Karl-Heinz Keitel on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wilhelm Bodewin Johann Gustav Keitel (; 22 September 188216 October 1946) was a German
 In December 1941, Hitler instructed the OKW to subject, with the exception of Denmark, Western Europe (which was under military occupation) to the
In December 1941, Hitler instructed the OKW to subject, with the exception of Denmark, Western Europe (which was under military occupation) to the
 After the war, Keitel faced the
After the war, Keitel faced the 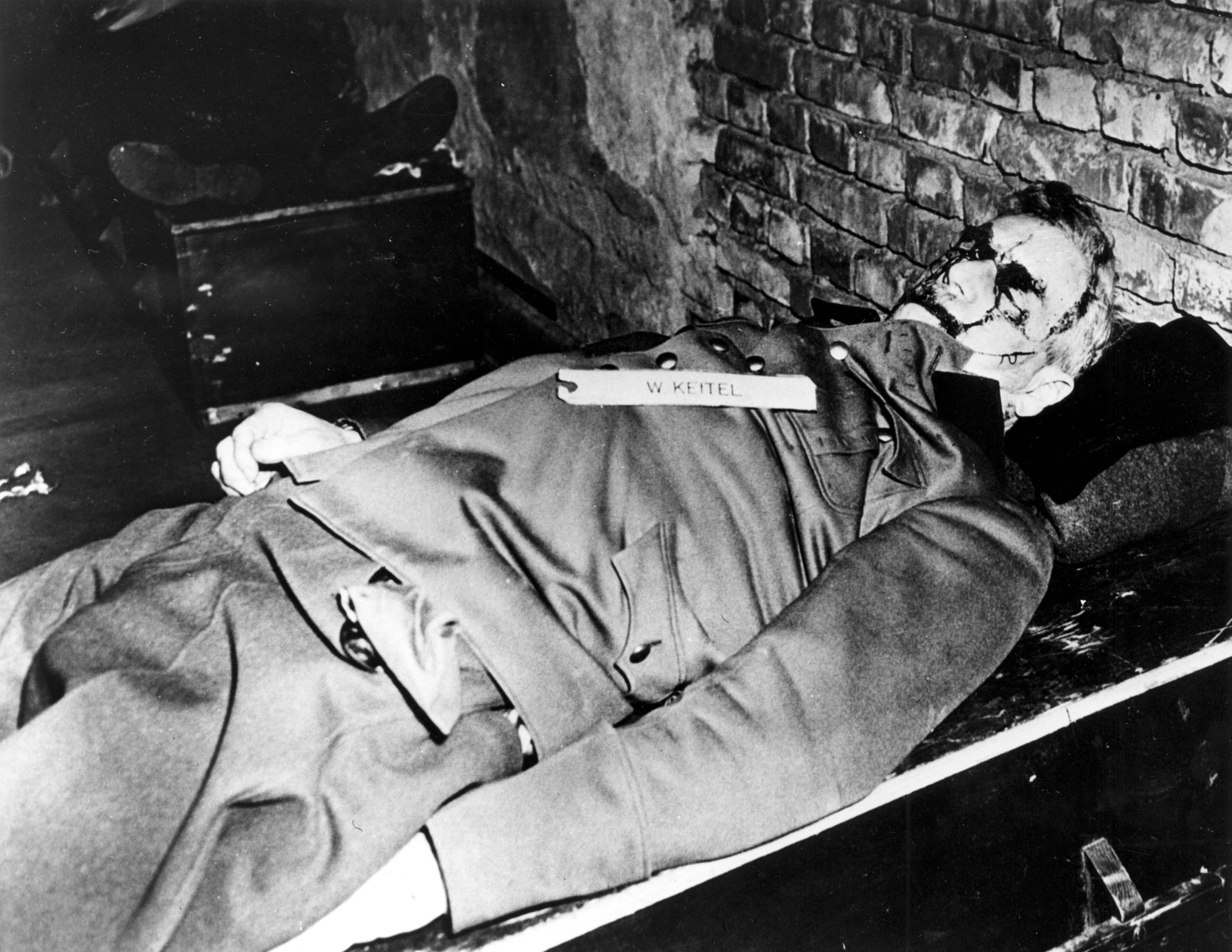 The IMT rejected this defence and convicted him on all charges. Although the tribunal's charter allowed "superior orders" to be considered a mitigating factor, it found Keitel's crimes were so egregious that "there is nothing in mitigation". In its judgment against him, the IMT wrote, "Superior orders, even to a soldier, cannot be considered in mitigation where crimes as shocking and extensive have been committed consciously, ruthlessly and without military excuse or justification." It also noted several instances where he issued illegal orders on his own authority.
In his statement before the Tribunal, Keitel said: "As these atrocities developed, one from the other, step by step, and without any foreknowledge of the consequences, destiny took its tragic course, with its fateful consequences." To underscore the criminal rather than military nature of Keitel's acts, the
The IMT rejected this defence and convicted him on all charges. Although the tribunal's charter allowed "superior orders" to be considered a mitigating factor, it found Keitel's crimes were so egregious that "there is nothing in mitigation". In its judgment against him, the IMT wrote, "Superior orders, even to a soldier, cannot be considered in mitigation where crimes as shocking and extensive have been committed consciously, ruthlessly and without military excuse or justification." It also noted several instances where he issued illegal orders on his own authority.
In his statement before the Tribunal, Keitel said: "As these atrocities developed, one from the other, step by step, and without any foreknowledge of the consequences, destiny took its tragic course, with its fateful consequences." To underscore the criminal rather than military nature of Keitel's acts, the
field marshal
Field marshal (or field-marshal, abbreviated as FM) is the most senior military rank, senior to the general officer ranks. Usually, it is the highest rank in an army (in countries without the rank of Generalissimo), and as such, few persons a ...
who held office as chief of the (OKW), the high command of Nazi Germany's armed forces, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. He signed a number of criminal orders and directives that led to numerous war crimes
A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hos ...
.
Keitel's rise to the high command began with his appointment as the head of the Armed Forces Office at the Reich Ministry of War in 1935. Having taken command of the in 1938, Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the lea ...
replaced the ministry with the OKW and Keitel became its chief. He was reviled among his military colleagues as Hitler's habitual " yes-man".
After the war, Keitel was indicted by the International Military Tribunal
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
in Nuremberg
Nuremberg (, ; ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the Franconia#Towns and cities, largest city in Franconia, the List of cities in Bavaria by population, second-largest city in the States of Germany, German state of Bav ...
as one of the "major war criminals". He was found guilty on all counts of the indictment: crimes against humanity
Crimes against humanity are certain serious crimes committed as part of a large-scale attack against civilians. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity can be committed during both peace and war and against a state's own nationals as well as ...
, crimes against peace
The crime of aggression was conceived by Soviet jurist Aron Trainin in the wake of the German invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II. Pictured: Stalingrad in ruins, December 1942
A crime of aggression or crime against peace is the p ...
, criminal conspiracy
In criminal law, a conspiracy is an agreement between two or more people to commit a crime at some time in the future. Criminal law in some countries or for some conspiracies may require that at least one overt act be undertaken in furtherance ...
, and war crimes
A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hos ...
. He was sentenced to death and executed by hanging in 1946.
Early life and career
Wilhelm Keitel was born in the village of Helmscherode near Gandersheim in theDuchy of Brunswick
The Duchy of Brunswick () was a historical German state that ceased to exist in 1918. Its capital city, capital was the city of Braunschweig, Brunswick (). It was established as the successor state of the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel ...
, Germany. He was the eldest son of Carl Keitel (1854–1934), a middle-class landowner, and his wife Apollonia Vissering (1855–1888). As a youngster his main interests were hunting and riding horses, hobbies which he pursued also later in life. He was also interested in farming and wanted to take over his family's estates after completing his education at a gymnasium. This plan failed as his father did not want to retire. Instead, he embarked on a military career in 1901, becoming an officer cadet of the Prussian Army. As a commoner, he did not join the cavalry, but a field artillery regiment in Wolfenbüttel
Wolfenbüttel (; ) is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany, the administrative capital of Wolfenbüttel District
Wolfenbüttel (; ) is a town in Lower Saxony, Germany, the administrative capital of Wolfenbüttel (district), Wolfenbüttel Distri ...
, serving as adjutant
Adjutant is a military appointment given to an Officer (armed forces), officer who assists the commanding officer with unit administration, mostly the management of “human resources” in an army unit. The term is used in French-speaking armed ...
from 1908. On 18 April 1909, Keitel married Lisa Fontaine, a wealthy landowner's daughter at Wülfel near Hanover
Hanover ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the States of Germany, German state of Lower Saxony. Its population of 535,932 (2021) makes it the List of cities in Germany by population, 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-l ...
.
Keitel was tall, later described as a solidly built and square-jawed Prussian.
During World War I, Keitel served on the Western Front and took part in the fighting in Flanders
Flanders ( or ; ) is the Dutch language, Dutch-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to culture, la ...
, where he was severely wounded. After being promoted to captain, Keitel was posted to the staff
Staff may refer to:
Pole
* Walking staff, an instrument used for balance when walking
* Staff, a weapon used in stick-fighting
** Quarterstaff, a European pole weapon
* Staff of office, a pole that indicates a position
* Staff (railway signalling) ...
of an infantry division in 1915. After the war, Keitel was retained in the newly created ''Reichswehr
''Reichswehr'' (; ) was the official name of the German armed forces during the Weimar Republic and the first two years of Nazi Germany. After Germany was defeated in World War I, the Imperial German Army () was dissolved in order to be reshaped ...
'' of the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
and played a part in organizing the paramilitary ''Freikorps
(, "Free Corps" or "Volunteer Corps") were irregular German and other European paramilitary volunteer units that existed from the 18th to the early 20th centuries. They effectively fought as mercenaries or private military companies, rega ...
'' units on the Polish border. In 1924, Keitel was transferred to the Ministry of the Reichswehr
The Ministry of the Reichswehr () was the defence ministry of Germany from 1919 to 1938 during the Weimar Republic and early Nazi Germany periods. It was responsible for the '' Reichswehr'' under the leadership of the Minister of Defence and base ...
in Berlin, serving with the ''Truppenamt
The ''Truppenamt'' () was the cover organisation for the German General Staff from 1919 through until 1935 when the General Staff of the German Army (''Heer'') was re-created. This subterfuge was deemed necessary in order for Germany to be seen ...
'' ('Troop Office'), the post-Versailles disguised German General Staff
The German General Staff, originally the Prussian General Staff and officially the Great General Staff (), was a full-time body at the head of the Prussian Army and later, the Imperial German Army, German Army, responsible for the continuous stu ...
. Three years later, he returned to field command.
Now a lieutenant-colonel, Keitel was again assigned to the war ministry in 1929 and was soon promoted to Head of the Organizational Department ("T-2"), a post he held until Adolf Hitler took power in 1933. Playing a vital role in the German rearmament
German rearmament (''Aufrüstung'', ) was a policy and practice of rearmament carried out by Germany from 1918 to 1939 in violation of the Treaty of Versailles, which required German disarmament after World War I to prevent it from starting an ...
, he traveled at least once to the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
to inspect secret ''Reichswehr'' training camps. In the autumn of 1932, he suffered a heart attack and double pneumonia. Shortly after his recovery, in October 1933, Keitel was appointed as deputy commander of the 3rd Infantry Division; in 1934, he was given command of the 22nd Infantry Division at Bremen.
Rise to the ''Wehrmacht'' High Command
In 1935, at the recommendation of GeneralWerner von Fritsch
Thomas Ludwig Werner Freiherr von Fritsch (4 August 1880 – 22 September 1939) was a German ''Generaloberst'' (Full General, full general) who served as Oberkommando des Heeres, Commander-in-Chief of the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army fro ...
, Keitel was promoted to the rank of major general and appointed chief of the Reich Ministry of War's Armed Forces Office (''Wehrmachtsamt''), which oversaw the army, navy, and air force. After assuming office, Keitel was promoted to lieutenant general on 1 January 1936.
On 21 January 1938, Keitel received evidence revealing that the wife of his superior, War Minister Werner von Blomberg
Werner Eduard Fritz von Blomberg (2 September 1878 – 13 March 1946) was a German general and politician who served as the first Minister of War in Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1938. Blomberg had served as Chief of the ''Truppenamt'', equivalent ...
, was a former prostitute. Upon reviewing this information, Keitel suggested that the dossier be forwarded to Hitler's deputy, Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German Nazism, Nazi politician, aviator, military leader, and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which gov ...
, who used it to bring about Blomberg's resignation.
Hitler took command of the ''Wehrmacht'' in 1938 and replaced the war ministry with the Supreme Command of the Armed Forces (''Oberkommando der Wehrmacht
The (; abbreviated OKW
''), with Keitel as its chief. As a result of his appointment, Keitel assumed the responsibilities of Germany's war minister. Although not officially appointed a ''ː kaːˈve
The colon alphabetic letter is used in a number of languages and phonetic transcription systems, for vowel length in Americanist Phonetic Notation, for the vowels and in a number of languages of Papua New Guinea, and for grammatical tone in s ...
Armed Forces High Command) was the Command (military formation), supreme military command and control Staff (military), staff of Nazi Germany during World War II, that was directly subordinated to Adolf ...Reichsminister
Reichsminister (in German singular and plural; 'minister of the realm') was the title of members of the German Government during two historical periods: during the March Revolution of 1848/1849 in the German Reich of that period, and in the mode ...
'', Keitel was granted cabinet-level rank. When von Blomberg was asked by Hitler (out of respect for him, after his dismissal in 1938) who he would recommend to replace him, he had said that Hitler himself should take over the job. He told Hitler that Keitel (who was his son-in-law's father) "is just the man who runs my office". Hitler snapped his fingers and exclaimed "That's exactly the man I'm looking for". So on 4 February 1938 when Hitler became Commander-in-Chief of the ''Wehrmacht'', Keitel (to the astonishment of the General Staff, including himself) became chief of staff.
Soon after his promotion, Keitel convinced Hitler to appoint Walther von Brauchitsch
Walther Heinrich Alfred Hermann von Brauchitsch (4 October 1881 – 18 October 1948) was a German ''Generalfeldmarschall'' (Field Marshal) and Commander-in-Chief (''Oberbefehlshaber'') of the German Army during the first two years of World War ...
as Commander-in-Chief of the Army, replacing von Fritsch. Keitel was promoted to ''Generaloberst
A ("colonel general") was the second-highest general officer rank in the German '' Reichswehr'' and ''Wehrmacht'', the Austro-Hungarian Common Army, the East German National People's Army and in their respective police services. The rank w ...
'' (Colonel General) in November 1938, and in April 1939 he was awarded the Golden Party Badge
__NOTOC__
The Golden Party Badge () was an award authorised by Adolf Hitler in a decree in October 1933. It was a special award given to all Nazi Party members who had, as of 9 November 1933, registered numbers from 1 to 100,000 (issued on 1 Oc ...
by Hitler.
