Joseph Jonas (Cincinnati) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of the Jews in Cincinnati occupies a prominent place in the development of Jewish secular and religious life in the United States.
The history of the Jews in Cincinnati occupies a prominent place in the development of Jewish secular and religious life in the United States.
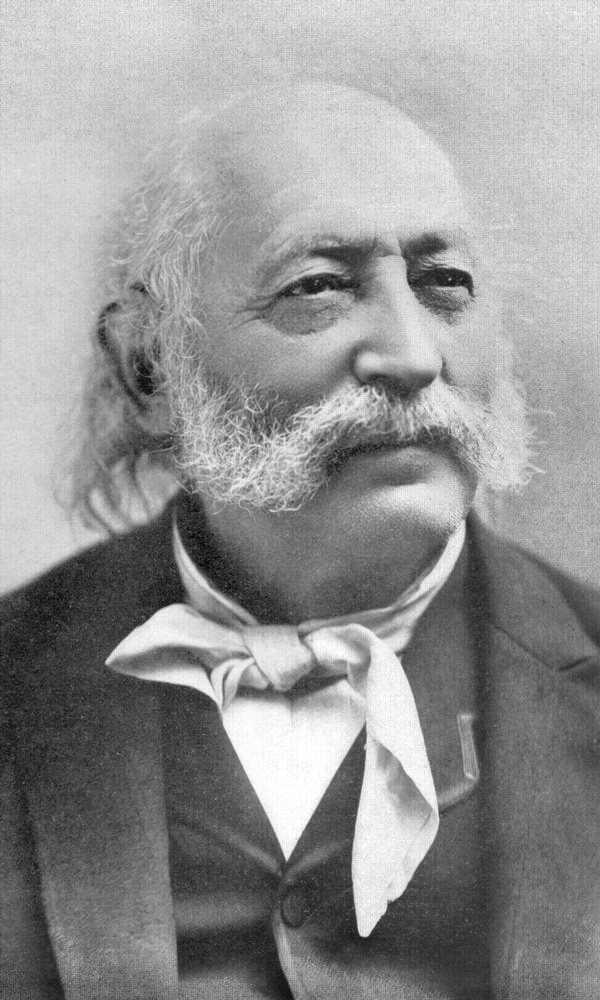 In April 1854,
In April 1854,
“Bloch & Company: Pioneer Jewish Publishing House in the West”
, Jewish Book Annual, Vol. 52, pp.110-130 (1994-95). In 1951, the UAHC (now called the Union for Reform Judaism) moved its headquarters to the demographic center of American Jewry in

 In 1866, the congregation built the architecturally notable Plum Street Temple, as the Isaac M. Wise Temple. Dr. Lilienthal died in office April 5, 1882. He was succeeded as rabbi of the Congregation B'ne Israel by Raphael Benjamin, who served till November 1888, when
In 1866, the congregation built the architecturally notable Plum Street Temple, as the Isaac M. Wise Temple. Dr. Lilienthal died in office April 5, 1882. He was succeeded as rabbi of the Congregation B'ne Israel by Raphael Benjamin, who served till November 1888, when
Hidden Jewish CincinnatiJewish Federation of CincinnatiDavid's Voice - The Voice of Cincinnati's Jewish CommunityThe Jewish Community of Cincinnati
''Die Deborah''
is a digitized periodical at the
 The history of the Jews in Cincinnati occupies a prominent place in the development of Jewish secular and religious life in the United States.
The history of the Jews in Cincinnati occupies a prominent place in the development of Jewish secular and religious life in the United States. Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...
is not only the oldest Jew
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly inte ...
ish community west of the Allegheny Mountains
The Allegheny Mountain Range ( ) — also spelled Alleghany or Allegany, less formally the Alleghenies — is part of the vast Appalachian Mountain Range of the Eastern United States and Canada. Historically it represented a significant barr ...
but has also been an institutional center of American Reform Judaism
Reform Judaism, also known as Liberal Judaism or Progressive Judaism, is a major Jewish religious movements, Jewish denomination that emphasizes the evolving nature of Judaism, the superiority of its Jewish ethics, ethical aspects to its ceremo ...
for more than a century. '' The Israelite'', the oldest American Jewish newspaper still (2019) being published, began publication in Cincinnati in 1854.
19th century
Arrival of British Jews
The first known Jew to settle in Cincinnati wasJoseph Jonas
Joseph Jonas (1845 – 22 August 1921) was the German-born Lord Mayor of Sheffield, England in 1904–05.
Background
Jonas was born in Bingen am Rhein, in the Grand Duchy of Hesse in 1845, and became a naturalized British citizen in 1876. (tra ...
, an English emigrant who arrived in the city via Philadelphia in 1817. Jonas, a young man, decided to leave his home in Exeter
Exeter ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and the county town of Devon in South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter w ...
, England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, with the avowed intention of settling in Cincinnati. Friends in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
originally endeavored to dissuade him from going to a place so isolated from all association with his coreligionists. However, Jonas reassured them that he would succeed. For the first two years, he was the only Jew in the Midwestern town.
In 1819, Jonas was joined by three others, Lewis Cohen of London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, Barnet Levi of Liverpool
Liverpool is a port City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. It is situated on the eastern side of the River Mersey, Mersey Estuary, near the Irish Sea, north-west of London. With a population ...
, and Jonas Levy of Exeter. On the High Holidays
In Judaism, the High Holy Days, also known as High Holidays or Days of Awe (Yamim Noraim; , ''Yāmīm Nōrāʾīm'') consist of:
#strictly, the holidays of Rosh Hashanah ("Jewish New Year") and Yom Kippur ("Day of Atonement");
#by extension, th ...
in the autumn of 1819, these four men, together with David Israel Johnson of Brookville, Indiana
Brookville is a town in Brookville Township, Franklin County, Indiana, United States. The town is the county seat of and the largest community entirely within Franklin County. The population was 2,596 at the 2010 census.
History
Brookville was ...
(a frontier trading-station), conducted the first Jewish service west of the Appalachians. Similar services were held for the next three years. Newcomers continued to arrive, the early settlers being mostly Jews from England.
The first Jewish child born in Cincinnati, Frederick A. Johnson (June 2, 1821), was the son of the above-mentioned David Israel Johnson and his wife, Eliza. This couple, also English, had removed to Cincinnati from Brookville, where they had first settled. The first couple to be married
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognised union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children (if any), and b ...
were Morris Symonds and Rebekah Hyams, whose wedding was celebrated on September 15, 1824. The first death in the community was that of Benjamin Leib (or Lape) in 1821. This man, who had not been known as a Jew, when he felt death to be approaching, asked that three of the Jewish residents of the town be called. He disclosed to them that he was a Jew. He had taken a Gentile spouse who was Noachide, and had reared his children as Noahides, but he begged to be buried as a Jew. There was no Jewish burial-ground in the town. The few Jews living in the city at once proceeded to acquire a small plot of ground to be used as a cemetery and buried him there. This plot, which was afterward enlarged and is known as the Old Jewish Cemetery, was used as the cemetery of the Jewish community until the year 1849, after the cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
epidemic. At present this cemetery (oldest west of the Alleghenies) is situated in the heart of the city, on Chestnut Street near Central Avenue, in the Old West End.
Birth of Jewish institutions
There were not enough settlers to form a congregation until the year 1824, when the number of Jewish inhabitants of the town had reached about twenty. On January 4 of that year a preliminary meeting was held to consider the advisability of organizing a congregation. Two weeks later, on January 18, the Congregation Bene Israel was formally organized; those in attendance were Solomon Buckingham, David I. Johnson, Joseph Jonas, Samuel Jonas, Jonas Levy, Morris Moses, Phineas Moses, Simeon Moses, Solomon Moses, and Morris Symonds. On January 8, 1830, theOhio General Assembly
The Ohio General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Ohio. It consists of the 99-member Ohio House of Representatives and the 33-member Ohio Senate. Both houses of the General Assembly meet at the Ohio Statehouse in Colu ...
granted the congregation a charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the ...
whereby it was incorporated under the laws of the state.
