JCUKEN on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
JCUKEN (''ąÖą”ąŻąÜąĢąØ'', also known as ''YCUKEN'', ''YTsUKEN'' and ''JTSUKEN'') is the main


 After the reform, the ''JIUKEN'' layout sees the following modifications:
* the Cyrillic dotted or "decimal" I is replaced by the number 1;
* the letter čó (yat) is replaced by the letter ąü (yo).
After the reform, the ''JIUKEN'' layout sees the following modifications:
* the Cyrillic dotted or "decimal" I is replaced by the number 1;
* the letter čó (yat) is replaced by the letter ąü (yo).














Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
keyboard layout
A keyboard layout is any specific physical, visual, or functional arrangement of the keys, legends, or key-meaning associations (respectively) of a computer keyboard, mobile phone, or other computer-controlled typographic keyboard. Standard keybo ...
for the Russian language
Russian is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language belonging to the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of the four extant East Slavic languages, and is ...
in computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
s and typewriter
A typewriter is a Machine, mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of Button (control), keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an i ...
s.
Earlier in Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, the ''JIUKEN'' (''ąÖąåąŻąÜąĢąØ'') layout was the main layout, but it was replaced by ''JCUKEN'' in 1953.
Alternative layouts include the Russian phonetic keyboard layouts, in which Cyrillic letters correspond to similar-sounding Latin letter
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Gree ...
s in QWERTY
QWERTY ( ) is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six Computer keyboard keys#Types, keys on the top letter row of the keyboard: . The QWERTY design is based on a layout included in the Sh ...
and other layouts.
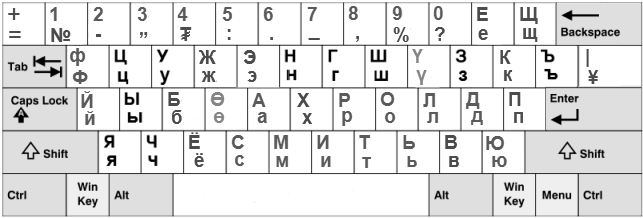
JCUKEN for Russian
MICROSOFT layout
APPLE layout
Typewriters and UNIX layout
Used ontypewriters
A typewriter is a Machine, mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of Button (control), keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an i ...
before personal computers. In Unix-like operating systems this layout is standard (Keyboard GOST 6431-90). It is available in Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
as a legacy layout.
JIUKEN, the predecessor
The ''JIUKEN'' layout was used before the Russian spelling reform of 1917. It includes the Cyrillic dotted or "decimal" I as well as čó, which were eliminated after the reform, but it does not include the letters č▓ and č┤, which were rare even before the reform. The numbers 1, 3 and 0 do not appear on the layout, and this forced the typist to replace them with the letters decimal I, Ze, and O respectively. The letters ą” and ąŁ are located side-by-side; the čó was between the letters ą¦ (Che) and ąĪ (Es). The letter ąü (yo) was not included in this layout.JCUKEN, from typewriter to computer
It is only on July 1, 1953, that the norm GOST 6431-52 on the arrangement of letters, numbers and symbols on the keyboard began to operate. Within a few years, Soviet typewriters switched to the new ''JCUKEN'' layout with the following modifications: * all numbers 1, 3, 0 are present in the first line; * the letter ą” is moved to the previous emplacement of number 1; * letters ą¬, ąŁ, ąü are moved to the end of the three lines of letters. This version is also known today in modern computer as '' Russian (typewriter).'' In OpenSolaris and other Unix-like operating systems this layout is standard (Keyboard GOST 6431-90). At the end of the 80s, when the Soviet Union began issuing analogues of IBM PC/XT personal computers, the Committee on Computer Science and Engineering proposed its own norm (GOST 14289-88). But this version did not follow the same locations of punctuations (and various signs), neither those of the American QWERTY version, nor those of the 6431-90 version. Instead, Microsoft and the keyboard manufacturers delivered a Russian JCUKEN-QWERTY version for MS-DOS, almost analogous to the future version delivered in 1994 with Windows.Other languages
JCUKEN is the basis for many other Cyrillic layouts. For the current momentMicrosoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
supports the following layouts: Azerbaijani (Cyrillic), Bashkir, Belarusian, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Mongolian, Tajik, Ukrainian, Uzbek (Cyrillic), Yakut (Sakha). The Belarusian, Ukrainian and Mongolian layouts have been available since Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft and the first of its Windows 9x family of operating systems, released to manufacturing on July 14, 1995, and generally to retail on August 24, 1995. Windows 95 merged ...
; Azeri, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Tatar, Uzbek since Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users a ...
; Bashkir and Tajik since Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft W ...
; Yakut since Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RTM), released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, ...
.
Other operating systems such as Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
may have their own additional custom layouts for the same or other languages.
Belarusian
Theshort U
Short U (ąÄ č×; italics: ) or U with breve is a letter of the Cyrillic script. The only Slavic language using the letter in its orthography is Belarusian, but it is also used as a phonetic symbol in some Russian and Ukrainian dictionari ...
(ąÄ┬Āč×) is located in place of the shcha
Shcha (ą® čē; italics: ), Shta, or Scha is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Russian, it represents the long voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative , similar to the pronunciation of one of the s in ''Welsh''-''sheep''. In Ukrainian and R ...
(ą®┬Āčē). It is the only JCUKEN keyboard that lacks a key for ąś, as it is the only language in the Cyrillic script that does not contain the letter ąś itself; the decimal I (ąå┬Āč¢) replaces it. It also lacks a hard sign
The letter ą¬ čŖ (italics ) of the Cyrillic script is known as er golyam ( ŌĆō "big er") in the Bulgarian alphabet, as the hard sign (, , ) in the modern Russian and Rusyn alphabets (although in Rusyn, čŖ could also be known as č¢čĆ), as t ...
(ą¬┬ĀčŖ), usually seen just to the right of letter ha (ąź┬Āčģ), as that position is taken by the apostrophe
The apostrophe (, ) is a punctuation mark, and sometimes a diacritical mark, in languages that use the Latin alphabet and some other alphabets. In English, the apostrophe is used for two basic purposes:
* The marking of the omission of one o ...
.
Ukrainian
The decimal I replaces the yeru (ą½ čŗ) and the yest (ąä čö) replaces the E (ąŁ čŹ). The letter Yi (ąć čŚ) substitutes for thehard sign
The letter ą¬ čŖ (italics ) of the Cyrillic script is known as er golyam ( ŌĆō "big er") in the Bulgarian alphabet, as the hard sign (, , ) in the modern Russian and Rusyn alphabets (although in Rusyn, čŖ could also be known as č¢čĆ), as t ...
(ą¬ čŖ), and Ghe with upturn
Ge or G (ęÉ ęæ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It is part of the Ukrainian alphabet, the Pannonian Rusyn alphabet and both the Carpathian Rusyn alphabets, and also some variants of the Urum and Belarusian (i.e. Belarus ...
(ęÉ ęæ) is also used.
Tatar
The Russian letters which are rarely used in Tatar are typed with (right ). This layout is also suitable for Kalmyk and Turkmen (Cyrillic) as their alphabets are practically identical to Tatar. It is called as YÛUKEN.Bashkir
Kazakh
Kyrgyz
An "upgraded" version based on the basic Russian one, the additional Kyrgyz letters are typed with (right ). Thus, + ąŻ is ę«, + ą× is ė©, and + ąØ is ęó.Yakut
Tajik
This┬Āis a modified version of JCUKEN called YQUKEN, in which the Ka with descender (ęÜ ęø) substitutes the C (ą” čå). The yeru (ą½ čŗ) is replaced by the letterChe with descender
Che with descender (ęČ ęĘ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Che (ą¦ čć ). In the ISO 9 system of romanization, Che with descender is transliterated using the Latin letter ...
(ęČ ęĘ). Also, the soft sign
The soft sign (ą¼ čī; italics: ) is a letter in the Cyrillic script that is used in various Slavic languages. In Old Church Slavonic, it represented a short or reduced front vowel. However, over time, the specific vowel sound it denote ...
(ą¼ čī) is replaced by the I with macron (ėó ėŻ). Further, the Kha with descender
Kha with descender (ę▓ ę│; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Unicode, this letter is called "Ha with descender". Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Kha (ąź čģ ).
Kha with descender is used in the alpha ...
