Jasmolone on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jasmolone is an irregular

monoterpene
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen func ...
. Irregular monoterpenes are derived from two isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)ŌłÆCH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. It is produced by many plants and animals (including humans) and its polymers ar ...
C5 units, but do not follow the usual head-to-tail coupling mechanism. Jasmolins are found in pyrethrum
''Pyrethrum'' was a genus of several Old World plants now classified in either '' Chrysanthemum'' or '' Tanacetum'' which are cultivated as ornamentals for their showy flower heads. Pyrethrum continues to be used as a common name for plants form ...
flowers. They can specifically be found in the flower heads of ''Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium
''Pyrethrum'' was a genus of several Old World plants now classified in either ''Chrysanthemum'' or ''Tanacetum'' which are cultivated as ornamentals for their showy Pseudanthium, flower heads. Pyrethrum continues to be used as a common name for ...
''. Jasmolins act as an insecticide for the flower. It is found in the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
of plants.
Jasmolone is part of the secondary alcohol family. Jasmolone is found in the alcohol portion of pyrethrins. It is thought that jasmolone is a derivative of cyclized and altered fatty acids. The cyclization of the fatty acids is similar to the biosynthetic pathway cyclization of prostaglandin
Prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiology, physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids that have diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every Tissue (biology), tissue in humans and ot ...
s.
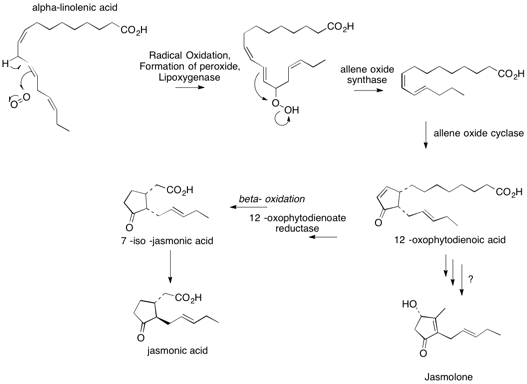
A precursor of jasmolone could be alpha-linolenic acid with a 12-oxophytodienoic acid intermediate. The chain shortening could be produced by a beta-oxidation then a decarboxylation.
12-Oxophytodienoic acid is also used in the production of jasmonic acid
Jasmonic acid (JA) is an organic compound found in several plants including jasmine. The molecule is a member of the jasmonate class of plant hormones. It is biosynthesized from linolenic acid by the octadecanoid pathway. It was first isolated ...
. Jasmonic acid is used in the production of secondary metabolites in a plants signaling system. Jasmonic acid is used in a plant's response to a microbial infection or wound.
Natural production
Jasmolone is one of the three alcohols (along with pyrethrolone and cinerolone) needed in combination with two specific acids (chrysanthemic acid
Chrysanthemic acid is an organic compound that is related to a variety of natural and synthetic insecticides. It is related to the pyrethrin I and II, as well as the pyrethroids. One of the four stereoisomers, (1''R'',3''R'')- or (+)-''trans''-c ...
and pyrethric acid) to form insecticidal esters. These six insecticidal esters are part of the pyrethrin
The pyrethrins are a class of organic compounds normally derived from ''Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium'' that have potent Insecticide, insecticidal activity by targeting the nervous systems of insects. Pyrethrin naturally occurs in chrysanthemum f ...
s family. So far, pyrethrins have been found in ''Chrysanthemum cinerariaefolium
''Pyrethrum'' was a genus of several Old World plants now classified in either ''Chrysanthemum'' or ''Tanacetum'' which are cultivated as ornamentals for their showy Pseudanthium, flower heads. Pyrethrum continues to be used as a common name for ...
'', ''Tagetes erecta
''Tagetes erecta'', the Aztec marigold, Mexican marigold, big marigold, ''cempaxochitl'' or ''cempas├║chil'', is a species of flowering plant in the genus ''Tagetes'' native to Mexico and Guatemala. Despite being native to the Americas, it is of ...
'', '' C. coccinum'', ''Tagetes minuta
Edit'Tagetes minuta'' is a tall upright marigold plant from the genus ''Tagetes'', with small flowers, native to the southern half of South America. Since Spanish colonization, it has been introduced around the world, and has become naturalized ...
'', '' Z. linnearis'', ''Calendula officinalis
''Calendula officinalis'', Mary's gold, common marigold, the pot marigold, Scotch marigold, or ruddles, is a flowering plant in the daisy family, Asteraceae. It is probably native plant, native to southern Europe, but its long history of cultivat ...
'', '' Demorphotheca sinuate'' and ''Zinnia elegans
''Zinnia elegans'' ( syn. ''Zinnia violacea'') known as youth-and-age, common zinnia or elegant zinnia, is an annual flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to Mexico but grown as an ornamental in many places and naturalised in se ...
''. Pyrethrins are found mostly in the head of the flowers, but have also been found in the callus
A callus (: calluses) is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, b ...
tissue of the flowers.K.Ramawat, J.Merillon, ŌĆ£Biotechnology: Secondary Metabolites Plants and MicrobesŌĆØ, Boca Raton: CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, 2007, 136.
Biosynthesis
╬▒-Linolenic acid
╬▒-Linolenic acid, also known as ''alpha''-linolenic acid (ALA) (from Greek ''alpha'' denoting "first" and ''linon'' meaning flax), is an ''n''ŌłÆ3, or omega-3, essential fatty acid. ALA is found in many seeds and oils, including flaxseed, ...
undergoes a radical oxidation with O2 and lipoxygenase
Lipoxygenases () (LOX) are a family of (non- heme) iron-containing enzymes, more specifically oxidative enzymes, most of which catalyze the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in lipids containing a cis,cis-1,4- pentadiene into ce ...
to form a peroxide. Lipoxygenase is an iron-containing enzyme that is used to catalyze dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in this case, ╬▒-linolenic acid. Lipooxygenase specifically binds to polyunsaturated fatty acids that have a ''cis'',''cis''-1,4-pentadiene present. Next, an allene oxide synthase occurs followed by allene oxide cyclase. 12-Oxophytodienoic acid is formed. It is unknown how jasmolone is formed from 12-oxophytodienoic acid after this step.

Laboratory synthesis
(''Z'')-Jasmolone was synthesized by Jacqueline Ficini and Jean Pierre Genet in June 1975.References
{{reflist Monoterpenes