koala on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The koala (''Phascolarctos cinereus''), sometimes inaccurately called the koala bear, is an
 The modern koala is the only
The modern koala is the only
 For a mammal, the koala has a disproportionately small brain, 60% smaller than that of a typical diprotodont, weighing only on average. The brain's surface is fairly smooth and "primitive". It does not entirely fill the cranial cavity, unlike most mammals, and is lightened by large amounts of cerebrospinal fluid. It is possible that the fluid protects the brain should the animal fall from a tree. The koala's small brain may be an adaptation to the energy restrictions imposed by its diet, which is insufficient to sustain a larger brain. Its small brain limits its ability to perform complex behaviours. For example, it will not eat plucked eucalyptus leaves on a flat surface, which does not match its feeding routine.
The koala has a broad, dark nose with a good sense of smell, and it is known to sniff the oils of individual branchlets to assess their edibility. Its relatively small eyes are unusual among marsupials in that the pupils have vertical slits, an adaptation to living on a more vertical plane. Its round ears provide it with good hearing, and it has a well-developed middle ear. The koala larynx is located relatively low in the vocal tract and can be pulled further down. They possess unique folds in the velum (soft palate), known as velar vocal folds, in addition to the typical
For a mammal, the koala has a disproportionately small brain, 60% smaller than that of a typical diprotodont, weighing only on average. The brain's surface is fairly smooth and "primitive". It does not entirely fill the cranial cavity, unlike most mammals, and is lightened by large amounts of cerebrospinal fluid. It is possible that the fluid protects the brain should the animal fall from a tree. The koala's small brain may be an adaptation to the energy restrictions imposed by its diet, which is insufficient to sustain a larger brain. Its small brain limits its ability to perform complex behaviours. For example, it will not eat plucked eucalyptus leaves on a flat surface, which does not match its feeding routine.
The koala has a broad, dark nose with a good sense of smell, and it is known to sniff the oils of individual branchlets to assess their edibility. Its relatively small eyes are unusual among marsupials in that the pupils have vertical slits, an adaptation to living on a more vertical plane. Its round ears provide it with good hearing, and it has a well-developed middle ear. The koala larynx is located relatively low in the vocal tract and can be pulled further down. They possess unique folds in the velum (soft palate), known as velar vocal folds, in addition to the typical 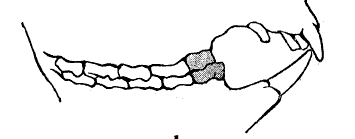 The koala has several adaptations for its low nutrient, toxic, and fibrous diet. The animal's dentition consists of incisors and cheek teeth (a single premolar and four molars on each jaw) that are separated by a large gap (a characteristic feature of herbivorous mammals). The koala bites a leaf with the incisors and clips it with the premolars at the petiole, before chewing it to pieces with the cusped molars. Koalas may store food in their cheek pouches before it is ready to be chewed. The partially worn molars of koalas in their prime are optimal for breaking leaves into small particles, resulting in more efficient stomach digestion and nutrient absorption in the small intestine, which digests the eucalyptus leaves to provide most of the animal's energy. A koala sometimes regurgitates the food into the mouth to be chewed a second time.
Koalas are hindgut fermenters, and their digestive retention can last 100 hours in the wild or 200 hours in captivity. This is made possible by their
The koala has several adaptations for its low nutrient, toxic, and fibrous diet. The animal's dentition consists of incisors and cheek teeth (a single premolar and four molars on each jaw) that are separated by a large gap (a characteristic feature of herbivorous mammals). The koala bites a leaf with the incisors and clips it with the premolars at the petiole, before chewing it to pieces with the cusped molars. Koalas may store food in their cheek pouches before it is ready to be chewed. The partially worn molars of koalas in their prime are optimal for breaking leaves into small particles, resulting in more efficient stomach digestion and nutrient absorption in the small intestine, which digests the eucalyptus leaves to provide most of the animal's energy. A koala sometimes regurgitates the food into the mouth to be chewed a second time.
Koalas are hindgut fermenters, and their digestive retention can last 100 hours in the wild or 200 hours in captivity. This is made possible by their
 Koalas are herbivorous, and while most of their diet consists of
Koalas are herbivorous, and while most of their diet consists of
 Koalas are seasonal breeders, and they give birth from October to May. Females in oestrus lean their heads back and shake their bodies. Despite these obvious signals, males try to copulate with any female during this period, mounting them from behind. Because of his much larger size, a male can overpower a female. A female may scream and vigorously fight off her suitors but will accede to one that is dominant or familiar. The commotion can attract other males to the scene, obliging the incumbent to delay mating and fight off the intruders. A female may learn who is more dominant during these fights. Older males typically accumulate scratches, scars, and cuts on the exposed parts of their noses and their eyelids.
Koalas are induced ovulators. The gestation period lasts 33–35 days, and a female gives birth to one joey or occasionally, twins. The young are born tiny and barely formed, weighing no more than . However, their lips, forelimbs, and shoulders are relatively advanced, and they can breathe, defecate, and urinate. The joey crawls into its mother's pouch to continue its development. Female koalas do not clean their pouches, while an unusual trait among marsupials.
The joey latches on to one of the female's two teats and suckles it. The female lactates for as long as a year to make up for her low energy production. Unlike in other marsupials, koala milk becomes less fatty as the joey grows. After seven weeks, the joey has a proportionally large head, clear edges around its face, more colouration, and a visible pouch (if female) or scrotum (male). At 13 weeks, the joey weighs around , and its head doubles in size. The eyes begin to open and hair begins to appear. At 26 weeks, the fully furred animal resembles an adult and can look outside the pouch.
Koalas are seasonal breeders, and they give birth from October to May. Females in oestrus lean their heads back and shake their bodies. Despite these obvious signals, males try to copulate with any female during this period, mounting them from behind. Because of his much larger size, a male can overpower a female. A female may scream and vigorously fight off her suitors but will accede to one that is dominant or familiar. The commotion can attract other males to the scene, obliging the incumbent to delay mating and fight off the intruders. A female may learn who is more dominant during these fights. Older males typically accumulate scratches, scars, and cuts on the exposed parts of their noses and their eyelids.
Koalas are induced ovulators. The gestation period lasts 33–35 days, and a female gives birth to one joey or occasionally, twins. The young are born tiny and barely formed, weighing no more than . However, their lips, forelimbs, and shoulders are relatively advanced, and they can breathe, defecate, and urinate. The joey crawls into its mother's pouch to continue its development. Female koalas do not clean their pouches, while an unusual trait among marsupials.
The joey latches on to one of the female's two teats and suckles it. The female lactates for as long as a year to make up for her low energy production. Unlike in other marsupials, koala milk becomes less fatty as the joey grows. After seven weeks, the joey has a proportionally large head, clear edges around its face, more colouration, and a visible pouch (if female) or scrotum (male). At 13 weeks, the joey weighs around , and its head doubles in size. The eyes begin to open and hair begins to appear. At 26 weeks, the fully furred animal resembles an adult and can look outside the pouch.
