|
Ministry Of The Reichswehr
The Ministry of the Reichswehr () was the defence ministry of Germany from 1919 to 1938 during the Weimar Republic and early Nazi Germany periods. It was responsible for the '' Reichswehr'' under the leadership of the Minister of Defence and based in the Bendlerblock building in Berlin. The Ministry of the Reichswehr was formed from the Prussian Ministry of War in the aftermath of World War I as part of a centralisation of the armed forces to Berlin from the states of Germany. Its longest serving Weimar-era Defence Ministers were the civilian Otto Gessler (almost 8 years) and General Wilhelm Groener (4 years). It was renamed the Reich Ministry of War in 1935 under the Nazis and led by General Werner von Blomberg as the Minister of War. It was abolished in 1938 and replaced with the '' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' (Armed Forces High Command) under the direct command of Adolf Hitler. History Formation On 6 March 1919, the Weimar National Assembly – Germany's post-war i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
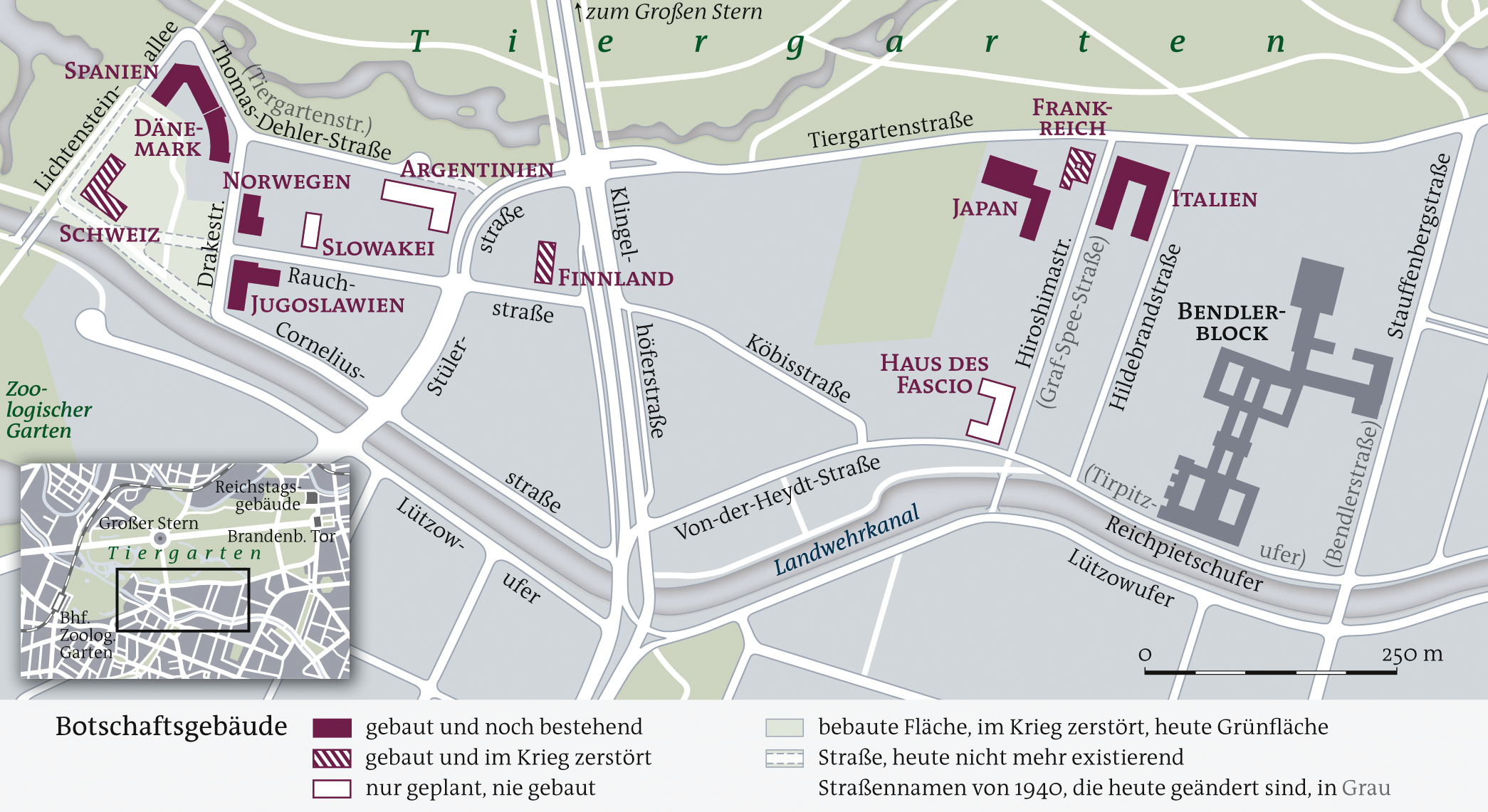
Bendlerblock
The Bendlerblock () is a building complex in the Tiergarten (Berlin), Tiergarten district of Berlin, Germany, located on Stauffenbergstraße (formerly named ''Bendlerstraße''). Erected in 1914 as headquarters of several Imperial German Navy (''Kaiserliche Marine'') offices, it served the Ministry of the Reichswehr after World War I. Significantly enlarged under Nazi Germany, Nazi rule, it was used by several departments of the ''Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' (OKW) from 1938, especially the ''Oberkommando des Heeres'' and the ''Abwehr'' intelligence agency. The building is notable as the headquarters of a German Resistance to Nazism, resistance band of Wehrmacht officers who staged the 20 July plot against Adolf Hitler in 1944. As the leaders of the conspiracy were summarily shot in the courtyard, the Bendlerblock also includes the Memorial to the German Resistance. Since 1993, the building complex has served as a secondary seat of the German Federal Ministry of Defence (Germany), F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Of The Weimar Republic
The states of the Weimar Republic were the first-level administrative divisions and constituent states of the Weimar Republic. The states were established in 1918–1920 following the German Empire's defeat in World War I and the territorial losses that came with it. They were based on the 22 states and three city-states of the German Empire. During the revolution of 1918–1919, the states abolished their local monarchies and adopted republican constitutions. Several attempts were made to reorganize the states under the Weimar Republic, particularly because of Prussia's disproportionately large size and influence, but the attempts were unsuccessful. The one significant change was the formation of Thuringia from a number of smaller states. The Weimar Constitution created a federal republic with certain basic powers reserved for the federal government, some powers shared between the central government and the states, and the remainder in the hands of the states. The federal gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Von Trotha
Adolf von Trotha (1 March 1868 – 11 October 1940) was a German admiral in the '' Kaiserliche Marine''. After the German revolution he briefly served as the first ''Chef der Admiralität'', which replaced the imperial '' Reichsmarineamt''. After supporting the Kapp-Lüttwitz Putsch of March 1920 he resigned his post. He later held several political and maritime posts in the Third Reich. Family Trotha was born 1 March 1868 at Koblenz, at the time part of the Rhine Province of the Kingdom of Prussia. Trotha was the third son of Karl von Trotha (1834–1870), who was killed in the Franco-Prussian War, when his son was only two years old. Trotha married Anna von Veltheim (15 January 1877 – 8 August 1964) on 4 June 1902, the daughter of Fritz von Veltheim and Elizabeth von Krosigk. Naval career Trotha entered the Imperial Navy in 1886 as an officer candidate and was promoted to '' Leutnant zur See'' in 1891. He served as a commander of the torpedo boat ''D3'' and as a navigatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Minister Of War