Criticism of capabilities
Field Marshal Ewald von Kleist labelled Keitel nothing more than a "stupid follower of Hitler" because of his servile "yes man" attitude toward Hitler. His sycophancy was well known in the army, and he acquired the nickname 'Lakeitel', a pun derived from ("lackey
Lackey may refer to:
__NOTOC__ Places
* Lackey, Kentucky, United States, an unincorporated community
* Lackey, Mississippi, United States, an unincorporated community
* Lackey, Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community
* Lackey Ridge, ...
") and his surname. Hermann Göring's description of Keitel as having "a sergeant's mind inside a field marshal's body" was a feeling often expressed by his peers. He had been promoted because of his willingness to function as Hitler's mouthpiece. He was known by his peers as a ''"blindingly loyal toady"'' of Hitler, nicknamed "Nickgeselle", after a popular metal toy nodding donkey, the "Nickesel". During the war he was subject to verbal abuse from Hitler, who said to other officers (according to Gerd von Rundstedt
Karl Rudolf Gerd von Rundstedt (12 December 1875 – 24 February 1953) was a German ''Generalfeldmarschall'' (Field Marshal) in the ''German Army (1935–1945), Heer'' (Army) of Nazi Germany and OB West, ''Oberbefehlshaber West'' (Commande ...
) that "you know he has the brains of a movie usher ... (but he was made the highest ranking officer in the Army) ... because the man's as loyal as a dog" (said by Hitler with a sly smile).
Keitel was predisposed to manipulation because of his limited intellect and nervous disposition; Hitler valued his diligence and obedience. On one occasion, ''Generalleutnant
() is the German-language variant of lieutenant general, used in some German speaking countries.
Austria
Generalleutnant is the second highest general officer rank in the Austrian Armed Forces (''Bundesheer''), roughly equivalent to the NATO ...
'' asked who Keitel was: upon finding out he became horrified at his own failure to salute his superior. Franz Halder
Franz Halder (30 June 1884 – 2 April 1972) was a German general and the chief of staff of the Oberkommando des Heeres, Army High Command (OKH) in Nazi Germany from 1938 until September 1942. During World War II, he directed the planning and i ...
, however, told him: "Don't worry, it's only Keitel". German officers consistently bypassed him and went directly to Hitler.
World War II
On 30 August 1939, immediately prior to the outbreak of the Second World War, Keitel was appointed by Hitler to the six-personCouncil of Ministers for the Defense of the Reich
The Council of Ministers for the Defense of the Reich (German: ''Ministerrat für die Reichsverteidigung'') was a six-member ministerial council created in Nazi Germany by Adolf Hitler on 30 August 1939, in anticipation of the invasion of Poland &n ...
which was set up to operate as a "war cabinet". After Germany defeated France in the Battle of France
The Battle of France (; 10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign (), the French Campaign (, ) and the Fall of France, during the Second World War was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of the Low Countries (Belgium, Luxembour ...
in six weeks, Keitel described Hitler as "the greatest warlord of all time". Keitel conducted the negotiations of the French armistice, and on 19 July 1940 was promoted to ''Generalfeldmarschall
''Generalfeldmarschall'' (; from Old High German ''marahscalc'', "marshal, stable master, groom"; ; often abbreviated to ''Feldmarschall'') was a rank in the armies of several German states and the Holy Roman Empire, (''Reichsgeneralfeldmarsch ...
'' (field marshal).
The planning for Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along ...
, the 1941 invasion of the Soviet Union, was begun tentatively by Halder with the redeployment of the 18th Army into an offensive position against the Soviet Union. On 31 July 1940, Hitler held a major conference that included Keitel, Halder, Alfred Jodl
Alfred Josef Ferdinand Jodl (; born Alfred Josef Baumgärtler; 10 May 1890 – 16 October 1946) was a German Wehrmacht Heer, Army ''Generaloberst'' (the rank was equal to a four-star full general) and War crime, war criminal, who served as th ...
, Erich Raeder
Erich Johann Albert Raeder (24 April 1876 – 6 November 1960) was a German admiral who played a major role in the naval history of World War II and was convicted of war crimes after the war. He attained the highest possible naval rank, that of ...
, Brauchitsch, and Hans Jeschonnek
Hans Jeschonnek (9 April 1899 – 18 August 1943) was a German military aviator in the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' during World War I, a general staff officer in the ''Reichswehr'' in the inter–war period and ''Generaloberst'' (Colonel-General) and a ...
which further discussed the invasion. The participants did not object to the invasion. Hitler asked for war studies to be completed and Georg Thomas
Georg Thomas (20 February 1890 – 29 December 1946) was a German general who served during World War II.Mitcham and Mueller, ''Hitler's Commanders'', pgs. 17-20. He was a leading participant in planning and carrying out economic exploitation of ...
was given the task of completing two studies on economic matters. The first study by Thomas detailed serious problems with fuel and rubber supplies. Keitel bluntly dismissed the problems, telling Thomas that Hitler would not want to see it. This influenced Thomas' second study which offered a glowing recommendation for the invasion based upon fabricated economic benefits.
In January 1943, just before the final surrender at Stalingrad
Volgograd,. geographical renaming, formerly Tsaritsyn. (1589–1925) and Stalingrad. (1925–1961), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Volgograd Oblast, Russia. The city lies on the western bank of the Volga, covering an area o ...
, Hitler agreed to the creation of a three-man committee with representatives of the State, the Armed Forces High Command, and the Party in an attempt to centralize control of the war economy and over the home front. The committee members were Keitel, (Chief of OKW) Hans Lammers
Hans Heinrich Lammers (27 May 1879 – 4 January 1962) was a German jurist and prominent Nazi Party politician. From 1933 until 1945 he served as Chief of the Reich Chancellery under Adolf Hitler. In 1937, he additionally was given the post of ' ...
(Chief of the Reich Chancellery), and Martin Bormann
Martin Ludwig Bormann (17 June 1900 – 2 May 1945) was a German Nazi Party official and head of the Nazi Party Chancellery, private secretary to Adolf Hitler, and a war criminal. Bormann gained immense power by using his position as Hitler ...
(Chief of the Party Chancellery). The committee, soon known as the ''Dreierausschuß'' (Committee of Three), met eleven times between January and August 1943. However, it had little autonomy, with Hitler reserving most of the final decisions to himself. In addition, it ran up against resistance from cabinet ministers, who headed deeply entrenched spheres of influence and, seeing it as a threat to their power, worked together to undermine it. The result was that nothing changed, and the Committee declined into irrelevance.
Keitel played an important role after the failed 20 July plot
The 20 July plot, sometimes referred to as Operation Valkyrie, was a failed attempt to assassinate Adolf Hitler, the chancellor and leader of Nazi Germany, and overthrow the Nazi regime on 20 July 1944. The plotters were part of the German r ...
in 1944. He sat on the army "court of honour A court of honor may be:
* A Court of Honor, an official event constituted to determine various questions of social protocol, breaches of etiquette
* A manorial court, the medieval court of honor
* The Court of Honor, the 1949 Soviet film known
* ...
" that handed over many officers who were involved, including Field Marshal Erwin von Witzleben
Job Wilhelm Georg Erwin Erdmann von Witzleben (4 December 1881 – 8 August 1944) was a German ''Generalfeldmarschall'' (Field Marshal) in the ''Wehrmacht'' and ''Oberbefehlshaber West'' (Commander in Chief in the West), during the Second World ...
, to Roland Freisler
Karl Roland Freisler (30 October 1893 – 3 February 1945) was a German jurist, judge and politician who served as the State Secretary of the Reich Ministry of Justice from 1935 to 1942 and as President of the People's Court from 1942 to 194 ...
's notorious People's Court. Around 7,000 people were arrested, many of whom were tortured by the Gestapo, and around 5,000 were executed.
In April and May 1945, during the Battle of Berlin
The Battle of Berlin, designated as the Berlin Strategic Offensive Operation by the Soviet Union, and also known as the Fall of Berlin, was one of the last major offensives of the European theatre of World War II.
After the Vistula–Od ...
, Keitel called for counterattacks to drive back the Soviet forces and relieve Berlin. However, there were insufficient German forces to carry out such counterattacks. After Hitler's suicide
Adolf Hitler, chancellor and dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945, committed suicide via a gunshot to the head on 30 April 1945 in the in Berlin after it became clear that Germany would lose the Battle of Berlin, which led to the e ...
on 30 April, Keitel stayed on as a member of the short-lived Flensburg Government
The Flensburg Government (), also known as the Flensburg Cabinet (''Flensburger Kabinett''), the Dönitz Government (''Regierung Dönitz''), or the Schwerin von Krosigk Cabinet (''Kabinett Schwerin von Krosigk''), was the rump government of Naz ...
under Grand Admiral
Grand admiral is a historic naval rank, the highest rank in the several European navies that used it. It is best known for its use in Germany as . A comparable rank in modern navies is that of admiral of the fleet.
Grand admirals in individual ...
Karl Dönitz
Karl Dönitz (; 16 September 1891 – 24 December 1980) was a German grand admiral and convicted war criminal who, following Adolf Hitler's Death of Adolf Hitler, suicide, succeeded him as head of state of Nazi Germany during the Second World ...
. Upon arriving in Flensburg, Albert Speer
Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer (; ; 19 March 1905 – 1 September 1981) was a German architect who served as Reich Ministry of Armaments and War Production, Minister of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany during most of W ...
, the Minister of Armaments and War Production, said that Keitel grovelled to Dönitz in the same way as he had done to Hitler. On 7 May 1945, Alfred Jodl, on behalf of Dönitz, signed Germany's unconditional surrender on all fronts. Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
considered this an affront, so a second signing was arranged at the Berlin suburb of Karlshorst
Karlshorst (, ; ; literally meaning ''Karl's nest'') is a locality in the borough of Lichtenberg in Berlin. It is home to a harness racing track, the Hochschule für Technik und Wirtschaft Berlin (''HTW''), the largest University of Applied Scien ...
on 8 May. There, Keitel signed the German Instrument of Surrender
The German Instrument of Surrender was a legal document effecting the unconditional surrender of the remaining German armed forces to the Allies, ending World War II in Europe. It was signed at 22:43 CET on 8 May 1945 and took effect at 23 ...
on 8 May 1945. Five days later on 13 May, he was arrested at the request of the United States and interned at Camp Ashcan
Central Continental Prisoner of War Enclosure No. 32, code-named ''Ashcan'', was an Allied prisoner-of-war camp in the ''Palace Hotel'' of Mondorf-les-Bains, Luxembourg during World War II. Operating from May to August 1945, it served as a proce ...
in Mondorf-les-Bains
Mondorf-les-Bains (; ; ) is a Communes of Luxembourg, commune and town in south-eastern Luxembourg.
It is part of the Remich (canton), canton of Remich. Mondorf-les-Bains is a spa town (hence its name), and has the only casino in Luxembourg.
, ...
. Jodl succeeded him as Chief of OKW until the final dissolution of the Flensburg Government on 23 May.
Role in crimes of the ''Wehrmacht'' and the Holocaust
Keitel had full knowledge of the criminal nature of the planning and the subsequentinvasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign, Polish Campaign, and Polish Defensive War of 1939 (1 September – 6 October 1939), was a joint attack on the Second Polish Republic, Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany, the Slovak R ...
, agreeing to its aims in principle. The Nazi plans included mass arrests, population transfers, and mass murder. Keitel did not contest the regime's assault upon basic human rights or counter the role of the ''Einsatzgruppen
(, ; also 'task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the imp ...
'' in the murders. The criminal nature of the invasion was now obvious; local commanders continued to express shock and protest over the events they were witnessing. Keitel continued to ignore the protests among the officer corps while they became morally numbed to the atrocities.
Keitel issued a series of criminal orders from April 1941. The orders went beyond established codes of conduct for the military and broadly allowed the execution of Jews, civilians, and non-combatants for any reason. Those carrying out the murders were exempted from court-martial or later being tried for war crimes. The orders were signed by Keitel; however, other members of the OKW and the OKH
The (; abbreviated OKH) was the high command of the Army of Nazi Germany. It was founded in 1935 as part of Adolf Hitler's rearmament of Germany. OKH was ''de facto'' the most important unit within the German war planning until the defeat ...
, including Halder, wrote or changed the wording of his orders. Commanders in the field interpreted and carried out the orders.
In the summer and autumn of 1941, German military lawyers unsuccessfully argued that Soviet prisoners of war should be treated in accordance with the Geneva Conventions
upright=1.15, The original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are international humanitarian laws consisting of four treaties and three additional protocols that establish international legal standards for humanitarian t ...
. Keitel rebuffed them, writing: "These doubts correspond to military ideas about wars of chivalry. Our job is to suppress a way of life." In September 1941, concerned that some field commanders on the Eastern Front did not exhibit sufficient harshness in implementing the May 1941 order on the "Guidelines for the Conduct of the Troops in Russia
Guidelines for the Conduct of the Troops in Russia was a criminal order issued on May 19, 1941, during World War II. The guidelines detailed the expected behaviour of German troops during the invasion of the Soviet Union. Civilians were included a ...
", Keitel issued a new order, writing: " hestruggle against Bolshevism demands ruthless and energetic action especially also against the Jews, the main carriers of Bolshevism". Also in September, Keitel issued an order to all commanders, not just those in the occupied Soviet Union, instructing them to use "unusual severity" to stamp out resistance. In this context, the guideline stated that execution of 50 to 100 "Communists" was an appropriate response to a loss of a German soldier. Such orders and directives further radicalised the army's occupational policies and enmeshed it in the genocide of the Jews.
 In December 1941, Hitler instructed the OKW to subject, with the exception of Denmark, Western Europe (which was under military occupation) to the
In December 1941, Hitler instructed the OKW to subject, with the exception of Denmark, Western Europe (which was under military occupation) to the Night and Fog Decree
''Nacht und Nebel'' ( German: ), meaning Night and Fog, also known as the Night and Fog Decree, was a directive issued by Adolf Hitler on 7 December 1941 targeting political activists and resistance "helpers" in the territories occupied by Na ...
. Signed by Keitel, the decree made it possible for foreign nationals to be transferred to Germany for trial by special courts, or simply handed to the Gestapo
The (, ), Syllabic abbreviation, abbreviated Gestapo (), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of F ...
for deportation to concentration camps. The OKW further imposed a blackout on any information concerning the fate of the accused. At the same time, Keitel increased pressure on Otto von Stülpnagel
Otto Edwin von Stülpnagel (16 June 1878 – 6 February 1948) was a German military commander of occupied France during the Second World War. Arrested by Allied authorities after the war, he committed suicide in prison in 1948.
Career
Otto von ...
, the military commander in France, for a more ruthless reprisal policy in the country. In October 1942, Keitel signed the Commando Order
The Commando Order () was issued by the Oberkommando der Wehrmacht, OKW, the high command of the Wehrmacht, German Armed Forces, on 18 October 1942. This order stated that all Allies of World War II, Allied commandos captured in Europe and Africa ...
that authorized the killing of enemy special operations troops even when captured in uniform.
In the spring and summer of 1942, as the deportations of the Jews to extermination camps
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe, primarily in occupied Poland, during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocau ...
progressed, the military initially protested when it came to the Jews that laboured for the benefit of the ''Wehrmacht''. The army lost control over the matter when the SS assumed command of all Jewish forced labour in July 1942. Keitel formally endorsed the state of affairs in September, reiterating for the armed forces that "evacuation of the Jews must be carried out thoroughly and its consequences endured, despite any trouble it may cause over the next three or four months".
Trial, conviction, and execution
 After the war, Keitel faced the
After the war, Keitel faced the International Military Tribunal
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
(IMT), where he was examined by Chief Medical Officer Lt. Col. Rene Juchli who reported that Keitel was suffering from "high blood pressure, varicose veins, and dysentery". He was indicted on all four counts before the IMT: conspiracy to commit crimes against peace
The crime of aggression was conceived by Soviet jurist Aron Trainin in the wake of the German invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II. Pictured: Stalingrad in ruins, December 1942
A crime of aggression or crime against peace is the p ...
, planning, initiating and waging wars of aggression, war crimes
A war crime is a violation of the laws of war that gives rise to individual criminal responsibility for actions by combatants in action, such as intentionally killing civilians or intentionally killing prisoners of war, torture, taking hos ...
, and crimes against humanity
Crimes against humanity are certain serious crimes committed as part of a large-scale attack against civilians. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity can be committed during both peace and war and against a state's own nationals as well as ...
. Most of the case against him was based on his signature being present on dozens of orders that called for soldiers and political prisoners to be killed or 'disappeared
An enforced disappearance (or forced disappearance) is the secret abduction or imprisonment of a person with the support or acquiescence of a state followed by a refusal to acknowledge the person's fate or whereabouts with the intent of placing ...
'. In court, Keitel admitted that he knew many of Hitler's orders were illegal. His defence relied almost entirely on the argument that he was merely following orders in conformity to "the leader principle" (''Führerprinzip
The (, ''Leader Principle'') was the basis of authority, executive authority in the government of Nazi Germany. It placed the Führer's word above all written law, and meant that Law of Nazi Germany, government policies, decisions, and officia ...
'') and his personal oath of loyalty to Hitler.
 The IMT rejected this defence and convicted him on all charges. Although the tribunal's charter allowed "superior orders" to be considered a mitigating factor, it found Keitel's crimes were so egregious that "there is nothing in mitigation". In its judgment against him, the IMT wrote, "Superior orders, even to a soldier, cannot be considered in mitigation where crimes as shocking and extensive have been committed consciously, ruthlessly and without military excuse or justification." It also noted several instances where he issued illegal orders on his own authority.
In his statement before the Tribunal, Keitel said: "As these atrocities developed, one from the other, step by step, and without any foreknowledge of the consequences, destiny took its tragic course, with its fateful consequences." To underscore the criminal rather than military nature of Keitel's acts, the
The IMT rejected this defence and convicted him on all charges. Although the tribunal's charter allowed "superior orders" to be considered a mitigating factor, it found Keitel's crimes were so egregious that "there is nothing in mitigation". In its judgment against him, the IMT wrote, "Superior orders, even to a soldier, cannot be considered in mitigation where crimes as shocking and extensive have been committed consciously, ruthlessly and without military excuse or justification." It also noted several instances where he issued illegal orders on his own authority.
In his statement before the Tribunal, Keitel said: "As these atrocities developed, one from the other, step by step, and without any foreknowledge of the consequences, destiny took its tragic course, with its fateful consequences." To underscore the criminal rather than military nature of Keitel's acts, the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
denied his request to be shot by firing squad
Firing may refer to:
* Dismissal (employment), sudden loss of employment by termination
* Firemaking, the act of starting a fire
* Burning; see combustion
* Shooting, specifically the discharge of firearms
* Execution by firing squad, a method of ...
. Instead, he was executed at Nuremberg Prison by hanging
Hanging is killing a person by suspending them from the neck with a noose or ligature strangulation, ligature. Hanging has been a standard method of capital punishment since the Middle Ages, and has been the primary execution method in numerou ...
.
On the day of the execution, Keitel told prison chaplain Henry F. Gerecke "You have helped me more than you know. May Christ, my saviour, stand by me all the way. I shall need him so much." He then received Communion and was executed later that day. Keitel was executed by US Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United Stat ...
Master Sergeant
A master sergeant is the military rank for a senior non-commissioned officer in the armed forces of some countries.
Israel Defense Forces
The (abbreviated "", master sergeant) is a non-commissioned officer () rank in the Israel Defense Force ...
John C. Woods
John Clarence Woods (June 5, 1911 – July 21, 1950) was a United States Army master sergeant who, with Joseph Malta, carried out the Nuremberg executions of ten former top leaders of the Third Reich on October 16, 1946, after they were senten ...
. His last words were: "I call on God Almighty to have mercy on the German people. More than two million German soldiers went to their death for the fatherland before me. I follow now my sons – all for Germany." The trap door was small, causing head injuries to Keitel and several other condemned men as they dropped. Many of the executed Nazis fell from the gallows with insufficient force to snap their necks, resulting in convulsions that in Keitel's case lasted 24 minutes. The corpses of Keitel and the other nine executed men were, like Hermann Göring's, cremated at Ostfriedhof (Munich)
The Ostfriedhof () is a cemetery in Munich, situated in the district of Obergiesing, established in 1821 and still in use. It contains an area of more than 30 hectares and approximately 34,700 burial plots.
The buildings were constructed betwe ...
and the ashes were scattered in the river Isar
The Isar () is a river in Austria and in Bavaria, Germany. Its source is in the Karwendel mountain range of the Alps. The Isar river enters Germany near Mittenwald and flows through Krün, Wallgau, Bad Tölz, Munich, and Landshut before reaching ...
.
Works
Before his execution, Keitel published his memoirs, which were titled in English as ''In the Service of the Reich''. It was later re-edited byWalter Görlitz
Walter may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Walter (name), including a list of people and fictional and mythical characters with the given name or surname
* Little Walter, American blues harmonica player Marion Walter Jacobs (1930–19 ...
as ''The Memoirs of Field-Marshal Keitel'' (). Another work by Keitel later published in English was ''Questionnaire on the Ardennes Offensive''.
Family
Keitel was the uncle of Katherine "Kitty" Oppenheimer, wife of thephysicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
J. Robert Oppenheimer
J. Robert Oppenheimer (born Julius Robert Oppenheimer ; April 22, 1904 – February 18, 1967) was an American theoretical physics, theoretical physicist who served as the director of the Manhattan Project's Los Alamos Laboratory during World ...
, the director of the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada.
From 1942 to 1946, the ...
's Los Alamos Laboratory
The Los Alamos Laboratory, also known as Project Y, was a secret scientific laboratory established by the Manhattan Project and overseen by the University of California during World War II. It was operated in partnership with the United State ...
, where the first atomic bomb
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear expl ...
s were developed.
Legacy
Keitel was frequently depicted inWorld War II films
This is a list of fictional feature films or miniseries which feature events of World War II in the narrative.
There is a separate list of List of World War II TV series, World War II TV series.
Criteria
* The film or miniseries must be concer ...
, such as by Dieter Mann
Dieter Mann (20 June 1941 – 3 February 2022) was a German actor, director, university professor, and radio personality. In his career, he acted in several theater productions and in over 140 film and television productions. Between 1984 and 19 ...
in ''Downfall'' (2004). Notably, East German actor Gerd Michael Henneberg
Gerd Michael Henneberg (14 July 1922 – 1 January 2011) was a German actor and theater director.
Biography
Gerd Henneberg's father, Richard, was a theater director. After the young Henneberg took private acting classes, he debuted on stage at a ...
repeatedly reprised his role as Keitel in several Soviet-East German co-productions directed by Yuri Ozerov in the 1970s and 1980s, such as ''Soldiers of Freedom
''Soldiers of Freedom'' () is a four-part 1977 film epic directed by Yuri Ozerov and starring Mikhail Ulyanov, Yevgeny Matveyev, Vasily Lanovoy. It is a World War II historical drama and the sequel to 1970-71's '' Liberation''.
Plot
The film ...
'' (1977), ''Battle of Moscow'' (1985) and ''Stalingrad'' (1990). He is also briefly depicted in the movie ''Valkyrie
In Norse mythology, a valkyrie ( or ; from ) is one of a host of female figures who guide souls of the dead to the god Odin's hall Valhalla. There, the deceased warriors become ('single fighters' or 'once fighters').Orchard (1997:36) and Li ...
'' (2008) as played by Kenneth Cranham
Kenneth Cranham (born 12 December 1944) is a British film, television, radio and stage actor. His most notable screen roles were in '' Oliver!'' (1968), '' Up Pompeii'' (1971), '' Hellbound: Hellraiser II'' (1988), '' Chocolat'' (1988), '' Layer ...
.
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Keitel, Wilhelm 1882 births 1946 deaths 19th-century German people 20th-century Freikorps personnel 20th-century German writers Articles containing video clips Executed German mass murderers Executed military leaders Executed people from Lower Saxony German Army personnel of World War I German Army World War II field marshals 20th-century German memoirists German Christians German people convicted of crimes against humanity German people convicted of the international crime of aggression German people convicted of war crimes Holocaust perpetrators Major generals of the Reichswehr Military personnel from Lower Saxony Ministers of the Reichswehr People executed by the International Military Tribunal in Nuremberg People executed for crimes against humanity People from Bad Gandersheim Prussian Army personnel Recipients of the clasp to the Iron Cross, 1st class Recipients of the Hanseatic Cross (Bremen) Recipients of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross