Jacques Cartier on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from
 On April 20, 1534, Cartier set sail under a commission from the king, hoping to discover a western passage to the wealthy markets of the East Indies. In the words of the commission, he was to "discover certain islands and lands where it is said that a great quantity of gold and other precious things are to be found".
It took him twenty days to sail across the ocean. Starting on May 10 of that year, he explored parts of
On April 20, 1534, Cartier set sail under a commission from the king, hoping to discover a western passage to the wealthy markets of the East Indies. In the words of the commission, he was to "discover certain islands and lands where it is said that a great quantity of gold and other precious things are to be found".
It took him twenty days to sail across the ocean. Starting on May 10 of that year, he explored parts of
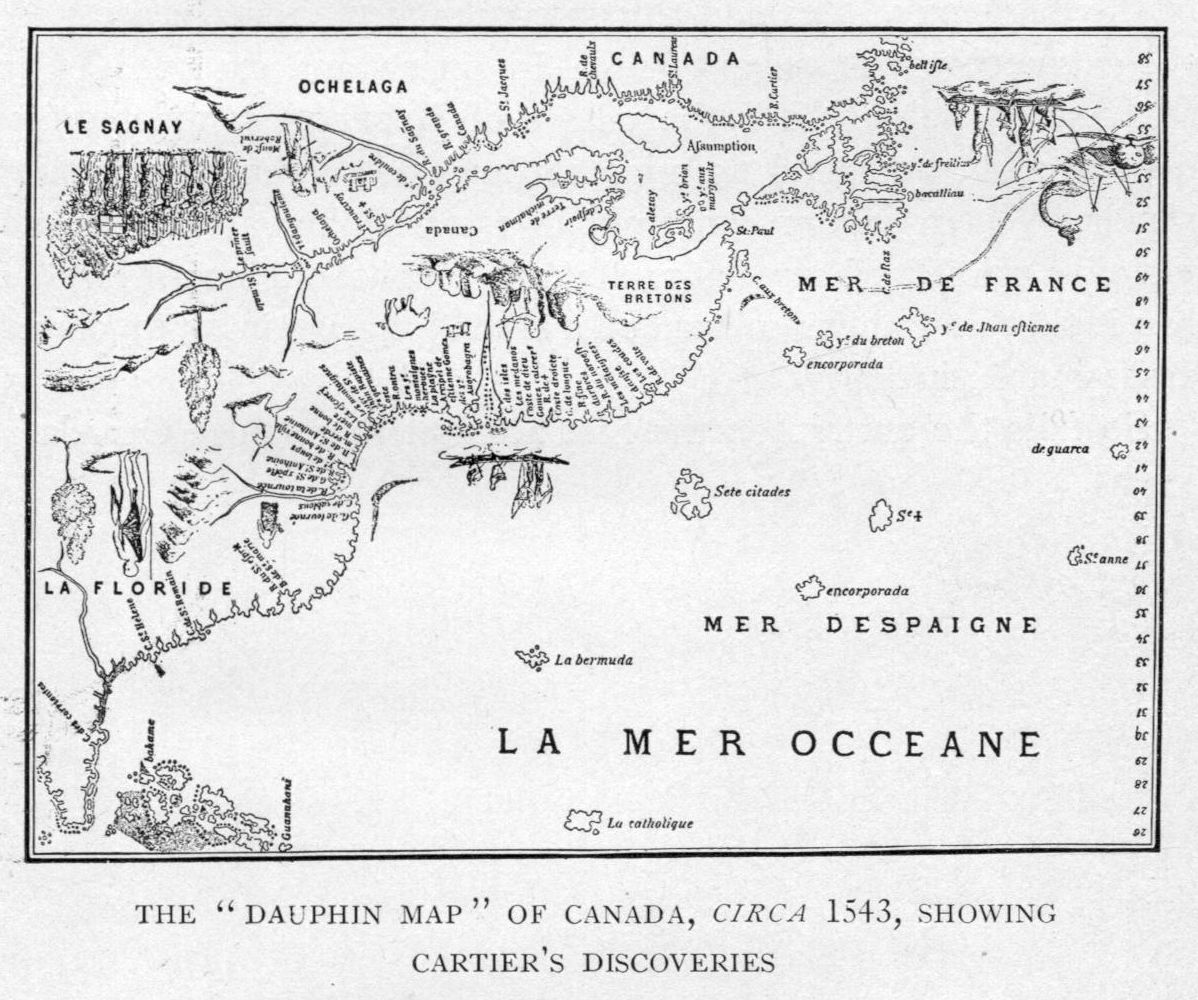
 Cartier left his main ships in a harbour close to Stadacona, and used his smallest ship to continue on to Hochelaga (now Montreal), arriving on October 2, 1535. Hochelaga was far more impressive than the small and squalid village of Stadacona, and a crowd of over a thousand came to the river's edge to greet the Frenchmen. The site of their arrival has been confidently identified as the beginning of the Sainte-Marie Sault – where the bridge named after him now stands. The expedition could proceed no further, as the river was blocked by rapids. So certain was Cartier that the river was the
Cartier left his main ships in a harbour close to Stadacona, and used his smallest ship to continue on to Hochelaga (now Montreal), arriving on October 2, 1535. Hochelaga was far more impressive than the small and squalid village of Stadacona, and a crowd of over a thousand came to the river's edge to greet the Frenchmen. The site of their arrival has been confidently identified as the beginning of the Sainte-Marie Sault – where the bridge named after him now stands. The expedition could proceed no further, as the river was blocked by rapids. So certain was Cartier that the river was the 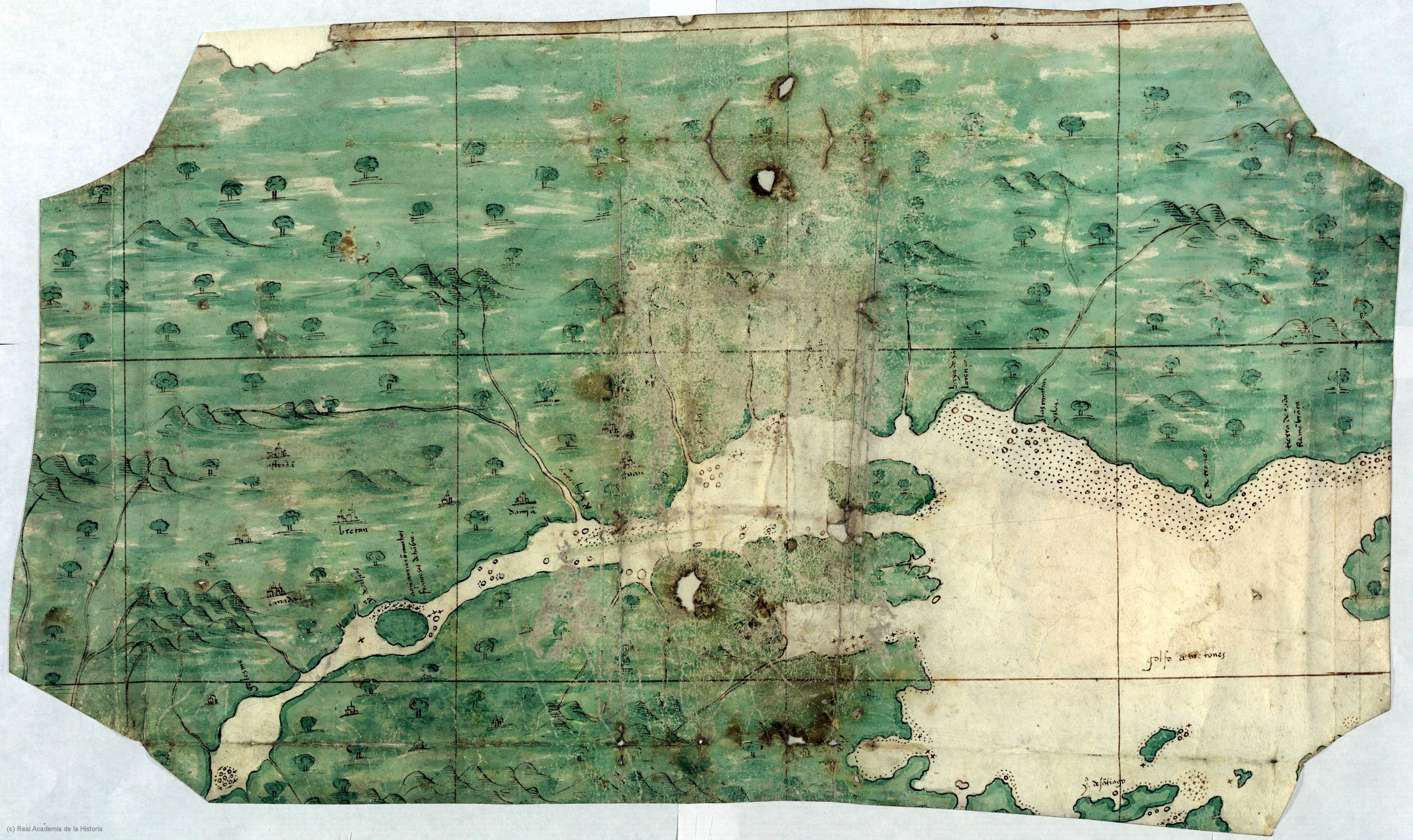 From mid-November 1535 to mid-April 1536, the French fleet lay frozen solid at the mouth of the St. Charles River, under the Rock of Quebec. Ice was over a
From mid-November 1535 to mid-April 1536, the French fleet lay frozen solid at the mouth of the St. Charles River, under the Rock of Quebec. Ice was over a
 On October 17, 1540, Francis ordered the navigator Jacques Cartier to return to Canada to lend weight to a colonization project of which he would be "captain general". However, January 15, 1541, saw Cartier supplanted by Jean-François de La Rocque de Roberval, a
On October 17, 1540, Francis ordered the navigator Jacques Cartier to return to Canada to lend weight to a colonization project of which he would be "captain general". However, January 15, 1541, saw Cartier supplanted by Jean-François de La Rocque de Roberval, a
 Having located the entrance to the St. Lawrence on his first voyage, he opened up a major waterway for the European penetration of North America. He produced an intelligent estimate of the resources of Canada, both natural and human, albeit with a considerable exaggeration of its mineral wealth. While some of his actions toward the St. Lawrence Iroquoians were dishonourable, he did try at times to establish friendship with them and other native peoples living along the St. Lawrence River—an indispensable preliminary to French settlement in their lands.
Cartier was the first to document the name
Having located the entrance to the St. Lawrence on his first voyage, he opened up a major waterway for the European penetration of North America. He produced an intelligent estimate of the resources of Canada, both natural and human, albeit with a considerable exaggeration of its mineral wealth. While some of his actions toward the St. Lawrence Iroquoians were dishonourable, he did try at times to establish friendship with them and other native peoples living along the St. Lawrence River—an indispensable preliminary to French settlement in their lands.
Cartier was the first to document the name
 * '' Grande Hermine''
** Built: France 1534; given in 1535 to Cartier by the King of France; used in the 1535–1536 and 1541–1542 voyages; replica 1967 built for
* '' Grande Hermine''
** Built: France 1534; given in 1535 to Cartier by the King of France; used in the 1535–1536 and 1541–1542 voyages; replica 1967 built for

 Jacques Cartier Island, located on the tip of the
Jacques Cartier Island, located on the tip of the
/ref> ** bronze at PEI's Jacques Cartier Provincial Park ** cast iron sculptures at Gaspe, Quebec ** cross monument at Gaspe, Quebec ** cross monument at Saint-Quentin Island near
/ref> ** Walter Baker, ''Jacques Cartier's Return to Stadacona, 1541'' ** Théophile Hamel, ''Portrait imaginaire de Jacques Cartier'' (reproduced on many stamps) ** Léopold Massard and de Clugny, ''Jacques Cartier Navigateur'' ** Auguste Lemoine (1895) after François Riss, ''Portrait of Jacques Cartier'' (Musée d'Histoire de Saint-Malo) ** Charles William Jefferys, ''Cartier meets the Indians of the St. Lawrence, 1535'' **
"What Howie Meeker and Atwood have in common"
''
Canadian rock band
English translation of Cartier's accountsWatch a Heritage Minutes feature on Jacques Cartier
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cartier, Jacques Explorers of Canada 1491 births 1557 deaths 16th century in Canada 16th century in Quebec French Roman Catholics People from Saint-Malo 16th-century Breton people French explorers of North America Persons of National Historic Significance (Canada)
Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duch ...
. Jacques Cartier was the first European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence
The Gulf of St. Lawrence is a gulf that fringes the shores of the provinces of Quebec, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, Newfoundland and Labrador, in Canada, plus the islands Saint-Pierre and Miquelon, possessions of France, in ...
and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawrenc ...
, which he named "The Country of Canadas" after the Iroquoian names for the two big settlements he saw at Stadacona (Quebec City) and at Hochelaga (Montreal Island)..
Early life
Jacques Cartier was born in 1491 inSaint-Malo
Saint-Malo (, , ; Gallo language, Gallo: ; ) is a historic French port in Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany (administrative region), Brittany.
The Fortification, walled city on the English Channel coast had a long history of piracy, earning much wealth ...
, the port on the north-east coast of Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duch ...
. Cartier, who was a respectable mariner
A sailor, seaman, mariner, or seafarer is a person who works aboard a watercraft as part of its crew, and may work in any one of a number of different fields that are related to the operation and maintenance of a ship. While the term ''sailor' ...
, improved his social status in 1520 by marrying Mary Catherine des Granches, member of a leading aristocratic family. His good name in Saint-Malo is recognized by its frequent appearance in baptismal registers as godfather or witness.
First voyage (1534)
In 1534, two years after theDuchy of Brittany
The Duchy of Brittany (, ; ) was a medieval feudal state that existed between approximately 939 and 1547. Its territory covered the northwestern peninsula of France, bordered by the Bay of Biscay to the west, and the English Channel to the north. ...
was formally united with the French crown in the Edict of Union, Cartier was introduced to King Francis I by Jean Le Veneur
Jean Le Veneur (died 8 August 1543), son of a Norman baron, was a French Abbot, Bishop, Courtier, royal official, and Roman Catholic cardinal.
Biography
He was born into a noble family of Normandy. He was the second son of Philippe, baron of Til ...
, bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
of Saint-Malo and abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the head of an independent monastery for men in various Western Christian traditions. The name is derived from ''abba'', the Aramaic form of the Hebrew ''ab'', and means "father". The female equivale ...
of Mont Saint-Michel
Mont-Saint-Michel (; Norman: ''Mont Saint Miché''; ) is a tidal island and mainland commune in Normandy, France.
The island lies approximately off France's north-western coast, at the mouth of the Couesnon River near Avranches and is i ...
, at the Manoir de Brion. The King had previously invited (although not formally commissioned) the Florentine explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano
Giovanni da Verrazzano ( , ; often misspelled Verrazano in English; 1491–1528) was an Italian ( Florentine) explorer of North America, who led most of his later expeditions, including the one to America, in the service of King Francis I of ...
to explore the eastern coast of North America on behalf of France in 1524. Le Veneur cited voyages to Newfoundland and Brazil as proof of Cartier's ability to "lead ships to the discovery of new lands in the New World".