 At six or seven months, the joey weighs and fully emerges from the pouch for the first time. It explores its new surroundings cautiously, clutching its mother for support. Around this time, the mother prepares it for a eucalyptus diet by producing a faecal pap that the joey eats from her cloaca. This pap comes from the cecum, is more liquid than regular faeces, and is filled with bacteria. A nine month old joey has its adult coat colour and weighs . Having permanently left the pouch, it rides on its mother's back for transportation, learning to climb by grasping branches. Gradually, it becomes more independent. The mother becomes pregnant again after a year after the offspring reaches around . She permanently severs her bond with her previous offspring and no longer allows it to suckle, but it remains nearby until it is one-and-a-half to two years old.
Females become sexually mature at about three years of age; in comparison, males reach sexual maturity at about age four although they can experience spermatogenesis as early as two years. Males do not start marking their scent until they reach sexual maturity though their chest glands become functional much earlier. Koalas can breed every year if environmental conditions are good, though the long dependence of the young usually leads to year-long gaps in births.
At six or seven months, the joey weighs and fully emerges from the pouch for the first time. It explores its new surroundings cautiously, clutching its mother for support. Around this time, the mother prepares it for a eucalyptus diet by producing a faecal pap that the joey eats from her cloaca. This pap comes from the cecum, is more liquid than regular faeces, and is filled with bacteria. A nine month old joey has its adult coat colour and weighs . Having permanently left the pouch, it rides on its mother's back for transportation, learning to climb by grasping branches. Gradually, it becomes more independent. The mother becomes pregnant again after a year after the offspring reaches around . She permanently severs her bond with her previous offspring and no longer allows it to suckle, but it remains nearby until it is one-and-a-half to two years old.
Females become sexually mature at about three years of age; in comparison, males reach sexual maturity at about age four although they can experience spermatogenesis as early as two years. Males do not start marking their scent until they reach sexual maturity though their chest glands become functional much earlier. Koalas can breed every year if environmental conditions are good, though the long dependence of the young usually leads to year-long gaps in births.
 The first written reference to the koala was recorded by John Price, servant of John Hunter, the
The first written reference to the koala was recorded by John Price, servant of John Hunter, the  Naturalist and popular artist
Naturalist and popular artist
 The song "Ode to a Koala Bear" appears on the B-side of the 1983
The song "Ode to a Koala Bear" appears on the B-side of the 1983
 The koala was originally classified as
The koala was originally classified as
images and movies of the koala ''Phascolarctos cinereus''
Animal Diversity Web – ''Phascolarctos cinereus''
*iNaturalist crowdsource
koala sighting photos
(mapped, graphed)
Koala Science Community
"Koala Crunch Time"
– an ABC documentary (2012)
Cracking the Koala Code
– a PBS Nature documentary (2012)
The Aussie Koala Ark Conservation Project
{{Taxonbar, from=Q36101 Articles containing video clips Clawed herbivores Extant Middle Pleistocene first appearances Herbivorous mammals Mammals described in 1817 Mammals of New South Wales Mammals of Queensland Mammals of South Australia Mammals of Victoria (state) Marsupials of Australia Vombatiforms Symbols of Queensland Taxa named by Georg August Goldfuss
arboreal
Arboreal locomotion is the locomotion of animals in trees. In habitats in which trees are present, animals have evolved to move in them. Some animals may scale trees only occasionally (scansorial), but others are exclusively arboreal. The hab ...
herbivorous marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
native to Australia. It is the only extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
representative of the family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
'' Phascolarctidae''. Its closest living relatives are the wombats. The koala is found in coastal areas of the island's eastern and southern regions, inhabiting Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
, New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
, Victoria, and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a States and territories of Australia, state in the southern central part of Australia. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, which in ...
. It is easily recognisable by its stout, tailless body and large head with round, fluffy ears and large, dark nose. The koala has a body length of and weighs . Its fur colour ranges from silver grey to chocolate brown. Koalas from the northern populations are typically smaller and lighter in colour than their counterparts further south. These populations are possibly separate subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
, but not all researchers accept this.
Koalas typically inhabit open ''Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of more than 700 species of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae. Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are trees, often Mallee (habit), mallees, and a few are shrubs. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalyp ...
'' woodland, as the leaves of these trees make up most of their diet. This eucalypt diet has low nutritional and caloric content and contains toxic compounds that deter most other mammals from feeding on them. Koalas are largely sedentary and sleep up to twenty hours a day. They are asocial; only mothers bond to dependent offspring. Adult males communicate with bellows that intimidate rivals and attract mates. Males mark their presence with secretions from scent glands located on their chests. Like other marsupials, koalas give birth to young known as joeys at a very early stage of development. They crawl into their mothers' pouches, where they live for their first six to seven months. They are fully weaned around a year old. Koalas have few natural predators and parasites, but are threatened by pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s such as '' Chlamydiaceae'' bacteria and ''koala retrovirus
Koala retrovirus (KoRV) is a retrovirus that is present in many populations of koalas. It has been implicated as the agent of koala immune deficiency syndrome (KIDS), an HIV/AIDS, AIDS-like immunodeficiency that leaves infected koalas more susce ...
''.
Because of their distinctive appearance, koalas, along with kangaroo
Kangaroos are marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use, the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern gre ...
s, are recognised worldwide as symbols of Australia. They were hunted by Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians are people with familial heritage from, or recognised membership of, the various ethnic groups living within the territory of contemporary Australia prior to History of Australia (1788–1850), British colonisation. The ...
and depicted in myths
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
and cave art for millennia. The first recorded encounter between a European and a koala was in 1798, and an image of the animal was published in 1810 by naturalist George Perry. Botanist Robert Brown Robert Brown may refer to: Robert Brown (born 1965), British Director, Animator and author
Entertainers and artists
* Washboard Sam or Robert Brown (1910–1966), American musician and singer
* Robert W. Brown (1917–2009), American printmaker ...
wrote the first detailed scientific description in 1814 although his work remained unpublished for 180 years. Artist John Gould
John Gould (; 14 September 1804 – 3 February 1881) was an English ornithologist who published monographs on birds, illustrated by plates produced by his wife, Elizabeth Gould (illustrator), Elizabeth Gould, and several other artists, includ ...
illustrated and described the koala, thereby introducing the species to the British public. Further details about the animal's biology were revealed in the 19th century by English scientists. Koalas are listed as a vulnerable species
A vulnerable species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as being threatened species, threatened with extinction unless the circumstances that are threatened species, ...
by the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the stat ...
. Among the many threats to their existence are habitat destruction caused by agriculture, urbanisation, droughts, and associated bushfires, some related to climate change. In February 2022, the koala was officially listed as endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
in the Australian Capital Territory
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory until 1938, is an internal States and territories of Australia, territory of Australia. Canberra, the capital city of Australia, is situated within the territory, an ...
, New South Wales, and Queensland.
Etymology
The word "koala" comes from theDharug
The Dharug or Darug people, are a nation of Aboriginal Australian clans, who share ties of kinship, country and culture. In pre-colonial times, they lived as hunters in the region of current day Sydney. The Darug speak one of two dialects o ...
