Kintyre Way Walk on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kintyre (, ) is a
 Kintyre, like Knapdale, contains several
Kintyre, like Knapdale, contains several
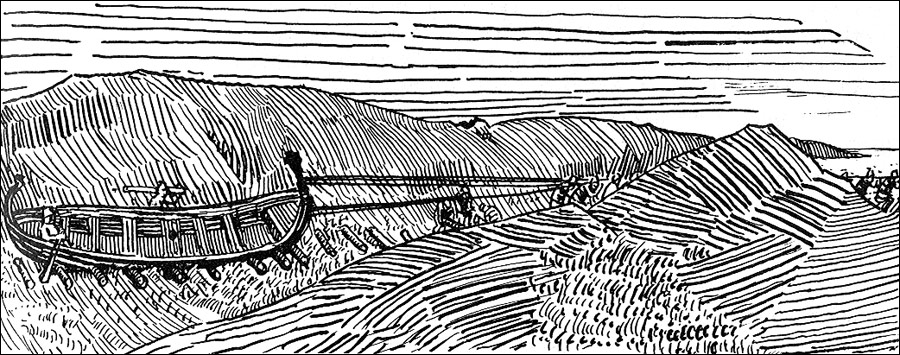 In 1093, Magnus, the Norwegian king, launched a military campaign to assert his authority over the isles. Malcolm, the king of Scotland, responded with a written agreement, accepting that Magnus' had sovereign authority of over all the western lands that Magnus could encircle by boat. The unspecific wording led Magnus to have his boat dragged across the narrow
In 1093, Magnus, the Norwegian king, launched a military campaign to assert his authority over the isles. Malcolm, the king of Scotland, responded with a written agreement, accepting that Magnus' had sovereign authority of over all the western lands that Magnus could encircle by boat. The unspecific wording led Magnus to have his boat dragged across the narrow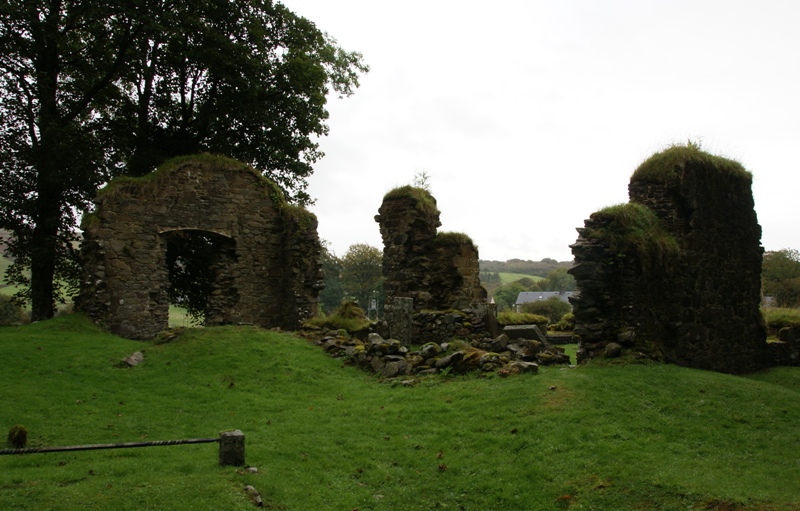  In the mid 12th century,
In the mid 12th century,
 At an uncertain date before 1481, the sheriffdom of Kintyre became '' Tarbertshire'', based at
At an uncertain date before 1481, the sheriffdom of Kintyre became '' Tarbertshire'', based at
Traveline Scotland
West Coast Motors
on behalf of
West Coast Motors
alone.
Kintyre Express
**
VisitKintyre.info - Web Site including webcam, accommodation, news, photo galleries etc
EasyWays - walking holiday and guided walk round Kintyre
Explore Kintyre & Gigha
- official Marketing Organisation for Kintyre & Gigha {{Authority control Peninsulas of Scotland Landforms of Argyll and Bute Firth of Clyde Ramsar sites in Scotland
peninsula
A peninsula is a landform that extends from a mainland and is only connected to land on one side. Peninsulas exist on each continent. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula.