 On April 20, 1534, Cartier set sail under a commission from the king, hoping to discover a western passage to the wealthy markets of the East Indies. In the words of the commission, he was to "discover certain islands and lands where it is said that a great quantity of gold and other precious things are to be found".
It took him twenty days to sail across the ocean. Starting on May 10 of that year, he explored parts of
On April 20, 1534, Cartier set sail under a commission from the king, hoping to discover a western passage to the wealthy markets of the East Indies. In the words of the commission, he was to "discover certain islands and lands where it is said that a great quantity of gold and other precious things are to be found".
It took him twenty days to sail across the ocean. Starting on May 10 of that year, he explored parts of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, the Strait of Belle Isle
The Strait of Belle Isle ( ; ) is a waterway in eastern Canada, that separates Labrador from the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Location
The strait is located in the southeast of the ...
and southern shore of the Labrador Peninsula
The Labrador Peninsula, also called Quebec-Labrador Peninsula, is a large peninsula in eastern Canada. It is bounded by Hudson Bay to the west, the Hudson Strait to the north, the Labrador Sea to the east, Strait of Belle Isle and the Gulf of ...
, the Gaspé and North Shore coastlines on the Gulf of St. Lawrence, and some parts of the coasts of the Gulf's main islands, including Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
, Anticosti Island and the Magdalen Islands
The Magdalen Islands (, ) are a Canadian archipelago in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Since 2005, the 12-island archipelago is divided into two municipalities: the majority-francophone Municipality of Îles-de-la-Madeleine and the majority-angloph ...
. During one stop at Îles aux Oiseaux (Islands of the Birds, now the Rochers-aux-Oiseaux federal bird sanctuary
An animal sanctuary is a facility where animals are brought to live and to be protected for the rest of their lives. In addition, sanctuaries are an experimental staging ground for transformative human–animal relations. There are five types of ...
, northeast of Brion Island in the Magdalen Islands), his crew slaughtered around 1000 birds, most of them great auk
The great auk (''Pinguinus impennis''), also known as the penguin or garefowl, is an Extinction, extinct species of flightless bird, flightless auk, alcid that first appeared around 400,000 years ago and Bird extinction, became extinct in the ...
s (extinct since 1852). Cartier's first two encounters with aboriginal peoples in Canada
Indigenous peoples in Canada (also known as Aboriginals) are the Indigenous peoples within the boundaries of Canada. They comprise the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis, representing roughly 5.0% of the total Canadian population. There are over ...
on the north side of Chaleur Bay
frame, Satellite image of Chaleur Bay (NASA). Chaleur Bay is the large bay in the centre of the image; the Gulf_of_St._Lawrence.html" ;"title="Gaspé Peninsula is to the north and the Gulf of St. Lawrence">Gaspé Peninsula is to the north and t ...
, most likely the Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Mi'kmaw'' or ''Mi'gmaw''; ; , and formerly Micmac) are an Indigenous group of people of the Northeastern Woodlands, native to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces, primarily Nova Scotia, New Bru ...
, were brief; some trading occurred.
His third encounter took place on the shores of Gaspé Bay with a party of St. Lawrence Iroquoians, where on July 24 he planted a cross to claim the land for France. The 10-metre cross bearing the words "Long Live the King of France" claimed possession of the territory in the King's name. The change in mood was a clear indication that the Iroquoians understood Cartier's actions. Here he kidnapped the two sons of their chief, Donnacona. Cartier wrote that they later told him this region where they were captured (Gaspé) was called by them ''Honguedo''. The natives' chief at last agreed that they could be taken, under the condition that they return with European goods to trade.
Cartier returned to France in September 1534, sure that he had reached an Asian land.
Second voyage (1535–1536)
Jacques Cartier set sail for a second voyage on May 19 of the following year with three ships, 110 men, and his two Iroquoian captives. Reaching the St. Lawrence, he sailed upriver for the first time, and reached the Iroquoian capital of Stadacona, where Chief Donnacona ruled. Cartier claimed a land near St. Lawrence River in 1534; but France paid little attention to the colony for 60 years. Not until KingHenry
Henry may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Henry (given name), including lists of people and fictional characters
* Henry (surname)
* Henry, a stage name of François-Louis Henry (1786–1855), French baritone
Arts and entertainmen ...
IV sent Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; 13 August 1574#Fichier]For a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see #Ritch, RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December ...
in 1608 to New France as its governor and built a permanent settlement and a fur-trading post called Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
.
 Cartier left his main ships in a harbour close to Stadacona, and used his smallest ship to continue on to Hochelaga (now Montreal), arriving on October 2, 1535. Hochelaga was far more impressive than the small and squalid village of Stadacona, and a crowd of over a thousand came to the river's edge to greet the Frenchmen. The site of their arrival has been confidently identified as the beginning of the Sainte-Marie Sault – where the bridge named after him now stands. The expedition could proceed no further, as the river was blocked by rapids. So certain was Cartier that the river was the
Cartier left his main ships in a harbour close to Stadacona, and used his smallest ship to continue on to Hochelaga (now Montreal), arriving on October 2, 1535. Hochelaga was far more impressive than the small and squalid village of Stadacona, and a crowd of over a thousand came to the river's edge to greet the Frenchmen. The site of their arrival has been confidently identified as the beginning of the Sainte-Marie Sault – where the bridge named after him now stands. The expedition could proceed no further, as the river was blocked by rapids. So certain was Cartier that the river was the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic ...