, meaning . Although the vowel "u" was originally written in the English orthography
English orthography comprises the set of rules used when writing the English language, allowing readers and writers to associate written graphemes with the sounds of spoken English, as well as other features of the language. English's orthograp ...
as "oo" (in spellings such as ''coola'' or ''koolah''—two syllables), the spelling for that sound later became "oa"; the word is now pronounced in three syllables (''ko-a-la'') possibly in error based on that new spelling. Another hypothesis is that "koala" was an aboriginal name from the Hawkesbury River district near Sydney.
Adopted by white settlers, the word "koala" became one of hundreds of Aboriginal loan words in Australian English, where it was also commonly referred to as "native bear", later "koala bear", for its resemblance to a bear. It is one of several Aboriginal words that made it into International English alongside words like "didgeridoo" and "kangaroo".
The koala's generic name, '' Phascolarctos'', is derived from the Greek words () and () . The specific name, , is Latin for .
Taxonomy
The generic name ''Phascolarctos'' was given in 1816 by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville, who did not give it a specific name until further review. In 1819, German zoologist Georg August Goldfuss gave it the binomial ''Lipurus cinereus''. Because ''Phascolarctos'' was published first, according to theInternational Code of Zoological Nomenclature
The International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) is a widely accepted Convention (norm), convention in zoology that rules the formal scientific name, scientific naming of organisms treated as animals. It is also informally known as the I ...
, it has priority as the official genus name. French naturalist Anselme Gaëtan Desmarest
Anselme Gaëtan Desmarest (6 March 1784 – 4 June 1838) was a French Zoology, zoologist and author. He was the son of Nicolas Desmarest and the father of Eugène Anselme Sébastien Léon Desmarest.
Career
Desmarest was a disciple of Georges Cu ...
coined the name ''Phascolarctos fuscus'' in 1820, suggesting that the brown-coloured versions were a different species than the grey ones. Other names suggested by European authors included ''Marodactylus cinereus'' by Goldfuss in 1820, ''P. flindersii'' by René Primevère Lesson
René (''Born again (Christianity), born again'' or ''reborn'' in French language, French) is a common given name, first name in French-speaking, Spanish-speaking, and German-speaking countries. It derives from the Latin name Renatus.
René is th ...
in 1827, and ''P. koala'' by John Edward Gray
John Edward Gray (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Samuel Frederick Gray (1766–1828). The same is used for a z ...
in 1827.
Evolution
The koala is classified with wombats (family '' Vombatidae'') and several extinct families (including marsupial tapirs, marsupial lions and giant wombats) in the suborder Vombatiformes within the orderDiprotodontia
Diprotodontia (, from Greek language, Greek "two forward teeth") is the largest extant order (biology), order of marsupials, with about 155 species, including the kangaroos, Wallaby, wallabies, Phalangeriformes, possums, koala, wombats, and many ...
. The Vombatiformes are a sister group
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
to a clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
that includes macropods (kangaroos and wallabies) and possums
Possum may refer to:
Animals
* Didelphimorphia, or (o)possums, an order of marsupials native to the Americas
** Didelphis, a genus of marsupials within Didelphimorphia
*** Common opossum, native to Central and South America
*** Virginia opossum, ...
. The koala's lineage possibly branched off around 40 million years ago during the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
.
extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
member of '' Phascolarctidae'', a family that includes several extinct genera and species. During the Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
and Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
, koalas lived in rainforests and had broader diets. Some species, such as ''Nimiokoala greystanesi'' and some species of '' Perikoala'', were around the same size as the modern koala, while others, such as species of '' Litokoala'', were one-half to two-thirds its size. Like the modern species, prehistoric koalas had well developed ear structures, which suggests that they also made long-distance vocalisations and had a relatively inactive lifestyle. During the Miocene, the Australian continent began drying out, leading to the decline of rainforests and the spread of open ''Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of more than 700 species of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae. Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are trees, often Mallee (habit), mallees, and a few are shrubs. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalyp ...
'' woodlands. The genus ''Phascolarctos'' split from ''Litokoala'' in the late Miocene, and had several adaptations that allowed it to live on a eucalyptus diet: the palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly sep ...
shifted towards the front of the skull; the upper teeth were lined by thicker bone, molars became relatively low compared to the jaw joint and with more chewing surface; the pterygoid fossa shrank; and a larger gap separated the incisor teeth and the molars.
''P. cinereus'' may have emerged as a dwarf form of the giant koala (''P. stirtoni''), following the disappearance of several giant animals in the late Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
. A 2008 study questioned this hypothesis, noting that ''P. cinereus'' and ''P. stirtoni'' were sympatric
In biology, two closely related species or populations are considered sympatric when they exist in the same geographic area and thus frequently encounter each other. An initially interbreeding population that splits into two or more distinct spe ...
during the mid-late Pleistocene, and that their teeth morphology displayed the major differences. The fossil record of the modern koala extends back at least to the middle Pleistocene.
Genetics and variations
Three subspecies have been described: the Queensland koala (''Phascolarctos cinereus adustus'', Thomas 1923), the New South Wales koala (''Phascolarctos cinereus cinereus'', Goldfuss 1817), and the Victorian koala (''Phascolarctos cinereus victor'', Troughton 1935). These forms are distinguished by pelage colour and thickness, body size, and skull shape. The Queensland koala is the smallest, with silver or grey short hairs and a shorter skull. The Victorian koala is the largest, with shaggier, brown fur and a wider skull. The geographic limits of these variations are based on state borders, and their status as subspecies is disputed. A 1999 genetic study suggests koalas exist as acline
Cline may refer to:
Science
* Cline (biology), a measurable gradient in a single trait in a species across its geographical range
* Cline (hydrology), a fluid layer with a property that varies
* Cline (mathematics) or generalised circle, a ci ...
within a single evolutionarily significant unit with limited gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as migration and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation, genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent ...
between local populations. In 2016, a comprehensive phylogenetic study did not support the recognition of any subspecies.
Other studies have found that koala populations are highly inbred with low genetic variation
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations among the same species. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources ...
. Such low genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
may have been caused by population declines during the late Pleistocene. Rivers and roads limit gene flow and contribute to the isolation of southeast Queensland populations. In April 2013, scientists from the Australian Museum
The Australian Museum, originally known as the Colonial Museum or Sydney Museum. is a heritage-listed museum at 1 William Street, Sydney, William Street, Sydney central business district, Sydney CBD, New South Wales. It is the oldest natural ...
and Queensland University of Technology
The Queensland University of Technology (QUT) is a public university, public research university located in the city of Brisbane in Queensland, Australia. It has two major campuses, a modern city campus in Gardens Point, Brisbane, Gardens Point ...
announced they had fully sequenced the koala genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
.
Characteristics
The koala is a robust animal with a large head and vestigial or non-existent tail. It has a body length of and a weight of , making it among the largest arboreal marsupials. Koalas from Victoria are twice as heavy as those from Queensland. The species issexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
: males are 50% larger than females. Males' noses are more curved and sport chest glands, which are visible as bald patches. The female's pouch opening is secured by a sphincter which holds the young in.
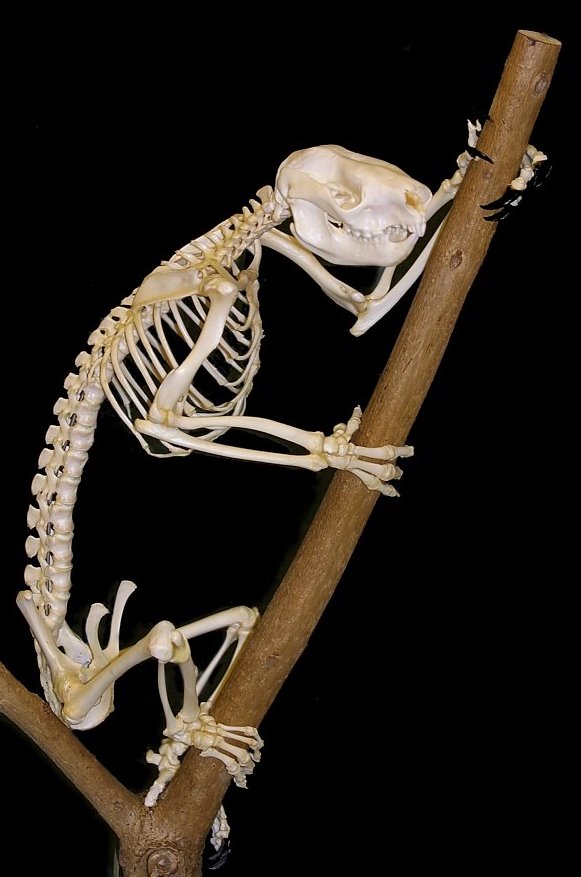
The pelage of the koala is denser on the back. Back fur colour varies from light grey to chocolate brown. The belly fur is whitish; on the rump it is mottled whitish and dark. The koala has the most effective insulating back fur of any marsupial and is resilient to wind and rain, while the belly fur can reflect solar radiation. The koala has curved, sharp claws well adapted for climbing trees. The large forepaws have two opposable digits (the first and second, which are opposable to the other three) that allow them to grip small branches. On the hind paws, the second and third digits are fused, a typical condition for members of the ''Diprotodontia'', and the attached claws (which are still separate) function like a comb. The animal has a robust skeleton and a short, muscular upper body with relatively long upper limbs that contribute to its ability to climb. The thigh muscles are anchored further down the shinbone, increasing its climbing power.
 For a mammal, the koala has a disproportionately small brain, 60% smaller than that of a typical diprotodont, weighing only on average. The brain's surface is fairly smooth and "primitive". It does not entirely fill the cranial cavity, unlike most mammals, and is lightened by large amounts of cerebrospinal fluid. It is possible that the fluid protects the brain should the animal fall from a tree. The koala's small brain may be an adaptation to the energy restrictions imposed by its diet, which is insufficient to sustain a larger brain. Its small brain limits its ability to perform complex behaviours. For example, it will not eat plucked eucalyptus leaves on a flat surface, which does not match its feeding routine.
The koala has a broad, dark nose with a good sense of smell, and it is known to sniff the oils of individual branchlets to assess their edibility. Its relatively small eyes are unusual among marsupials in that the pupils have vertical slits, an adaptation to living on a more vertical plane. Its round ears provide it with good hearing, and it has a well-developed middle ear. The koala larynx is located relatively low in the vocal tract and can be pulled further down. They possess unique folds in the velum (soft palate), known as velar vocal folds, in addition to the typical
For a mammal, the koala has a disproportionately small brain, 60% smaller than that of a typical diprotodont, weighing only on average. The brain's surface is fairly smooth and "primitive". It does not entirely fill the cranial cavity, unlike most mammals, and is lightened by large amounts of cerebrospinal fluid. It is possible that the fluid protects the brain should the animal fall from a tree. The koala's small brain may be an adaptation to the energy restrictions imposed by its diet, which is insufficient to sustain a larger brain. Its small brain limits its ability to perform complex behaviours. For example, it will not eat plucked eucalyptus leaves on a flat surface, which does not match its feeding routine.
The koala has a broad, dark nose with a good sense of smell, and it is known to sniff the oils of individual branchlets to assess their edibility. Its relatively small eyes are unusual among marsupials in that the pupils have vertical slits, an adaptation to living on a more vertical plane. Its round ears provide it with good hearing, and it has a well-developed middle ear. The koala larynx is located relatively low in the vocal tract and can be pulled further down. They possess unique folds in the velum (soft palate), known as velar vocal folds, in addition to the typical vocal folds
In humans, the vocal cords, also known as vocal folds, are folds of throat tissues that are key in creating sounds through Speech, vocalization. The length of the vocal cords affects the pitch of voice, similar to a violin string. Open when brea ...
of the larynx. These features allow the koala to produce deeper sounds than would otherwise be possible for their size.
 The koala has several adaptations for its low nutrient, toxic, and fibrous diet. The animal's dentition consists of incisors and cheek teeth (a single premolar and four molars on each jaw) that are separated by a large gap (a characteristic feature of herbivorous mammals). The koala bites a leaf with the incisors and clips it with the premolars at the petiole, before chewing it to pieces with the cusped molars. Koalas may store food in their cheek pouches before it is ready to be chewed. The partially worn molars of koalas in their prime are optimal for breaking leaves into small particles, resulting in more efficient stomach digestion and nutrient absorption in the small intestine, which digests the eucalyptus leaves to provide most of the animal's energy. A koala sometimes regurgitates the food into the mouth to be chewed a second time.
Koalas are hindgut fermenters, and their digestive retention can last 100 hours in the wild or 200 hours in captivity. This is made possible by their
The koala has several adaptations for its low nutrient, toxic, and fibrous diet. The animal's dentition consists of incisors and cheek teeth (a single premolar and four molars on each jaw) that are separated by a large gap (a characteristic feature of herbivorous mammals). The koala bites a leaf with the incisors and clips it with the premolars at the petiole, before chewing it to pieces with the cusped molars. Koalas may store food in their cheek pouches before it is ready to be chewed. The partially worn molars of koalas in their prime are optimal for breaking leaves into small particles, resulting in more efficient stomach digestion and nutrient absorption in the small intestine, which digests the eucalyptus leaves to provide most of the animal's energy. A koala sometimes regurgitates the food into the mouth to be chewed a second time.
Koalas are hindgut fermenters, and their digestive retention can last 100 hours in the wild or 200 hours in captivity. This is made possible by their caecum
The cecum ( caecum, ; plural ceca or caeca, ) is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix, ...
— long and in diameter—possibly the largest for an animal of its size. Koalas can retain food particles for longer fermentation if needed. They are more likely keep smaller particles as larger ones take longer to digest. While the hindgut is relatively large, only 10% of the animal's energy is obtained from digestion in this chamber. The koala's metabolic rate is only 50% of the typical mammalian rate, owing to its low energy intake, although this can vary across seasons and sexes. They can digest the toxic plant secondary metabolites, phenolic compounds and terpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predomi ...
s due to their production of cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for examp ...
, which neutralises these poisons in the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
. The koala replaces lost water at a lower rate than species such as some possums. It maintains water by absorbing it in the caecum, resulting in drier faecal pellets packed with undigested fibre.
Distribution and habitat
The koala's range covers roughly , and 30ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and c ...
s. It ranges throughout mainland eastern and southeastern Australia, including the states of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, and South Australia. The koala was introduced to several nearby islands. The population on Magnetic Island represents the northern limit of its range.
Fossil evidence shows that the koala's range stretched as far west as southwestern Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Aust ...
during the late Pleistocene. They were likely driven to extinction in these areas by environmental changes and hunting by Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians are people with familial heritage from, or recognised membership of, the various ethnic groups living within the territory of contemporary Australia prior to History of Australia (1788–1850), British colonisation. The ...
. Koalas were introduced to Western Australia at Yanchep in 1938 but that population was reduced to 4 individuals by 2022. Koalas can be found in both tropical and temperate habitats ranging from dense woodlands to more spaced-out forests. In semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of se ...
s, they prefer riparian habitats, where nearby streams and creeks provide refuge during times of drought and extreme heat.
Behaviour and ecology
Foraging and activities
 Koalas are herbivorous, and while most of their diet consists of
Koalas are herbivorous, and while most of their diet consists of eucalypt
Eucalypt is any woody plant with Capsule (fruit), capsule fruiting bodies belonging to one of seven closely related genera (of the tribe Eucalypteae) found across Australia:
''Eucalyptus'', ''Corymbia'', ''Angophora'', ''Stockwellia'', ''Allosyn ...
leaves, they can be found in trees of other genera, such as ''Acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Austral ...
'', '' Allocasuarina'', '' Callitris'', '' Leptospermum'', and ''Melaleuca
''Melaleuca'' () is a genus of nearly 300 species of plants in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae, commonly known as paperbarks, honey-myrtles, bottlebrushes or tea-trees (although the last name is also applied to species of '' Leptospermum''). They ...
''. Though the foliage of over 600 species of ''Eucalyptus'' is available, the koala shows a strong preference for around 30. They prefer plant matter with higher protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
than fibre and lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidit ...
. The most favoured species are '' Eucalyptus microcorys'', '' E. tereticornis'', and '' E. camaldulensis'', which, on average, make up more than 20% of their diet. Despite its reputation as a picky eater, the koala is more generalist than some other marsupial species, such as the greater glider. The koala does not need to drink often as it can get enough water from the leaves, though larger males may additionally drink water found on the ground or in tree hollows. When feeding, a koala reaches out to grab leaves with one forepaw while the other paws hang on to the branch. Depending on the size of the individual, a koala can walk to the end of a branch or must stay near the base. Each day, koalas eat up to of leaves, spread over four to six feeding periods. Despite their adaptations to a low-energy lifestyle, they have meagre fat reserves.
Their low-energy diet limits their activity and they sleep 20 hours a day. They are predominantly active at night and spend most of their waking hours foraging. They typically eat and sleep in the same tree, possibly for as long as a day. On warm days, a koala may rest with its back against a branch or lie down with its limbs dangling. When it gets hot, the koala rests lower in the canopy and near the trunk, where the surface is cooler than the surrounding air. It curls up when it gets cold and wet. It resorts to a lower, thicker, branch during high winds. While it spends most of the time in the tree, the animal descends to the ground to move to another tree, with either a walking or leaping gait. The koala usually grooms itself with its hind paws, with their double claws, but it sometimes uses its forepaws or mouth.
Social life
Koalas are asocial and spend just 15 minutes a day on social behaviours. In areas of higher density and fewer trees, home ranges are smaller and more clumped. Koala society appears to consist of "residents" and "transients": the former are mostly adult females and the latter are males. Resident males appear to be territorial and dominant. The territories of dominant males are found near breeding females, while younger males must wait until they reach full size to challenge for breeding rights. Adult males occasionally venture outside their home ranges; when they do, dominant ones retain their status. As a male climbs a new tree, he rubs his chest against it and sometimes dribbles urine. This scent-marking behaviour probably serves as communication, and individuals are known to sniff the bottom of a newly found tree. Chest gland secretions are complex chemical mixtures—about 40 compounds were identified in one analysis—that vary in composition and concentration across season and age. Adult males communicate with loud bellows—"a long series of deep, snoring inhalations and belching exhalations". Because of their low frequency, these bellows can travel far through the forest. Koalas may bellow at any time, particularly during the breeding season, when it serves to attract females and possibly intimidate other males. They also bellow to advertise their presence when they change trees. These sounds signal and exaggerate the male's body size; females pay more attention to bellows by larger males. Female koalas bellow, though more softly, in addition to making snarls, wails, and screams. These calls are produced when in distress and when making defensive threats. Younger animals squeak and older ones squawk when distraught. When another individual climbs over it, a koala makes a low closed-mouth grunt. Koalas also communicate with facial expressions. When snarling, wailing, or squawking, the animal curls the upper lip and points its ears forward. Screaming koalas pull their lips and ears back. Females form an oval shape with their lips when annoyed. Agonistic behaviour typically consists of quarrels between individuals who are trying to pass each other on a tree. This occasionally involves biting. Strangers may wrestle, chase, and bite. In extreme situations, a larger male may try to displace a smaller rival from a tree, chasing, cornering, and biting it. Once the individual is driven away, the victor bellows and marks the tree. Pregnant and lactating females are particularly aggressive and attack individuals who come too close. In general, however, koalas tend to avoid fighting due to energy costs.Reproduction and development
 Koalas are seasonal breeders, and they give birth from October to May. Females in oestrus lean their heads back and shake their bodies. Despite these obvious signals, males try to copulate with any female during this period, mounting them from behind. Because of his much larger size, a male can overpower a female. A female may scream and vigorously fight off her suitors but will accede to one that is dominant or familiar. The commotion can attract other males to the scene, obliging the incumbent to delay mating and fight off the intruders. A female may learn who is more dominant during these fights. Older males typically accumulate scratches, scars, and cuts on the exposed parts of their noses and their eyelids.
Koalas are induced ovulators. The gestation period lasts 33–35 days, and a female gives birth to one joey or occasionally, twins. The young are born tiny and barely formed, weighing no more than . However, their lips, forelimbs, and shoulders are relatively advanced, and they can breathe, defecate, and urinate. The joey crawls into its mother's pouch to continue its development. Female koalas do not clean their pouches, while an unusual trait among marsupials.
The joey latches on to one of the female's two teats and suckles it. The female lactates for as long as a year to make up for her low energy production. Unlike in other marsupials, koala milk becomes less fatty as the joey grows. After seven weeks, the joey has a proportionally large head, clear edges around its face, more colouration, and a visible pouch (if female) or scrotum (male). At 13 weeks, the joey weighs around , and its head doubles in size. The eyes begin to open and hair begins to appear. At 26 weeks, the fully furred animal resembles an adult and can look outside the pouch.
Koalas are seasonal breeders, and they give birth from October to May. Females in oestrus lean their heads back and shake their bodies. Despite these obvious signals, males try to copulate with any female during this period, mounting them from behind. Because of his much larger size, a male can overpower a female. A female may scream and vigorously fight off her suitors but will accede to one that is dominant or familiar. The commotion can attract other males to the scene, obliging the incumbent to delay mating and fight off the intruders. A female may learn who is more dominant during these fights. Older males typically accumulate scratches, scars, and cuts on the exposed parts of their noses and their eyelids.
Koalas are induced ovulators. The gestation period lasts 33–35 days, and a female gives birth to one joey or occasionally, twins. The young are born tiny and barely formed, weighing no more than . However, their lips, forelimbs, and shoulders are relatively advanced, and they can breathe, defecate, and urinate. The joey crawls into its mother's pouch to continue its development. Female koalas do not clean their pouches, while an unusual trait among marsupials.
The joey latches on to one of the female's two teats and suckles it. The female lactates for as long as a year to make up for her low energy production. Unlike in other marsupials, koala milk becomes less fatty as the joey grows. After seven weeks, the joey has a proportionally large head, clear edges around its face, more colouration, and a visible pouch (if female) or scrotum (male). At 13 weeks, the joey weighs around , and its head doubles in size. The eyes begin to open and hair begins to appear. At 26 weeks, the fully furred animal resembles an adult and can look outside the pouch.
 At six or seven months, the joey weighs and fully emerges from the pouch for the first time. It explores its new surroundings cautiously, clutching its mother for support. Around this time, the mother prepares it for a eucalyptus diet by producing a faecal pap that the joey eats from her cloaca. This pap comes from the cecum, is more liquid than regular faeces, and is filled with bacteria. A nine month old joey has its adult coat colour and weighs . Having permanently left the pouch, it rides on its mother's back for transportation, learning to climb by grasping branches. Gradually, it becomes more independent. The mother becomes pregnant again after a year after the offspring reaches around . She permanently severs her bond with her previous offspring and no longer allows it to suckle, but it remains nearby until it is one-and-a-half to two years old.
Females become sexually mature at about three years of age; in comparison, males reach sexual maturity at about age four although they can experience spermatogenesis as early as two years. Males do not start marking their scent until they reach sexual maturity though their chest glands become functional much earlier. Koalas can breed every year if environmental conditions are good, though the long dependence of the young usually leads to year-long gaps in births.
At six or seven months, the joey weighs and fully emerges from the pouch for the first time. It explores its new surroundings cautiously, clutching its mother for support. Around this time, the mother prepares it for a eucalyptus diet by producing a faecal pap that the joey eats from her cloaca. This pap comes from the cecum, is more liquid than regular faeces, and is filled with bacteria. A nine month old joey has its adult coat colour and weighs . Having permanently left the pouch, it rides on its mother's back for transportation, learning to climb by grasping branches. Gradually, it becomes more independent. The mother becomes pregnant again after a year after the offspring reaches around . She permanently severs her bond with her previous offspring and no longer allows it to suckle, but it remains nearby until it is one-and-a-half to two years old.
Females become sexually mature at about three years of age; in comparison, males reach sexual maturity at about age four although they can experience spermatogenesis as early as two years. Males do not start marking their scent until they reach sexual maturity though their chest glands become functional much earlier. Koalas can breed every year if environmental conditions are good, though the long dependence of the young usually leads to year-long gaps in births.
Health and mortality
Koalas live from 13 to 18 years in the wild although males may die sooner because of their more risky lives. Koalas usually survive falls from trees, yet they can get hurt and even die, particularly inexperienced young and fighting males. Around age six, the koala's chewing teeth begin to wear down and their chewing efficiency decreases. Eventually, the cusps disappear completely and the animal dies of starvation. Koalas have few predators. Dingos and large pythons and somebirds of prey
Birds of prey or predatory birds, also known as (although not the same as) raptors, are hypercarnivorous bird species that actively predation, hunt and feed on other vertebrates (mainly mammals, reptiles and smaller birds). In addition to speed ...
may take them. Koalas are generally not subject to external parasites other than ticks around the coast. The mite '' Sarcoptes scabiei'' gives koalas mange, while the bacterium '' Mycobacterium ulcerans'' skin ulcers, but these are uncommon. Internal parasites are few and have little effect. These include the ''Bertiella obesa'' tapeworm, commonly found in the intestine, and the '' Marsupostrongylus longilarvatus'' and '' Durikainema phascolarcti nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (h ...
s'', which are infrequently found in the lungs. In a three-year study of almost 600 koalas taken to the Australia Zoo Wildlife Hospital in Queensland, 73.8% of the animals were infected with parasitic protozoal genus '' Trypanosoma'', the most frequent of which was '' T. irwini''.
Koalas can be subject to pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s such as '' Chlamydiaceae'' bacteria, which can cause keratoconjunctivitis, urinary tract infection, and reproductive tract infection. Such infections are common on the mainland, but absent in some island populations. , efforts are underway to use vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
to try to stem the koala chlamydia epidemic. The koala retrovirus
Koala retrovirus (KoRV) is a retrovirus that is present in many populations of koalas. It has been implicated as the agent of koala immune deficiency syndrome (KIDS), an HIV/AIDS, AIDS-like immunodeficiency that leaves infected koalas more susce ...
(KoRV) may cause koala immune deficiency syndrome (KIDS) which is similar to AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
in humans. Prevalence of KoRV in koala populations suggests it spread from north to south, for only southern populations have virus-free individuals.
The animals are vulnerable to bushfires due to their slow speed and the flammability of eucalypt trees. The koala instinctively seeks refuge in the higher branches where it is vulnerable to heat and fire. Bushfires divide the animal's habitat, which isolates them, decreases their numbers, and creates genetic bottlenecks. Dehydration and overheating can prove fatal. Consequently, the koala is vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Models of climate change predict warmer and drier climates, suggesting that the koala's range will shrink in the east and south to more mesic habitats.
Relation to humans
History
 The first written reference to the koala was recorded by John Price, servant of John Hunter, the
The first written reference to the koala was recorded by John Price, servant of John Hunter, the Governor of New South Wales
The governor of New South Wales is the representative of the monarch, King Charles III, in the state of New South Wales. In an analogous way to the governor-general of Australia, Governor-General of Australia at the national level, the governor ...
. Price encountered the "cullawine" on 26 January 1798, during an expedition to the Blue Mountains, but his remarks would first be published in '' Historical Records of Australia'', nearly a century later. In 1802, French-born explorer Francis Louis Barrallier encountered the animal when his two Aboriginal guides, returning from a hunt, brought back two koala feet they were intending to eat. Barrallier preserved the appendages and sent them and his notes to Hunter's successor, Philip Gidley King
Captain Philip Gidley King (23 April 1758 – 3 September 1808) was a Royal Navy officer and colonial administrator who served as the governor of New South Wales from 1800 to 1806. When the First Fleet arrived in January 1788, King was detai ...
, who forwarded them to Joseph Banks
Sir Joseph Banks, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1820) was an English Natural history, naturalist, botanist, and patron of the natural sciences.
Banks made his name on the European and American voyages of scientific exploration, 1766 natural-history ...
. Similar to Price, Barrallier's notes were not published until 1897. Reports of the "Koolah" appeared in the Sydney Gazette in late 1803, and helped provide the impetus for King to send artist John Lewin to create watercolours of the animal. Lewin painted three pictures, one of which was printed
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and Printmaking, images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabon ...
in Georges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, baron Cuvier (23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier (; ), was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuv ...
's ''Le Règne Animal
''Le Règne Animal'' () is the most famous work of the French naturalist Georges Cuvier. It sets out to describe the natural structure of the whole of the animal, animal kingdom based on comparative anatomy, and its natural history. Cuvier divid ...
(The Animal Kingdom)'' (1827).
Botanist Robert Brown Robert Brown may refer to: Robert Brown (born 1965), British Director, Animator and author
Entertainers and artists
* Washboard Sam or Robert Brown (1910–1966), American musician and singer
* Robert W. Brown (1917–2009), American printmaker ...
was the first to write a formal scientific description in 1803, based on a female specimen captured near what is now Mount Kembla in the Illawarra region of New South Wales. Austrian botanical illustrator Ferdinand Bauer drew the animal's skull, throat, feet, and paws. Brown's work remained unpublished and largely unnoticed, however; his field books and notes remained in his possession until his death, when they were bequeathed to the British Museum in London. They were not identified until 1994, while Bauer's koala watercolours were not published until 1989. William Paterson, who had befriended Brown and Bauer during their stay in New South Wales, wrote an eyewitness report of his encounters with the animals and this would be the basis for British surgeon Everard Home's anatomical writings on them. Home, who in 1808 published his report, coined the scientific name ''Didelphis coola''.
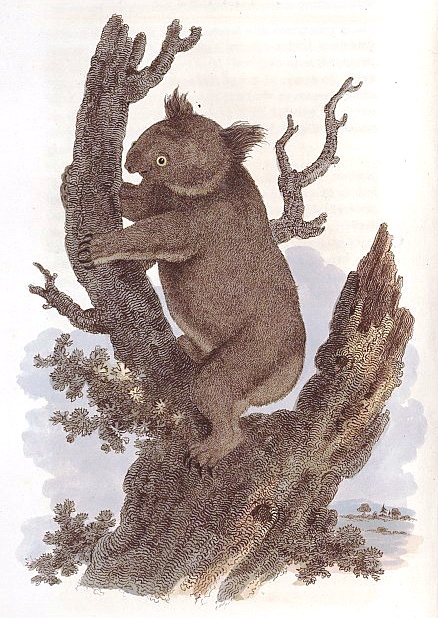
George Perry officially published the first image of the koala in his 1810 natural history work ''Arcana''. Perry called it the "New Holland Sloth", and his dislike for the koala, evident in his description of the animal, was reflected in the contemporary British attitudes towards Australian animals as strange and primitive:
... the eye is placed like that of the Sloth, very close to the mouth and nose, which gives it a clumsy awkward appearance, and void of elegance in the combination ... they have little either in their character or appearance to interest the Naturalist or Philosopher. As Nature however provides nothing in vain, we may suppose that even these torpid, senseless creatures are wisely intended to fill up one of the great links of the chain of animated nature ...
 Naturalist and popular artist
Naturalist and popular artist John Gould
John Gould (; 14 September 1804 – 3 February 1881) was an English ornithologist who published monographs on birds, illustrated by plates produced by his wife, Elizabeth Gould (illustrator), Elizabeth Gould, and several other artists, includ ...
illustrated and described the koala in his three-volume work '' The Mammals of Australia'' (1845–1863) and introduced the species, as well as other members of Australia's little-known faunal community, to the public. Comparative anatomist Richard Owen
Sir Richard Owen (20 July 1804 – 18 December 1892) was an English biologist, comparative anatomy, comparative anatomist and paleontology, palaeontologist. Owen is generally considered to have been an outstanding naturalist with a remarkabl ...
, in a series of publications on the physiology and anatomy of Australian mammals, presented a paper on the anatomy of the koala to the Zoological Society of London. In this widely cited publication, he provided an early description of its internal anatomy, and noted its general structural similarity to the wombat. English naturalist George Robert Waterhouse
George Robert Waterhouse (6 March 1810 – 21 January 1888) was an English natural history, naturalist. He was a keeper at the department of geology and later curator of the Zoological Society of London's museum.
Early life
George was born ...
, curator of the Zoological Society of London, was the first to correctly classify the koala as a marsupial in the 1840s, and compared it to fossil species '' Diprotodon'' and '' Nototherium'', which had been discovered just recently. Similarly, Gerard Krefft, curator of the Australian Museum
The Australian Museum, originally known as the Colonial Museum or Sydney Museum. is a heritage-listed museum at 1 William Street, Sydney, William Street, Sydney central business district, Sydney CBD, New South Wales. It is the oldest natural ...
in Sydney, noted evolutionary mechanisms at work when comparing the koala to fossil marsupials in his 1871 ''The Mammals of Australia''.
Britain received its first living koala in 1881, which was obtained by the Zoological Society of London. As related by prosecutor to the society, William Alexander Forbes, the animal suffered an accidental demise when the heavy lid of a washstand fell on it and it was unable to free itself. Forbes dissected the specimen and wrote about the female reproductive system, the brain, and the liver—parts not previously described by Owen, who had access only to preserved specimens. Scottish embryologist William Caldwell—well known in scientific circles for determining the reproductive mechanism of the platypus—described the uterine development of the koala in 1884, and used this new information to convincingly map out the evolutionary timeline of the koala and the monotremes.
Cultural significance
The koala is known worldwide and is a major draw for Australian zoos and wildlife parks. It has been featured in popular culture and as soft toys. It benefited the Australian tourism industry by over $1'' ''billion in 1998, and subsequently grown. Its international popularly rose after World War II, when tourism increased and the animals were exported to zoos overseas. In 1997, about 75% of European and Japanese tourists placed the koala at the top of their list of animals to see. According to biologist Stephen Jackson: "If you were to take a straw poll of the animal most closely associated with Australia, it's a fair bet that the koala would come out marginally in front of the kangaroo". Factors that contribute to the koala's enduring popularity include its teddy bear-like appearance with childlike body proportions. The koala features in theDreamtime
The Dreaming, also referred to as Dreamtime, is a term devised by early anthropologists to refer to a religio-cultural worldview attributed to Australian Aboriginal religion and mythology, Australian Aboriginal mythology. It was originally u ...
stories and mythology
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
of Indigenous Australians. The Tharawal people believed that the animal helped them get to Australia by rowing the boat. Another myth tells of a tribe that killed a koala and used its long intestines to create a bridge for people from other parts of the world. How the koala lost its tail is the subject of many tales. In one, a kangaroo cuts it off to punish the koala for uncouth behaviour. Tribes in Queensland and Victoria regarded the koala as a wise animal that gave valuable guidance. Bidjara-speaking people credited the koala for making trees grow in their arid lands. The animal is depicted in rock carvings, though less so than some other species.
Early European settlers in Australia considered the koala to be a creeping sloth
Sloths are a Neotropical realm, Neotropical group of xenarthran mammals constituting the suborder Folivora, including the extant Arboreal locomotion, arboreal tree sloths and extinct terrestrial ground sloths. Noted for their slowness of move ...
-like animal with a "fierce and menacing look". At the turn of the 20th century, the koala's reputation took a positive turn. It appears in Ethel Pedley's 1899 book '' Dot and the Kangaroo'', as the "funny native bear". Artist Norman Lindsay
Norman Alfred William Lindsay (22 February 1879 – 21 November 1969) was an Australian artist, etcher, sculptor, writer, art critic, novelist, cartoonist and amateur boxing, boxer. One of the most prolific and popular Australian artists of hi ...
depicted a more anthropomorphic koala in '' The Bulletin'' cartoons, starting in 1904. This character also appeared as Bunyip Bluegum in Lindsay's 1918 book ''The Magic Pudding
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The ...
''. The most well known fictional koala is Blinky Bill. Created by Dorothy Wall in 1933, the character appeared in books, films, TV series, merchandise, and a 1986 environmental song by John Williamson. The koala first appeared on an Australian stamp in 1930.
 The song "Ode to a Koala Bear" appears on the B-side of the 1983
The song "Ode to a Koala Bear" appears on the B-side of the 1983 Paul McCartney
Sir James Paul McCartney (born 18 June 1942) is an English singer, songwriter and musician who gained global fame with the Beatles, for whom he played bass guitar and the piano, and shared primary songwriting and lead vocal duties with John ...
/Michael Jackson
Michael Joseph Jackson (August 29, 1958 – June 25, 2009) was an American singer, songwriter, dancer, and philanthropist. Dubbed the "King of Pop", he is regarded as Cultural impact of Michael Jackson, one of the most culturally significan ...
duet single " Say Say Say". A koala is the main character in animated cartoons in the early 1980s: Hanna-Barbera
Hanna-Barbera Cartoons, Inc. ( ; formerly known as H-B Enterprises, Hanna-Barbera Productions, Inc. and H-B Production Co.), simply and commonly known as Hanna-Barbera, was an American animation studio and production company, which was acti ...
's '' The Kwicky Koala Show'' and Nippon Animation's '' Noozles''. Food products shaped like the koala include the Caramello Koala chocolate bar and the bite-sized cookie snack Koala's March. Dadswells Bridge in Victoria features a tourist complex shaped like a giant koala and the Queensland Reds rugby team has a koala as its icon.
Koala diplomacy
Political leaders and members of royal families had their pictures taken with koalas, includingQueen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 19268 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until Death and state funeral of Elizabeth II, her death in 2022. ...
, Prince Harry, Crown Prince Naruhito, Crown Princess Masako, Pope John Paul II
Pope John Paul II (born Karol Józef Wojtyła; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 16 October 1978 until Death and funeral of Pope John Paul II, his death in 2005.
In his you ...
, US President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
, Soviet premier Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet and Russian politician who served as the last leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
and South African President Nelson Mandela
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela ( , ; born Rolihlahla Mandela; 18 July 1918 – 5 December 2013) was a South African Internal resistance to apartheid, anti-apartheid activist and politician who served as the first president of South Africa f ...
At the 2014 G20 Brisbane summit, hosted by Prime Minister Tony Abbott
Anthony John Abbott (; born 4 November 1957) is an Australian former politician who served as the 28th prime minister of Australia from 2013 to 2015. He held office as the leader of the Liberal Party of Australia and was the member of parli ...
, many world leaders, including Russian President Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has served as President of Russia since 2012, having previously served from 2000 to 2008. Putin also served as Prime Minister of Ru ...
and US President Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. O ...
, were photographed holding koalas. The event gave rise to the term "koala diplomacy", which became the Oxford Word of the Month for December 2016. The term also includes the loan of koalas by the Australian government to overseas zoos in countries such as Singapore and Japan, as a form of "soft power diplomacy", like the " panda diplomacy" practised by China.
Conservation
 The koala was originally classified as
The koala was originally classified as Least Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been evaluated and categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as not being a focus of wildlife conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wil ...
on the Red List, and reassessed as Vulnerable in 2014. In the Australian Capital Territory, New South Wales and Queensland, the species was listed under the EPBC Act in February 2022 as endangered by extinction. The described population was determined in 2012 to be "a species for the purposes of the EPBC Act 1999" in Federal legislation.
Australian policymakers declined a 2009 proposal to include the koala in the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999. A 2017 WWF report found a 53% decline per generation in Queensland, and a 26% decline in New South Wales. The koala population in South Australia and Victoria appear to be abundant; however, the Australian Koala Foundation (AKF) argued that the exclusion of Victorian populations from protective measures was based on a misconception that the total population was 200,000, whereas they believed in 2012 that it was probably less than 100,000. AKF estimated in 2022 that there could be 43,000–100,000. This compares with 8 to 10'' ''million at the start of the 20th century. The Australian Government's Threatened Species Scientific Committee estimated that the 2021 koala population was 92,000, down from 185,000 two decades prior.
The koala was heavily hunted by European settlers in the early 20th century, largely for its fur. Australia exported as many as two million pelts by 1924. Koala furs were used to make rugs, coat linings, muffs, and on women's garment trimmings. The first successful efforts at conserving the species were initiated by the establishment of Brisbane's Lone Pine Koala Sanctuary and Sydney's Koala Park Sanctuary in the 1920s and 1930s. Its owner Noel Burnet created the first successful breeding program.
One of the biggest anthropogenic
Anthropogenic ("human" + "generating") is an adjective that may refer to:
* Anthropogeny, the study of the origins of humanity
Anthropogenic may also refer to things that have been generated by humans, as follows:
* Human impact on the enviro ...
threats to the koala is habitat destruction and fragmentation. Near the coast, the main cause of this is urbanisation, while in rural areas, habitat is cleared for agriculture. Its favoured trees are harvested for wood products. In 2000, Australia had the fifth highest rate of land clearance globally, stripping of native plants. The koalas' distribution has shrunk by more than 50% since European arrival, largely due to habitat fragmentation in Queensland. Nevertheless, koalas live in many protected areas.
While urbanisation can pose a threat to koala populations, the animals can survive in urban areas given enough trees. Urban populations have distinct vulnerabilities: collisions with vehicles and attacks by domestic dogs. Cars and dogs kill about 4,000 animals every year. To reduce road deaths, government agencies have been exploring various wildlife crossing options, such as the use of fencing to channel animals toward an underpass, in some cases adding a walkway to an existing culvert. Injured koalas are often taken to wildlife hospitals and rehabilitation centres. In a 30-year retrospective study performed at a New South Wales koala rehabilitation centre, trauma was found to be the most frequent cause of admission, followed by symptoms of ''Chlamydia'' infection.
See also
* Drop bear – A predatory and dangerous version of the koala in popular folklore * Fauna of Australia *List of monotremes and marsupials of Australia
Mammals are divided into two subclasses based on reproductive techniques: egg laying mammals (the monotremes), and live birth mammals. The second subclass is divided into two infraclasses: pouched mammals (the marsupials) and placental mammals.
...
* Sam (koala), a female koala known for being rescued during the Black Saturday bushfires in 2009
References
External links
* Archive �images and movies of the koala ''Phascolarctos cinereus''
Animal Diversity Web – ''Phascolarctos cinereus''
*iNaturalist crowdsource
koala sighting photos
(mapped, graphed)
Koala Science Community
"Koala Crunch Time"
– an ABC documentary (2012)
Cracking the Koala Code
– a PBS Nature documentary (2012)
The Aussie Koala Ark Conservation Project
{{Taxonbar, from=Q36101 Articles containing video clips Clawed herbivores Extant Middle Pleistocene first appearances Herbivorous mammals Mammals described in 1817 Mammals of New South Wales Mammals of Queensland Mammals of South Australia Mammals of Victoria (state) Marsupials of Australia Vombatiforms Symbols of Queensland Taxa named by Georg August Goldfuss