabdayogi avyaya''
# ''kevalaprayogi avyaya'' (interjection
An interjection is a word or expression that occurs as an utterance on its own and expresses a spontaneous feeling, situation or reaction. It is a diverse category, with many different types, such as exclamations ''(ouch!'', ''wow!''), curses (''da ...
)
Like most of the Indo-Aryan languages, Konkani is an SOV language, meaning among other things that not only is the verb found at the end of the clause but also modifiers
In linguistics, a modifier is an optional element in phrase structure or clause structure which ''modifies'' the meaning of another element in the structure. For instance, the adjective "red" acts as a modifier in the noun phrase "red ball", provi ...
and complements tend to precede the head and postpositions
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complemen ...
are far more common than prepositions
Adpositions are a class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complemen ...
. In terms of syntax, Konkani is a ''head-last'' language, unlike English, which is an SVO language.
Verbs
Verbs are either ''tatsama'' or ''tadbhava'':present participle
In linguistics, a participle (; abbr. ) is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from a verb and used as an adject ...
of the primary verb, and the auxiliary is partially dropped.grammatical cases
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and numerals) that corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal ...
, Konkani has totally lost the dative
In grammar, the dative case (abbreviated , or sometimes when it is a core argument) is a grammatical case used in some languages to indicate the recipient or beneficiary of an action, as in "", Latin for "Maria gave Jacob a drink". In this exampl ...
, the locative
In grammar, the locative case ( ; abbreviated ) is a grammatical case which indicates a location. In languages using it, the locative case may perform a function which in English would be expressed with such prepositions as "in", "on", "at", and " ...
, and the ablative
In grammar, the ablative case (pronounced ; abbreviated ) is a grammatical case for nouns, pronouns, and adjectives in the grammars of various languages. It is used to indicate motion away from something, make comparisons, and serve various o ...
.accusative
In grammar, the accusative case (abbreviated ) of a noun is the grammatical case used to receive the direct object of a transitive verb.
In the English language, the only words that occur in the accusative case are pronouns: "me", "him", "her", " ...
and the instrumental case
In grammar, the instrumental case ( abbreviated or ) is a grammatical case used to indicate that a noun is the ''instrument'' or means by or with which the subject achieves or accomplishes an action. The noun may be either a physical object or ...
s too.nominative
In grammar, the nominative case ( abbreviated ), subjective case, straight case, or upright case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb, or (in Latin and formal variants of E ...
, the genitive
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can ...
, and the vocative case
In grammar, the vocative case (abbreviated ) is a grammatical case which is used for a noun that identifies a person (animal, object, etc.) being addressed or occasionally for the noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and numeral ...
.
Apabhramsha and metathesis
* Like Marathi and Gujarati, the Konkani language has three genders. During the Middle Ages, most of the Indo-Aryan languages lost their neuter gender, except Maharashtri, in which it is retained much more in Marathi than Konkani.anusvara
Anusvara ( ; , , ), also known as Bindu ( ; ), is a symbol used in many Indic scripts to mark a type of nasal sound, typically transliterated or in standards like ISO 15919 and IAST. Depending on its location in a word and the language for ...
'' has great importance in Konkani. A characteristic of Middle Indo-Aryan
The Middle Indo-Aryan languages (or Middle Indic languages, sometimes conflated with the Prakrits, which are a stage of Middle Indic) are a historical group of languages of the Indo-Aryan family. They are the descendants of Old Indo-Aryan (OIA; ...
dialects, Konkani still retains the ''anusvara'' on the initial or final syllable.visarga
In Sanskrit phonology, Visarga () is the name of the voiceless glottal fricative, written in Devanagari as '' . It was also called, equivalently, ' by earlier grammarians. The word ''visarga'' () literally means "sending forth, discharge".
Visa ...
'', is totally lost and is assimilated with उ and/or ओ. For example, in Sanskrit दीपः becomes दिवो and दुःख becomes दुख.
* Konkani retains the pitch accent, which is a direct derivative of Vedic accent, which probably would account for "nasalism" in Konkani.Declension
In linguistics, declension (verb: ''to decline'') is the changing of the form of a word, generally to express its syntactic function in the sentence by way of an inflection. Declension may apply to nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, and det ...
also affects the accent.
Vocabulary
The vocabulary from Konkani comes from a number of sources. The main source is Prakrits. So Sanskrit as a whole has played a very important part in Konkani vocabulary. Konkani vocabulary is made of (Sanskrit loanwords without change), (evolved Sanskrit words), (indigenous words) and (foreign words). Other sources of vocabulary are Arabic, Persian, and Turkish. Finally, Kannada, Marathi, and Portuguese have enriched its lexical content.
Loanwords
Since Goa was a major trade centre for visiting Arabs and Turks, many Arabic and Persian words infiltrated the Konkani language.Goan Catholics
Goan Catholics () are an Ethnoreligious group, ethno-religious community adhering to the Latin Church, Latin Rite of the Catholic Church from the Goa state, in the southern part of the Konkan region along the west coast of India. They are Konka ...
in their literature shows a prominent Portuguese influence. As a result, many Portuguese loanwords are now commonly found in common Konkani speech.Thane
Thane (; previously known as Thana, List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city located on the northwestern side of the list of Indian states, state of Maharashtra in India and on ...
a variant of Konkani used by Bombay East Indians
The Bombay East Indians, also called East Indian Catholics or simply East Indians, are an ethno-religious Christianity in India, Indian Christian community native to the Seven Islands of Bombay, the Mumbai Metropolitan Area and the northern Ko ...
Catholic community.
Sanskritisation
Konkani is not highly Sanskritised like Marathi
Marathi may refer to:
*Marathi people, an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group of Maharashtra, India
**Marathi people (Uttar Pradesh), the Marathi people in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh
*Marathi language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Mar ...
, but still retains Prakrit
Prakrit ( ) is a group of vernacular classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 5th century BCE to the 12th century CE. The term Prakrit is usually applied to the middle period of Middle Ind ...
and apabhramsa structures, verbal forms, and vocabulary. Though the Goan Hindu dialect is highly Prakritised, numerous Sanskrit loanwords
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term t ...
are found, while the Catholic dialect has historically drawn many terms from Portuguese. The Catholic literary dialect has now adopted Sanskritic vocabulary itself, and the Catholic Church has also adopted a Sanskritisation
Sanskritisation (or Sanskritization) is a term in sociology which refers to the process by which castes or tribes placed lower in the caste hierarchy seek upward mobility by emulating the rituals and practices of the dominant castes or upper c ...
policy.Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
− one of the languages of Dravidian origin − have undergone re-Sanskritisation over time.
Writing systems
 Konkani has been compelled to become a language using a multiplicity of scripts, and not just one single script used everywhere. This has led to an outward splitting up of the same language, which is spoken and understood by all, despite some inevitable dialectal convergences.
Konkani has been compelled to become a language using a multiplicity of scripts, and not just one single script used everywhere. This has led to an outward splitting up of the same language, which is spoken and understood by all, despite some inevitable dialectal convergences.
Past
The Brahmi script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as ...
for Konkani fell into disuse. Later, some inscriptions were written in old Nagari. However, owing to the Portuguese conquest in 1510 and the subsequent various restrictions imposed by the Inquisition, some early forms of Devanagari fell out of use in Goa.Kadambas
The Kadamba dynasty were an ancient royal family from modern Karnataka, India, that ruled northern Karnataka and the Konkan from Banavasi in present-day Uttara Kannada, Uttara Kannada district in India. The kingdom was founded by Mayurash ...
, although it lost its popularity after the 17th century. Kandevi/Goykandi is very different from the Halegannada script, with strikingly similar features.Kadamba script
The Kadamba script is the first writing system devised specifically for writing Kannada, and Telugu language. The Kadamba script is also known as ''Pre-Old-Kannada script.''
The Kadamba script is one of the oldest scripts of the southern grou ...
, which was extensively used in Goa and Konkan.Roman script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Gree ...
has the oldest preserved and protected literary tradition, beginning from the 16th century.
Present
Konkani is written in five scripts: Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
, Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
, Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
, and Perso-Arabic
The Persian alphabet (), also known as the Perso-Arabic script, is the right-to-left script, right-to-left alphabet used for the Persian language. It is a variation of the Arabic script with four additional letters: (the sounds 'g', 'zh', ' ...
.[Mother Tongue blues](_blank)
nbsp;– Madhavi Sardesai Because Devanagari is the official script used to write Konkani in Goa and Maharashtra, most Konkanis (especially Hindus) in those two states write the language in Devanagari. However, Konkani is widely written in the Roman script (called Romi Konkani
Konkani in the Roman script, commonly known as Roman Konkani or ''Romi Konknni'' () refers to the writing of the Konkani language in the Roman script. While Konkani is written in five different scripts altogether, Roman Konkani is widely used. ...
) by many Konkanis, (especially Catholics).liturgy
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and participation in the sacred through activities reflecting praise, thanksgiving, remembra ...
and other religious literature has always been in the Roman script. Most people of Karnataka use the Kannada script
The Kannada script ( IAST: ''Kannaḍa lipi''; obsolete: Kanarese or Canarese script in English) is an abugida of the Brahmic family, used to write Kannada, one of the Dravidian languages of South India especially in the state of Karnataka. I ...
; however, the Saraswats of Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
use the Devanagari script in the uttara Kannada
Uttara Kannada is a fifth largest district in the Indian state of Karnataka, It is bordered by the state of Goa and Belagavi districts to the north, Dharwad District and Haveri District to the east, Shivamogga District, and Udupi District to ...
district. Malayalam script
Malayalam script (; / ) is a Brahmic scripts, Brahmic script used to write Malayalam, the principal language of Kerala, India, spoken by 45 million people. It is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union ter ...
was used by the Konkani community in Kerala, but there has been a move towards the usage of the Devanagari script in recent years. Konkani Muslims
Konkani Muslims (or ''Kokani'' Muslims) are an ethnoreligious subgroup of the Konkani people of the Konkani region along the west coast of India, who practice Islam. '' Nawayath'' and " Nakhuda" Muslims from the North Canara district of Karn ...
use Arabic script to write Konkani. There has been to trend towards the usage of the Arabic script among Muslim communities; this coincides with them mixing more Urdu and Arabic words into their Konkani dialects. When the Sahitya Akademi recognised Konkani in 1975 as an independent and literary language, one of the important factors was the literary heritage of Romi Konkani since the year 1556. However, after Konkani in the Devanagari script was made the official language of Goa in 1987, the Sahitya Akademi has supported only writers in the Devanagari script. For a very long time there has been a rising demand for official recognition of Romi Konkani by Catholics in Goa because a sizeable population of the people in Goa use the Roman script. Also a lot of the content on the Internet and the staging of the famed Tiatr
''Tiatr'' (; ) is a type of musical theatre that is popular in the state of Goa on the west coast of India, as well as in Mumbai and among the Goan expatriate communities in the Middle East, United Kingdom, and other cities with a significant pr ...
is written in Romi Konkani. In January 2013, the Goa Bench of the Bombay High Court issued a notice to the state government on a Public Interest Litigation
The chief instrument through which judicial activism has flourished in India is public interest litigation (PIL) or social action litigation (SAL). It refers to litigation undertaken to secure public interest and demonstrates the availability ...
filed by the Romi Lipi Action Front seeking to amend the Official Language Act to grant official language status to Romi Konkani but has not yet been granted.
Alphabet/''vaṇamāḷha''
The vowels, consonants, and their arrangement are as follows:
Dialects
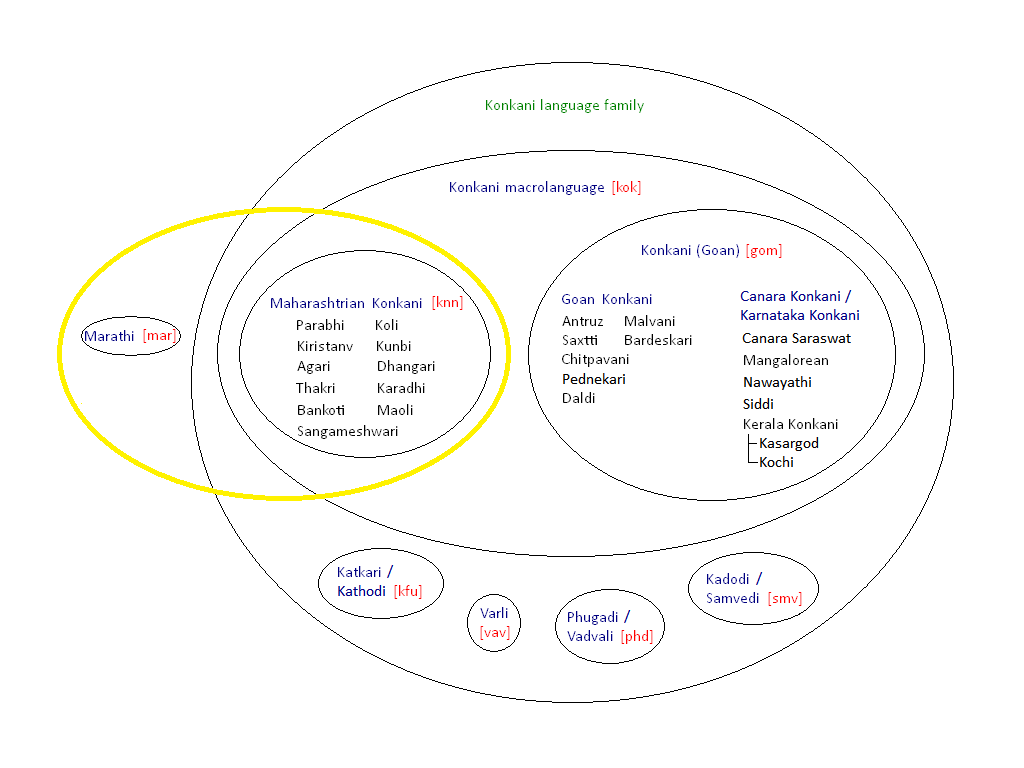 Konkani, despite having a small population, shows a very high number of
Konkani, despite having a small population, shows a very high number of dialect
A dialect is a Variety (linguistics), variety of language spoken by a particular group of people. This may include dominant and standard language, standardized varieties as well as Vernacular language, vernacular, unwritten, or non-standardize ...
s. The dialect tree structure of Konkani can easily be classified according to the region, religion, caste, and local tongue influence.Konkan division
Konkan division is one of the six administrative divisions of Maharashtra state in India. It comprises the central portions of the Konkani region, excluding Goa and Damaon, which were absorbed into Maharashtra owing to the States Reorganisat ...
of Maharashtra with cultural ties to Mahratti
Marathi (; , 𑘦𑘨𑘰𑘙𑘲, , ) is a classical Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by Marathi people in the Indian state of Maharashtra and is also spoken in Goa, and parts of Gujarat, Karnataka and the territory of Dadra and Naga ...
.
* Central Konkani: Dialects in Goa, where Konkani came in close contact with Portuguese history & culture.
*Southern Konkani: Dialects spoken in Karnataka, and the Kassergode
Kasaragod ( (, , ; English language, English: ''Kassergode'') is one of the 14 List of districts of Kerala, districts in the southern Indian state of Kerala. Its northern border Thalappady, Kasaragod, Thalappady is located just 9 km south ...
district & the Cochin
Kochi ( , ), formerly known as Cochin ( ), is a major port city along the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea. It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of Kerala. The city is also commonly referred to as Ernaku ...
district of Kerala. Southern Konkani has absorbed substantial amounts of loanwords from Kanarese, Tulu & Malabarese.
Goan Konkani
Goan Konkani refers to all the central dialects of the Konkani macrolanguage
A macrolanguage is a group of mutually intelligible speech varieties, or dialect continuum, that have no traditional name in common, and which may be considered distinct languages by their speakers. Macrolanguages are used as a book-keeping mech ...
except for those that fall under Maharashtri Konkani. These dialects are collectively assigned the language code under the ISO 639-3
ISO 639-3:2007, ''Codes for the representation of names of languages – Part 3: Alpha-3 code for comprehensive coverage of languages'', is an international standard for language codes in the ISO 639 series. It defines three-letter codes for ...
classification.
In common usage, Goan Konkani refers collectively only to those dialects of Konkani spoken primarily in the state of Goa
Goa (; ; ) is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north, and Karnataka to the ...
, for eg. The Antruz, Bardeskari & Saxtti dialects. But in the broader linguistic context, Goan Konkani also includes dialects spoken outside the official boundaries of Goa, such as Malvani Konkani
Malvani is a dialect of Konkani with significant number of loanwords from Marathi. Although Malvani does not have a unique script, the Devanagari script is used by most speakers. Malvani is sometimes used for sarcastic newspaper articles and ...
, Chitpavani Konkani, Karwari Konkani, Mangalorean
Mangaloreans ( Tulu: ''Kudladaklu''; Kannada: ''Mangaloorinavaruu''; Konkani: ''Kodialkar''; Beary: ''Maikaltanga''; Urdu: ''Kaudalvale'') are a collection of diverse ethnic groups that hail from the historical locales of South Canara ( Tuluna ...
Konkani etc.
Organisations
 There are organisations working for Konkani but, primarily, these were restricted to individual communities. The All India Konkani Parishad founded on 8 July 1939, provided a common ground for Konkani people from all regions. A new organisation known as Vishwa Konkani Parishad, which aims to be an all-inclusive and pluralistic umbrella organisation for Konkanis around the world, was founded on 11 September 2005.
Mandd Sobhann is the premier organisation that is striving hard to preserve, promote, propagate, and enrich the Konkani language and culture. It all began with the experiment called 'Mandd Sobhann' – a search for a Konkani identity in Konkani music on 30 November 1986 at Mangalore. What began as a performance titled 'Mandd Sobhann', grew into a movement of revival and rejuvenation of Konkani culture; and solidified into an organization called Mandd Sobhann. Today, Mandd Sobhann boasts of all these 3 identities namely - a performance, a movement and an organization.https://www.manddsobhann.org/
The Konkan Daiz Yatra, started in 1939 in
There are organisations working for Konkani but, primarily, these were restricted to individual communities. The All India Konkani Parishad founded on 8 July 1939, provided a common ground for Konkani people from all regions. A new organisation known as Vishwa Konkani Parishad, which aims to be an all-inclusive and pluralistic umbrella organisation for Konkanis around the world, was founded on 11 September 2005.
Mandd Sobhann is the premier organisation that is striving hard to preserve, promote, propagate, and enrich the Konkani language and culture. It all began with the experiment called 'Mandd Sobhann' – a search for a Konkani identity in Konkani music on 30 November 1986 at Mangalore. What began as a performance titled 'Mandd Sobhann', grew into a movement of revival and rejuvenation of Konkani culture; and solidified into an organization called Mandd Sobhann. Today, Mandd Sobhann boasts of all these 3 identities namely - a performance, a movement and an organization.https://www.manddsobhann.org/
The Konkan Daiz Yatra, started in 1939 in Mumbai
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12 ...
, is the oldest Konkani organisation. The Konkani Bhasha Mandal was born in Mumbai on 5 April 1942, during the Third Adhiveshan of All India Konkani Parishad. On 28 December 1984, Goa Konkani Akademi (GKA) was founded by the government of Goa to promote Konkani language, literature, and culture. The Thomas Stephens Konknni Kendr (TSKK) is a popular research institute based in the Goa
Goa (; ; ) is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north, and Karnataka to the ...
n capital Panaji
Panaji (; , , )also known as Panjim, is the capital of the Indian state of Goa and the headquarters of North Goa district. Previously, it was the territorial capital of the former Portuguese India. It lies on the banks of the Mandovi river est ...
. It works on issues related to the Konkani language, literature, culture, and education. The Dalgado Konkani Academy is a popular Konkani organisation based in Panaji.
 The Konkani Triveni Kala Sangam is one more famed Konkani organisation in
The Konkani Triveni Kala Sangam is one more famed Konkani organisation in Mumbai
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12 ...
, which is engaged in the vocation of patronising Konkani language through the theatre movement. The government of Karnataka
The Government of Karnataka, abbreviated as GoK or GoKA, formerly known as Government of Mysore (1956–1974), is a democratically elected state body with the governor as the ceremonial head to govern the Southwest Indian state of Karnataka ...
established the Karnataka Konkani Sahitya Akademy on 20 April 1994. The Konkani Ekvott is an umbrella organisation of the Konkani bodies in Goa.
The First World Konkani Convention was held in Mangalore in December 1995. The Konkani Language and Cultural Foundation came into being immediately after the World Konkani Convention in 1995.
The World Konkani Centre built on a three-acre plot called Konkani Gaon (Konkani Village) at Shakti Nagar, Mangalore
Mangaluru (), formerly called Mangalore ( ), is a major industrial port city in the Indian state of Karnataka and on the west coast of India. It is located between the Laccadive Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bengaluru, the st ...
was inaugurated on 17 January 2009, "to serve as a nodal agency for the preservation and overall development of Konkani language, art, and culture involving all the Konkani people the world over."
The North American Konkani Association (NAKA) serves to unite Konkanis across the United States and Canada. It serves as a parent organization for smaller Konkani associations in various states. Furthermore, the Konkani Young Adult Group serves as a platform under NAKA to allow young adults across America (18+) of Konkani descent to meet each other and celebrate their heritage. Every 2–4 years, a Konkani Sammelan, where Konkanis from across the continent attend, is held in a different city in the US. A Konkani Youth Convention is held yearly. Past locations have included NYC and Atlanta; the upcoming youth convention is slated to be held in Chicago, IL in June.
Literature
During the Goa Inquisition
The Goa Inquisition (, ) was an extension of the Portuguese Inquisition in Portuguese India. Its objective was to enforce Catholic orthodoxy and allegiance to the Apostolic See of the Pontifex.
The inquisition primarily focused on the New Chr ...
which commenced in 1560, all books found in the Konkani language were burnt, and it is possible that old Konkani literature was destroyed as a consequence.prose
Prose is language that follows the natural flow or rhythm of speech, ordinary grammatical structures, or, in writing, typical conventions and formatting. Thus, prose ranges from informal speaking to formal academic writing. Prose differs most n ...
style. The manuscripts have not been found, although transliterations in Roman script are found in Braga
Braga (; ) is a cities of Portugal, city and a Municipalities of Portugal, municipality, capital of the northwestern Portugal, Portuguese Braga (district), district of Braga and of the historical and cultural Minho Province. Braga Municipality ...
in Portugal. The script used by him for his work is not known.Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
priest, Fr. Thomas Stephens in 1622, and entitled '' Doutrina Christam em Lingoa Bramana Canarim'' (Old Portuguese for: ''Christian Doctrine in the Canarese Brahman Language''). The first book exclusively on Konkani grammar, '' Arte da Lingoa Canarim'', was printed in 1640 by Father Stephens in Portuguese.
Media
Radio
All India Radio
All India Radio (AIR), also known as Akashvani (), is India's state-owned public broadcasting, public radio broadcaster. Founded in 1936, it operates under the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India), Ministry of Information and Broa ...
started broadcasting Konkani news and other services. Radio Goa Pangim started a Konkani broadcast in 1945. AIR Mumbai and Dharwad later started Konkani broadcasts in the years 1952 and 1965 respectively. Portuguese Radio, Lisbon started services in 1955 for India, East Africa, and Portugal. Similarly Trivandrum
Thiruvananthapuram ( ), also known as Trivandrum, is the capital city of the Indian state of Kerala. As of 2011, the Thiruvananthapuram Municipal Corporation had a population of 957,730 over an area of 214.86 sq. km, making it the largest and ...
, Alleppey
Alappuzha (, आलप्पुळ) or Alleppey is a municipality and town on the Laccadive Sea in the southern Indian state of Kerala. It is the district headquarters of the district, and is located about north of the state capital Thiruvana ...
, Trichur, and Calicut
Kozhikode (), also known as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. Known as the City of Spices, Kozhikode is listed among the City of Literature, UNESCO's Cities of Literature.
It is the nineteenth large ...
AIR centres started Konkani broadcasts.
Print
''Udentichem Sallok'' was the first Konkani periodical published in 1888, from Poona, by Eduardo Bruno de Souza. It started as a monthly and then as a fortnightly. It closed down in 1894.
Dailies
''Sanjechem Nokhetr'' was started in 1907 by B. F. Cabral in Bombay
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial centre, financial capital and the list of cities i ...
, and is the first ''Concanim'' (or Konkani) newspaper. It contained detailed news of Bombay
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial centre, financial capital and the list of cities i ...
, British India, as it was published from there.
In 1982, ''Novem Goem'' was a daily edited by Gurunath Kelekar, F. M. Rebello and Felicio Cardozo. It was started due to people's initiative. In 1989, Fr. Freddy J. da Costa, began a Konkani daily ''Goencho Avaz''. It became a monthly after one and a half year. Presently there is just a single Konkani daily newspaper, called ''Bhaangar Bhuin''. For a long time, there was another Konkani daily, '' Sunaparant'', which was published in Panjim
Panaji (; , , )also known as Panjim, is the capital of the Indian state of Goa and the headquarters of North Goa district. Previously, it was the territorial capital of the former Portuguese India. It lies on the banks of the Mandovi river est ...
.
Weeklies
''O Luzo-Concanim'' was a Concanim (Konkani)- Portuguese bilingual weekly, begun in 1891, by Aleixo Caitano José Francisco. From 1892 to 1897, ''A Luz, O Bombaim Esse, A Lua, "O Intra Jijent'' and ''O Opinião Nacional'' were bilingual Concanim- Portuguese weeklies published. In 1907, ''O Goano'' was putblished from Bombay by Honorato Furtado and Francis Xavier Furtado. It was a trilingual weekly in Portuguese, Konkani and English.
The Society of the Missionaries of Saint Francis Xavier, publish the Konkani weekly (satollem) named '' Vauraddeancho Ixtt''. from Pilar. It was started in 1933 by Fr. Arsencio Fernandes and Fr. Graciano Moraes.
Fortnightly
There is a fortnightly published newspaper since 2007 called ''Kodial Khaber'', edited by Venkatesh Baliga Mavinakurve and published by Baliga Publications, Mangalore.
Monthlies
'' Katolik Sovostkai'' was started in 1907 by Roldão Noronha. It later became a fortnightly before ceasing publication.
'' Dor Mhoineachi Rotti'' is the oldest running Konkani periodical. It is dedicated to the spreading of the devotion to the Sacred Heart of Jesus
The Most Sacred Heart of Jesus () is one of the most widely practised and well-known Catholic devotions, wherein the heart of Jesus Christ is viewed as a symbol of "God's boundless and passionate love for mankind". This devotion to Christ is p ...
, and was initially named Dor Muineachi Rotti Povitra Jesucha Calzachem Devoçãõ Vaddounchi. Note that the til (tilde mark) over ãõ in Devoçãõ is one single til. Fr. Vincent Lobo, from Sangolda in Goa, who was then curator at the St. Patrick's Church in Karachi, began it in 1915, to feed the spiritual thirst and hunger of the large number of Konkani speaking people there, on noticing the absence of Konkani spiritual literature. The name was changed subsequently to "Dor Muiniachi Rotti, Concanim Messenger of the Sacred Heart". On Fr. Vincent Lobo's passing away on 11 November 1922, Fr. António Ludovico Pereira, also from Sangolda, took over the responsibility. Dor Mhoineachi Rotti had an estimated readership of around 12,000 people then. After the passing away of Fr. António Ludovico Pereira on 26 July 1936, Fr. Antanasio Moniz, from Verna, took over. On his passing away in 1953, Fr. Elias D'Souza, from Bodiem, Tivim in Goa
Goa (; ; ) is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north, and Karnataka to the ...
became the fourth editor of Dor Mhoineachi Rotti. After shifting to Velha Goa
Old Goa (Konkani: ; ) is a historical site and city situated on the southern banks of the River Mandovi, within the Tiswadi ''taluka'' (''Ilhas'') of North Goa district, in the Indian state of Goa.
The city was established by the Bijapur ...
in Goa
Goa (; ; ) is a state on the southwestern coast of India within the Konkan region, geographically separated from the Deccan highlands by the Western Ghats. It is bound by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north, and Karnataka to the ...
around 1964, Fr. Moreno de Souza was editor for around 42 years. Presently the Dor Mhuineachi Rotti is owned by the Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
in Goa, edited by Fr. Vasco do Rego, S. J. and printed and published by Fr. Jose Silveira, S.J. on behalf of the Provincial Superior of the Jesuits in Goa. Dor Mhoineachi Rotti will complete 100 years on 1 January 2015.
''Gulab'' is a monthly from Goa. It was started by late Fr. Freddy J. da Costa in 1983, and was printed in colour, then uncommon.
Konkani periodicals published in Goa include '' Vauraddeancho Ixtt'' (Roman script, weekly), ''Gulab'' (Roman script, monthly), ''Bimb'' (Devanagari script, monthly), ''Panchkadayi'' (Kannada script, monthly) and ''Poddbimb'' (Roman script, monthly).
Konkani periodicals published in Mangalore include "Raknno" (Kannada script, weekly), "DIVO" (Kannada Script, weekly from Mumbai), "Kutmacho Sevak" (Kannada script, monthly), "Dirvem" (Kannada script, monthly),"Amcho Sandesh" (Kannada script, monthly) and "Kajulo" (Kannda script, children's magazine, monthly).
Konkani periodical published in Udupi include "Uzwad" (Kannada script, monthly) and Naman Ballok Jezu (Kannada script, monthly).
Ekvottavorvim Uzvadd (Devanagari Script, monthly) is published from Belgaum since 1998. Panchkadayi Konkani Monthly magazine from Manipal since 1967.
Digital and audible
The first complete literary website in Konkani started in 2001 using Kannada script was www.maaibhaas.com by Naveen Sequeira of Brahmavara. In 2003 www.daaiz.com started by Valley Quadros Ajekar from Kuwait, this literary portal was instrumental in creating a wider range of readers across the globe, apart from various columns, literary contests, through Ashawadi Prakashan, he published several books in Konkani, including the first e-book 'Sagorachea Vattecheo Zori' released by Gerry DMello Bendur in 2005 at Karkala.
www.poinnari.com is the first literary webportal in Konkani using three scripts (Kannada, Nagari and Romi), started in 2015, is also conducted the first National level literary contest in dual scripts in Konkani in 2017.
'Sagorachea Vattecheo Zori' is the first e-book in Konkani, a compilation of 100 poems digitally published by www.daaiz.com and digitally published in 2005 by Ashawadi Prakashan in Karkala.
'Kathadaaiz' is the first digital audio book digitally published in 2018 by www.poinnari.com. This audio book is also available in the YouTube channel of Ashawari Prakashan.
'Pattim Gamvak' is the first e-Novel written in Kannada script Konkani in 2002 by Valley Quadros Ajekar from Kuwait, published in www.maaibhaas.com in 2002–3.
'Veez' is the first digital weekly in Konkani, started in 2018 by Austine D'Souza Prabhu in Chicago, USA. Veez is the only magazine publishing Konkani in 4 scripts; Kannada, Nagari, Romi and Malayalam.
Television
The Doordarshan
Doordarshan (), abbreviated as DD, is India's State-owned enterprise, state-owned public broadcasting, public television broadcaster. Established by the Government of India on 15 September 1959, it is owned by the Ministry of Information and B ...
centre in Panjim produces Konkani programs, which are broadcast in the evening. Many local Goan channels also broadcast Konkani television programs. These include: Prudent Media, Goa 365, HCN, RDX Goa, and others.
Film
Music
On 1 February 2024, the song 'Addicted' by EZD and Chrystal Farrell entered Spotify
Spotify (; ) is a List of companies of Sweden, Swedish Music streaming service, audio streaming and media service provider founded on 23 April 2006 by Daniel Ek and Martin Lorentzon. , it is one of the largest providers of music streaming services ...
charts of UAE
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a federal elective monarchy made up of seven emirates, with Abu Dhabi serving as i ...
at 3rd position alongside artists like Taylor Swift
Taylor Alison Swift (born December 13, 1989) is an American singer-songwriter. Known for her autobiographical songwriting, artistic versatility, and Cultural impact of Taylor Swift, cultural impact, Swift is one of the Best selling artists, w ...
and The Weeknd
Abel Makkonen Tesfaye (; born February 16, 1990), known professionally as the Weeknd, is a Canadian singer-songwriter, record producer, and actor. He is best known for adding Pop music, pop, electronic music, electronic and hip-hop stylings ...
, creating a record of becoming the first ever Konkani song on the charts.
In popular culture
Many Konkani songs of the Goan fisher-folk appear recurrently in a number of Hindi films
Hindi cinema, popularly known as Bollywood and formerly as Bombay cinema, is primarily produced in Mumbai. The popular term Bollywood is a portmanteau of "Bombay" (former name of Mumbai) and "Hollywood". The industry, producing films in th ...
. Many Hindi movies feature characters with a Goan Catholic accent. A famous song from the 1957 movie '' Aasha'', contains the Konkani words "mhaka naka" and became extremely popular. Children were chanting "Eeny, meeny, miny, moe
"Eeny, meeny, miny, moe" – which can be spelled a number of ways – is a children's counting-out rhyme, used to select a person in games such as tag, or for selecting various other things. It is one of a large group of similar rhymes in whic ...
", which inspired C Ramchandra and his assistant John Gomes to create the first line of the song, "Eena Meena Deeka, De Dai Damanika". Gomes, who was a Goan
Goans ( Romi Konkani: , ) is the demonym used to describe the people native to Goa, India, formerly part of Portuguese India (''Estado Português da Índia''). They form an ethno-linguistic group resulting from the assimilation of Indo-Aryan, ...
, added the words "mhaka naka" (Konkani for "I don't want"). They kept on adding more nonsense rhymes until they ended with "Rum pum po!".Nike
Nike often refers to:
* Nike, Inc., a major American producer of athletic shoes, apparel, and sports equipment
* Nike (mythology), a Greek goddess who personifies victory
Nike may also refer to:
People
* Nike (name), a surname and feminine giv ...
for the 2007 Cricket World Cup
The 2007 ICC Cricket World Cup was the ninth Cricket World Cup, a One Day International (ODI) cricket tournament that took place in the West Indies from 13 March to 28 April 2007. There were a total of 51 matches played, three fewer than at the 2 ...
featured a Konkani song "Rav Patrao Rav" as the background theme. It was based on the tune of an older song " Bebdo", composed by Chris Perry and sung by Lorna Cordeiro. The new lyrics were written by Agnello Dias (who worked in the ad agency that made the ad), recomposed by Ram Sampat, and sung by Ella Castellino.
A Konkani cultural event, Konkani Nirantari, organised by Mandd Sobhann, was held in Mangalore
Mangaluru (), formerly called Mangalore ( ), is a major industrial port city in the Indian state of Karnataka and on the west coast of India. It is located between the Laccadive Sea and the Western Ghats about west of Bengaluru, the st ...
on 26 and 27 January 2008, and entered the Guinness Book of World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a British reference book published annually, listi ...
for holding a 40-hour-long non-stop musical singing marathon, beating a Brazilian musical troupe who had previously held the record of singing non-stop for 36 hours.
See also
* Bombay East Indian dialect
* Southern Saraswat Konkani
* Konkani in the Roman script
Konkani in the Roman script, commonly known as Roman Konkani or ''Romi Konknni'' () refers to the writing of the Konkani language in the Roman script. While Konkani is written in five different scripts altogether, Roman Konkani is widely used. ...
* Konkani Language Agitation
The Konkani language agitations were a series of protests in India, concerning the uncertain future of the Konkani language. They were held by Goans in the former territory of Goa, Daman and Diu; then under the administration of the Maharashtr ...
* Konkani people
The Konkani people are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group native to the Konkan region of the Indian subcontinent. They speak various dialects of the Konkani language. Following the Konkani language agitation, Konkani becam ...
* Konkani phonology
KonkaniDisambiguation: Konkani is a name given to a group of several cognate dialects spoken along the narrow strip of land called Konkan, on the west coast of India. This is, however, somewhat an over-generalisation. Geographically, Konkan is ...
* Konkani Poets
* Konkani Script
* List of loanwords in Konkani
* Languages of India
Languages of India belong to several list of language families, language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indian people, Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians; both fami ...
* Languages with official status in India
, 22 languages have been classified as scheduled languages under the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India. There is no national language of India.
While the constitution was adopted in 1950, article 343 declared that Hindi would be th ...
* List of languages by number of native speakers in India
The Republic of India is home to several hundred languages. Most Indians speak a language belonging to the families of the Indo-Aryan branch of Indo-European (c. 77%), the Dravidian (c. 20.61%), the Austroasiatic (precisely Munda and Kha ...
* Maharashtri
Maharashtri or Maharashtri Prakrit (') is a Prakrit language of ancient as well as medieval India.
Maharashtri Prakrit was commonly spoken until 875 CEV.Rajwade, ''Maharashtrache prachin rajyakarte''
* Malvani people
Malvani people or Malvanis are an ethnic group from the Malvan region, which includes Malvan region, Malvan, Kudal, Sawantwadi and Dodamarg tehsils of Sindhudurg district, Sindhudurg, India, speaking the Malvani Konkani, Malvani language. Malvani ...
* Marathi–Konkani languages
* Paisaci
Paishachi or Paisaci () is a largely unattested literary language of the middle kingdoms of India mentioned in Prakrit and Sanskrit grammars of antiquity. It is generally grouped with the Prakrits, with which it shares some linguistic similari ...
* Sahitya Akademi Award to Konkani Writers
* World Konkani Centre
* World Konkani Hall of Fame
Footnotes
References
Further reading
*
External links
Vauraddeancho Ixtt
Konkani language site
Konkani News
Konkani language site
Kital
, Konkani language site
Chilume.com
Konkani Literature
Niz Goenkar
Konkani-English bilingual site
Learn Goan Konkani online
Read Konkani News online
Learn Mangalorean Catholic Konkani online
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20110502055206/http://manglorean.net/konkani/ Online Manglorean Konkani Dictionary Project
Online Konkani (GSB) dictionary
World Konkani Centre, Mangalore
Konkanverter-Konkani script conversion utility
{{DEFAULTSORT:Konkani Language
Languages written in Brahmic scripts
Languages attested from the 12th century
Konkani
Southern Indo-Aryan languages
Indo-Aryan languages
Official languages of India
Subject–object–verb languages
Konkani languages
The Marathi—Konkani languages are the mainland Southern Indo-Aryan languages, spoken in Maharashtra and the Konkan region of India. The other branch of Southern Indo-Aryan languages is called Insular Indic languages, which are spoken in Insu ...
Languages written in Devanagari
 A piece of hymn dedicated to Lord
A piece of hymn dedicated to Lord  Konkani, despite having a small population, shows a very high number of
Konkani, despite having a small population, shows a very high number of  There are organisations working for Konkani but, primarily, these were restricted to individual communities. The All India Konkani Parishad founded on 8 July 1939, provided a common ground for Konkani people from all regions. A new organisation known as Vishwa Konkani Parishad, which aims to be an all-inclusive and pluralistic umbrella organisation for Konkanis around the world, was founded on 11 September 2005.
Mandd Sobhann is the premier organisation that is striving hard to preserve, promote, propagate, and enrich the Konkani language and culture. It all began with the experiment called 'Mandd Sobhann' – a search for a Konkani identity in Konkani music on 30 November 1986 at Mangalore. What began as a performance titled 'Mandd Sobhann', grew into a movement of revival and rejuvenation of Konkani culture; and solidified into an organization called Mandd Sobhann. Today, Mandd Sobhann boasts of all these 3 identities namely - a performance, a movement and an organization.https://www.manddsobhann.org/
The Konkan Daiz Yatra, started in 1939 in
There are organisations working for Konkani but, primarily, these were restricted to individual communities. The All India Konkani Parishad founded on 8 July 1939, provided a common ground for Konkani people from all regions. A new organisation known as Vishwa Konkani Parishad, which aims to be an all-inclusive and pluralistic umbrella organisation for Konkanis around the world, was founded on 11 September 2005.
Mandd Sobhann is the premier organisation that is striving hard to preserve, promote, propagate, and enrich the Konkani language and culture. It all began with the experiment called 'Mandd Sobhann' – a search for a Konkani identity in Konkani music on 30 November 1986 at Mangalore. What began as a performance titled 'Mandd Sobhann', grew into a movement of revival and rejuvenation of Konkani culture; and solidified into an organization called Mandd Sobhann. Today, Mandd Sobhann boasts of all these 3 identities namely - a performance, a movement and an organization.https://www.manddsobhann.org/
The Konkan Daiz Yatra, started in 1939 in  The Konkani Triveni Kala Sangam is one more famed Konkani organisation in
The Konkani Triveni Kala Sangam is one more famed Konkani organisation in