(ę▓ ę│) substitutes for Shcha (ą® čē), and the U with macron (ė« ė»), and the ghayn
The Arabic letter (, or ) is one of the six letters the Arabic alphabet added to the twenty-two inherited from the Phoenician alphabet (the others being , , , , ). It represents the sound or . In name and shape, it is a variant of ╩╗ayn ...
(ęÆ ęō) are used. (In Unicode, Kha with descender is known as "Ha with descender".)
Uzbek
Theshort U
Short U (ąÄ č×; italics: ) or U with breve is a letter of the Cyrillic script. The only Slavic language using the letter in its orthography is Belarusian, but it is also used as a phonetic symbol in some Russian and Ukrainian dictionari ...
substitutes the shcha
Shcha (ą® čē; italics: ), Shta, or Scha is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Russian, it represents the long voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative , similar to the pronunciation of one of the s in ''Welsh''-''sheep''. In Ukrainian and R ...
, like the Belarusian keyboard (see above), and the ka with descender substitutes the yery
Yeru or Eru (ą½ čŗ; italics: ''ą½'' ''čŗ''), usually called Y in modern Russian language, Russian or Yery or Ery historically and in modern Church Slavonic, is a letter in the Cyrillic script. It represents the close central unround ...
. Moreover, the letter ghayn
The Arabic letter (, or ) is one of the six letters the Arabic alphabet added to the twenty-two inherited from the Phoenician alphabet (the others being , , , , ). It represents the sound or . In name and shape, it is a variant of ╩╗ayn ...
substitutes the minus sign
The plus sign () and the minus sign () are mathematical symbols used to denote positive and negative functions, respectively. In addition, the symbol represents the operation of addition, which results in a sum, while the symbol represent ...
and the underscore
An underscore or underline is a line drawn under a segment of text. In proofreading, underscoring is a convention that says "set this text in italic type", traditionally used on manuscript or typescript as an instruction to the printer. Its ...
, while the kha with descender
Kha with descender (ę▓ ę│; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Unicode, this letter is called "Ha with descender". Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Kha (ąź čģ ).
Kha with descender is used in the alpha ...
substitutes the plus sign
The plus sign () and the minus sign () are mathematical symbols used to denote positive and negative functions, respectively. In addition, the symbol represents the operation of addition, which results in a sum, while the symbol represents ...
and equal sign
The equals sign (British English) or equal sign (American English), also known as the equality sign, is the mathematical symbol , which is used to indicate equality. In an equation it is placed between two expressions that have the same value, ...
.
Azerbaijani
This layout is a modified version called the JÜUKEN, and includes theChe with vertical stroke
Che with vertical stroke (ęĖ ę╣; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Che (ą¦ čć ).
Che with vertical stroke is used in the alphabet of the Azeri language and Altai language ...
, shha, Ka with vertical stroke
Ka with vertical stroke (ę£ ęØ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Ka (ąÜ ą║) by the addition of a stroke through the short horizontal bar in the center of the letter.
Ka with ...
, and the Je. It is the only JCUKEN without the usual ąÖ, as the language lacks the glyph, which was replaced by Je in 1958.
Substitutions to this keyboard are: having the schwa replacing the ya, the oe replacing the yu, the ghayn
The Arabic letter (, or ) is one of the six letters the Arabic alphabet added to the twenty-two inherited from the Phoenician alphabet (the others being , , , , ). It represents the sound or . In name and shape, it is a variant of ╩╗ayn ...
replacing the soft sign
The soft sign (ą¼ čī; italics: ) is a letter in the Cyrillic script that is used in various Slavic languages. In Old Church Slavonic, it represented a short or reduced front vowel. However, over time, the specific vowel sound it denote ...
, the Che with vertical stroke
Che with vertical stroke (ęĖ ę╣; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Che (ą¦ čć ).
Che with vertical stroke is used in the alphabet of the Azeri language and Altai language ...
replacing the hard sign
The letter ą¬ čŖ (italics ) of the Cyrillic script is known as er golyam ( ŌĆō "big er") in the Bulgarian alphabet, as the hard sign (, , ) in the modern Russian and Rusyn alphabets (although in Rusyn, čŖ could also be known as č¢čĆ), as t ...
, the ue replacing the tsa and the shha replacing the shcha
Shcha (ą® čē; italics: ), Shta, or Scha is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Russian, it represents the long voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative , similar to the pronunciation of one of the s in ''Welsh''-''sheep''. In Ukrainian and R ...
.
Mongolian
The Mongolian keyboard uses a modified version of JCUKEN, called FCUZHEN (ążą”ąŻą¢ąŁąØ), where letters specific to Russian are replaced by letters that see more use in Mongolian.
Other Cyrillic layouts
Serbian
Because Serbian andRussian alphabet
The Russian alphabet (, or , more traditionally) is the script used to write the Russian language.
The modern Russian alphabet consists of 33 letters: twenty consonants (, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ), ten vowels (, , , , , , , , , ) ...
are different, the Serbian keyboard LjNjERTZ (ąēąŖąĢąĀąóąŚ) lacks the yers and yeru (ą¬ čŖ, ą¼ čī and ą½ čŗ), ąŁ, and ąü, as they are not used in the Serbian language, but has a key for dze (ąģ čĢ) in spite of that. It is based on the QWERTZ
The QWERTZ ( ) QWERTZU ( ), or QWERTZUIOP keyboard is a typewriter and keyboard layout widely used in Central and Southeast Europe. The name comes from the first six letters at the top left of the keyboard: ( ).
Overview
The main differ ...
keyboard layout.
Macedonian
The Macedonian layout is a modification of the Serb-style keyboard layout. On the Macedonian keyboard layouts under Microsoft Windows, AltGr can be used to access additional letters and punctuation. Notably, it resemblesQWERTY
QWERTY ( ) is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six Computer keyboard keys#Types, keys on the top letter row of the keyboard: . The QWERTY design is based on a layout included in the Sh ...
to a larger extent and has the placement of ąģ and ąŚ switched.
Bulgarian Keyboards
Phonetic, Traditional

Phonetic, BDS 5237:2006
In 2006, Dimiter Skordev, from the Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics atSofia University
Sofia University "St. Kliment Ohridski" () is a public university, public research university in Sofia, Bulgaria. It is the oldest institution of higher education in Bulgaria.
Founded on 1 October 1888, the edifice of the university was constr ...
, co-authored a proposal for a new phonetic keyboard layout. This proposal was included in the draft of the national standard BDS 5237:2006, titled "Keyboard Layouts for Devices Typing in Bulgarian".
The introduction of the new phonetic keyboard layout as part of the BDS 5237:2006 standard sparked considerable controversy. It was not announced to the public until its implementation. There were no extensive public consultations, nor was the opinion of the taken into account. According to the creators of the standard, tests were conducted in elite schools in Sofia
Sofia is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain, in the western part of the country. The city is built west of the Is ...
during the project's development. However, the methodology and results of these tests were not disclosed.
The creators argued that new generations would adapt to the layout and type faster. However, it was unclear why a more efficient layout from 1978, which is still in use, was not promoted, especially since the new phonetic layout differs from the widely used traditional one.

Typewriter layout
In October 1907, , then head of the Stenographic Bureau of theNational Assembly of Bulgaria
The National Assembly () is the Unicameralism, unicameral parliament and Legislature, legislative body of the Republic of Bulgaria. The first National Assembly was established in 1879 with the Tarnovo Constitution.
During the People's Republic ...
, conducted, along with a team of stenographers, the first corpus study of the Bulgarian language
Bulgarian (; , ) is an Eastern South Slavic, Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeast Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians.
Along with the closely related Macedonian language (collectively forming the ...
. The study analyzed "10,000 words from various fields of human life" to create a unified Bulgarian keyboard layout. Although typewriters had been available in Bulgaria since 1902, no standard letter arrangement existed. The study resulted in a booklet, the first documented source regulating Bulgarian typewriting and introducing professional ten-finger typing. It was published in early 1908.
The layout is highly ergonomic, and its efficiency has been demonstrated in competitions among keyboard operators. No significant changes have been made to the layout ever since, and in 1978, it was officially recognized as the Bulgarian National Standard (BDS 5237:1978).
See also
*QWERTY
QWERTY ( ) is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six Computer keyboard keys#Types, keys on the top letter row of the keyboard: . The QWERTY design is based on a layout included in the Sh ...
* ąü ("yo") letter, often instinctively disregarded by JCUKEN users.
References