Ketone Halogenation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In 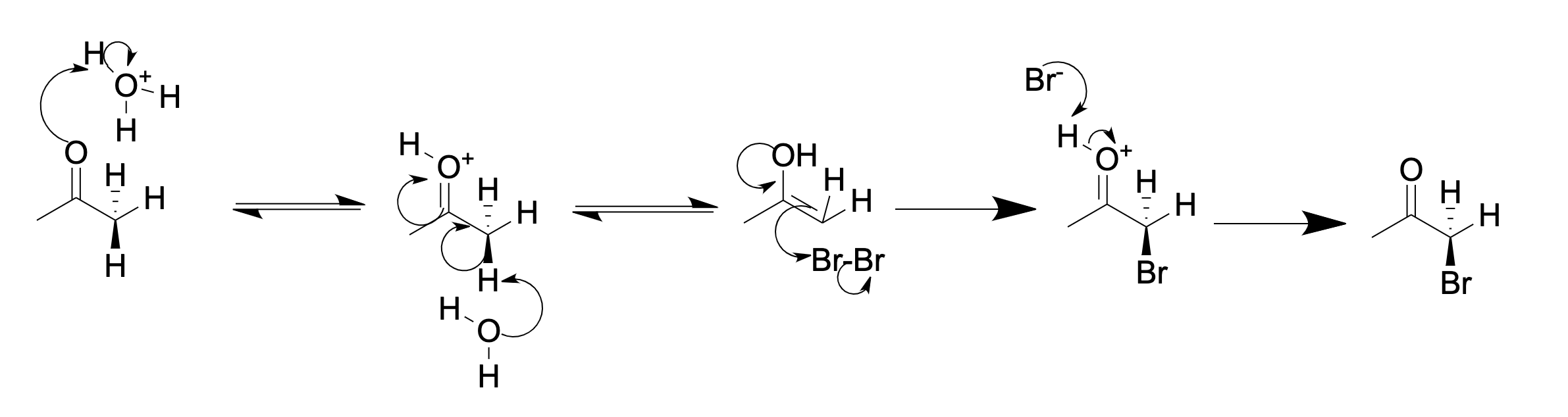 Basic (in aqueous
Basic (in aqueous  In acidic solution, usually only one alpha hydrogen is replaced by a halogen, as each successive halogenation is slower than the first. The halogen decreases the basicity of the carbonyl oxygen, thus making
In acidic solution, usually only one alpha hydrogen is replaced by a halogen, as each successive halogenation is slower than the first. The halogen decreases the basicity of the carbonyl oxygen, thus making
 On α,β-Unsaturated ketones or enones, it's possible to halogenate with
On α,β-Unsaturated ketones or enones, it's possible to halogenate with
organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
, α-keto halogenation is a special type of halogenation
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drug ...
.
The reaction may be carried out under either acidic or basic conditions in an aqueous
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water. It is mostly shown in chemical equations by appending (aq) to the relevant chemical formula. For example, a solution of table salt, also known as sodium chloride (NaCl), in wat ...
medium with the corresponding elemental halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
. In this way, chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pr ...
, bromide
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retard ...
, and iodide
An iodide ion is I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency ...
(but notably not fluoride
Fluoride (). According to this source, is a possible pronunciation in British English. is an Inorganic chemistry, inorganic, Monatomic ion, monatomic Ion#Anions and cations, anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula (also written ), whose ...
) functionality can be inserted selectively in the alpha position of a ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
.
The position alpha to the carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such a ...
group () in a ketone is easily halogenated. This is due to its ability to form an enolate
In organic chemistry, enolates are organic anions derived from the deprotonation of carbonyl () compounds. Rarely isolated, they are widely used as reagents in the Organic synthesis, synthesis of organic compounds.
Bonding and structure
Enolate ...
() in basic
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
solution, or an enol
In organic chemistry, enols are a type of functional group or intermediate in organic chemistry containing a group with the formula (R = many substituents). The term ''enol'' is an abbreviation of ''alkenol'', a portmanteau deriving from "-ene ...
() in acidic
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
The first category of acids are the ...
solution. An example of alpha halogenation is the mono-bromination of acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone) is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly Volatile organic compound, volatile, and flammable liquid with a charact ...
(), carried out under either acidic or basic conditions, to give bromoacetone
Bromoacetone is an organic compound with the formula . It is a colorless liquid although impure samples appear yellow or even brown. It is a lachrymatory agent and a precursor to other organic compounds.
Occurrence in nature
Bromoacetone is pr ...
:
Acidic (in acetic acid):
 Basic (in aqueous
Basic (in aqueous NaOH
Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations and hydroxide anions .
Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive base and alkali t ...
):
 In acidic solution, usually only one alpha hydrogen is replaced by a halogen, as each successive halogenation is slower than the first. The halogen decreases the basicity of the carbonyl oxygen, thus making
In acidic solution, usually only one alpha hydrogen is replaced by a halogen, as each successive halogenation is slower than the first. The halogen decreases the basicity of the carbonyl oxygen, thus making protonation
In chemistry, protonation (or hydronation) is the adding of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), usually denoted by H+, to an atom, molecule, or ion, forming a conjugate acid. (The complementary process, when a proton is removed from a Brø ...
less favorable. However, in basic solutions, successive halogenation is more rapid due to inductive electron withdrawal by the halogen. This makes the remaining hydrogens more acidic. In the case of methyl ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
s, this reaction often occurs a third time to form a ketone trihalide, which can undergo rapid substitution with water to form a carboxylate
In organic chemistry, a carboxylate is the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid, (or ). It is an anion, an ion with negative charge.
Carboxylate salts are salts that have the general formula , where M is a metal and ''n'' is 1, 2,... ...
() in what is known as the haloform reaction
In chemistry, the haloform reaction (also referred to as the Lieben haloform reaction) is a chemical reaction in which a haloform (, where X is a halogen) is produced by the exhaustive halogenation of an acetyl group (, where R can be either a ...
.
The regioselectivity
In organic chemistry, regioselectivity is the preference of chemical bonding or breaking in one direction over all other possible directions. It can often apply to which of many possible positions a reagent will affect, such as which proton a str ...
also differs: The halogenation of an unsymmetrical ketone in acid results in the more substituted alkyl group
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl group is derived from a cy ...
being halogenated. A second equivalent of halogen results in the halogenation of the other alkyl substituent (without the halogen). In contrast, in basic solutions, an unsymmetrical ketone halogenates at the less substituted alkyl group. Subsequent halogenation (which usually cannot be stopped by control of stoichiometry) occurs at the position which already has a halogen substituent, until all hydrogens have been replaced by halogen atoms. For methyl alkyl ketones (2-alkanones), the haloform reaction proceeds to give the carboxylic acid selectively.
Halogenation of α,β-unsaturated ketones
 On α,β-Unsaturated ketones or enones, it's possible to halogenate with
On α,β-Unsaturated ketones or enones, it's possible to halogenate with iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
selectively on the more saturated alpha on the ketone selectively over the unsaturated side. Iodine is preferred due to it being more reactive than alkyl bromides which makes this reaction quite useful. By using CuO
Copper(II) oxide or cupric oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula CuO. A black solid, it is one of the two stable oxides of copper, the other being Cu2O or copper(I) oxide (cuprous oxide). As a mineral, it is known as tenorite, or some ...
in conjunction with I2, it is possible to achieve this reaction under relatively mild conditions. This reaction undergoes a very reactive enol
In organic chemistry, enols are a type of functional group or intermediate in organic chemistry containing a group with the formula (R = many substituents). The term ''enol'' is an abbreviation of ''alkenol'', a portmanteau deriving from "-ene ...
mechanism, facilitated by the CuO, which allows for the selective addition of I2 on the saturated alpha carbon of the ketone. However, the effectiveness of this reaction depends on the presence of aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used ...
functional groups.
Applications in green chemistry
Alpha halogenated products are very useful compounds as they have high reactivity which makes them very prone to reacting. Alpha halogenatedketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is an organic compound with the structure , where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group (a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone ( ...
s react with nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
s to create many valuable compounds. However, many of the current method for ketone halogenation use hazardous chemicals, have complex procedures, and/or require a long time to go to completion. Additionally, the polar solvents that are primarily used (DMF, DMSO, and CH3CN) are major environmental pollutants.
An experiment conducted by Meshram et al. in 2005 investigated making ketone halogenation a greener reaction, according to the principles of green chemistry
Green chemistry, similar to sustainable chemistry or circular chemistry, is an area of chemistry and chemical engineering focused on the design of products and processes that minimize or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. Wh ...
. Meshram et al. investigated alternatives to the hazardous chemicals that are primarily used in ketone halogenation, finding that room temperature ionic liquids were a promising option. Room temperature ionic liquids are interesting prospects as they have unique chemical and physical properties, and their properties can be modified by changing the cations that are attached. Additionally, these ionic liquids have high polarity and their ability to solubilize organic and inorganic molecules leads to enhanced reaction rates, which makes them more desirable.
Many experiments found that ionic liquids with N-halosuccinimides as the solvent were an effective, greener alternative to conventional solvents. This process also resulted in enhanced yields, reduced reaction time, simplified the procedure, used less harmful chemicals (no strong acids), and did not require catalysts
Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst ...
, all of which made the process greener.
References
{{Reflist Halogenation reactions