|
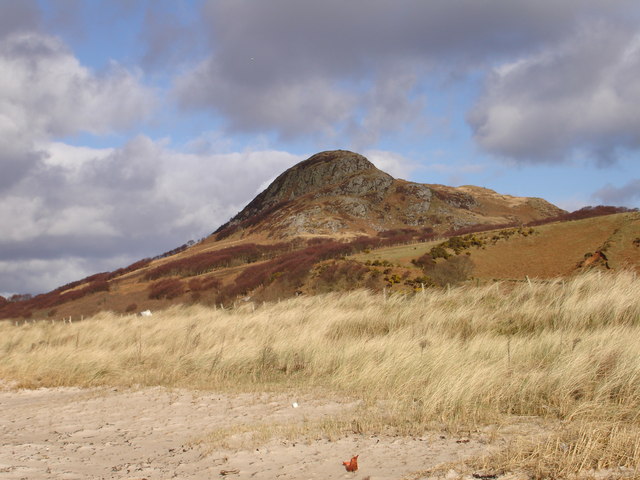
Dun Skeig
Dun Skeig is an oval Iron Age dun (fort) complex which is perched atop a rocky outcropping about above sea level overlooking West Loch Tarbert in Kintyre, Argyll and Bute, Scotland, about northwest of the village of Clachan. The dun site includes a collection of prehistoric buildings and evidence of human habitation. Most notable of the buildings on the site are a rocky Iron Age fort and a vitrified fort that has been grown over with ground vegetation. The Iron Age fort measures about in diameter with an outer wall of thick and has a single entrance. The moderately challenging climb to the peak and the views of the surrounding landscape that the vantage point offers make it clear why the site was selected as a defensive position. Other nearby prehistoric sites Other nearby sites on the Kintyre Peninsula Kintyre (, ) is a peninsula in western Scotland, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute. The peninsula stretches about , from the Mull of Kintyre in the south to Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dun Skeig From The Beach - Geograph
Dun most commonly refers to: *Dun gene, which produces a brownish-gray color (dun) in horses and other Equidae *Dun (fortification), an ancient or medieval fort Dun or DUN may also refer to: Places Scotland * Dun, Angus, a civil parish in Scotland * Dun Bhruichlinn, an Iron Age fort south of Esknish, Islay, Scotland * Dun Borrafiach, an Iron Age broch on the island of Skye, Scotland * Dun Guaidhre, an Iron Age fort southwest of Kilmeny, Islay, Scotland * Dun Nosebridge, an Iron Age fort southeast of Bridgend, Islay, Scotland * Dun Ringill, an Iron Age hill fort on the Strathaird peninsula on the island of Skye, Scotland * Dùn, an island of St Kilda, Scotland * House of Dun, a Scottish estate Iran * Dun, Iran, a village in Hormozgan Province, Iran * Dun Sar, a village in Gatab-e Shomali Rural District, Gatab District, Babol County, Mazandaran Province, Iran France * Dun, Ariège, a commune in southern France * Dun-le-Poëlier, a commune in central France * Dun- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progressing to protohistory (before written history). In this usage, it is preceded by the Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the ancient Near East. In the archaeology of the Americas, a five-period system is conventionally used instead; indigenous cultures there did not develop an iron economy in the pre-Columbian era, though some did work copper and bronze. Indigenous metalworking arrived in Australia with European contact. Although meteoric iron has been used for millennia in many regions, the beginning of the Iron Age is defined locally around the world by archaeological convention when the production of Smelting, smelted iron (espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dun (fortification)
A dun is an ancient or medieval fort. In Great Britain and Ireland it is mainly a kind of hillfort and also a kind of Atlantic roundhouse. Etymology The term comes from Irish ''dún'' or Scottish Gaelic ''dùn'' (meaning "fort"), and is cognate with Old Welsh ''din'' (whence Welsh ''dinas'' "city" comes). In certain instances, place-names containing ''Dun-'' or similar in Northern England and Southern Scotland, may be derived from a Brittonic cognate of the Welsh form ''din''. In this region, substitution of the Brittonic form by the Gaelic equivalent may have been widespread in toponyms. The Dacian dava (hill fort) is probably etymologically cognate. Details In some areas duns were built on any suitable crag or hillock, particularly south of the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. There are many duns on the west coast of Ireland and they feature in Irish mythology. For example, the tale of the '' Táin Bó Flidhais'' features Dún Chiortáin and Dún Chaochá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Loch Tarbert, Argyll
West Loch Tarbert is a long, narrow sea loch on the western side of the Kintyre Peninsula, in Argyll and Bute, west of Scotland. Geography The head of the loch lies near the village of Tarbert and it reaches the open sea at Ardpatrick Point some distant. The island of Eilean Ceann na Creige, off the south shore, is connected to the mainland by a causeway. It is a ferry terminal for island of Islay. History Around the year 1093, Magnus Barefoot, King of Norway had his longship dragged across the isthmus at Tarbert between West Loch Tarbert and East Loch Tarbert as part of a campaign to increase his possessions in the Hebrides. He made an arrangement with King Malcolm III of Scotland that he could take possession of land on the west coast around which a ship could sail. Magnus declared that Kintyre had "better land than the best of the Hebrides", and by taking command of his ship's tiller and "sailing" across the isthmus he was able to claim the entire peninsula, which rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kintyre
Kintyre (, ) is a peninsula in western Scotland, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute. The peninsula stretches about , from the Mull of Kintyre in the south to East Loch Tarbert, Argyll, East and West Loch Tarbert, Argyll, West Loch Tarbert in the north. The region immediately north of Kintyre is known as Knapdale. Kintyre is long and narrow, at no point more than from west coast to east coast, and is less than wide where it connects to Knapdale at the north. Kintyre is the lower Firth of Clyde western coast and protects the Firth from the Atlantic Ocean. The southerly tip of Kintyre is on the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel that separates southwestern Scotland from Northern Ireland. The east side of the Kintyre Peninsula is bounded by Kilbrannan Sound, with a number of coastal peaks such as Torr Mor. The central spine of the peninsula is mostly hilly moorland, the highest point being Beinn an Tuirc at . The coastal areas and hinterland, however, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argyll And Bute