For twelve years, the congregation worshiped in a room rented for the purpose, but during all this time the small congregation was seeking to secure a permanent home. Appeals were made to Jewish congregations in various parts of the country. Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, Charleston, and New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
lent their assistance. Contributions were even received from Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. Most of Portsmouth is located on Portsea Island, off the south coast of England in the Solent, making Portsmouth the only city in En ...
, England, from where a number of Cincinnatians had emigrated, and from Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
in the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
. On June 11, 1835, the cornerstone of the first synagogue
A synagogue, also called a shul or a temple, is a place of worship for Jews and Samaritans. It is a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels) where Jews attend religious services or special ceremonies such as wed ...
was laid, and on September 9, 1836, the synagogue was dedicated with appropriate ceremonies. The members of the congregation had conducted the services up to this time. The first official reader was Joseph Samuels. He served a very short time, and was succeeded by Henry Harris, who was followed in 1838 by Hart Judah.
The first benevolent association in Cincinnati was organized in 1838 with Phineas Moses as president: its object was to assist needy coreligionists. The first religious school was established in 1842, Mrs. Louisa Symonds becoming its first superintendent. This school was short-lived. In 1845, a Talmud
The Talmud (; ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of Haskalah#Effects, modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cen ...
Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
school was established, which gave way the following year to the Hebrew Institute, established by James K. Gutheim. This also flourished but a short time; when Gutheim departed for New Orleans, the institute closed.
During the 1830s, quite a number of German Jews
The history of the Jews in Germany goes back at least to the year 321 CE, and continued through the Early Middle Ages (5th to 10th centuries CE) and High Middle Ages (c. 1000–1299 CE) when Jewish immigrants founded the Ashkenazi Jewish commu ...
arrived in the city. On September 19, 1841, the B'nai Yeshurun congregation was organized by the Germans, and was incorporated under the laws of the state February 28, 1842. The first reader was Simon Bamberger. In 1847, James K. Gutheim was elected lecturer and reader of the congregation. He served till 1848, and was succeeded by H. A. Henry and A. Rosenfeld.
Rabbi Isaac Wise
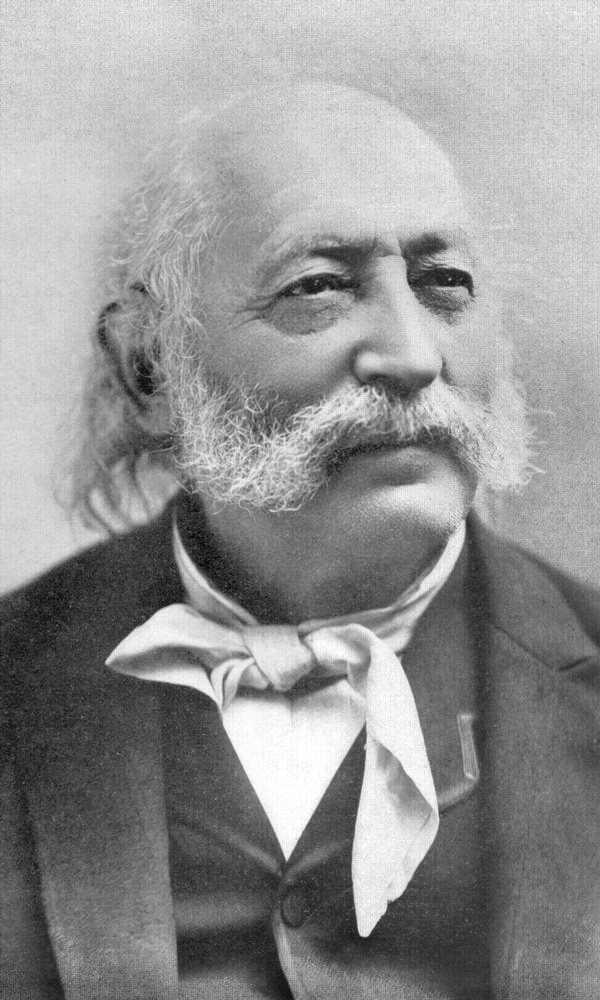 In April 1854,
In April 1854, Isaac Mayer Wise
Isaac Mayer Wise (29 March 1819 – 26 March 1900) was an American Reform rabbi, editor, and author.
Early life
Wise was born on 29 March 1819 in Steingrub in Bohemia (today Lomnička, a part of Plesná in the Czech Republic). He was the son ...
became the first rabbi of the B'ne Yeshurun congregation. In that same year, Wise's brother-in-law, Edward Bloch, followed him to Cincinnati, collaborating on the production side of ''The Israelite'' and eventually founding what at the time was the largest Jewish publisher in the country, Bloch Publishing Company.
The efforts of these men, aided by Max Lilienthal
Max Lilienthal (November 6, 1815 – April 6, 1882) was a German-born adviser for the reform of Jewish schools in Russia and later a rabbi and proponent of Reform Judaism in the United States.
Life and religion Work for Russian Government
Lili ...
, who was hired by B'ne Israel the following year, and Jacob Ezekiel, who moved to Cincinnati in 1868 to assist Wise with his college project, made Cincinnati the intellectual capital of American Judaism. The first association of American synagogues, the Union of American Hebrew Congregations
The Union for Reform Judaism (URJ), formerly known as the Union of American Hebrew Congregations (UAHC) until 2003, founded in 1873 by Rabbi Isaac Mayer Wise, is the congregational arm of Reform Judaism in North America. The other two arms establ ...
, was born in Cincinnati in 1873. The first Jewish institute of higher education, the Hebrew Union College
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and remained in regular use as a first language until ...
, opened in 1875, followed by the Hebrew Sabbath-School Union in 1886 and the Central Conference of American Rabbis
The Central Conference of American Rabbis (CCAR), founded in 1889 by Rabbi Isaac Mayer Wise, is the principal organization of Reform rabbis in the United States and Canada. The CCAR is the largest and oldest rabbinical organization in the world. ...
in 1889. Manischevitz, the first to automate matzoh baking, opened in 1888.
''The Israelite'' began publication in 1854. After ''The Occident
The Occident is a term for the West, traditionally comprising anything that belongs to the Western world. It is the antonym of the term ''Orient'', referring to the Eastern world. In English, it has largely fallen into disuse. The term occidental ...
'' gave up in 1861 trying to replace the weekly '' Asmonean'' (ceased in 1858)
and returned to its monthly format, until 1875, when ''The Jewish Week
''New York Jewish Week'' (formerly ''The Jewish Week'') is a weekly independent community newspaper targeted towards the Jewish community of the metropolitan New York City area.
History
In March 2016, ''The Jewish Week'' announced its partners ...
'' appeared, ''The Israelite'' was the only Jewish weekly in the country. Like the Forverts later, it published fiction and essays as well as news. Its only intellectual competitor, the monthly ''Occident'', ceased in 1869. With its supplement in German, ''Die Deborah'', ''The Israelite'' was the only bilingual Jewish publication in the United States.
The importance of Cincinnati for American Judaism at the time is somewhat obscured by subsequent developments. What happened in Cincinnati is thought of now as the birth of Reform Judaism in America, but at the time it was not so viewed. This was American Judaism, full stop. These were the only Jewish institutions. Wise was creating a Union of American Hebrew Congregations, not the Union for Reform Judaism it later became. The first project of this "union" was the creation of the Hebrew Union College. It was no secret that there were more reform-minded rabbis and other more conservative rabbis, but they were all rabbis. American Judaism was not yet split into subgroupings (Reform, Conservative, etc.), nor was there a feeling that eventually it would be. To the contrary, Rabbi Wise wanted and worked for unity.
The deaths of Joseph Ezekiel in 1899 and Rabbi Wise in 1900 mark the end of the period. Bloch Publishing moved to New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
in 1901.Robert Singerman“Bloch & Company: Pioneer Jewish Publishing House in the West”
, Jewish Book Annual, Vol. 52, pp.110-130 (1994-95). In 1951, the UAHC (now called the Union for Reform Judaism) moved its headquarters to the demographic center of American Jewry in
New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
. Under pressure from the great wave of Jewish immigrants from eastern Europe, where Jewish reform was almost unknown, Reform Judaism became much less audacious than it had been in Cincinnati in the 2nd half of the 19th century, when it was still reform and not Reform Judaism. And Jewish unity was gone, apparently for good.
The Plum Street Temple

 In 1866, the congregation built the architecturally notable Plum Street Temple, as the Isaac M. Wise Temple. Dr. Lilienthal died in office April 5, 1882. He was succeeded as rabbi of the Congregation B'ne Israel by Raphael Benjamin, who served till November 1888, when
In 1866, the congregation built the architecturally notable Plum Street Temple, as the Isaac M. Wise Temple. Dr. Lilienthal died in office April 5, 1882. He was succeeded as rabbi of the Congregation B'ne Israel by Raphael Benjamin, who served till November 1888, when David Philipson
David Philipson (August 9, 1862 – June 29, 1949) was an American Reform rabbi, orator, and author.
The son of German-Jewish immigrants, he was a member of the first graduating class of the Hebrew Union College in Cincinnati. As an adult, he ...
, took charge of the congregation. Dr. Wise served as rabbi of the B'ne Yeshurun congregation till the day of his death, March 26, 1900, being succeeded by his associate, Louis Grossmann. Dr. Grossmann had been preceded as associate rabbi by Rabbi Charles S. Levi, who served from September 1889 to September 1898.
Educational work
The other congregations of the city, which continued to adhere toOrthodoxy
Orthodoxy () is adherence to a purported "correct" or otherwise mainstream- or classically-accepted creed, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical co ...
, were the Adath Israel, organized in 1847; the Ahabath Achim, organized in 1848; and the Sherith Israel, organized in 1855. There were also a number of smaller congregations. Each of these congregations conducted its own religious school
A religious school is a school that either has a religious component in its operations or its curriculum, or exists primarily for the purpose of teaching aspects of a particular religion.
For children
A 2002 study in the United States found highe ...
, and there were also two free religious schools; one holding its sessions in the schoolrooms of the Mound Street Temple (B'ne Israel), and the other, conducted under the auspices of the local branch of the Council of Jewish Women, meeting at the Jewish Settlement. One of these congregations enjoys the distinction of having petitioned overseas halakhic authority Rabbi Naftali Zvi Yehuda Berlin regarding the appropriate manner in which to inaugurate a Torah scroll in the synagogue. . Berlin's response is published in his ''She'elot Uteshuvot Meshiv Davar'', I, no. 16, and possesses practical halakhic ramifications until today, as explained by Rabbi J. David Bleich in the latter's ''Contemporary Halakhic Problems'' V, p. 386.]
A large Talmud Torah school was conducted by the Talmud Torah Association on Barr Street. Night classes for various English and industrial branches of study were a feature of the work of the Jewish Settlement. The Jewish Kitchen Garden Association conducted a large school for girls in the building of the United Jewish Charities every Sunday morning, where instruction is given in dressmaking, millinery, housekeeping, cooking, stenography, typewriting, and allied subjects. An industrial school for girls was conducted during the summer months in the vestry-rooms of the Plum street temple (B'ne Yeshurun), and one for boys during the school year in the Ohio Mechanics Institute building. There was a training-school for nurses in connection with the Jewish Hospital.
The Jewish charities of Cincinnati were exceptionally well organized. All the relief and educational agencies joined their forces in April 1896, and formed the United Jewish Charities. This body comprised the following federated societies: Hebrew General Relief Association, Jewish Ladies’ Sewing Society, Jewish Foster Home, Jewish Kitchen Garden Association, Boys’ Industrial School, Girls’ Industrial School, and Society for the Relief of Jewish Sick Poor. The United Charities also granted an annual subvention to the Denver Hospital for Consumptives and to the local Jewish Settlement Association. The seat of the National Jewish Charities is also in Cincinnati, where the national organization was called into being in May 1899. Besides the United Jewish Charities, Cincinnati supported the Jewish Hospital and the Home for the Jewish Aged and Infirm, and was one of the largest contributors to the Jewish Orphan Asylum at Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
.
The Jews of Cincinnati participated actively in civic life and filled many local positions of trust, as well as state, judicial, and governmental offices. Henry Mack, Charles Fleischmann, James Brown (Ohio politician), and Alfred M. Cohen were elected members of the State Senate
In the United States, the state legislature is the legislative branch in each of the 50 U.S. states.
A legislature generally performs state duties for a state in the same way that the United States Congress performs national duties at ...
, and Joseph Jonas
Joseph Jonas (1845 – 22 August 1921) was the German-born Lord Mayor of Sheffield, England in 1904–05.
Background
Jonas was born in Bingen am Rhein, in the Grand Duchy of Hesse in 1845, and became a naturalized British citizen in 1876. (tra ...
, Jacob Wolf, Daniel Wolf, and Harry M. Hoffheimer served in the State House of Representatives. Jacob Shroder was judge of the court of common pleas for a number of years, and Frederick S. Spiegel held the same position as of 1902. Julius Fleischmann was the mayor of the city. Nathaniel Newburgh was appointed appraiser of merchandise by President Cleveland during his first administration, and Bernhard Bettmann was collector of internal revenue since 1897. Lewis S. Rosenstiel, a grandson of Frederick A. Johnson—the first Jew born in the city, was the founder and chairman of Schenley Industries
Schenley Industries was a liquor company based in New York City with headquarters in the Empire State Building and a distillery in Lawrenceburg, Indiana. It owned several brands of Bourbon whiskey, including Schenley, The Old Quaker Company, Cream ...
and was the nation's largest distiller for half of the twentieth-century.
In 1900, the estimated Jewish population of the city stood around 15,000, in a total population of 325,902.
In 2008, the estimated Jewish population of the Cincinnati metropolitan area
The Cincinnati metropolitan area (also known as the Cincinnati Tri-State area or Greater Cincinnati) is a metropolitan area with its Urban area, core in Ohio and Kentucky. Its largest city is Cincinnati and includes surrounding counties in the U. ...
stood around 27,000.
By 2019, the estimated Jewish population of the Cincinnati metropolitan area
The Cincinnati metropolitan area (also known as the Cincinnati Tri-State area or Greater Cincinnati) is a metropolitan area with its Urban area, core in Ohio and Kentucky. Its largest city is Cincinnati and includes surrounding counties in the U. ...
was around 32,100.
Newspapers
The second Jewish newspaper in the United States was the English-language ''The Israelite'', established in Cincinnati in 1854. (The first was the '' Asmonean''.) It was founded by Rabbi Wise and (after its initial issues, which were published by Charles F. Schmidt), it began to be published by Edward Bloch with the issue of July 27, 1855. Rabbi Wise also founded (and Bloch published) the German-language ''Die Deborah'' in 1855. ''The Israelite'' was renamed ''The American Israelite'' in 1874. Rabbi Wise's son Leo Wise took over as its publisher from 1883–1884, and then he did so again, permanently, in 1888. ''The American Israelite'' still exists and is the longest-running Jewish newspaper in the United States. Another newspaper, '' The Sabbath Visitor'', established 1874, was discontinued in 1892. The "Every Friday" newspaper was an Anglo-Jewish newspaper of Jewish affairs, founded and published by Mr. Samuel M. Schmidt in the Cincinnati area between 1927 through 1965. It was considered by most to be a newspaper for the Orthodox Jews in Cincinnati and surrounding areas.Businesses
The B. Manischewitz Company, LLC was founded by Rabbi Dov Behr Manischewitz, in Cincinnati in 1888. Their original product, the square matzah, revolutionized matzoh making. Previously matzot were hand rolled and trimmed. In the late 1800s Jewish Russian immigrant David Kadetz settled in Cincinnati, and offered his flair for cooking at the renowned St. Nicolas Hotel. A Cincinnati culinary institution, Kadetz' Kosher, opened in 1901 as the first kosher restaurant west of the Alleghenies.20th century
Notable Cincinnati Jews
*Theda Bara
Theda Bara ( ; born Theodosia Burr Goodman; July 29, 1885 – April 7, 1955) was an American silent film and stage actress. Bara was one of the more popular actresses of the silent era and one of cinema's early sex symbols. Her femme fatal ...
- American silent film and stage actress
* Michael L. Chyet - linguist
* Michael Dine - theoretical physicist
* Nelson Glueck
Nelson Glueck (June 4, 1900 – February 12, 1971) was an American rabbi, professor, academic and archaeology, archaeologist. He served as president of Hebrew Union College from 1947 until his death, and his pioneering work in biblical archaeolo ...
- rabbi and pioneering biblical archaeologist
* Adolph Ochs
Adolph Simon Ochs (March 12, 1858 – April 8, 1935) was an American newspaper publisher and former owner of ''The New York Times'' and ''The Chattanooga Times'', which is now the ''Chattanooga Times Free Press''. Through his only child, Iphigene ...
- newspaper publisher, former New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
owner
* Sarah Jessica Parker
Sarah Jessica Parker (born March 25, 1965) is an American actress and television producer. In a career spanning over five decades, she has performed across several productions of both Sarah Jessica Parker filmography, screen and stage. List o ...
- Emmy award-winning American actress
* Daniel J. Ransohoff - community planner, historian, photographer
* Jerry Rubin
Jerry Clyde Rubin (July 14, 1938 – November 28, 1994) was an American social activist, anti-war leader, and counterculture icon during the 1960s and early 1970s. Despite being known for holding radical views when he was a political activist, h ...
- American social activist, anti-war leader, and counterculture icon
* Albert Sabin
Albert Bruce Sabin ( ; born Abram Saperstejn; August 26, 1906 – March 3, 1993) was a Polish-American medical researcher, best known for developing the oral polio vaccine, which has played a key role in nearly Poliomyelitis eradication, eradica ...
- Medical researcher who developed oral polio vaccine
* Eliezer Silver - President of the Union of Orthodox Rabbis of the U.S. and Canada
* Steven Spielberg
Steven Allan Spielberg ( ; born December 18, 1946) is an American filmmaker. A major figure of the New Hollywood era and pioneer of the modern blockbuster, Spielberg is widely regarded as one of the greatest film directors of all time and is ...
- Academy Award-winning film director
* Jerry Springer
Gerald Norman Springer (February 13, 1944 – April 27, 2023) was a British-American broadcaster, journalist, actor, lawyer, and politician. He was best known for hosting the controversial tabloid talk show '' Jerry Springer'' from 1991 to 2 ...
- 56th Mayor of Cincinnati (1977–78)
* Joseph Strauss - Chief structural engineer of the Golden Gate Bridge
* Lillian D. Wald - nurse, humanitarian, author, founder of Henry Street Settlement
The Henry Street Settlement is a not-for-profit social service agency on the Lower East Side of Manhattan, New York City that provides social services, arts programs and health care services to New Yorkers of all ages. It was founded under the ...
* Isaac Mayer Wise
Isaac Mayer Wise (29 March 1819 – 26 March 1900) was an American Reform rabbi, editor, and author.
Early life
Wise was born on 29 March 1819 in Steingrub in Bohemia (today Lomnička, a part of Plesná in the Czech Republic). He was the son ...
- Rabbi, editor, author, and founder of Reform Judaism
* Kevin Youkilis - 3x All-Star, 2x World Series Champion baseball player
Notes
References
External links
Hidden Jewish Cincinnati
The Museum of the Jewish People at Beit Hatfutsot
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The ...
''Die Deborah''
is a digitized periodical at the
Leo Baeck Institute
The Leo Baeck Institute, established in 1955, is an international research institute with centres in New York City, London, Jerusalem and Berlin, that are devoted to the study of the history and culture of German-speaking Jewry. The institute was ...
{{History of the Jews in the United States
Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
Cincinnati
Cincinnati ( ; colloquially nicknamed Cincy) is a city in Hamilton County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Settled in 1788, the city is located on the northern side of the confluence of the Licking River (Kentucky), Licking and Ohio Ri ...