Etymology
The word ''peninsula'' derives , . T ...
in western Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute
Argyll and Bute (; , ) is one of 32 unitary authority, unitary council areas of Scotland, council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area. The current lord-lieutenant for Argyll and Bute is Jane Margaret MacLeod ...
. The peninsula stretches about , from the Mull of Kintyre
The Mull of Kintyre is the southwesternmost tip of the Kintyre Peninsula (formerly ''Cantyre'') in southwest Scotland. From here, the Antrim coast of Northern Ireland is visible on a calm and clear day, and a historic lighthouse, the second ...
in the south to East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and West Loch Tarbert
West Loch Tarbert () is a sea loch that separates the northern and southern parts of Harris in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. A small isthmus joins these two areas, on which is to be found the village of Tarbert. The loch contains the islands ...
in the north. The region immediately north of Kintyre is known as Knapdale
Knapdale (, ) forms a rural district of Argyll and Bute in the Scottish Highlands, adjoining Kintyre to the south, and divided from the rest of Argyll to the north by the Crinan Canal. It includes two parishes, North Knapdale and South Knapdale. ...
.
Kintyre is long and narrow, at no point more than from west coast to east coast, and is less than wide where it connects to Knapdale at the north. Kintyre is the lower Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde, is the estuary of the River Clyde, on the west coast of Scotland. The Firth has some of the deepest coastal waters of the British Isles. The Firth is sheltered from the Atlantic Ocean by the Kintyre, Kintyre Peninsula. The ...
western coast and protects the Firth from the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
. The southerly tip of Kintyre is on the North Channel that separates southwestern Scotland from Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
. The east side of the Kintyre Peninsula is bounded by Kilbrannan Sound
Kilbrannan Sound (Scottish Gaelic: ''An Caolas Branndanach'') is a marine water body in the west of Scotland. It separates the Kintyre Peninsula from the island of Arran. Kilbrannan Sound is the western arm of the lower Firth of Clyde.
S ...
, with a number of coastal peaks such as Torr Mor
Torr Mor is a hill peak landform on the coastal east side of the Kintyre Peninsula in Scotland. The peak offers views over the Kilbrannan Sound.
The Forestry Commission maintain a footpath over the hill.
See also
* Kildonald Bay
Kildonald Bay i ...
. The central spine of the peninsula is mostly hilly moorland, the highest point being Beinn an Tuirc at . The coastal areas and hinterland, however, are rich and fertile. Kintyre has long been a prized area for settler
A settler or a colonist is a person who establishes or joins a permanent presence that is separate to existing communities. The entity that a settler establishes is a Human settlement, settlement. A settler is called a pioneer if they are among ...
s, including the early Scots who migrated from Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
to western Scotland and the Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9â ...
or Norsemen
The Norsemen (or Northmen) were a cultural group in the Early Middle Ages, originating among speakers of Old Norse in Scandinavia. During the late eighth century, Scandinavians embarked on a Viking expansion, large-scale expansion in all direc ...
who conquered and settled the area just before the start of the second millennium.
The principal town of the area is Campbeltown
Campbeltown (; or ) is a town and former royal burgh in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies by Campbeltown Loch on the Kintyre Peninsula. Campbeltown became an important centre for Scotch whisky, and a busy fishing port.
The 2018 populatio ...
(about by road from the Mull), which has been a royal burgh since the mid-18th century. The area's economy has long relied on fishing and farming, although Campbeltown has a reputation as a producer of some of the world's finest single malt whisky
Whisky or whiskey is a type of liquor made from Fermentation in food processing, fermented grain mashing, mash. Various grains (which may be Malting, malted) are used for different varieties, including barley, Maize, corn, rye, and wheat. Whisky ...
. Campbeltown single malts
Campbeltown single malts are single malt Scotch whiskies distilled in the burgh of Campbeltown, on the Kintyre peninsula in Scotland. Once a major producer of whisky with as many as 30 distilleries, and claiming the title "whisky capital of th ...
include Springbank.
Kintyre Pursuivant
Kintyre Pursuivant of Arms was a Scottish pursuivant of arms of the Court of the Lord Lyon.
The Kintyre Pursuivant was formerly a private officer of arms in the service of the Lord of the Isles, but along with Dingwall Pursuivant, Ross Heral ...
, one of the officers of arms
An officer of arms is a person appointed by a sovereign or state with authority to perform one or more of the following functions:
* to control and initiate armorial matters;
* to arrange and participate in ceremonies of state;
* to conserve a ...
at the Court of the Lord Lyon
The Court of the Lord Lyon, or Lyon Court, is a standing court of law, based in New Register House in Edinburgh, which regulates heraldry in Scotland. The Lyon Court maintains the register of grants of arms, known as the Public Register of All ...
, is named after this peninsula.
History
Beginnings
 Kintyre, like Knapdale, contains several
Kintyre, like Knapdale, contains several Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
sites; at Ballochroy
Ballochroy is a megalithic site in Kintyre on the Argyll peninsula in Scotland. It consists of three vertical stones, side by side, aligned with various land features away.
Alexander Thom, known for his work on Stonehenge, maintained that th ...
is a trio of megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging geographically f ...
s aligned with land features on the island of Jura, while a number of burial cairns still stand at Blasthill (near Southend, Argyll
Southend (, ) is the main settlement at the southern end of the Kintyre peninsula in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies south of Campbeltown, the main town in the area. The civil parish of Southend comprises the village and the surrounding la ...
). Remains from the Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
are no less present, with the imposing Dun Skeig, a Celtic hillfort, located at the northern edge of Kintyre. The history of the presumed Pictish
Pictish is an extinct Brittonic Celtic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from late antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geog ...
inhabitants of Kintyre is not recorded, but a 2nd-century BC stone fort survives at Kildonan (near Saddell), and it is not implausible that they continued to use Dun Skeig.
The tip of Kintyre is just from Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
, and there has long been interaction across the straits of Moyle
The North Channel (known in Irish and Scottish Gaelic as , in Scots as the ) is the strait between north-eastern Northern Ireland and south-western Scotland. The Firth of Clyde merges with the channel, between the southern tip of the Kintyr ...
, as evidenced by Neolithic finds in Kintyre, such as flint tools characteristic of Antrim. In the early first millennium, an Irish invasion led to Gaelic
Gaelic (pronounced for Irish Gaelic and for Scots Gaelic) is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". It may refer to:
Languages
* Gaelic languages or Goidelic languages, a linguistic group that is one of the two branches of the Insul ...
colonisation of an area centred on the Kintyre peninsula, establishing the Gaelic kingdom of Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaels, Gaelic Monarchy, kingdom that encompassed the Inner Hebrides, western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North ...
. The latter was divided into a handful of regions, controlled by particular kin groups, of which the most powerful, the Cenél nGabráin
The Cenél nGabráin was a kin group, presumed to descend from Gabrán mac Domangairt, which dominated the kingship of Dál Riata until the late 7th century and continued to provide kings thereafter. Kings of kingdom of Alba, Alba and of Scotland ...
, ruled over Kintyre, along with Knapdale
Knapdale (, ) forms a rural district of Argyll and Bute in the Scottish Highlands, adjoining Kintyre to the south, and divided from the rest of Argyll to the north by the Crinan Canal. It includes two parishes, North Knapdale and South Knapdale. ...
, the region between Loch Awe
Loch Awe (Scottish Gaelic: ''Loch Obha''; also sometimes anglicised as Lochawe, Lochaw, or Lochow) is a large body of freshwater in Argyll and Bute, Scottish Highlands. It has also given its name to a village on its banks, variously known as Lo ...
and Loch Fyne
Loch Fyne (, ; meaning "Loch of the Vine/Wine"), is a sea loch off the Firth of Clyde and forms part of the coast of the Cowal, Cowal Peninsula. Located on the west coast of Argyll and Bute, west of Scotland. It extends inland from the Sound o ...
(Craignish
Craignish (Scottish Gaelic, ''Creiginis'') is a peninsula in Argyll and Bute, on the west coast of Scotland. It lies around south of Oban, and north-west of Lochgilphead. The peninsula is around long, and is aligned along a north-east to ...
, Ardscotnish
Ardscotnish, also known as Ardskeodnish, is a former location, in Argyll and Bute, Scotland approximating to the present parish of Kilmartin
Kilmartin (, meaning "church of MĂ rtainn") is a small village in Argyll and Bute, western Scotland ...
, Glassary, and Glenary), Arran, and Moyle (in Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
).
The kingdom thrived for a few centuries, and formed a springboard for Christianisation of the mainland. Sanda, an island adjacent the south coast of Kintyre, is strongly associated with Ninian
Ninian is a Christian saint, first mentioned in the 8th century as being an early missionary among the Pictish peoples of what is now Scotland. For this reason, he is known as the Apostle to the Southern Picts, and there are numerous dedicatio ...
, the first known missionary to the Picts, and contains an early 5th century chapel said to have been built by him. In 563, Columba
Columba () or Colmcille (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is today Scotland at the start of the Hiberno-Scottish mission. He founded the important abbey ...
arrived in Kintyre, to pay his respects to the kings of Dal Riata, before continuing to Iona
Iona (; , sometimes simply ''ĂŚ'') is an island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though there are other buildings on the island. Iona Abbey was a centre of Gaeli ...
, where he established a base for missionary activity throughout the Pictish regions beyond.
Norwegian dominion
Dál Riata was ultimately destroyed when Norse Vikings invaded, and established their own domain, spreading more extensively over the islands north and west of the mainland. Following the unification ofNorway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
, they had become the Norwegian Kingdom of the Isles
The Kingdom of the Isles, also known as Sodor, was a Norse–Gaelic kingdom comprising the Isle of Man, the Hebrides and the islands of the Clyde from the 9th to the 13th centuries. The islands were known in Old Norse as the , or "Southern I ...
, locally controlled by Godred Crovan
Godred Crovan (died 1095), known in Gaelic as Gofraid Crobán, Gofraid Meránach, and Gofraid Méránach, was a Norse-Gaelic ruler of the kingdoms of Kingdom of Dublin, Dublin and the Kingdom of the Isles, Isles. Although his precise parentage h ...
, and known by Norway as ''SuĂ°reyjar'' (Old Norse, traditionally anglicised as ''Sodor''), meaning ''southern isles''. The former territory of Dal Riata acquired the geographic description ''Argyle'' (now ''Argyll''): the ''Gaelic coast''.
 In 1093, Magnus, the Norwegian king, launched a military campaign to assert his authority over the isles. Malcolm, the king of Scotland, responded with a written agreement, accepting that Magnus' had sovereign authority of over all the western lands that Magnus could encircle by boat. The unspecific wording led Magnus to have his boat dragged across the narrow
In 1093, Magnus, the Norwegian king, launched a military campaign to assert his authority over the isles. Malcolm, the king of Scotland, responded with a written agreement, accepting that Magnus' had sovereign authority of over all the western lands that Magnus could encircle by boat. The unspecific wording led Magnus to have his boat dragged across the narrow isthmus
An isthmus (; : isthmuses or isthmi) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea count ...
at Tarbert
Tarbert () is a place name in Scotland and Ireland. Places named Tarbert are characterised by a narrow strip of land, or isthmus. This can be where two lochs nearly meet, or a causeway out to an island.
Etymology
All placenames that variously s ...
, while he rode within it, so that he would thereby acquire Kintyre, in addition to the more natural ''islands'' of Arran and Bute.
Supposedly, Magnus's campaign had been part of a conspiracy against Malcolm, by Donalbain, Malcolm's younger brother. When Malcolm was killed in battle a short time later, Donalbain invaded, seized the Scottish kingdom, and displaced Malcolm's sons from the throne; on becoming king, Donalbain confirmed Magnus' gains. Donalbain's apparent keenness to do this, however, weakened his support among the nobility, and Malcolm's son, Duncan
Duncan may refer to:
People
* Duncan (given name), various people
* Duncan (surname), various people
* Clan Duncan
* Justice Duncan (disambiguation)
Places
* Duncan Creek (disambiguation)
* Duncan River (disambiguation)
* Duncan Lake (di ...
, was able to depose him.
A few years later, following a rebellion against Magnus' authority in the Isles, he launched another, fiercer, expedition. In 1098, aware of Magnus' actions, the new Scottish king, Edgar
Edgar is a commonly used masculine English given name, from an Anglo-Saxon name ''Edgar'' (composed of ''wikt:en:ead, ead'' "rich, prosperous" and ''Gar (spear), gar'' "spear").
Like most Anglo-Saxon names, it fell out of use by the Late Midd ...
(another son of Malcolm), quitclaim
Generally, a quitclaim is a formal renunciation of a legal claim against some other person, or of a right to land. A person who quitclaims renounces or relinquishes a claim to some legal right, or transfers a legal interest in land. Originally a c ...
ed to Magnus all sovereign authority over the isles, and the whole of Kintyre and Knapdale.
 In the mid 12th century,
In the mid 12th century, Somerled
Somerled (died 1164), known in Middle Irish as Somairle, Somhairle, and Somhairlidh, and in Old Norse as SumarliĂ°i , was a mid-12th-century Norse-Gaelic lord who, through marital alliance and military conquest, rose in prominence to create the ...
, the husband of Godred Crovan's granddaughter, led a successful revolt against Norway, transforming SuĂ°reyjar (including Kintyre) into an independent kingdom. After his death, nominal Norwegian authority was re-established, but de facto authority was split between Somerled's sons and the Crovan dynasty
The Crovan dynasty, from the late 11th century to the mid 13th century, was the ruling family of an insular kingdom known variously in secondary sources as the Kingdom of Mann, the Kingdom of the Isles, and the Kingdom of Mann and the Isles. The ...
. The exact allocation to Somerled's sons is unclear, but following a family dispute, Donald
Donald is a Scottish masculine given name. It is derived from the Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinter ...
, Somerled's grandson, acquired Kintyre, together with Knapdale, Islay
Islay ( ; , ) is the southernmost island of the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. Known as "The Queen of the Hebrides", it lies in Argyll and Bute just south west of Jura, Scotland, Jura and around north of the Northern Irish coast. The island's cap ...
, and Jura. Donald's father, Reginald, established Saddell Abbey
Saddell Abbey is a ruined Cistercian monastery located in western Scotland. The abbey was established in 1160 by Somerled, Lord of Kintyre, who was killed in 1164. The abbey was completed by his son, Ragnall, a few years later. The original la ...
, in 1207.
In the mid 13th century, increased tension between Norway and Scotland led to a series of Battles, culminating in the Battle of Largs
The Battle of Largs (2 October 1263) was a battle between the kingdoms of Kingdom of Norway (872–1397), Norway and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, on the Firth of Clyde near Largs, Scotland. The conflict formed part of the Scottish–Norwegian ...
, shortly after which the Norwegian king died. In 1266, his more peaceable successor ceded his nominal authority over SuĂ°reyjar to the Scottish king ( Alexander III) by the Treaty of Perth
The Treaty of Perth, signed 2 July 1266, ended military conflict between Magnus the Lawmender of Norway and Alexander III of Scotland over possession of the Hebrides and the Isle of Man.
The Hebrides and the Isle of Man had become Norwegian t ...
, in return for a very large sum of money. Although Alexander III generally acknowledged the semi-independent authority of Somerled's heirs, he did not give them back control of the mainland territory which Scottish forces had taken during the strife, including parts of Kintyre.
Early Scottish rule
In 1293, kingJohn Balliol
John Balliol or John de Balliol ( – late 1314), known derisively as Toom Tabard (meaning 'empty coat'), was King of Scots from 1292 to 1296. Little is known of his early life. After the death of Margaret, Maid of Norway, Scotland entered an ...
established shrieval authority by creating the post of sheriff of Kintyre. Shortly after, Robert de Bruys launched a civil war challenging John for the throne. By this point, Somerled's descendants had formed into three families - the MacRory, the MacDougalls, and the MacDonalds; the MacDougalls took John's side, while the MacDonalds and MacRory backed de Bruys. When de Bruys defeated John, he declared the MacDougall lands forfeit, and gave them to the MacDonalds.
The head of the MacDonald family married the heir of the MacRory family, thereby acquiring the remaining share of Somerled's realm, and transforming it into the Lordship of the Isles
Lord of the Isles or King of the Isles
( or ; ) is a title of nobility in the Baronage of Scotland with historical roots that go back beyond the Kingdom of Scotland. It began with Somerled in the 12th century and thereafter the title was h ...
, which lasted for over a century. After 4 years and 3 children, however, he divorced Amy, and married Margaret, the daughter of Robert II, the Scottish king, who gave him the remaining parts of Kintyre, along with the whole of Knapdale, as a dowry.
In 1462, however, John, the then Lord of the Isles, plotted with the English king to conquer Scotland; civil war in England delayed the discovery of this for a decade. Upon the discovery, in 1475, there was a call for forfeiture, but a year later John calmed the matter, by quitclaiming Ross (Easter, Wester, and Skye), Kintyre, and Knapdale, to Scotland.
The Campbells and later
 At an uncertain date before 1481, the sheriffdom of Kintyre became '' Tarbertshire'', based at
At an uncertain date before 1481, the sheriffdom of Kintyre became '' Tarbertshire'', based at Tarbert
Tarbert () is a place name in Scotland and Ireland. Places named Tarbert are characterised by a narrow strip of land, or isthmus. This can be where two lochs nearly meet, or a causeway out to an island.
Etymology
All placenames that variously s ...
at the northern end of Kintyre; in that year, Tarbertshire was expanded to include Knapdale. However, comital authority remained absent following the quitclaim
Generally, a quitclaim is a formal renunciation of a legal claim against some other person, or of a right to land. A person who quitclaims renounces or relinquishes a claim to some legal right, or transfers a legal interest in land. Originally a c ...
from the Lord of the Isles; following a law and order crisis in the region, king James IV of Scotland
James IV (17 March 1473 – 9 September 1513) was List of Scottish monarchs, King of Scotland from 11 June 1488 until his death at the Battle of Flodden in 1513. He inherited the throne at the age of fifteen on the death of his father, James I ...
appointed Archibald Campbell, the Earl of Argyll as governor of Tarbert Castle
Tarbert Castle is located on the southern shore of East Loch Tarbert, at Tarbert, Argyll, Scotland, at the north end of Kintyre. Tarbert Castle was a strategic royal stronghold during the Middle Ages and one of three castles at Tarbert. The cas ...
, with implied authority over nearby castles such as Skipness.
Following the Scottish Reformation
The Scottish Reformation was the process whereby Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland broke away from the Catholic Church, and established the Protestant Church of Scotland. It forms part of the wider European 16th-century Protestant Reformation.
Fr ...
, the MacDonalds (opponents) and Campbells (supporters) came into more direct dispute. In 1607, after a series of hostile actions by the MacDonalds, King James VI
James may refer to:
People
* James (given name)
* James (surname)
* James (musician), aka Faruq Mahfuz Anam James, (born 1964), Bollywood musician
* James, brother of Jesus
* King James (disambiguation), various kings named James
* Prince Ja ...
ordered their lands in Kintyre to be transferred to Archibald Campbell, heir of the earlier Archibald. Under pressure from the Campbells, the sheriff court
A sheriff court () is the principal local civil and criminal court in Scotland, with exclusive jurisdiction over all civil cases with a monetary value up to , and with the jurisdiction to hear any criminal case except treason, murder, and ra ...
moved to Inveraray
Inveraray ( or ; meaning "mouth of the Aray") is a town in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. Located on the western shore of Loch Fyne, near its head, Inveraray is a former royal burgh and known affectionately as "The Capital of Argyll." It is the ...
at the extreme northeast of Tarbertshire, near the heart of Campbell power; somewhat inevitably, in 1633 shrieval authority was annexed by the sheriff of Argyll
The Sheriff of Argyll was historically a royal officer charged with enforcing the king's rights in Argyll; in Scotland, the concept of ''sheriff'' gradually evolved into a judicial position.
Originally, the region of Argyll was served by the sher ...
.
Archibald's son, a dedicated supporter of the religious reformers, developed a plan to establish a large settlement, around the village of Kinlochkilkerran, at the south of Kintyre, composed of loyal Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
s from Lowland Scotland
The Lowlands ( or , ; , ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland.
The region is characterised by its relatively flat or gently rolling terrain as opposed to the mountainous landscapes of the Scottish Highlands. This area includes ci ...
, in order to outnumber and undermine the local Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
population, and reduce resistance to the state's religious reforms. Under his son, Archibald, this became Campbeltown
Campbeltown (; or ) is a town and former royal burgh in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies by Campbeltown Loch on the Kintyre Peninsula. Campbeltown became an important centre for Scotch whisky, and a busy fishing port.
The 2018 populatio ...
. Their actions also had the effect of diluting Gaelic culture, gradually replacing it with a Lowlands one.
Comital powers were abolished by the Heritable Jurisdictions Act, leaving only the shrieval unit. In 1899, counties were formally created, on shrieval boundaries, by a Scottish Local Government Act; Kintyre became part of the County of Argyll
Argyll (; archaically Argyle; , ), sometimes called Argyllshire, is a historic county and registration county of western Scotland. The county ceased to be used for local government purposes in 1975 and most of the area now forms part of ...
. Following late 20th century reforms, it is now within the wider region of Argyll and Bute
Argyll and Bute (; , ) is one of 32 unitary authority, unitary council areas of Scotland, council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area. The current lord-lieutenant for Argyll and Bute is Jane Margaret MacLeod ...
.
Towns and villages in Kintyre
Transport
Information on all forms of public transport is available froTraveline Scotland
Bus and coach services
*Long-distance coach services to and fromGlasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
are operated bWest Coast Motors
on behalf of
Scottish Citylink
Scottish Citylink is a long-distance express coach operator in Scotland and Ireland (where it operates as Irish Citylink) and formerly England (where it operated as Stansted Citylink). The company was formed as a subsidiary of Scottish Transp ...
*Bus services throughout the Kintyre peninsula are operated bWest Coast Motors
alone.
Flights
*Available between Glasgow International Airport andCampbeltown Airport
Campbeltown Airport () is located at Machrihanish, west of Campbeltown, near the tip of the Kintyre peninsula in Argyll and Bute on the west coast of Scotland.
The airport was formerly known as RAF Machrihanish (after the village of Machrih ...
Ferry services
*Operated byCaledonian MacBrayne
Caledonian MacBrayne (), in short form CalMac, is the trade name of CalMac Ferries Ltd, the major operator of passenger and vehicle ferries to the west coast of Scotland, serving ports on the mainland and 22 of the major islands. It is a subsid ...
on the following routes:
**Claonaig
Claonaig (, ) is a hamlet on the east coast of the Kintyre peninsula in western Scotland, linked to Lochranza on the Isle of Arran by the CalMac ferry in the summer months.
Claonaig is a hamlet south of Skipness, and is the location of the ...
- Lochranza
Lochranza () is a village located on the Isle of Arran in the Firth of Clyde, Scotland. The population, somewhat in decline, is around 200 people.
Geography
Lochranza is the northernmost of Arran's villages and is located in the northwestern c ...
(in summer)
**Kennacraig
Kennacraig () is a hamlet situated on West Loch Tarbert, a southwest of Tarbert on the Kintyre peninsula, Argyll and Bute, in the west of Scotland.
Ferry terminal
Caledonian MacBrayne ferries sail from the terminal, on the rocky islet Eil ...
- Islay
Islay ( ; , ) is the southernmost island of the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. Known as "The Queen of the Hebrides", it lies in Argyll and Bute just south west of Jura, Scotland, Jura and around north of the Northern Irish coast. The island's cap ...
**Tarbert
Tarbert () is a place name in Scotland and Ireland. Places named Tarbert are characterised by a narrow strip of land, or isthmus. This can be where two lochs nearly meet, or a causeway out to an island.
Etymology
All placenames that variously s ...
- Lochranza
Lochranza () is a village located on the Isle of Arran in the Firth of Clyde, Scotland. The population, somewhat in decline, is around 200 people.
Geography
Lochranza is the northernmost of Arran's villages and is located in the northwestern c ...
(in winter)
**Tarbert
Tarbert () is a place name in Scotland and Ireland. Places named Tarbert are characterised by a narrow strip of land, or isthmus. This can be where two lochs nearly meet, or a causeway out to an island.
Etymology
All placenames that variously s ...
- Portavadie
Portavadie () is a village on the shores of Loch Fyne on the coast of the Cowal Peninsula, in Argyll and Bute, West of Scotland.
The Portavadie complex was built in 1975 by the then Scottish Office for the purpose of constructing concrete pl ...
** Tayinloan - Gigha
Gigha ( ; ; ) or the Isle of Gigha (and formerly Gigha Island) is an island off the west coast of Kintyre in Scotland. The island forms part of Argyll and Bute and has a population of 163 people. The climate is mild with higher than average suns ...
**Campbeltown
Campbeltown (; or ) is a town and former royal burgh in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies by Campbeltown Loch on the Kintyre Peninsula. Campbeltown became an important centre for Scotch whisky, and a busy fishing port.
The 2018 populatio ...
- Ardrossan
Ardrossan (; ) is a town on the North Ayrshire coast in southwestern Scotland. The town has a population of 10,670 and forms part of a conurbation with Saltcoats and Stevenston known as the 'Three Towns#Scotland, Three Towns'. Ardrossan is loca ...
(in summer) (suspended for the 2025 season)
*Operated bKintyre Express
**
Campbeltown
Campbeltown (; or ) is a town and former royal burgh in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies by Campbeltown Loch on the Kintyre Peninsula. Campbeltown became an important centre for Scotch whisky, and a busy fishing port.
The 2018 populatio ...
- Ballycastle, County Antrim
Ballycastle () is a small seaside town in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It is on the north-easternmost coastal tip of Ireland, in the Antrim Coast and Glens Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.
Ballycastle lies at roughly the midpoint of the ...
Railways
No railways remain in use today. From 1876 until 1931 theCampbeltown and Machrihanish Light Railway
The Campbeltown and Machrihanish Light Railway was a narrow-gauge railway in Kintyre, Scotland, between Campbeltown and the coalmining village of Machrihanish. Only three other passenger-carrying lines in the UK operated on the same track gaug ...
operated, initially built to transport coal.
Places of historic interest
Prehistoric sites
Associated peerage titles
* Duke of Kintyre (extinct) * Marquess of Kintyre and Lorne (subsidiary title of the Duke of Argyll)Test
The Mull of Kintyre test is, according to anurban legend
Urban legend (sometimes modern legend, urban myth, or simply legend) is a genre of folklore concerning stories about an unusual (usually scary) or humorous event that many people believe to be true but largely are not.
These legends can be e ...
, an unofficial guideline to classify erections in film and TV by the British Board of Film Classification
The British Board of Film Classification (BBFC) is a non-governmental organization, non-governmental organisation founded by the British film industry in 1912 and responsible for the national classification and censorship of films exhibited ...
for the censorship
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governmen ...
of adult films and images.
See also
*Kildonald Bay
Kildonald Bay is a bay on the eastern side of the Kintyre Peninsula of Scotland.Ron Scholes. 1985 Kildonald Bay is an element of Kilbrannan Sound that separates the Kintyre Peninsula from the Isle of Arran. Other bays along the east side of the K ...
* Kintyre Way
The Kintyre Way is a waymarked footpath through the Kintyre Peninsula in Argyll and Bute, west of Scotland. It runs between Machrihanish near the southern end of the peninsula's west coast, and Tarbert at the northern end of Kintyre where the ...
Related songs
* The best known of these isPaul McCartney
Sir James Paul McCartney (born 18 June 1942) is an English singer, songwriter and musician who gained global fame with the Beatles, for whom he played bass guitar and the piano, and shared primary songwriting and lead vocal duties with John ...
's 1977 track "Mull of Kintyre
The Mull of Kintyre is the southwesternmost tip of the Kintyre Peninsula (formerly ''Cantyre'') in southwest Scotland. From here, the Antrim coast of Northern Ireland is visible on a calm and clear day, and a historic lighthouse, the second ...
", performed by Wings
A wing is a type of fin that produces both lift and drag while moving through air. Wings are defined by two shape characteristics, an airfoil section and a planform. Wing efficiency is expressed as lift-to-drag ratio, which compares the bene ...
. The song was written in tribute to the picturesque peninsula, where McCartney has owned High Park Farm since 1966, and its headland or Mull of Kintyre. The song was Wings' biggest hit in the United Kingdom where it became Christmas number one, and was the first single to sell over two million copies in the United Kingdom.
References
External links
VisitKintyre.info - Web Site including webcam, accommodation, news, photo galleries etc
EasyWays - walking holiday and guided walk round Kintyre
Explore Kintyre & Gigha
- official Marketing Organisation for Kintyre & Gigha {{Authority control Peninsulas of Scotland Landforms of Argyll and Bute Firth of Clyde Ramsar sites in Scotland