Argyll and Bute (; , ) is one of 32 unitary authority, unitary council areas of Scotland, council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area. The current lord-lieutenant for Argyll and Bute is Jane Margaret MacLeod (14 July 2020). The administrative centre for the council area is in Lochgilphead at Kilmory Castle, a 19th-century Gothic Revival building and estate. The current council leader is Councillor Jim Lynch. Argyll and Bute covers the second-largest administrative area of any Scottish council. The council area adjoins those of Highland (council area), Highland, Perth and Kinross, Stirling (council area), Stirling and West Dunbartonshire. History The County of County of Bute, Bute and the County of Argyll were two of the shires of Scotland, historic counties of Scotland. They were both "''shires''" (context; the area controlled by a sheriff principal, sheriff) in the Middle Ages. From 1890 until 1975 both counties had individual separate ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clachan, Kintyre
Clachan is a small village in North Kintyre, Argyll & Bute, Scotland. Clachan is the site of an old church, which was the principal church for the North Kintyre area. The church is surrounded by carved stone statues of the chiefs of the Clan Alasdair. Another group of standing stones (the tallest of which is 3.4 metres), and a burial cist, are found to the south of Clachan, near Ballochroy Farm. In 1971 it had a population of 108. The last major battle to be fought in Kintyre took place on the steep slopes of Loup Hill in May 1689. Here, the local forces of MacDonald of Largie, McAlester of Loup and McNeill of Gallichoille, all strong supporters of King James VII, were defeated by a government force. Clachan is also the site of Balinakill House. It was once the home of Coll McAlester, who led the first large settlement of highlanders in North Carolina North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitrified
Vitrification (, via French ') is the full or partial transformation of a substance into a glass, that is to say, a non- crystalline or amorphous solid. Glasses differ from liquids structurally and glasses possess a higher degree of connectivity with the same Hausdorff dimensionality of bonds as crystals: dimH = 3. In the production of ceramics, vitrification is responsible for their impermeability to water. Vitrification is usually achieved by heating materials until they liquify, then cooling the liquid, often rapidly, so that it passes through the glass transition to form a glassy solid. Certain chemical reactions also result in glasses. In terms of chemistry, vitrification is characteristic for amorphous materials or disordered systems and occurs when bonding between elementary particles (atoms, molecules, forming blocks) becomes higher than a certain threshold value. Thermal fluctuations break the bonds; therefore, the lower the temperature, the higher the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kintyre Peninsula
Kintyre (, ) is a peninsula in western Scotland, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute. The peninsula stretches about , from the Mull of Kintyre in the south to East and West Loch Tarbert in the north. The region immediately north of Kintyre is known as Knapdale. Kintyre is long and narrow, at no point more than from west coast to east coast, and is less than wide where it connects to Knapdale at the north. Kintyre is the lower Firth of Clyde western coast and protects the Firth from the Atlantic Ocean. The southerly tip of Kintyre is on the North Channel that separates southwestern Scotland from Northern Ireland. The east side of the Kintyre Peninsula is bounded by Kilbrannan Sound, with a number of coastal peaks such as Torr Mor. The central spine of the peninsula is mostly hilly moorland, the highest point being Beinn an Tuirc at . The coastal areas and hinterland, however, are rich and fertile. Kintyre has long been a prized area for settlers, including the early Sco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avinagillan Standing Stone
The Avinagillan standing stone is a prehistoric menhir on the Kintyre Peninsula of Scotland. The stone is near the hamlet of Avinagillan.Megalithic Portal See also * Kilbrannan Sound Kilbrannan Sound (Scottish Gaelic: ''An Caolas Branndanach'') is a marine water body in the west of Scotland. It separates the Kintyre Peninsula from the island of Arran. Kilbrannan Sound is the western arm of the lower Firth of Clyde. S ... Line notes References * Megalithic Porta''Avinagillan standing stone'' Standing stones in Scotland History of Argyll and Bute Stone Age Scotland Kintyre {{Scotland-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballochroy
Ballochroy is a megalithic site in Kintyre on the Argyll peninsula in Scotland. It consists of three vertical stones, side by side, aligned with various land features away. Alexander Thom, known for his work on Stonehenge, maintained that the great length between the stones and the features of distant landscape lent precision to pinpointing the midsummer and winter solstices for ancient observers. These three stones are considered the most spectacular set of megalithic monuments that cluster around south Argyll. The three mica schist stones were measured at in height. It is possible that this last, smallest, stone may have been broken off at the top. The line of stones is orientated north-east to south-west. The flat face of the central stone (at right angles to the alignment) indicates the mountain of Cora Bheinn, on the island of Jura, which is away. The shortest stone also faces across the alignment, and points to Beinn a' Chaolais, the southernmost of the three Pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |