Khas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Khas peoples or Khas Tribes, (; ) popularly known as Khashiya are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group native to the Himalayan region of the
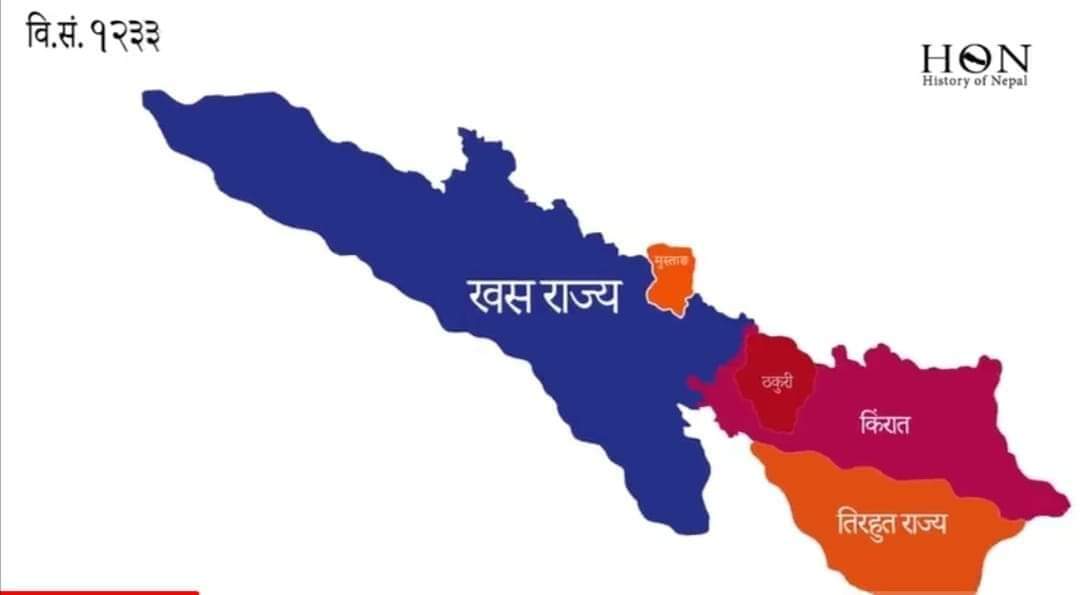
 Until the 19th century, the Gorkhali referred to their country as ''Khas Desh'' (Khas country). As they annexed the various neighboring countries (such as Nepal or Newa of the Newar people) to the Gorkha kingdom, the terms such as ''Khas'' and ''Newar'' ceased to be used as the names of countries. The 1854 legal code (''Muluki Ain''), promulgated by the Nepali Prime Minister Jung Bahadur Rana, himself a Khas, no longer referred to ''Khas'' as a country, rather as a '' jāt'' (species or community) within the Gorkha kingdom.
Until the 19th century, the Gorkhali referred to their country as ''Khas Desh'' (Khas country). As they annexed the various neighboring countries (such as Nepal or Newa of the Newar people) to the Gorkha kingdom, the terms such as ''Khas'' and ''Newar'' ceased to be used as the names of countries. The 1854 legal code (''Muluki Ain''), promulgated by the Nepali Prime Minister Jung Bahadur Rana, himself a Khas, no longer referred to ''Khas'' as a country, rather as a '' jāt'' (species or community) within the Gorkha kingdom.
 The Shah dynasty of the Gorkha Kingdom, as well as the later prime-ministerial Rana dynasty, spoke the Khas language (now called the Nepali language). However, they claimed to be Rajputs of western Indian origin, rather than the native Khas Kshatriyas. Since outside Nepal, the Khas social status was seen as inferior to that of the Rajputs, the rulers started describing themselves as natives of the Hill country, rather than that of the Khas country. Most people, however, considered the terms ''Khas'' and ''Parbatiya'' (''Pahari/Pahadi'' or Hill people) as synonymous.
Jung Bahadur also re-labeled the Khas ''jāt'' as Chhetri in present-day Nepal. Originally, the
The Shah dynasty of the Gorkha Kingdom, as well as the later prime-ministerial Rana dynasty, spoke the Khas language (now called the Nepali language). However, they claimed to be Rajputs of western Indian origin, rather than the native Khas Kshatriyas. Since outside Nepal, the Khas social status was seen as inferior to that of the Rajputs, the rulers started describing themselves as natives of the Hill country, rather than that of the Khas country. Most people, however, considered the terms ''Khas'' and ''Parbatiya'' (''Pahari/Pahadi'' or Hill people) as synonymous.
Jung Bahadur also re-labeled the Khas ''jāt'' as Chhetri in present-day Nepal. Originally, the
 Modern-day Khas people are referred to as Hill Brahmin ( Bahun), Hill Kshatriya ( Thakuri/ Chhetri) and Hill Dalit. Further, historian Pokharel adds the Gharti, Damai,
Modern-day Khas people are referred to as Hill Brahmin ( Bahun), Hill Kshatriya ( Thakuri/ Chhetri) and Hill Dalit. Further, historian Pokharel adds the Gharti, Damai,
 The Khas people of Nepal originally referred to their language as '' Khas kurā'' (Khas speech), which was also known as ''Parbatiya'' (the language of the hill country). The Newar people used the term ''Khayan Bhaya'', ''Parbatiya'' and ''Gorkhali'' as a name for this language, Gorkhalis themselves started using this term to refer to their language at a later stage. In an attempt to disassociate himself with his Khas past, the Rana prime minister Jung Bahadur decreed that the term Gorkhali be used instead of ''Khas kurā'' to describe the language. Meanwhile, the
The Khas people of Nepal originally referred to their language as '' Khas kurā'' (Khas speech), which was also known as ''Parbatiya'' (the language of the hill country). The Newar people used the term ''Khayan Bhaya'', ''Parbatiya'' and ''Gorkhali'' as a name for this language, Gorkhalis themselves started using this term to refer to their language at a later stage. In an attempt to disassociate himself with his Khas past, the Rana prime minister Jung Bahadur decreed that the term Gorkhali be used instead of ''Khas kurā'' to describe the language. Meanwhile, the

Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, in what is now the South Asian country of Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, as well as the Indian states of Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; Sanskrit: ''himācāl prādes;'' "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a States and union territories of India, state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen Indian Himalayan ...
, West Bengal, Assam and Sikkim. Khas consists of many subtribes like Kshetri, Thakuri, Bahun and Sanyasis and all spread across the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
.
According to the Constitution of Nepal, Bahun, Kshetris, Thakuris, and Sanyasis (Dashnami) who are citizens of Nepal should be considered as "Khas Arya" for electoral purposes.
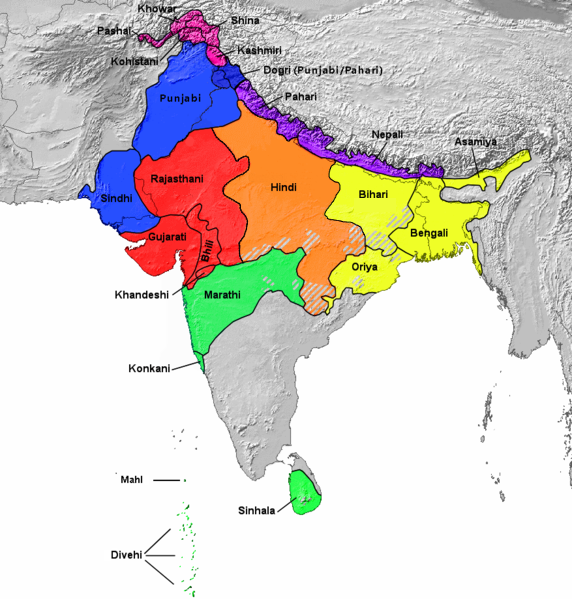
Historically, Khas were the speakers of an ancient ''Khas language'' from the Indo-Aryan language family and the earliest recorded speakers of the Western Pahari languages. The large portion of the Indo-Aryan speakers throughout lower Himalayas were the Masto people. An intrusion of this tribe from the Western and Northwestern Himalayas into Central Himalayas is substantiated by the early linguistic evidences related to the Nepali language
Nepali (; , ), or ''Gorkhali'' is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Himalayas region of South Asia. It is the official and most widely spoken Languages of Nepal, language of Nepal, where it also serves as a ''lingua fr ...
. They were also known as Parbatiyas/Parbates and are currently known as Paharis/Pahadis. (literally, "from the hills"). They were also referred to as Yartse in Tibet and are also known as Khasan by Bhotia people. The term ''Khas'' has now become obsolete, as the Khas people have adopted communal identities because of the negative stereotypes associated with the term ''Khas''. In Nepal the native speaker of Nepali language
Nepali (; , ), or ''Gorkhali'' is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Himalayas region of South Asia. It is the official and most widely spoken Languages of Nepal, language of Nepal, where it also serves as a ''lingua fr ...
are known as Khas people.
Origin
Indo-Aryan origin theories
They have been connected to the Khasas mentioned in the ancient Hindu literature. Irish linguist Sir G.A. Grierson asserted that "..the great mass of the Aryan speaking population of the lower Himalaya from Kashmir to Darjeeling is inhabited by tribes descended from the ancient Khasas of Mahabharata." Historian Bal Krishna Sharma and Dor Bahadur Bista speculates that the Khas people were of Indo-European origin. Historian Baburam Acharya speculates that Khas are a sub-clan of Aida, an "Aryas” clan that originated at Idavritt (modern day Kashmir toNepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
). Khas were living in the ''Idavaritt'' in the 3rd millennium BCE. and the original meaning of the term ''Khas'' was Raja
Raja (; from , IAST ') is a noble or royal Sanskrit title historically used by some Indian subcontinent, Indian rulers and monarchs and highest-ranking nobles. The title was historically used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
T ...
or Kshatriya (Yoddha). He further speculates that Kashmir has been named from its local residents Khas as Khasmir. In the 2nd millennium B.C.E., one group of Khas migrated towards Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
while the other group migrated east of Sutlej river settling only in the hill regions up to Bheri River. Historian Balkrishna Pokhrel contends that Khas were not the Vedic Aryans but Aryans of the latter periods like the Gurjara, Darada, Shaka, and Pallava
The Pallava dynasty existed from 275 CE to 897 CE, ruling a significant portion of South India, the Deccan, also known as Tondaimandalam. The Pallavas played a crucial role in shaping in particular southern Indian history and heritage. The ...
. He further asserts that post-Vedic Aryans were akin to Vedic Aryans in terms of language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
and culture. Irish linguist Sir George Abraham Grierson asserted that the Khasas were one of the warrior "Kshatriya tribe of Aryan origin" with linguistic connections to both Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
and Iranian languages
The Iranian languages, also called the Iranic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian langu ...
, who lost claim to Vedichood due to non-observance of Vedic rules. Roman geographer Pliny The Elder described the ancient Khasas/Khasiras (referred as 'Casiri') as one of the Indian ethnicity.
Saka origin theories
Historian Rahul Sankrityayan proposes the origin of the Khasha tribe from the Shaka tribe and further identifies Khashas and Shakas to have been two different waves of the same race. The Shakas were in Indian subcontinent before the first century BCE while the Khashas spread over theHimalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
and extensively populated the mountainous regions of Uttarakhand and the later waves of Shakas got diffused into them. Historian Omchand Handa contends that the "sun worship" among Khashas is a Shaka legacy and perhaps the standing Surya images with long boots which was commonly found at the Khasha belt of Himalaya. Some examples of it are the Bara-Aditya at Katarmal and Surya images of Baijnath, Bageshwar and Dwarahat.
History
Medieval history in Nepal and Uttarakhand
Khasas are believed to have arrived in the western reaches of Nepal at the beginning of first-millennium B.C. or middle of first-millennium A.D. from the north-west. The earliest linguistic evidences related toNepali language
Nepali (; , ), or ''Gorkhali'' is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Himalayas region of South Asia. It is the official and most widely spoken Languages of Nepal, language of Nepal, where it also serves as a ''lingua fr ...
also substantiates the linguistic intrusion of an Indo-Aryan speaking Khasa tribe from the West or Northwest Himalayas into Central Himalayas at the present day regions of Western Nepal. It is likely that they absorbed people from different ethnic groups during this immigration. They had extensively populated the mountainous regions of Uttarakhand and they had entirely dominated the inner Himalayan belt up to Nepal. Previously, Khashas had strongly established themselves from Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
to Nepal from ancient period and as per internal evidences, they managed the village level theocratic republics like Gram-Rajya and Mandals under various local clans and identities.
The ruling Katyuri dynasty (700-1065 CE) of Kumaon who were of Khas origin, was one of the ruling houses of Joshimath that claimed the sovereignty over other Gram Rajyas of the entire territory. The Katyuris ruled from Joshimath in the Alaknanda
The Alaknanda is a Himalayan river in the Indian state of Uttarakhand and one of the two headstreams of the Ganges, the major river of Northern India and a river considered holy in Hinduism. In hydrology, the Alaknanda is considered the headstr ...
Valley and later they shifted their capital to Baijnath. They have also been connected to the medieval Khasa Malla kingdom. The Khasa kings of West Nepal-Uttarakhand formed the famous Malla Kingdom, which ruled Humla from the eleventh century before collapsing and splintering into local chiefdoms during the fourteenth century. In the initial phase, majority of Khas people became Brahmins and others became Kshatriyas.
History in Kashmir
The ruling Lohara dynasty (1003-1320 CE) of Kashmir were from the Khas tribe as per the 12th century text '' Rajatarangini'' written by the local Kashmiri Pandit historian Kalhana. Furthermore, Rajatarangini describes the rulers of Rajapuri (modern Rajauri) as the "lord of the Khasas". The Khasa chiefs of Rajapuri freely intermarried with Kshatriya rulers of Kashmir while the Khasa chief of Lohara, Simharaja, married a daughter of Shahi Kings of Kabul. The descendants of the royal family of Rajauri later became Muslim Rajput chiefs and they retained the rulership of the territory till 19th century. The inhabitants of Karnah region in northwestern Kashmir, were Khasas and they were represented by the modern Bomba (tribe) who independently ruled the northwestern Kashmir till the Sikh conquest of Kashmir. There was also an independent Khasa lord at the castle located in the foot of Banahal Pass in the territory of Visalata and Dengapala ("Thakkura Dengapala") was a Khasa chief at the banks of Chandrabhaga (modern Chenab river).Modern history in Nepal
 Until the 19th century, the Gorkhali referred to their country as ''Khas Desh'' (Khas country). As they annexed the various neighboring countries (such as Nepal or Newa of the Newar people) to the Gorkha kingdom, the terms such as ''Khas'' and ''Newar'' ceased to be used as the names of countries. The 1854 legal code (''Muluki Ain''), promulgated by the Nepali Prime Minister Jung Bahadur Rana, himself a Khas, no longer referred to ''Khas'' as a country, rather as a '' jāt'' (species or community) within the Gorkha kingdom.
Until the 19th century, the Gorkhali referred to their country as ''Khas Desh'' (Khas country). As they annexed the various neighboring countries (such as Nepal or Newa of the Newar people) to the Gorkha kingdom, the terms such as ''Khas'' and ''Newar'' ceased to be used as the names of countries. The 1854 legal code (''Muluki Ain''), promulgated by the Nepali Prime Minister Jung Bahadur Rana, himself a Khas, no longer referred to ''Khas'' as a country, rather as a '' jāt'' (species or community) within the Gorkha kingdom.
 The Shah dynasty of the Gorkha Kingdom, as well as the later prime-ministerial Rana dynasty, spoke the Khas language (now called the Nepali language). However, they claimed to be Rajputs of western Indian origin, rather than the native Khas Kshatriyas. Since outside Nepal, the Khas social status was seen as inferior to that of the Rajputs, the rulers started describing themselves as natives of the Hill country, rather than that of the Khas country. Most people, however, considered the terms ''Khas'' and ''Parbatiya'' (''Pahari/Pahadi'' or Hill people) as synonymous.
Jung Bahadur also re-labeled the Khas ''jāt'' as Chhetri in present-day Nepal. Originally, the
The Shah dynasty of the Gorkha Kingdom, as well as the later prime-ministerial Rana dynasty, spoke the Khas language (now called the Nepali language). However, they claimed to be Rajputs of western Indian origin, rather than the native Khas Kshatriyas. Since outside Nepal, the Khas social status was seen as inferior to that of the Rajputs, the rulers started describing themselves as natives of the Hill country, rather than that of the Khas country. Most people, however, considered the terms ''Khas'' and ''Parbatiya'' (''Pahari/Pahadi'' or Hill people) as synonymous.
Jung Bahadur also re-labeled the Khas ''jāt'' as Chhetri in present-day Nepal. Originally, the Brahmin
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
immigrants from the plains considered the Khas as low-caste because of the latter's neglect of high-caste taboos (such as alcohol abstinence). The upper-class Khas people commissioned the Bahun (Brahmin) priests to initiate them into the high-caste Chhetri order and adopted high-caste manners. Other Khas families who could not afford to (or did not care to) pay the Bahun priests also attempted to assume the Chhetri status but were not recognized as such by others. They are now called Matwali (alcohol-drinker Khas) Chhetris. Because of the adoption of the ''Chhetri'' identity, the term ''Khas'' is rapidly becoming obsolete. According to Dor Bahadur Bista (1991), "the Khas have vanished from the ethnographic map of Nepal".
Modern
Nepal
 Modern-day Khas people are referred to as Hill Brahmin ( Bahun), Hill Kshatriya ( Thakuri/ Chhetri) and Hill Dalit. Further, historian Pokharel adds the Gharti, Damai,
Modern-day Khas people are referred to as Hill Brahmin ( Bahun), Hill Kshatriya ( Thakuri/ Chhetri) and Hill Dalit. Further, historian Pokharel adds the Gharti, Damai, Kami
are the Deity, deities, Divinity, divinities, Spirit (supernatural entity), spirits, mythological, spiritual, or natural phenomena that are venerated in the traditional Shinto religion of Japan. ''Kami'' can be elements of the landscape, forc ...
, Sarki, Hudka, Tamote, Gaine and Badi to the Khas communities. In modern times, Khas people are popularly referred by the term "Khas Arya".
India-Pakistan
In Kumaon and Garhwal regions of Uttarakhand in India, too, the term ''Khas'' has become obsolete. The Khas people of Kumaon termed as Kumaoni khash jimdar, after being elevated to the Rajput status by the Chand kings. During Chand rule in Kumaon, Khas and Rajput were differentiated by their sacred thread, Khas were allowed to wear only 3 thread (3 palli)sacred thread whereas Rajput used to wear 6 palli sacred thread.The term Khas is almost obsolete, and people resent being addressed as Khas because of the negative stereotypes associated with this term. Furthermore, the Kanets of Kangra and Garhwal, Khasa of Jaunsar-Bawar and the bulk population of Garhwal and Kumaon (referred as "Khasia") are descended from the Khasas. Generally, the Khas people are referred as Rajputs or Kanets in theHimachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; Sanskrit: ''himācāl prādes;'' "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a States and union territories of India, state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen Indian Himalayan ...
. According to E.T. Atkinson, the Jaunsar-Bawar is the representative Khasiya tract and it
Historian Sir Marc Aurel Stein identified the modern Khakha Rajputs of Azad Kashmir as the descendants of Khasas mentioned in the '' Rajatarangini''. The Khasa tribe in Karnah region in northwestern Kashmir were represented by the modern Bomba (tribe).
Communities
Historian Balkrishna Pokhrel writes the communities or caste in Khas group were hill Bahun, Chhetri, Thakuri, Gharti, Damai,Kami
are the Deity, deities, Divinity, divinities, Spirit (supernatural entity), spirits, mythological, spiritual, or natural phenomena that are venerated in the traditional Shinto religion of Japan. ''Kami'' can be elements of the landscape, forc ...
, Sarki, Hudka, Tamote, Gaine and Sunar, badi, luhar, parki etc . The tribal designation Khas refers to in some contexts only to the alcohol drinker Khas group, i.e. Thakuri and Chhetri, but in other contexts may also include the low status (occupational Khas groups such as Kāmi (blacksmiths), Damāi (tailors), and Sārki (shoemakers and leather workers). Khas people are addressed with the term ''Khayan'' or ''Parbatiya'' or ''Partyā'', ''Parbaté'' meaning hill-dweller by Newars. The hill Khas tribe are in large part associated with the Gorkhali warriors.
Khas people of the Western Himalayas are considered similar to the Khas people of the Garhwal, Kumaon and Nepal. They are generally referred as Rajputs or Kanets in the Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; Sanskrit: ''himācāl prādes;'' "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a States and union territories of India, state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen Indian Himalayan ...
. The Khasas of Jaunsar-Bawar who are represented by the Jaunsari Rajputs and Brahmins) practiced polyandrous marriages.
Culture and religion
Languages
Irish Linguist George Abraham Grierson in hisLinguistic Survey of India
The Linguistic Survey of India (LSI) is a comprehensive survey of the languages of British India, describing 364 languages and dialects. The Survey was first proposed by George Abraham Grierson, a member of the Indian Civil Service and a lingu ...
stated that the Khas tribe were the earliest recorded speakers of the Western Pahari languages. He further asserted that the Khas people made the bulk population of the Indo-Aryan speakers throughout the lower Himalaya from Kashmir to Darjeeling.
 The Khas people of Nepal originally referred to their language as '' Khas kurā'' (Khas speech), which was also known as ''Parbatiya'' (the language of the hill country). The Newar people used the term ''Khayan Bhaya'', ''Parbatiya'' and ''Gorkhali'' as a name for this language, Gorkhalis themselves started using this term to refer to their language at a later stage. In an attempt to disassociate himself with his Khas past, the Rana prime minister Jung Bahadur decreed that the term Gorkhali be used instead of ''Khas kurā'' to describe the language. Meanwhile, the
The Khas people of Nepal originally referred to their language as '' Khas kurā'' (Khas speech), which was also known as ''Parbatiya'' (the language of the hill country). The Newar people used the term ''Khayan Bhaya'', ''Parbatiya'' and ''Gorkhali'' as a name for this language, Gorkhalis themselves started using this term to refer to their language at a later stage. In an attempt to disassociate himself with his Khas past, the Rana prime minister Jung Bahadur decreed that the term Gorkhali be used instead of ''Khas kurā'' to describe the language. Meanwhile, the British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
n administrators had started using the term ''Nepal'' (after Newar) to refer to the Gorkha kingdom. In the 1930s, the Gorkha government also adopted this term to describe their country. Subsequently, the Khas language also came to be known as ''Nepali language''. It has become a national language of Nepal and lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
among the majority of population of Northern region of West Bengal, Sikkim and Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ...
. Historian Balkrishna Pokhrel contends that the Khas language of Nepal belonged to neither the Iranian
Iranian () may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Iran
** Iranian diaspora, Iranians living outside Iran
** Iranian architecture, architecture of Iran and parts of the rest of West Asia
** Iranian cuisine, cooking traditions and practic ...
language family, nor the Indian languages, but to the mid Indo-Iranian languages.
Music
Deuda song and folk dance performed on the occasion of various festivals in the Sudurpashchim and Karnali provinces ofNepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
.
Religion
The majority of Khas professHinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
; some of them also follow Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
and some were also converted to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
.
The Khas people also had their own sect of Shaivism known as Masto religion where 12 Masto gods were worshipped. These gods were said to be sons of Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
. Masto worship was prevalent throughout all of the Western Himalayan region.
Notable people

Medieval Khas families and dynasties
* Katyuri kings * Lohara dynasty * Khas Malla rulers * Gurkha Kingdom * Vanshala Kingdom * VishlataModern Khas
* Bir Bhadra Thapa * Sanukaji Amar Singh Thapa * Bhimsen Thapa * Jung Bahadur Rana * Kalu Pande (Kaji) * BP Koirala * Bhanubhakta Acharya * Prithvi Narayan Shah * Shivaram Singh Basnyat (Badabir senapanti) * Kehar Singh Basnyat * Damodar Pandey * Abhiman Singh Basnyat * Kirtiman Singh Basnyat * Bakhtawar Singh Basnyat * Dhokal Singh Basnyat * Rana Jang Pande * Kunwar Inderjit Singh * Subarna Shamsher Rana * Sher Bahadur Thapa * Surya Bahadur Thapa * Jhalak Man GandarbhaSee also
*Nepali language
Nepali (; , ), or ''Gorkhali'' is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Himalayas region of South Asia. It is the official and most widely spoken Languages of Nepal, language of Nepal, where it also serves as a ''lingua fr ...
* Kumaoni language
* Garhwali language
* Indo-Aryan migrations
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
{{Ethnic groups in Nepal Indo-Aryan peoples Ethnic groups in India Himalayan peoples Indigenous peoples of Nepal Ethnic groups in South Asia