Janaka on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Janaka (, 
 Janaka, originally named Sīradhvaja, was born to King Hrasvaroman of Mithila and his wife Keikasi. The Videha kingdom was situated historically between the Gandaki River to the east, the
Janaka, originally named Sīradhvaja, was born to King Hrasvaroman of Mithila and his wife Keikasi. The Videha kingdom was situated historically between the Gandaki River to the east, the

 Janaka was married to queen Sunayana. According to ''Ramayana'', Janaka and Sunayana found
Janaka was married to queen Sunayana. According to ''Ramayana'', Janaka and Sunayana found
 Late
Late 
IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Brahmic family, Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that ...
: ''Janaka'') is the King of Videha who ruled from Mithila
Mithila may refer to:
Places
* Mithilā, a synonym for the ancient Videha state
** Mithilā (ancient city), the ancient capital city of Videha
* Mithila (region), a cultural region (historical and contemporary), now divided between India and Nepa ...
, in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics ...
''. Janaka was married to Sunayana. He is the father of Sita
Sita (; ), also known as Siya, Jānaki and Maithili, is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Sita is the consort of Rama, the avatar of god Vishnu, and is regarded as an avatar of goddess Lakshmi. She is t ...
and Urmila in the epic. The term Janaka was also the title adopted by all the kings of Videha, who were the descendants of the King Nimi and his son King Mithi. The King Mithi is considered as the first King of Videha who was titled with the term ''Janaka''.
Janaka is revered as being an ideal example of non-attachment to material possessions. He was intensely interested in spiritual discourse and considered himself free from worldly illusions. His interactions with sages and seekers such as Ashtavakra and Sulabha are recorded in the ancient texts.

Legend
Birth and ancestry
 Janaka, originally named Sīradhvaja, was born to King Hrasvaroman of Mithila and his wife Keikasi. The Videha kingdom was situated historically between the Gandaki River to the east, the
Janaka, originally named Sīradhvaja, was born to King Hrasvaroman of Mithila and his wife Keikasi. The Videha kingdom was situated historically between the Gandaki River to the east, the Mahananda River
The Mahananda ( ) is a trans-boundary river that flows through the Indian states of Bihar and West Bengal before crossing into Bangladesh. It is an important tributary of the Ganges.
Course
The Mahananda river system consists of two streams- ...
to the west, the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
to the north, and the Ganga river to the south. Janaka had a younger brother named Kushadhvaja. Upon ascending to the throne as the King of Mithila, Janaka faced an attack from the King of Samkasya, Sudhanvan. In the ensuing war, Janaka emerged victorious by defeating and killing Sudhanvan, after which he appointed his brother Kushadhvaja as the new King of Samkasya.
King Nimi Nimi may refer to
* Nimi (king), a king of the Solar dynasty in Hindu mythology
* Nimi language, spoken in Papua New Guinea
* Niimi, Okayama, Japan
* Non-Instrumental Movement Inhibition, an aspect of body language
{{disambiguation ...
was the first ruler of the Videha kingdom. Janaka was descended from Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
in the following order:—Brahmā—Marīci—Kaśyapa—Vivasvān—Vaivasvata—Ikṣvāku—Nimi— Mithi—Udāvasu—Nandivardhana—Suketu— Devarāta—Bṛhadratha—Mahāvīra—Sudhṛti—Dhṛṣṭaketu—Haryaśva—Maru—Pratvantaka—Kīrtiratha—Devamīḍha—Vibudha—Mahīdhraka—Kīrtirāta—Mahāroman—Svarṇaroman— Hrasvaroman—Janaka.
Marriage and children

 Janaka was married to queen Sunayana. According to ''Ramayana'', Janaka and Sunayana found
Janaka was married to queen Sunayana. According to ''Ramayana'', Janaka and Sunayana found Sita
Sita (; ), also known as Siya, Jānaki and Maithili, is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Sita is the consort of Rama, the avatar of god Vishnu, and is regarded as an avatar of goddess Lakshmi. She is t ...
while ploughing as a part of a yagna and adopted her. Sita is considered as an avatar of goddess Lakshmi
Lakshmi (; , , sometimes spelled Laxmi, ), also known as Shri (, , ), is one of the principal goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of wealth, fortune, prosperity, beauty, fertility, sovereignty, and abundance. She along with Parvat ...
. Sunayana later gave birth to Urmila on Jaya ekadashi, who is an avatar of goddess Nagalakshmi.
When Sita reached adulthood, Janaka conducted her svayamvara, which was won by Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryāda' ...
. Alongside the wedding of Rama and Sita, Urmila married Rama's younger brother Lakshmana
Lakshmana (, ), also known as Laxmana, Lakhan, Saumitra, and Ramanuja, is the younger brother of Rama in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is considered as an incarnation of Shesha, the lord of serpents. Lakshmana was married to Urmila, and i ...
.
Establishment of Shivalingas
According to legend, it is said that King Janaka was a great devotee of Lord Shiva. He established some Shivalingas around the corners of the capital cityJanakpur
Janakpurdham or Janakpur (), is the capital city of Madhesh Province. This sub-metropolitan city is a central hub for the Maithili language, as well as for religious and cultural tourism in Nepal.
The city was founded in the early 18th centur ...
for performing his penance in the ancient Mithila Kingdom. The four major Shivalingas established by him on the four corners of his capital city Janakpur were Kalyaneshwar Mahadev Mandir, Jaleshwar Mahadev Mandir, Kshireshwar Nath Mahadev Mandir and Sapteshwar Nath Mahadev Mandir. Similarly he is also credited for building the temples Haleshwar Nath Mahadev Mandir at ''Haleshwar Sthan'' in Sitamarhi and Kapileshwar Nath Mahadev Mandir at the outskirts of Janakpur Dham.
Later role in Ayodhya
Janaka accompanied Bharata to Chitrakoot, where Bharata went to persuade Rama, Sita and Lakshmana to return to Ayodhya. After Rama returned from the exile and was then crowned the King of Kosala, Janaka became an important figure in his court. Rama would also take Janaka's advice on many important occasions.Assessment
 Late
Late Vedic literature
FIle:Atharva-Veda samhita page 471 illustration.png, upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the ''Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of relig ...
such as ''Shatapatha Brahmana
The Shatapatha Brahmana (, , abbreviated to 'SB') is a commentary on the Yajurveda, Śukla Yajurveda. It is attributed to the Vedic sage Yajnavalkya. Described as the most complete, systematic, and important of the Brahmanas (commentaries on the ...
'' and ''Brihadaranyaka Upanishad
The ''Brihadaranyaka Upanishad'' (, ) is one of the Mukhya Upanishads, Principal Upanishads and one of the first Upanishadic scriptures of Hinduism. A key scripture to various schools of Hinduism, the ''Brihadaranyaka Upanisad'' is tenth in the ...
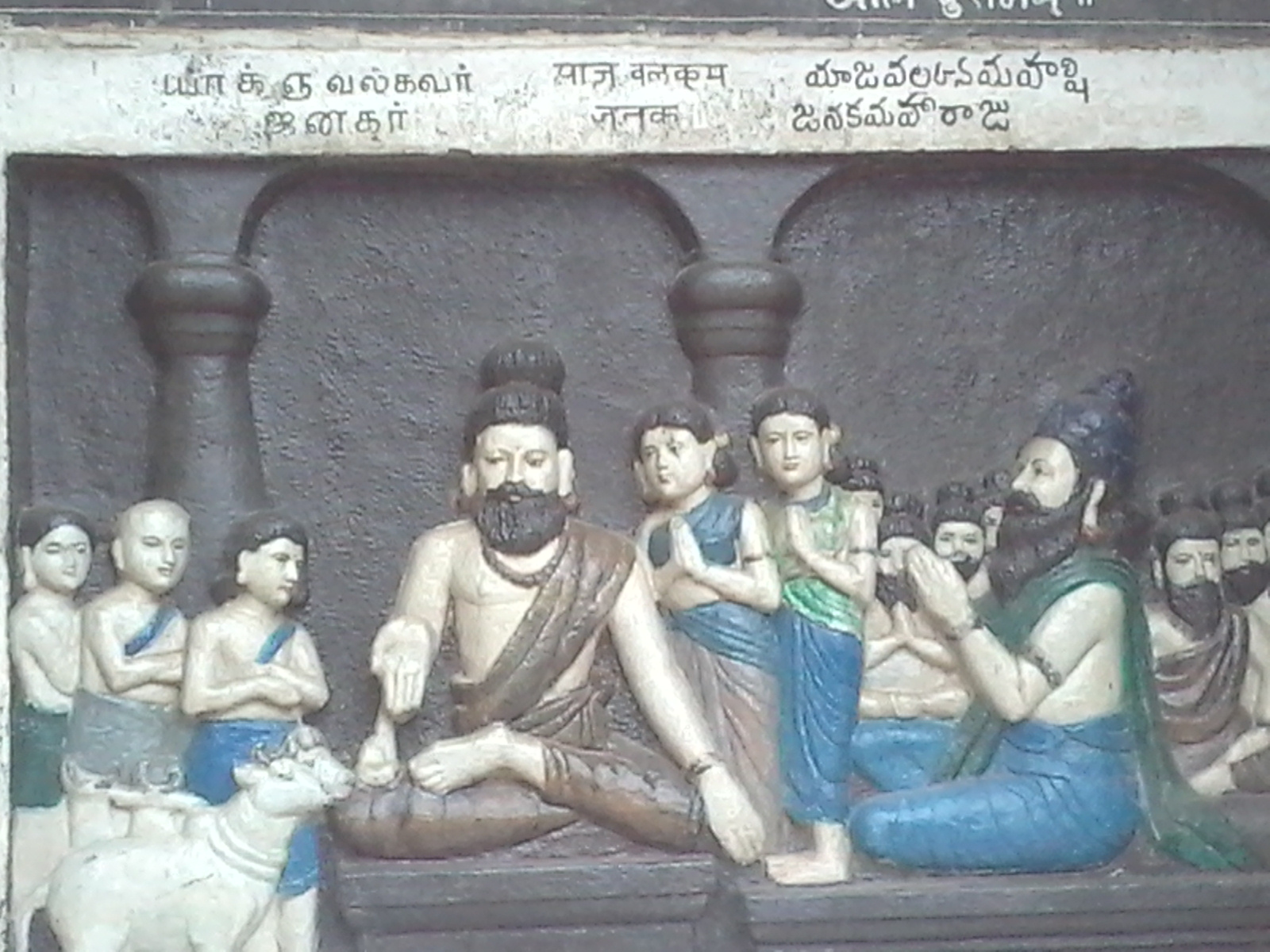
'' mention a certain King Janaka (c. 8th or 7th century BCE) as a great philosopher-king of Videha, renowned for his patronage of Vedic culture and philosophy and whose court was an intellectual center for Brahmin
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
sages such as Yajnavalkya
Yajnavalkya or Yagyavalkya (, International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST:) is a Hindu Vedic sage prominently mentioned in the Brihadaranyaka Upanishad (c. 700 BCE) and Taittiriya Upanishad, ''Tattiriya Upanishad''., Quote: "Yajnav ...
, Uddalaka Aruni, and Gargi Vachaknavi. Under his reign, Videha became a dominant political and cultural center of the Indian subcontinent.

Literature
Janaka's conversation with the sage Ashtavakra is recorded in the Ashtavakra Gita, wherein he is depicted as one who is realised and this was tested by the sage Ashtavakra. Many spiritual teachers have referred to this writing often translating and deducing its meaning. Similarly the philosophical dialogues between the king Janaka and the sage Parashara is recorded as Parashar Gita.In popular culture
Films
* Mikkilineni portrayed Janaka in the 1991 Telugu film '' Brahmarshi Viswamitra''. * Murali Mohan portrayed Janaka in the 2011 Telugu film '' Sri Rama Rajyam''.Television
*Mulraj Rajda
Mulraj Rajda (13 November 1931 – 23 September 2012) was an Indian people, Indian writer, actor and director who predominantly worked in Hindi and Gujarati language, Gujarati films, television shows and theatre. He is regarded as one of the mo ...
portrayed Janaka in the 1987 series '' Ramayan'' and the 1988 series '' Luv Kush''.
* Pradeep Sharma portrayed Janaka in the 2002 series '' Ramayan''.
* Gyan Prakash portrayed Janaka in the 2008 series '' Ramayan''.
* Mohit Chauhan portrayed Janaka in the 2011 series '' Devon Ke Dev...Mahadev''.
* Radha Krishna Dutta portrayed Janaka in the 2012 series '' Ramayan''.
* Bijay Anand portrayed Janaka in the 2015 series '' Siya Ke Ram''.
* Shahbaz Khan portrayed Janaka in the 2018 series '' Ram Siya Ke Luv Kush''.
* Jatin Sial portrayed Janaka in the 2021 web series ''Ramyug''.
* Jiten Lalwani portrayed Janaka in the 2024 series '' Shrimad Ramayan''.
See also
* Kings of Mithila * Maithils *Trikaranasuddhi
Manasa, vacha, karmana are three Sanskrit words. The word ''manasa'' refers to the mind, ''vacha'' refers to speech, and ''karmana'' refers to actions.
In several Indian languages, these three words are together used to describe a state of cons ...
* Pravahana Jaivali
* Ancient Mithila University
References
Sources
*'' Dictionary of Hindu Lord and Legend'' () by Anna Dhallapiccola *External links
{{Ramayana 7th-century BC Indian monarchs Characters in the Ramayana Kings of Videha