, and that the rapids were all that was preventing him from sailing to China, that the rapids and the town that eventually grew near them came to be named after the French word for China, ''La Chine'': the Lachine Rapids
The Lachine Rapids () are a series of rapids on the Saint Lawrence River, between the Island of Montreal and the South Shore. They are confusingly located near the borough of Lasalle and not Lachine.
The Lachine Rapids contain large standi ...
and the town of Lachine, Quebec
Lachine () is a borough (''arrondissement'') within the city of Montreal on the Island of Montreal in southwestern Quebec, Canada.
It was founded as a trading post in 1669. Developing into a parish and then an autonomous city, it was Montreal m ...
.
After spending two days among the people of Hochelaga, Cartier returned to Stadacona on October 11. It is not known exactly when he decided to spend the winter of 1535–1536 in Stadacona, and it was by then too late to return to France. Cartier and his men prepared for the winter by strengthening their fort, stacking firewood, and salting down game
A game is a structured type of play usually undertaken for entertainment or fun, and sometimes used as an educational tool. Many games are also considered to be work (such as professional players of spectator sports or video games) or art ...
and fish.
 From mid-November 1535 to mid-April 1536, the French fleet lay frozen solid at the mouth of the St. Charles River, under the Rock of Quebec. Ice was over a
From mid-November 1535 to mid-April 1536, the French fleet lay frozen solid at the mouth of the St. Charles River, under the Rock of Quebec. Ice was over a fathom
A fathom is a unit of length in the imperial and the U.S. customary systems equal to , used especially for measuring the depth of water. The fathom is neither an international standard (SI) unit, nor an internationally accepted non-SI unit. H ...
(1.8 m) thick on the river, with snow four feet (1.2 m) deep ashore. To add to the misery, scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease (state of malnutrition) resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, fatigue, and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum d ...
broke out – first among the Iroquoians, and then among the French. Cartier estimated the number of dead Iroquoians at 50. On a visit by Domagaya to the French fort, Cartier inquired and learned from him that a concoction made from a tree known as annedda, probably Spruce beer, or '' arbor vitae'', would cure scurvy. This remedy likely saved the expedition from destruction, allowing 85 Frenchmen to survive the winter. In his journal, Cartier states that by mid-February, "out of 110 that we were, not ten were well enough to help the others, a pitiful thing to see". The Frenchmen used up the bark of an entire tree in a week on the cure, and the dramatic results prompted Cartier to proclaim it a Godsend, and a miracle.Biggar, H.P. (1924) ''The Voyages of Jacques Cartier''. Ottawa: Publications of the Public Archives of Canada. No. 11. p. 204
Ready to return to France in early May 1536, Cartier decided to kidnap Chief Donnacona and take him to France, so that he might personally tell the tale of a country further north, called the " Kingdom of Saguenay", said to be full of gold, rubies and other treasures. After an arduous trip down the St. Lawrence and a three-week Atlantic crossing, Cartier and his men arrived in Saint-Malo on July 15, 1536, concluding the second, 14-month voyage, which was to be Cartier's most profitable.
Third voyage (1541–1542)
 On October 17, 1540, Francis ordered the navigator Jacques Cartier to return to Canada to lend weight to a colonization project of which he would be "captain general". However, January 15, 1541, saw Cartier supplanted by Jean-François de La Rocque de Roberval, a
On October 17, 1540, Francis ordered the navigator Jacques Cartier to return to Canada to lend weight to a colonization project of which he would be "captain general". However, January 15, 1541, saw Cartier supplanted by Jean-François de La Rocque de Roberval, a Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
courtier and friend of the king named as the first lieutenant general of French Canada. Roberval was to lead the expedition, with Cartier as his chief navigator. While Roberval waited for artillery and supplies, he gave permission to Cartier to sail on ahead with his ships.
On May 23, 1541, Cartier departed Saint-Malo on his third voyage with five ships. This time, any thought of finding a passage to the Orient was forgotten. The goals were now to find the "Kingdom of Saguenay" and its riches, and to establish a permanent settlement along the St. Lawrence River.
Anchoring at Stadacona, Cartier again met the Iroquoians, but found their "show of joy" and their numbers worrisome, and decided not to build his settlement there. Sailing a few kilometres upriver to a spot he had previously observed, he decided to settle on the site of present-day Cap-Rouge, Quebec. The convicts and other colonists were landed, the cattle that had survived three months aboard ship were turned loose, earth was broken for a kitchen garden, and seeds of cabbage, turnip, and lettuce were planted. A fortified settlement was thus created and was named Charlesbourg-Royal. Another fort was also built on the cliff overlooking the settlement, for added protection.
The men also began collecting what they believed to be diamonds and gold, but which upon return to France were discovered to be merely quartz crystals and iron pyrites, respectively—which gave rise to a French expression: "''faux comme les diamants du Canada''" ("As false as Canadian diamonds"). Two of the ships were sent on their journey home with some of these minerals on September 2.
Having set tasks for everyone, Cartier left with the longboats for a reconnaissance in search of "Saguenay" on September 7. Having reached Hochelaga, he was prevented by bad weather and the numerous rapids from continuing up to the Ottawa River
The Ottawa River (, ) is a river in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. It is named after the Algonquin word "to trade", as it was the major trade route of Eastern Canada at the time. For most of its length, it defines the border betw ...
.
Returning to Charlesbourg-Royal, Cartier found the situation ominous. The Iroquoians no longer made friendly visits or peddled fish and game, but prowled about in a sinister manner. No records exist about the winter of 1541–1542 and the information must be gleaned from the few details provided by returning sailors. It seems the natives attacked and killed about 35 settlers before the Frenchmen could retreat behind their fortifications. Even though scurvy was cured through the native remedy ( Thuja occidentalis infusion), the impression left is of a general misery, and of Cartier's growing conviction that he had insufficient manpower either to protect his base or to go in search of the Saguenay Kingdom.
Cartier left for France in early June 1542, encountering Roberval and his ships along the Newfoundland coast, at about the time Roberval marooned Marguerite de La Rocque. Despite Roberval's insistence that he accompany him back to Saguenay, Cartier slipped off under the cover of darkness and continued on to France, still convinced his vessels contained a wealth of gold and diamonds. He arrived there in October, in what proved to be his last voyage. Meanwhile, Roberval took command at Charlesbourg-Royal, but it was abandoned in 1543 after disease, foul weather and hostile natives drove the would-be settlers to despair.
Later life
Cartier spent the rest of his life in Saint-Malo and his nearby estate, where he often was useful as an interpreter in Portuguese. He died at age 65 on September 1, 1557, during an epidemic, possibly oftyphus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
, though many sources list his cause of death as unknown. Cartier is interred in Saint-Malo Cathedral.
No permanent European settlements were made in Canada before 1605, when Pierre Dugua, with Samuel Champlain, founded Port Royal
Port Royal () was a town located at the end of the Palisadoes, at the mouth of Kingston Harbour, in southeastern Jamaica. Founded in 1494 by the Spanish, it was once the largest and most prosperous city in the Caribbean, functioning as the cen ...
in Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
.
Legacy
 Having located the entrance to the St. Lawrence on his first voyage, he opened up a major waterway for the European penetration of North America. He produced an intelligent estimate of the resources of Canada, both natural and human, albeit with a considerable exaggeration of its mineral wealth. While some of his actions toward the St. Lawrence Iroquoians were dishonourable, he did try at times to establish friendship with them and other native peoples living along the St. Lawrence River—an indispensable preliminary to French settlement in their lands.
Cartier was the first to document the name
Having located the entrance to the St. Lawrence on his first voyage, he opened up a major waterway for the European penetration of North America. He produced an intelligent estimate of the resources of Canada, both natural and human, albeit with a considerable exaggeration of its mineral wealth. While some of his actions toward the St. Lawrence Iroquoians were dishonourable, he did try at times to establish friendship with them and other native peoples living along the St. Lawrence River—an indispensable preliminary to French settlement in their lands.
Cartier was the first to document the name Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
to designate the territory on the shores of the St-Lawrence River. The name is derived from the Huron–Iroquois
The Iroquois ( ), also known as the Five Nations, and later as the Six Nations from 1722 onwards; alternatively referred to by the Endonym and exonym, endonym Haudenosaunee ( ; ) are an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Ind ...
word , or village, which was incorrectly interpreted as the native term for the newly discovered land. Cartier used the name to describe Stadacona, the surrounding land and the river itself. And Cartier named the inhabitants (Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages () are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, almost all surviving I ...
s) he had seen there. Thereafter the name Canada was used to designate the small French colony on these shores, and the French colonists were called until the mid-nineteenth century, when the name started to be applied to the loyalist colonies on the Great Lakes and later to all of British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestown, ...
. In this way Cartier is not strictly the European discoverer of Canada as this country is understood today, a vast federation stretching (from sea to sea). Eastern parts had previously been visited by the Norse, as well as Basque, Galician and Breton fishermen, and perhaps the Corte-Real brothers and John Cabot
John Cabot ( ; 1450 – 1499) was an Italians, Italian navigator and exploration, explorer. His 1497 voyage to the coast of North America under the commission of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England is the earliest known Europe ...
(in addition of course to the natives who first inhabited the territory). Cartier's particular contribution to the discovery of Canada is as the first European to penetrate the continent, and more precisely the interior eastern region along the St. Lawrence River. His explorations consolidated France's claim of the territory that would later be colonized as New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
, and his third voyage produced the first documented European attempt at settling North America since that of Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón in 1526–27.
Cartier's professional abilities can be easily ascertained. Considering that Cartier made three voyages of exploration in dangerous and hitherto unknown waters without losing a ship, and that he entered and departed some 50 undiscovered harbours without serious mishap, he may be considered one of the most conscientious explorers of the period.
Cartier was also one of the first to formally acknowledge that the New World was a land mass separate from Europe/Asia.
Rediscovery of Cartier's first colony
On August 18, 2006, Quebec Premier Jean Charest announced that Canadian archaeologists had discovered the precise location of Cartier's lost first colony of Charlesbourg-Royal. The colony was built at the confluence of theRivière du Cap Rouge
The Cap-Rouge river () is a river flowing on the north shore of the Saint-Laurent river at the height of the Sainte-Foy–Sillery–Cap-Rouge borough of Quebec City and in the city of Saint-Augustin-de-Desmaures, both cities in the administrativ ...
with the St. Lawrence River and is based on the discovery of burnt wooden timber remains that have been dated to the mid-16th century, and a fragment of a decorative Istoriato plate manufactured in Faenza
Faenza (, ; ; or ; ) is an Italian city and comune of 59,063 inhabitants in the province of Ravenna, Emilia-Romagna, situated southeast of Bologna.
Faenza is home to a historical manufacture of majolica-ware glazed earthenware pottery, known ...
, Italy, between 1540 and 1550, that could only have belonged to a member of the French aristocracy in the colony. Most probably this was the Sieur de Roberval, who replaced Cartier as the leader of the settlement. This colony was the first known European settlement in modern-day Canada since the c. 1000 L'Anse aux Meadows
L'Anse aux Meadows () is an archaeological site, first excavated in the 1960s, of a Norse colonization of North America, Norse settlement dating to approximately 1,000 years ago. The site is located on the northernmost tip of the island of Newf ...
Viking village in northern Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
. Its rediscovery has been hailed by archaeologists as the most important find in Canada since the L'Anse aux Meadows rediscovery.
Ships
 * '' Grande Hermine''
** Built: France 1534; given in 1535 to Cartier by the King of France; used in the 1535–1536 and 1541–1542 voyages; replica 1967 built for
* '' Grande Hermine''
** Built: France 1534; given in 1535 to Cartier by the King of France; used in the 1535–1536 and 1541–1542 voyages; replica 1967 built for Expo 67
The 1967 International and Universal Exposition, commonly known as Expo 67, was a general exhibition from April 28 to October 29, 1967. It was a category one world's fair held in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is considered to be one of the most s ...
in Montréal; abandoned in 2001 from Saint-Charles River (Québec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a population of 839,311. It is the twelfth -lar ...
)
* ''Petite Hermine''
** Built: France; used in the 1535–1536 voyage and abandoned in 1536 springtime by Cartier in Saint-Charles River because too many of his sailors died in Québec City during last wintertime
* ''Émérillon''
** Built: France; used in the 1535–1536 and 1541–1542 voyages
* ''Georges'' (1541–1542)
** Built: France; used in the 1541–1542 voyage
* '' Saint-Brieux''
** Built: France; used in the 1541–1542 voyage
Monuments, remembrances and other art

 Jacques Cartier Island, located on the tip of the
Jacques Cartier Island, located on the tip of the Great Northern Peninsula
The Great Northern Peninsula (or simply just the Northern Peninsula) is the largest and longest peninsula of Newfoundland, Canada, approximately 270 km long and 90 km wide at its widest point and encompassing an area of 17,483 km2. ...
in Newfoundland and Labrador in the town of Quirpon, is said to have been named by Jacques Cartier himself on one of his voyages through the Strait of Belle Isle
The Strait of Belle Isle ( ; ) is a waterway in eastern Canada, that separates Labrador from the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland, in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Location
The strait is located in the southeast of the ...
during the 1530s.
* Jacques-Cartier River, a tributary at Donnacona, Quebec of the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawren ...
* Jacques Cartier Park in Gatineau, Quebec
Gatineau ( ; ) is a city in southwestern Quebec, Canada. It is located on the northern bank of the Ottawa River, directly across from Ottawa, Ontario. Gatineau is the largest city in the Outaouais administrative region of Quebec and is also par ...
* Jacques Cartier Bridge, a steel-truss bridge between Montreal and Longueil, Quebec
* Jacques Cartier Provincial Park, located 5 km east of Alberton, PEI
* Jacques-Cartier State Park, in St. Lawrence County, New York
* Place Jacques-Cartier, a square in Old Montreal
* Cartier Pavilion, built in 1955, at Royal Military College Saint-Jean
The Royal Military College Saint-Jean (), commonly referred to as RMC Saint-Jean and CMR, is a Canadian Military academy, military college and university. It is located on the historical site of Fort Saint-Jean (Quebec), Fort Saint-Jean, in Sai ...
* Jacques Cartier Monument, in Harrington Harbour, Quebec
* The province of Quebec's Parliament Building tower, which was built between 1877 and 1886 by Eugène-Étienne Taché, is dedicated to Cartier
* Manoir de Limoelou, Saint-Malo houses the Musee Jacques Cartier
* plaque at Saint-Malo cathedral
* Cartier-Brébeuf National Historic Site, Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
* Statuary
** at his birthplace, Rothéneuf
** Quebec City, in front of Gabrielle-Roy public library
** at Palais de la Découverte
Palais () may refer to:
* Dance hall, popularly a ''palais de danse'', in the 1950s and 1960s in the UK
* ''Palais'', French for palace
**Grand Palais, the Grand Palais des Champs-Elysées
**Petit Palais, an art museum in Paris
* Palais River in t ...
, Paris
** by Joseph-Arthur Vincent in Montreal: Place Jacques-Cartierameriquefrancaise.org: article on "Jacques Cartier"/ref> ** bronze at PEI's Jacques Cartier Provincial Park ** cast iron sculptures at Gaspe, Quebec ** cross monument at Gaspe, Quebec ** cross monument at Saint-Quentin Island near
Trois-Rivières
Trois-Rivières (, ; ) is a city in the Mauricie administrative region of Quebec, Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Saint-Maurice River, Saint-Maurice and Saint Lawrence River, Saint Lawrence rivers, on the north shore of the Sain ...
Quebec
** by Joseph-Émile Brunet
** in Saint-Malo
Saint-Malo (, , ; Gallo language, Gallo: ; ) is a historic French port in Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany (administrative region), Brittany.
The Fortification, walled city on the English Channel coast had a long history of piracy, earning much wealth ...
* Paintings
** Charles Walter Simpson, ''Saint-Malo, April 1534''
** C.W. Simpson, ''Jacques Cartier at Gaspé, 1534''
** Jean Antoine Théodore de Gudin, ''Jacques Cartier découvre et remonte le fleuve Saint-Laurent au Canada en 1535''
** Walter Baker, ''The Arrival of Cartier at Stadacona, 1535''
** Lawrence R. Batchelor, '' Jacques Cartier at Hochelaga (Montreal)''
** Adrien Hébert, ''Jacques Cartier atterit à Hochelaga en 1535''
** Lucien Boudot and Fernand Cerceau, ''Jacques Cartier est reçu par le chef Agouhana''
** Alfred Faniel, ''Jacques Cartier sur le sommet du mont Royal''
** Frank Craig, ''Jacques Cartier Relating the Story of His Discovery to Francis I at Fontainebleau''begbiecontestsociety.org: "New France – La Nouvelle France"/ref> ** Walter Baker, ''Jacques Cartier's Return to Stadacona, 1541'' ** Théophile Hamel, ''Portrait imaginaire de Jacques Cartier'' (reproduced on many stamps) ** Léopold Massard and de Clugny, ''Jacques Cartier Navigateur'' ** Auguste Lemoine (1895) after François Riss, ''Portrait of Jacques Cartier'' (Musée d'Histoire de Saint-Malo) ** Charles William Jefferys, ''Cartier meets the Indians of the St. Lawrence, 1535'' **
Napoleon Sarony
Napoléon Sarony (March 9, 1821 – November 9, 1896) was an American lithography, lithographer and photography, photographer. He was a highly popular portrait photographer, best known for his portraits of the stars of late-19th-century American ...
() ''Jacques Cartier – His First Interview with the Indians at Hochelaga''
** Paul-Émile Borduas, ''Les voyages de Jacques Cartier au Canada en 1534 et 1535''
** Paul-Émile Borduas, ''Plan d'Hochelaga par Jacques Cartier en 1535''
Popular references
The Banque Jacques-Cartier existed, and printed banknotes, between 1861 and 1899 inLower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada () was a British colonization of the Americas, British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence established in 1791 and abolished in 1841. It covered the southern portion o ...
, then Quebec. It was folded into the Banque provinciale du Canada, and later still the National Bank of Canada
The National Bank of Canada () is the sixth largest commercial bank in Canada. It is headquartered in Montreal, and has branches in most Canadian provinces and 2.4 million personal clients. National Bank is the largest bank in Quebec, and the se ...
.
In 2005, Cartier's '' Bref récit et succincte narration de la navigation faite en MDXXXV et MDXXXVI'' was named one of the 100 most important books in Canadian history by the '' Literary Review of Canada''.''
The Globe and Mail
''The Globe and Mail'' is a Newspapers in Canada, Canadian newspaper printed in five cities in Western Canada, western and central Canada. With a weekly readership of more than 6 million in 2024, it is Canada's most widely read newspaper on week ...
'', November 18, 2005.The Tragically Hip
The Tragically Hip, often referred to simply as the Hip, was a Canadian rock band formed in Kingston, Ontario in 1984, consisting of vocalist Gord Downie, guitarist Paul Langlois, guitarist Rob Baker (known as Bobby Baker until 1994), bassis ...
reference Jacques Cartier in their 1992 song " Looking for a Place to Happen". The song deals with the subject of European encroachment in the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
and the eventual annexation of indigenous lands in North America.
See also
* Jacques Cartier strait, in Gulf of St. Lawrence *Francis I of France
Francis I (; ; 12 September 1494 – 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law Louis&nbs ...
, send Jacques Cartier and others claimed lands in the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
for France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
* Timeline of New France history (1534 to 1607)
A timeline is a list of events displayed in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale representing t ...
* Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * Guitard, Michèle (1984). ''Jacques Cartier in Canada''. Ottawa: National Library of Canada. Text in English and in French, in parallel columns. * * Maura,Juan Francisco, (2021).Españoles y Portugueses en Canadá, en tiempos de Cristóbal Colón., Valencia, Universidad de Valencia.https://parnaseo.uv.es/Lemir/textos/Juan_Maura_Canada.pdf *External links
* *English translation of Cartier's accounts
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cartier, Jacques Explorers of Canada 1491 births 1557 deaths 16th century in Canada 16th century in Quebec French Roman Catholics People from Saint-Malo 16th-century Breton people French explorers of North America Persons of National Historic Significance (Canada)