The Prussian Ministry of War was the highest state authority of the Prussian Army, Royal Prussian Army and was responsible for the central administration of the army of the Kingdom of Prussia and, later, the Imperial German Army. The ministry existed from 1808 through the establishment of the German Empire and was dissolved in 1919, being succeeded by the Ministry of the Reichswehr. Formation The Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian Ministry of War was gradually established between 1808 and 1809 as part of a series of reforms initiated by the Military Reorganization Commission created after the disastrous Treaties of Tilsit. The War Ministry was to help bring the Prussian Army, Army under constitutional review, and, along with the German General Staff, General Staff, systematize the conduct of warfare. Gerhard von Scharnhorst, the most prominent and influential of the reformers, served as acting Minister of War from roughly 1808 until 1810 (he was also concurrently German General Staff# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walther Reinhardt
Walther Gustav Reinhardt (; 24 March 1872 in Stuttgart – 8 August 1930 in Berlin) was a German officer who served as the last Prussian Minister of War and the first head of the army command (''Chef der Heeresleitung'') within the newly created Ministry of the Reichswehr of the Weimar Republic. During the Kapp Putsch of 1920, Reinhardt remained loyal to the elected government and was one of the few senior officers of the Reichswehr willing to order troops to fire at the revolting units. Early life and family Reinhardt was born on 24 March 1872 in Stuttgart as the son of August von Reinhardt (1827–1907), a member of the ''Personenadel'' (lifelong, non-hereditary nobility) and officer of the Kingdom of Württemberg (Generalmajor and Commander of the 120th Infantry Regiment), and Emilie Reinhardt, née von Wiedenmann. His brother Ernst (1870-1939) also became an officer (''Generalleutnant'') and was the father of Hellmuth Reinhardt (1900–89, Generalmajor). In 1900, Walther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Ebert
Friedrich Ebert (; 4 February 187128 February 1925) was a German politician of the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD) who served as the first President of Germany (1919–1945), president of Germany from 1919 until his death in 1925. Ebert was elected leader of the SPD on the death in 1913 of August Bebel. In 1914, shortly after he assumed leadership, the party became deeply divided over Ebert's support of war loans to finance the German war effort in World War I. A moderate social democrat, Ebert was in favour of the ''Burgfriedenspolitik, Burgfrieden'', a political policy that sought to suppress discord over domestic issues among political parties in order to concentrate all forces in society on the conclusion of the war effort. He tried to isolate those in the party opposed to war and advocated a split. Ebert was a pivotal figure in the German revolution of 1918–1919. When Germany became a republic at the end of World War I, he became its firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Noske
Gustav Noske (9 July 1868 – 30 November 1946) was a German politician of the Social Democratic Party (SPD). He served as the first Minister of Defence (''Reichswehrminister'') of the Weimar Republic between 1919 and 1920. Noske was known for using army and paramilitary forces to suppress the socialist/communist uprisings of 1919. Early life Noske was born on 9 July 1868 in Brandenburg an der Havel, Prussia. He was the son of the weaver Karl Noske (born 1838) and the manual labourer Emma Noske (née Herwig, born 1843). From 1874 to 1882, he went to primary and secondary school (''Volks-'' and ''Bürgerschule''). In 1882 to 1886 he was apprenticed as a basket maker at the ''Reichsteinische Kinderwagenfabrik'' and travelled to Halle, Frankfurt, Amsterdam and Liegnitz as a journeyman. In 1884, Noske joined the Social Democratic Party (SPD) and he also became a union member. In 1892, Noske was elected chairman of the Brandenburg SPD. He married Martha Thiel (1872–1949) at Brande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reich Law
thumbnail, upright=1.0, German penal code (from pre II. World War but edited after) A Reich law is a law which is made for an entire realm, and decided on at the national level. In modern Germany such laws are called federal laws. An overview of Germany Up until 1806 Reich laws were made by the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire. The right to propose such laws was exclusive to the Holy Roman Emperor and the Prince-elector. Every proposal was firstly discussed by the Prince-electorate and after their appraisal it got passed onto the imperial Council of princes after which it reached the free imperial cities. For the law to officially come into effect they had to be approved by the Emperor. In 1871 the German Reich which developed out of the North German Confederation of 1867 as a Nation state. The laws of the confederation were taken over and from then on called ''Reich laws''. First, the Reichstag of the German Empire decided on the laws, which later had to be reviewed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Germany (1919–1945)
The president of Germany (, ) was the head of state under the Weimar Constitution, which was officially in force from 1919 to 1945, encompassing the periods of the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany. The Weimar constitution created a semi-presidential system in which power was divided between president, Cabinet (government), cabinet and Reichstag (Weimar Republic), parliament. The president was directly elected under universal adult suffrage for a seven-year term, although Germany's first president, Friedrich Ebert, was elected by the Weimar National Assembly rather than the people. The intention of the framers of the constitution was that the president would rule in conjunction with the Reichstag (Weimar Republic), Reichstag (legislature) and that his extensive emergency powers would be exercised only in extraordinary circumstances. The political instability of the Weimar period and an increasingly severe factionalism in the legislature, however, led to the president occupying a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weimar National Assembly
The Weimar National Assembly (German: ), officially the German National Constitutional Assembly (), was the popularly elected constitutional convention and de facto parliament of Germany from 6 February 1919 to 21 May 1920. As part of its duties as the interim government, it debated and reluctantly approved the Treaty of Versailles that codified the peace terms between Germany and the victorious Allies of World War I. The Assembly drew up and approved the Weimar Constitution that was in force from 1919 to 1933 (and technically until the end of Nazi rule in 1945). With its work completed, the National Assembly was dissolved on 21 May 1920. Following the election of 6 June 1920, the new Reichstag met for the first time on 24 June 1920, taking the place of the Assembly. Because the National Assembly convened in Weimar rather than in politically restive Berlin, the period in German history became known as the Weimar Republic. Background At the end of World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (20 April 1889 – 30 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was the dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his suicide in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming Chancellor of Germany#Nazi Germany (1933–1945), the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of in 1934. His invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 marked the start of the Second World War. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of Holocaust victims, about six million Jews and millions of other victims. Hitler was born in Braunau am Inn in Austria-Hungary and moved to German Empire, Germany in 1913. He was decorated during his service in the German Army in the First World War, receiving the Iron Cross. In 1919 he joined the German Workers' Party (DAP), the precursor of the Nazi Party, and in 1921 was app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Von Blomberg
Werner Eduard Fritz von Blomberg (2 September 1878 – 13 March 1946) was a German general and politician who served as the first Minister of War in Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1938. Blomberg had served as Chief of the ''Truppenamt'', equivalent to the German General Staff, during the Weimar Republic from 1927 to 1929. Blomberg served on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front during World War I and rose through the ranks of the ''Reichswehr'' until he was appointed chief of the ''Truppenamt''. Despite being dismissed from the ''Truppenamt'', he was later appointed Defence Minister by President Paul von Hindenburg in January 1933. Following the Nazis' rise to power in Germany, Blomberg was named Minister of War and Commander-in-Chief of the German Armed Forces. In this capacity, he played a central role in Germany's rearmament as well as purging the military of dissidents to the new regime. However, as Blomberg grew increasingly critical of the Nazis' foreign policy, he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |