Italian Irredentist on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Italian irredentism ( ) was a
Italian irredentism ( ) was a
 Italian irredentism was not a formal organization but rather an opinion movement, advocated by several different groups, claiming that Italy had to reach its " natural borders" or unify territories inhabited by Italians. Similar nationalistic ideas were common in
Italian irredentism was not a formal organization but rather an opinion movement, advocated by several different groups, claiming that Italy had to reach its " natural borders" or unify territories inhabited by Italians. Similar nationalistic ideas were common in
 The Corsican revolutionary
The Corsican revolutionary
 In the early 19th century the ideals of unification in a single Nation of all the territories populated by Italian-speaking people created the Italian irredentism. Many Istrian Italians and
In the early 19th century the ideals of unification in a single Nation of all the territories populated by Italian-speaking people created the Italian irredentism. Many Istrian Italians and  The
The
 Italian irredentism ( ) was a
Italian irredentism ( ) was a political movement
A political movement is a collective attempt by a group of people to change government policy or social values. Political movements are usually in opposition to an element of the status quo, and are often associated with a certain ideology. Some t ...
during the late 19th and early 20th centuries in Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
with irredentist
Irredentism () is one state's desire to annex the territory of another state. This desire can be motivated by ethnic reasons because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to or the same as the population of the parent state. Hist ...
goals which promoted the unification of geographic areas in which indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
were considered to be ethnic Italians. At the beginning, the movement promoted the annexation to Italy of territories where Italians formed the absolute majority of the population, but retained by the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
after the Third Italian War of Independence
The Third Italian War of Independence () was a war between the Kingdom of Italy and the Austrian Empire fought between June and August 1866. The conflict paralleled the Austro-Prussian War and resulted in Austria giving the region of Venetia (p ...
in 1866.
Even after the Capture of Rome
The Capture of Rome () occurred on 20 September 1870, as forces of the Kingdom of Italy took control of the city and of the Papal States. After a plebiscite held on 2 October 1870, Rome was officially made capital of Italy on 3 February 1871, c ...
(1871), the final event of the unification of Italy, many ethnic Italian speakers ( Trentino-Alto Adigan Italians, Savoyard Italians, Corfiot Italians, Niçard Italians
Niçard Italians ( ) are Italians who have full or partial County of Nice, Nice heritage by birth or ethnicity.
History
Niçard Italians have roots in Nice and the County of Nice. They often speak the Ligurian language after Nice joined the Genoa ...
, Swiss Italians, Corsican Italians, Maltese Italians, Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians (; ) are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Historically, Italian language-speaking Dalmatians accounted for 12.5% of population in 1865, 5.8% in 18 ...
) remained outside the borders of the Kingdom of Italy and this situation created the Italian irredentism. During World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
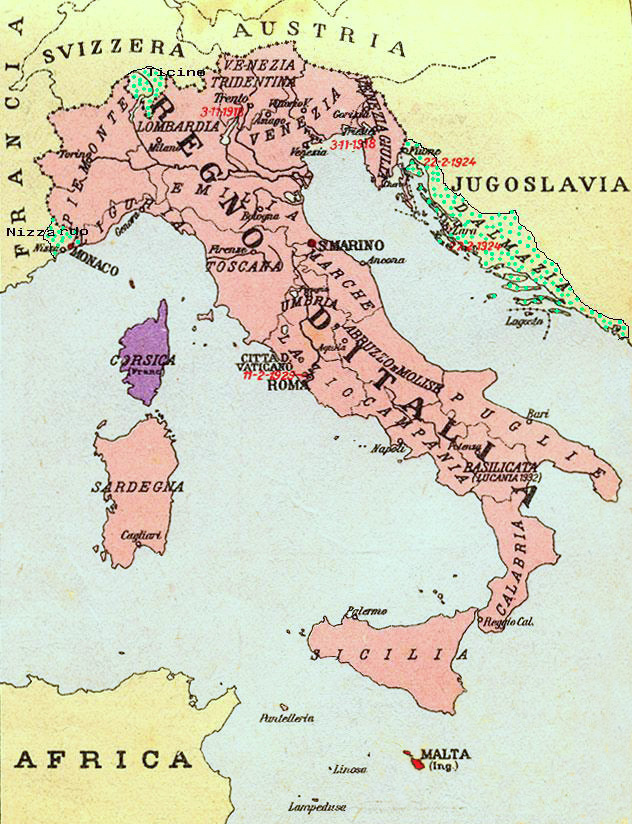
the main "irredent lands" (''terre irredente'') were considered to be the provinces of Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin language, Ladin and ; ; ; ; ; ), also known in English as Trent, is a city on the Adige, Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the Trentino, autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th ...
and Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
and, in a narrow sense, irredentists referred to the Italian patriots living in these two areas.
Italian irredentism was not a formal organization but rather an opinion movement, advocated by several different groups, claiming that Italy had to reach its " natural borders" or unify territories inhabited by Italians. Similar nationalistic ideas were common in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
in the late 19th century. The term "irredentism", coined from the Italian word, came into use in many countries (see List of irredentist claims or disputes). This idea of ''Italia irredenta'' is not to be confused with the ''Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
'', the historical events that led to irredentism, nor with nationalism or Imperial Italy, the political philosophy that took the idea further under fascism
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural social hie ...
.
The term was later expanded to also include multilingual and multiethnic areas, where Italians were a relative majority or a substantial minority, within the northern Italian region encompassed by the Alps, with German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
, Slovene, Croatian, Ladin and Istro-Romanian population, such as South Tyrol
South Tyrol ( , ; ; ), officially the Autonomous Province of Bolzano – South Tyrol, is an autonomous administrative division, autonomous provinces of Italy, province in northern Italy. Together with Trentino, South Tyrol forms the autonomo ...
, Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, Gorizia and Gradisca
The Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca (; ; ), historically sometimes shortened to and spelled "Goritz", was a crown land of the Habsburg dynasty within the Austrian Littoral on the Adriatic Sea, in what is now a multilingual border area of ...
and part of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
. The claims were further extended also to the city of Fiume
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( �fjuːme in Italian and in Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a po ...
, Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
, the island of Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, the County of Nice
The County of Nice (; ; Niçard ) was a historical region of France and Italy located around the southeastern city of Nice and roughly equivalent to the modern arrondissement of Nice. It was part of the Savoyard state within the Holy Roman Emp ...
and Italian Switzerland.
After the end of World War I, the Italian irredentist movement was hegemonised, manipulated and distorted by fascism, which made it an instrument of nationalist propaganda, placed at the center of a policy, conditioned by belated imperial ambitions, which took the form of "forced Italianization
Italianization ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is the spread of Italian culture, language and identity by way of integration or assimilation. It is also known for a process organized by the Kingdom of Italy to force cultural and ethnic assimilation of the nati ...
s", in the aspiration for the birth of a ''Great Italy'' and a vast Italian Empire
The Italian colonial empire (), also known as the Italian Empire (''Impero italiano'') between 1936 and 1941, was founded in Africa in the 19th century. It comprised the colonies, protectorates, concession (territory), concessions and depende ...
. After World War II, Italian irredentism disappeared along with the defeated Fascists and the Monarchy of the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy (, ) is a royal house (formally a dynasty) of Franco-Italian origin that was established in 1003 in the historical region of Savoy, which was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy and now lies mostly within southeastern F ...
. After the Treaty of Paris (1947) and the Treaty of Osimo (1975), all territorial claims were abandoned by the Italian Republic
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
(see Foreign relations of Italy
The foreign relations of the Italian Republic are the Italian government's external relations with the outside world. Located in Europe, Italy has been considered a major Western power since its unification in 1860. Its main allies are the NA ...
). The Italian irredentist movement thus vanished from Italian politics.
Characteristics
 Italian irredentism was not a formal organization but rather an opinion movement, advocated by several different groups, claiming that Italy had to reach its " natural borders" or unify territories inhabited by Italians. Similar nationalistic ideas were common in
Italian irredentism was not a formal organization but rather an opinion movement, advocated by several different groups, claiming that Italy had to reach its " natural borders" or unify territories inhabited by Italians. Similar nationalistic ideas were common in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
in the late 19th century. The term ''irredentism'', coined from the Italian word, came into use in many countries (see List of irredentist claims or disputes). This idea of ''Italia irredenta'' is not to be confused with the ''Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
'', the historical events that led to irredentism, nor with nationalism or Imperial Italy, the political philosophy that took the idea further under fascism
Fascism ( ) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It is characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural social hie ...
.
During the 19th century, Italian irredentism fully developed the characteristic of defending the Italian language from other people's languages such as, for example, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
in Switzerland and in the Austro-Hungarian Empire or French in Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionCorsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
.
The liberation of ''Italia irredenta'' was perhaps the strongest motive for Italy's entry into World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and the Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed on 28 June 1919. As the most important treaty of World War I, it ended the state of war between Germany and most of the Allies of World War I, Allied Powers. It was signed in the Palace ...
in 1919 satisfied many irredentist claims.
Italian irredentism has the characteristic of being originally moderate, requesting only the return to Italy of the areas with Italian majority of population, but after World War I it became aggressive – under fascist influence – and claimed to the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
even areas where Italians were a minority or had been present only in the past. In the first case there were the ''Risorgimento'' claims on Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin language, Ladin and ; ; ; ; ; ), also known in English as Trent, is a city on the Adige, Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the Trentino, autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th ...
, while in the second there were the fascist claims on the Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands (Modern Greek: , ; Ancient Greek, Katharevousa: , ) are a archipelago, group of islands in the Ionian Sea, west of mainland Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese ("Seven Islands"; , ''Heptanēsa'' or , ''Heptanē ...
, Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
and Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
.
History
Origins
 The Corsican revolutionary
The Corsican revolutionary Pasquale Paoli
Filippo Antonio Pasquale de' Paoli (; or ; ; 6 April 1725 – 5 February 1807) was a Corsican patriot, statesman, and military leader who was at the forefront of resistance movements against the Republic of Genoa, Genoese and later Kingd ...
was called "the precursor of Italian irredentism" by Niccolò Tommaseo
Niccolò Tommaseo (; 9 October 1802 – 1 May 1874) was a Dalmatian Italian linguist, journalist and essayist, the editor of a (''A Dictionary of the Italian Language'') in eight volumes (1861–74), of a dictionary of synonyms (1830) and other ...
because he was the first to promote the Italian language and socio-culture (the main characteristics of Italian irredentism) in his island; Paoli wanted the Italian language
Italian (, , or , ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. It evolved from the colloquial Latin of the Roman Empire. Italian is the least divergent language from Latin, together with Sardinian language, Sardinian. It is ...
to be the official language of the newly founded Corsican Republic
The Corsican Republic () was a short-lived state on the island of Corsica in the Mediterranean Sea. It was proclaimed in July 1755 by Pasquale Paoli, who was seeking independence from the Republic of Genoa. Paoli created the Corsican Constitutio ...
.
Pasquale Paoli's appeal in 1768 against the French invader said:
Paoli's Corsican Constitution
The first Corsican Constitution was drawn up in 1755 for the short-lived Corsican Republic independent from Genoa beginning in 1755, and remained in force until the annexation of Corsica by France in 1769. It was written in Tuscan Italian, the ...
of 1755 was written in Italian and the short-lived university he founded in the city of Corte in 1765 used Italian as the official language. Paoli was sympathetic to Italian culture
The culture of Italy encompasses the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, and customs of the Italian peninsula throughout history. Italy has been a pivotal center of civilisation, playing a crucial role in the development of Western culture. I ...
and regarded his own native language as an Italian dialect (Corsican is an Italo-Dalmatian tongue closely related to Tuscan).
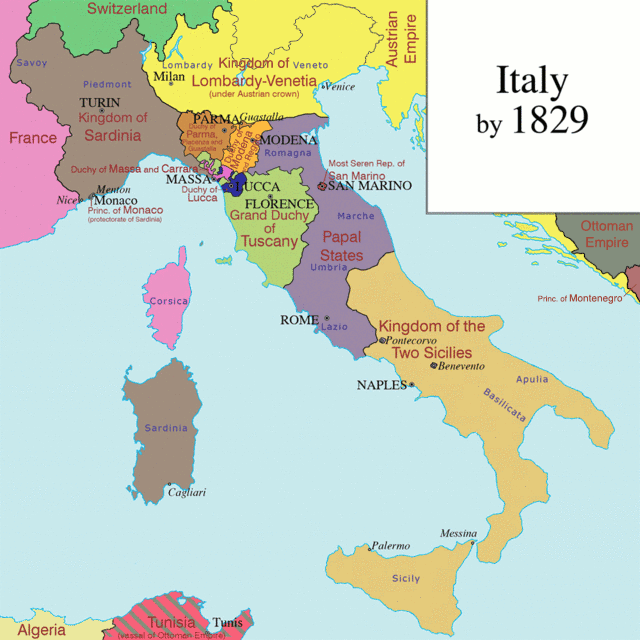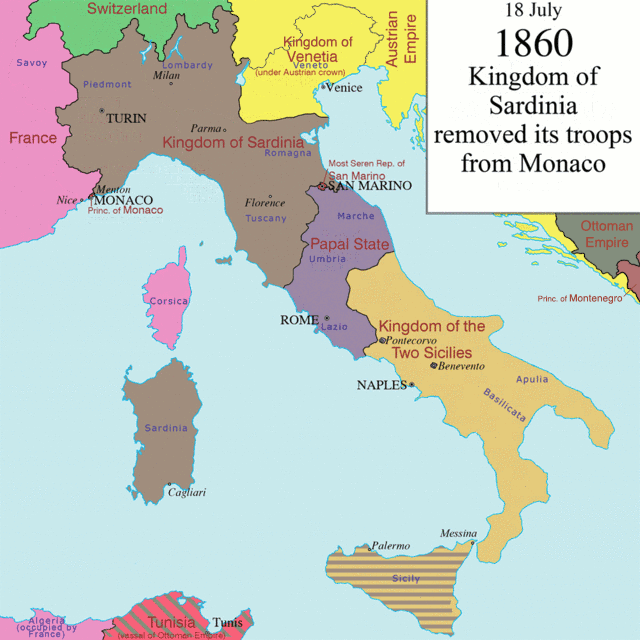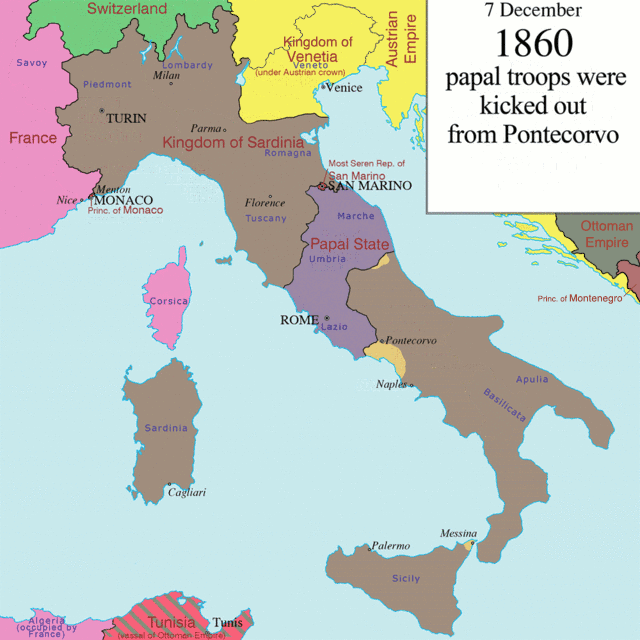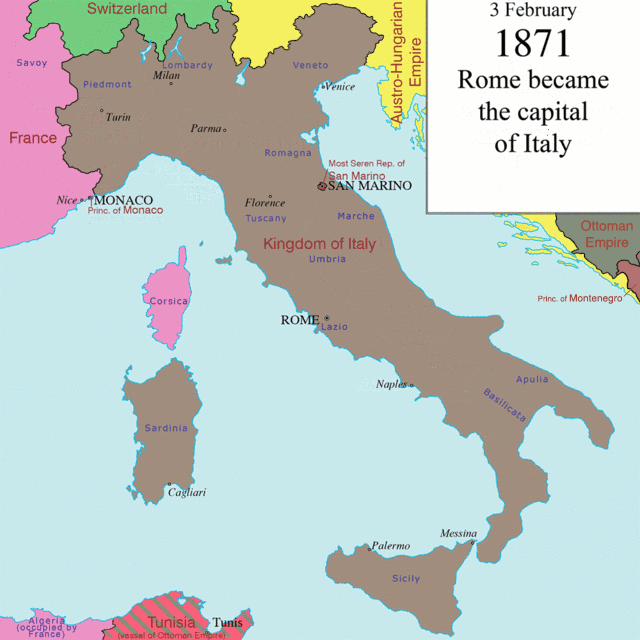
After the Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
and Third Italian War of Independence
The Third Italian War of Independence () was a war between the Kingdom of Italy and the Austrian Empire fought between June and August 1866. The conflict paralleled the Austro-Prussian War and resulted in Austria giving the region of Venetia (p ...
in 1866, there were areas with Italian-speaking communities within the borders of several countries around the newly created Kingdom of Italy. The irredentists sought to annex all those areas to the newly unified Italy. The areas targeted were Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
, Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, Gorizia
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, Region ...
, Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, County of Nice
The County of Nice (; ; Niçard ) was a historical region of France and Italy located around the southeastern city of Nice and roughly equivalent to the modern arrondissement of Nice. It was part of the Savoyard state within the Holy Roman Emp ...
, Ticino
Ticino ( ), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts ...
, small parts of Grisons
The Grisons (; ) or Graubünden (),Names include:
* ;
*Romansh language, Romansh:
**
**
**
**
**
**;
* ;
* ;
* .
See also list of European regions with alternative names#G, other names. more formally the Canton of the Grisons or the Canton ...
and of Valais
Valais ( , ; ), more formally, the Canton of Valais or Wallis, is one of the cantons of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of thirteen districts and its capital and largest city is Sion, Switzer ...
, Trentino
Trentino (), officially the Autonomous Province of Trento (; ; ), is an Autonomous province#Italy, autonomous province of Italy in the Northern Italy, country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the Regions of Italy, region of Tren ...
, Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
and Fiume
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( �fjuːme in Italian and in Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a po ...
.
Different movements or groups founded in this period included the Italian politician Matteo Renato Imbriani inventing the new term ''terre irredente'' ("unredeemed lands") in 1877; in the same year the movement ''Associazione in pro dell'Italia Irredenta'' ("Association for the Unredeemed Italy") was founded; in 1885 the ''Pro Patria'' movement ("For Fatherland") was founded and in 1891 the ''Lega Nazionale Italiana'' ("Italian National League") was founded in Trento and Trieste (in the Austrian Empire).
Initially, the movement can be described as part of the more general nation-building
Nation-building is constructing or structuring a national identity using the power of the state. Nation-building aims at the unification of the people within the state so that it remains politically stable and viable. According to Harris Mylonas, ...
process in Europe in the 19th and 20th centuries when the multi-national Austro-Hungarian
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consist ...
, Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
and Ottoman Empires were being replaced by nation-states. The Italian nation-building process can be compared to similar movements in Germany ('' Großdeutschland''), Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
and in pre-1914 Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
. Simultaneously, in many parts of 19th-century Europe liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality, the right to private property, and equality before the law. ...
and nationalism
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, I ...
were ideologies which were coming to the forefront of political culture. In Eastern Europe, where the Habsburg Empire had long asserted control over a variety of ethnic and cultural groups, nationalism appeared in a standard format. The beginning of the 19th century "was the period when the smaller, mostly indigenous nationalities of the empire – Czechs
The Czechs (, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common Bohemia ...
, Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
, Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, and History of Slove ...
, Croats
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
, Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
– remembered their historical traditions, revived their native tongues as literary languages, reappropriated their traditions and folklore, in short, reasserted their existence as nations".
19th century
 In the early 19th century the ideals of unification in a single Nation of all the territories populated by Italian-speaking people created the Italian irredentism. Many Istrian Italians and
In the early 19th century the ideals of unification in a single Nation of all the territories populated by Italian-speaking people created the Italian irredentism. Many Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians (; ) are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Historically, Italian language-speaking Dalmatians accounted for 12.5% of population in 1865, 5.8% in 18 ...
looked with sympathy towards the ''Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
'' movement that fought for the unification of Italy.
The current Italian Switzerland belonged to the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
until the 16th century
The 16th century began with the Julian calendar, Julian year 1501 (represented by the Roman numerals MDI) and ended with either the Julian or the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian year 1600 (MDC), depending on the reckoning used (the Gregorian calend ...
, when it became part of Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
. These territories have maintained their native Italian population speaking the Italian language
Italian (, , or , ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. It evolved from the colloquial Latin of the Roman Empire. Italian is the least divergent language from Latin, together with Sardinian language, Sardinian. It is ...
and the Lombard language
The Lombard language (,Classical Milanese orthography, and . ,Ticino, Ticinese orthography. Modern Western orthography and Classical Cremish Orthography. or ,Eastern Lombard, Eastern unified orthography. depending on the orthography; pronuncia ...
, specifically the Ticinese dialect. Italian irredentism in Switzerland was based on moderate ''Risorgimento'' ideals, and was promoted by Italian-Ticinese such as .
Following a brief French occupation (1798–1800) the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
established control over Malta while it was still formally part of the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
. During both the French and British periods, Malta officially remained part of the Sicilian Kingdom, although the French refused to recognise the island as such in contrast to the British. Malta became a British Crown Colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony governed by England, and then Great Britain or the United Kingdom within the English and later British Empire. There was usually a governor to represent the Crown, appointed by the British monarch on ...
in 1813, which was confirmed a year later through the Treaty of Paris (1814)
The Treaty of Paris, signed on 30 May 1814, ended the war between France and the Sixth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars, following an armistice signed on 23 April between Charles, Count of Artois, and the allies. The treaty set the bord ...
. Cultural changes were few even after 1814. In 1842, all literate Maltese learned Italian while only 4.5% could read, write and/or speak English. However, there was a huge increase in the number of Maltese magazines and newspapers in the Italian language during the 1800s and early 1900s, so as a consequence the Italian was understood (but not spoken fluently) by more than half the Maltese people before WW1.
 The
The Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
again attacked the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
in the Second Italian War of Independence
The Second Italian War of Independence, also called the Sardinian War, the Austro-Sardinian War, the Franco-Austrian War, or the Italian War of 1859 (Italian: ''Seconda guerra d'indipendenza italiana''; German: ''Sardinischer Krieg''; French: ...
of 1859, with the aid of France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, resulting in the liberation of Lombardy
The Lombardy Region (; ) is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in northern Italy and has a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of Italy's population. Lombardy is ...
. On the basis of the Plombières Agreement
The Plombières Agreement (, ) of 21 July 1858 was a secret verbal agreement which took place at Plombières-les-Bains between the chief minister of Kingdom of Sardinia, Piedmont-Sardinia, Camillo Benso, Count of Cavour, and the Emperor of the ...
, the Kingdom of Sardinia ceded Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
and Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionNiçard exodus, that was the emigration of a quarter of the 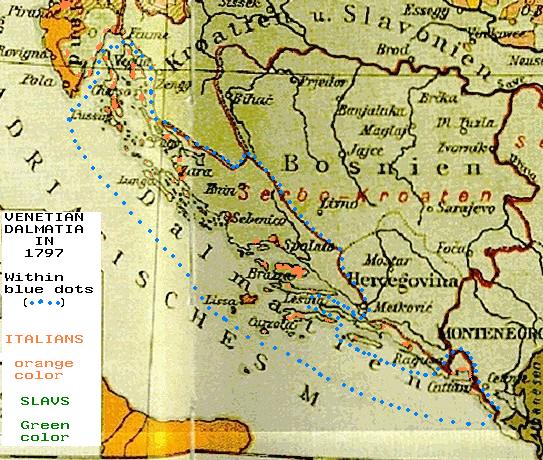 Istrian Italians made up about a third of the population in 1900. Dalmatia, especially its maritime cities, once had a substantial local ethnic Italian population (
Istrian Italians made up about a third of the population in 1900. Dalmatia, especially its maritime cities, once had a substantial local ethnic Italian population ( The Italian population in Dalmatia was concentrated in the major coastal cities. In the city of
The Italian population in Dalmatia was concentrated in the major coastal cities. In the city of
 After the end of
After the end of
Niçard Italians
Niçard Italians ( ) are Italians who have full or partial County of Nice, Nice heritage by birth or ethnicity.
History
Niçard Italians have roots in Nice and the County of Nice. They often speak the Ligurian language after Nice joined the Genoa ...
to Italy. Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as (). In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as () or (). 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, revolutionary and republican. H ...
was elected in 1871 in Nice at the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the repr ...
where he tried to promote the annexation of his hometown to the newborn Italian unitary state, but he was prevented from speaking. Because of this denial, between 1871 and 1872 there were riots in Nice, promoted by the Garibaldini and called " Niçard Vespers", which demanded the annexation of the city and its area to Italy. Fifteen Nice people who participated in the rebellion were tried and sentenced.
In the spring of 1860 Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
was annexed to France after a referendum and the administrative boundaries changed, but a segment of the Savoyard population demonstrated against the annexation. Indeed, the final vote count on the referendum announced by the Court of Appeals was 130,839 in favour of annexation to France, 235 opposed and 71 void, showing questionable complete support for French nationalism (that motivated criticisms about rigged results). At the beginning of 1860, more than 3000 people demonstrated in Chambéry against the annexation to France rumours. On 16 March 1860, the provinces of Northern Savoy (Chablais, Faucigny and Genevois) sent to Victor Emmanuel II
Victor Emmanuel II (; full name: ''Vittorio Emanuele Maria Alberto Eugenio Ferdinando Tommaso di Savoia''; 14 March 1820 – 9 January 1878) was King of Sardinia (also informally known as Piedmont–Sardinia) from 23 March 1849 until 17 March ...
, to Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles-Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was President of France from 1848 to 1852 and then Emperor of the French from 1852 until his deposition in 1870. He was the first president, second emperor, and last ...
, and to the Swiss Federal Council a declaration - sent under the presentation of a manifesto together with petitions - where they were saying that they did not wish to become French and shown their preference to remain united to the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
(or be annexed to Switzerland in the case a separation with Sardinia was unavoidable). Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as (). In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as () or (). 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, revolutionary and republican. H ...
complained about the referendum that allowed France to annex Savoy and Nice, and a group of his followers (among the Italian Savoyards) took refuge in Italy in the following years.
In 1861, with the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy
The proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy happened with a legal norm, normative act of the House of Savoy, Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia — the law 17 March 1861, n. 4761 — with which Victor Emmanuel II assumed for himself and for his successors ...
, the modern Italian state was born. On 21 July 1878, a noisy public meeting was held at Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
with Menotti Garibaldi, the son of Giuseppe Garibaldi, as chairman of the forum and a clamour was raised for the formation of volunteer battalions to conquer the Trentino. Benedetto Cairoli
Benedetto Cairoli (28 January 1825 – 8 August 1889) was an Italian politician, who served as Prime Minister of Italy for 2 years.
Biography
Cairoli was born at Pavia, Lombardy. From 1848 until the completion of Italian unity in 1870, his whol ...
, then Prime Minister of Italy
The prime minister of Italy, officially the president of the Council of Ministers (), is the head of government of the Italy, Italian Republic. The office of president of the Council of Ministers is established by articles 92–96 of the Co ...
, treated the agitation with tolerance. However, it was mainly superficial, as most Italians did not wish a dangerous policy against Austria or against Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
for Malta.
Many Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians (; ) are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Historically, Italian language-speaking Dalmatians accounted for 12.5% of population in 1865, 5.8% in 18 ...
looked with sympathy towards the ''Risorgimento'' movement that fought for the unification of Italy. However, after the Third Italian War of Independence
The Third Italian War of Independence () was a war between the Kingdom of Italy and the Austrian Empire fought between June and August 1866. The conflict paralleled the Austro-Prussian War and resulted in Austria giving the region of Venetia (p ...
(1866), when the Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
and Friuli
Friuli (; ; or ; ; ) is a historical region of northeast Italy. The region is marked by its separate regional and ethnic identity predominantly tied to the Friulians, who speak the Friulian language. It comprises the major part of the autono ...
regions were ceded by the Austrians
Austrians (, ) are the citizens and Nationality, nationals of Austria. The English term ''Austrians'' was applied to the population of Archduchy of Austria, Habsburg Austria from the 17th or 18th century. Subsequently, during the 19th century, ...
to the newly formed Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
, Istria and Dalmatia remained part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consist ...
, together with other Italian-speaking areas on the eastern Adriatic. This triggered the gradual rise of Italian irredentism among many Italians in Istria, Kvarner and Dalmatia, who demanded the unification of the Julian March, Kvarner and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
with Italy. The Italians in Istria, Kvarner and Dalmatia supported the Italian ''Risorgimento'': as a consequence, the Austrians saw the Italians as enemies and favored the Slav communities of Istria, Kvarner and Dalmatia.''Die Protokolle des Österreichischen Ministerrates 1848/1867. V Abteilung: Die Ministerien Rainer und Mensdorff. VI Abteilung: Das Ministerium Belcredi'', Wien, Österreichischer Bundesverlag für Unterricht, Wissenschaft und Kunst 1971 During the meeting of the Council of Ministers of 12 November 1866, Emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I ( ; ; 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the ruler of the Grand title of the emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 1848 until his death ...
outlined a wide-ranging project aimed at the Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, German people, people, and German culture, culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nati ...
or Slavization of the areas of the empire with an Italian presence:
 Istrian Italians made up about a third of the population in 1900. Dalmatia, especially its maritime cities, once had a substantial local ethnic Italian population (
Istrian Italians made up about a third of the population in 1900. Dalmatia, especially its maritime cities, once had a substantial local ethnic Italian population (Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians (; ) are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Historically, Italian language-speaking Dalmatians accounted for 12.5% of population in 1865, 5.8% in 18 ...
). According to Austrian census, the Dalmatian Italians formed 12.5% of the population in 1865. In the 1910 Austro-Hungarian census, Istria had a population of 57.8% Slavic-speakers (Croat and Slovene), and 38.1% Italian speakers. For the Austrian Kingdom of Dalmatia
The Kingdom of Dalmatia (; ; ) was a crown land of the Austrian Empire (1815–1867) and the Cisleithanian half of Austria-Hungary (1867–1918). It encompassed the entirety of the region of Dalmatia, with its capital at Zadar.
History
The Habs ...
, (i.e. Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
), the 1910 numbers were 96.2% Slavic speakers and 2.8% Italian speakers. In 1909 the Italian language
Italian (, , or , ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. It evolved from the colloquial Latin of the Roman Empire. Italian is the least divergent language from Latin, together with Sardinian language, Sardinian. It is ...
lost its status as the official language of Dalmatia in favor of Croatian only (previously both languages were recognized): thus Italian could no longer be used in the public and administrative sphere.
 The Italian population in Dalmatia was concentrated in the major coastal cities. In the city of
The Italian population in Dalmatia was concentrated in the major coastal cities. In the city of Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, enter ...
in 1890 there were Dalmatian Italians (12.5% of the population), in Zadar
Zadar ( , ), historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian, ; see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited city in Croatia. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar ...
(64.6%), in Šibenik
Šibenik (), historically known as Sebenico (), is a historic town in Croatia, located in central Dalmatia, where the river Krka (Croatia), Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea. Šibenik is one of the oldest Croatia, Croatian self-governing cities ...
(14.5%), in Kotor
Kotor (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: Котор, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian language, Italian: ), is a town in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has ...
(18.7%) and in Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik, historically known as Ragusa, is a city in southern Dalmatia, Croatia, by the Adriatic Sea. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, a Port, seaport and the centre of the Dubrovni ...
(4.6%). In other Dalmatian localities, according to Austrian censuses, Dalmatian Italians experienced a sudden decrease: in the twenty years 1890-1910, in Rab they went from 225 to 151, in Vis from 352 to 92, in Pag from 787 to 23, completely disappearing in almost all the inland locations.
One consequence of irredentist ideas outside of Italy was an assassination plot organized against the Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
Francis Joseph in Trieste in 1882, which was detected and foiled. Guglielmo Oberdan, a Triestine and thus Austrian citizen, was executed. When the irredentist movement became troublesome to Italy through the activity of Republicans and Socialists, it was subject to effective police control by Agostino Depretis.
Irredentism faced a setback when the French occupation of Tunisia in 1881 started a crisis in French–Italian relations. The government entered into relations with Austria and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, which took shape with the formation of the Triple Alliance in 1882. The irredentists' dream of absorbing the targeted areas into Italy made no further progress in the 19th century, as the borders of the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
remained unchanged and the Rome government began to set up colonies in Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
and Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
in Africa.
World War I
Italy entered theWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
in 1915 with the aim of completing national unity: for this reason, the Italian intervention in the World War I is also considered the Fourth Italian War of Independence, in a historiographical perspective that identifies in the latter the conclusion of the unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century Political movement, political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the Proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, annexation of List of historic states of ...
, whose military actions began during the revolutions of 1848
The revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the springtime of the peoples or the springtime of nations, were a series of revolutions throughout Europe over the course of more than one year, from 1848 to 1849. It remains the most widespre ...
with the First Italian War of Independence
The First Italian War of Independence (), part of the ''Risorgimento'' or unification of Italy, was fought by the Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia (Piedmont) and Italian volunteers against the Austrian Empire and other conse ...
.
Italy signed the Treaty of London (1915) and entered World War I with the intention of gaining those territories perceived by irredentists as being Italian under foreign rule. According to the pact, Italy was to leave the Triple Alliance and join the Entente Powers
The Allies or the Entente (, ) was an international military coalition of countries led by the French Republic, the United Kingdom, the Russian Empire, the United States, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan against the Central Powers ...
. Furthermore, Italy was to declare war
A declaration of war is a formal act by which one state announces existing or impending war activity against another. The declaration is a performative speech act (or the public signing of a document) by an authorized party of a national gover ...
on Germany and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
within a month. The declaration of war was duly published on 23 May 1915. In exchange, Italy was to obtain various territorial gains at the end of the war. In April 1918, in what he described as an open letter "to the American Nation" Paolo Thaon di Revel
Paolo Camillo Thaon, Marquess of Revel (10 June 1859 – 24 March 1948), latterly titled with the honorary title of 1st Duke of the Sea, was an Italian admiral of the ''Regia Marina'' during World War I and later a politician.
Early life a ...
, Commander in Chief of the Italian navy
The Italian Navy (; abbreviated as MM) is one of the four branches of Italian Armed Forces and was formed in 1946 from what remained of the ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) after World War II. , the Italian Navy had a strength of 30,923 active per ...
, appealed to the people of the United States to support Italian territorial claims over Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin language, Ladin and ; ; ; ; ; ), also known in English as Trent, is a city on the Adige, Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the Trentino, autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th ...
, Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
, Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
and the Adriatic
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
, writing that "we are fighting to expel an intruder from our home".
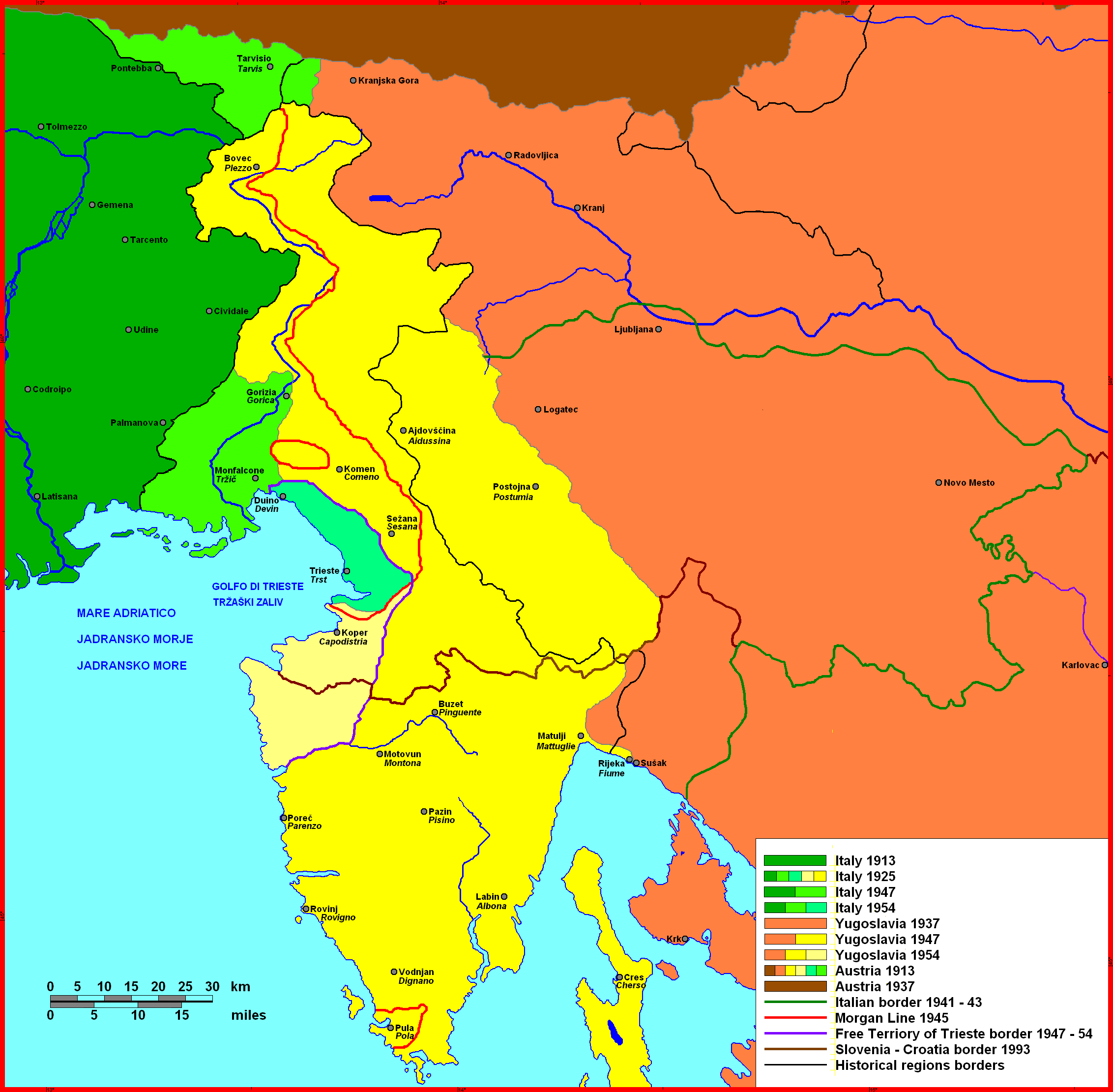
The outcome of the World War I and the consequent settlement of the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1919), Treaty of Saint-Germain met some Italian claims, including many (but not all) of the aims of the ''Italia irredenta'' party. Italy gained Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
, Gorizia
Gorizia (; ; , ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, Region ...
, Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
and the Dalmatian city of Zadar, Zara. In Dalmatia, despite the London Pact, only territories with Italian majority as Zara with some Dalmatian islands, such as Cres (island), Cherso, Lošinj, Lussino and Lastovo, Lagosta were annexed by Italy because Woodrow Wilson, supporting Yugoslav claims and not recognizing the treaty, rejected Italian requests on other Dalmatian territories, so this outcome was denounced as a "Mutilated victory". The rhetoric of "Mutilated victory" was adopted by Benito Mussolini and led to the Fascist Italy (1922–1943), rise of Italian fascism, becoming a key point in the propaganda of Fascist Italy. Historians regard "Mutilated victory" as a "political myth", used by fascists to fuel Italian imperialism and obscure the successes of liberal Italy in the aftermath of World War I.
The city of Fiume
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( �fjuːme in Italian and in Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a po ...
in the Kvarner was the subject of claim and counter-claim because it had an Italian majority, but Fiume had not been promised to Italy in the London Pact, though it was to become Italian by 1924 (see Italian Regency of Carnaro, Treaty of Rapallo, 1920 and Treaty of Rome, 1924). The stand taken by the irredentist Gabriele D'Annunzio, which briefly led him to become an enemy of the Italian state, was meant to provoke a Nationalism, nationalist revival through corporatism (first instituted during his rule over Fiume), in front of what was widely perceived as political corruption, state corruption engineered by governments such as Giovanni Giolitti's. D'Annunzio briefly annexed to this Italian Regency of Carnaro even the Dalmatian islands of Krk (island), Veglia and Rab (island), Arbe, where there was a numerous Italian community.
Fascism and World War II
 After the end of
After the end of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the Italian irredentist movement was hegemonised, manipulated and distorted by fascism, which made it an instrument of nationalist propaganda, placed at the centre of a policy, conditioned by belated imperial ambitions, which took the form of "forced Italianization
Italianization ( ; ; ; ; ; ) is the spread of Italian culture, language and identity by way of integration or assimilation. It is also known for a process organized by the Kingdom of Italy to force cultural and ethnic assimilation of the nati ...
s", in the aspiration for the birth of a ''Great Italy'' and a vast Italian Empire
The Italian colonial empire (), also known as the Italian Empire (''Impero italiano'') between 1936 and 1941, was founded in Africa in the 19th century. It comprised the colonies, protectorates, concession (territory), concessions and depende ...
..
Fascist Italy strove to be seen as the natural result of war heroism against a "Mutilated victory, betrayed Italy" that had not been awarded all it "deserved", as well as appropriating the image of Arditi soldiers. In this vein, irredentist claims were expanded and often used in Fascist Italy's desire to control the Mediterranean basin.
To the east of Italy, the Fascists claimed that Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
was a land of Italian culture whose Italians had been driven out of Dalmatia and into exile in Italy, and supported the return of Italians of Dalmatian heritage. Mussolini identified Dalmatia as having strong Italian cultural roots for centuries via the Roman Empire and the Republic of Venice.Larry Wolff. Venice And the Slavs: The Discovery of Dalmatia in the Age of Enlightenment. Stanford, California, USA: Stanford University Press, P. 355. The Fascists especially focused their claims based on the Venetian cultural heritage of Dalmatia, claiming that Venetian rule had been beneficial for all Dalmatians and had been accepted by the Dalmatian population. The Fascists were outraged after World War I, when the agreement between Italy and the Entente Allies in the Treaty of London (1915), Treaty of London of 1915 to have Dalmatia join Italy was revoked in 1919.
To the west of Italy, the Fascists claimed that the territories of Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
, Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionSavoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
held by France were Italian lands. The Fascist regime produced literature on Corsica that presented evidence of the island's ''italianità''.Davide Rodogno. ''Fascism's European Empire: Italian Occupation during the Second World War''. Cambridge, England, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2006. P. 88. The Fascist regime produced literature on Nice that justified that Nice was an Italian land based on historic, ethnic and linguistic grounds. The Fascists quoted Medieval Italian scholar Petrarch who said: "The border of Italy is the Var; consequently Nice is a part of Italy". The Fascists quoted Italian national hero Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as (). In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as () or (). 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, revolutionary and republican. H ...
, a native of Nizza (now called Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one million Mussolini initially pursued promoting annexation of Corsica through political and diplomatic means, believing that Corsica could be annexed to Italy through Italy first encouraging the existing autonomist tendencies in Corsica and then the independence of Corsica from France, that would be followed by the annexation of Corsica into Italy.
 In 1923, Mussolini temporarily occupied Corfiot Italians#Corfiot Italians and the Risorgimento, Corfu, using irredentist claims based on minorities of Italians in the island, the Corfiot Italians. Similar tactics may have been used towards the islands around the
In 1923, Mussolini temporarily occupied Corfiot Italians#Corfiot Italians and the Risorgimento, Corfu, using irredentist claims based on minorities of Italians in the island, the Corfiot Italians. Similar tactics may have been used towards the islands around the
 Dalmatia was a strategic region during World War I that both Italy and Serbia intended to seize from Austria-Hungary. Italy joined the Triple Entente Allies of World War I, Allies in 1915 upon agreeing to the Treaty of London (1915) that guaranteed Italy the right to annex a large portion of Dalmatia in exchange for Italy's participation on the Allied side. From 5–6 November 1918, Italian forces were reported to have reached Vis (island), Lissa, Lastovo, Lagosta, Šibenik, Sebenico, and other localities on the Dalmatian coast. By the end of hostilities in November 1918, the Italian military had seized control of the entire portion of Dalmatia that had been guaranteed to Italy by the Treaty of London and by 17 November had seized Fiume as well.Paul O'Brien. ''Mussolini in the First World War: the Journalist, the Soldier, the Fascist''. Oxford, England, UK; New York, New York, USA: Berg, 2005. Pp. 17. In 1918, Admiral Enrico Millo declared himself Italy's Governor of Dalmatia. Famous Italian nationalism, Italian nationalist Gabriele d'Annunzio supported the seizure of Dalmatia and proceeded to Zara in an Italian warship in December 1918.
Dalmatia was a strategic region during World War I that both Italy and Serbia intended to seize from Austria-Hungary. Italy joined the Triple Entente Allies of World War I, Allies in 1915 upon agreeing to the Treaty of London (1915) that guaranteed Italy the right to annex a large portion of Dalmatia in exchange for Italy's participation on the Allied side. From 5–6 November 1918, Italian forces were reported to have reached Vis (island), Lissa, Lastovo, Lagosta, Šibenik, Sebenico, and other localities on the Dalmatian coast. By the end of hostilities in November 1918, the Italian military had seized control of the entire portion of Dalmatia that had been guaranteed to Italy by the Treaty of London and by 17 November had seized Fiume as well.Paul O'Brien. ''Mussolini in the First World War: the Journalist, the Soldier, the Fascist''. Oxford, England, UK; New York, New York, USA: Berg, 2005. Pp. 17. In 1918, Admiral Enrico Millo declared himself Italy's Governor of Dalmatia. Famous Italian nationalism, Italian nationalist Gabriele d'Annunzio supported the seizure of Dalmatia and proceeded to Zara in an Italian warship in December 1918.
 The last city with a significant Italian presence in Dalmatia was the city of Zara (now called
The last city with a significant Italian presence in Dalmatia was the city of Zara (now called

 Under the Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947,
Under the Treaty of Peace with Italy, 1947,

 * Italian irredentism in Dalmatia was the political movement supporting the unification to Italy, during the 19th and 20th centuries, of Adriatic
* Italian irredentism in Dalmatia was the political movement supporting the unification to Italy, during the 19th and 20th centuries, of Adriatic
Unredeemed Italy (Google Books)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Italian Irredentism Italian irredentism, * History of Austria-Hungary History of Istria History of Dalmatia Political history of Malta Politics of World War II Politics of World War I National unifications, Italy de:Irredentismus#Italienischer Irredentismus
 In 1923, Mussolini temporarily occupied Corfiot Italians#Corfiot Italians and the Risorgimento, Corfu, using irredentist claims based on minorities of Italians in the island, the Corfiot Italians. Similar tactics may have been used towards the islands around the
In 1923, Mussolini temporarily occupied Corfiot Italians#Corfiot Italians and the Risorgimento, Corfu, using irredentist claims based on minorities of Italians in the island, the Corfiot Italians. Similar tactics may have been used towards the islands around the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
– through the Maltese Italians, Corfiot Italians and Corsican Italians in order to control the Mediterranean sea (his ''Mare Nostrum'', from the Latin "Our Sea").
In the 1930s Mussolini promoted the development of an initial Italian irredentism in Durrës, in order to occupy all of Albania later. Durrës (called "Durazzo" in Italian) has been for centuries, during the Middle Ages, a city with territory under the control of the Italian states (Naples, Sicily, Venice), and many Italians settled there. The Durazzo section of the Albania Fascist Party was created in 1938, which was formed by some citizens of the city with distant and recent Italian roots (they started the local Italian irredentism). In 1939, all of Albania was occupied and united to the Kingdom of Italy: Italian citizens (more than 11,000) began to settle in Albania as Italian colonists in Albania, colonists and to own land in 1940 so that they could gradually transform it into Italian territory. The italianization of Albania was one of Mussolini's plans.
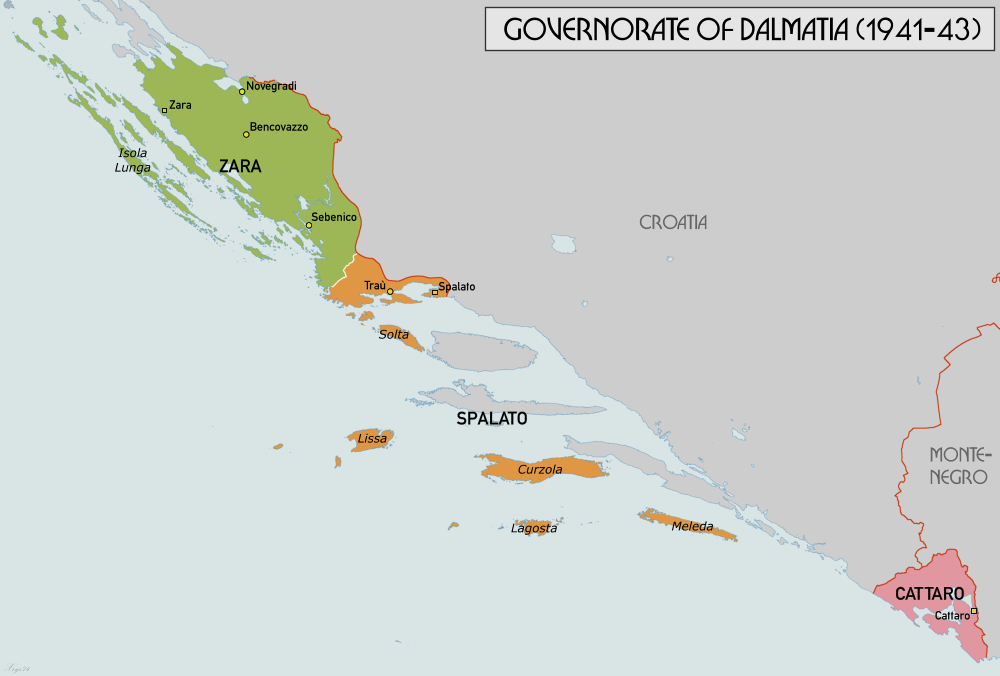
During World War II, large parts of Dalmatia were annexed by Italy into the Governorship of Dalmatia from 1941 to 1943. Corsica and Nice were also administratively annexed by Italy in November 1942. Malta was heavily bombed, but was not occupied due to Erwin Rommel's request to divert to North Africa the forces that had been prepared for the invasion of the island.
Dalmatia and the World Wars
 Dalmatia was a strategic region during World War I that both Italy and Serbia intended to seize from Austria-Hungary. Italy joined the Triple Entente Allies of World War I, Allies in 1915 upon agreeing to the Treaty of London (1915) that guaranteed Italy the right to annex a large portion of Dalmatia in exchange for Italy's participation on the Allied side. From 5–6 November 1918, Italian forces were reported to have reached Vis (island), Lissa, Lastovo, Lagosta, Šibenik, Sebenico, and other localities on the Dalmatian coast. By the end of hostilities in November 1918, the Italian military had seized control of the entire portion of Dalmatia that had been guaranteed to Italy by the Treaty of London and by 17 November had seized Fiume as well.Paul O'Brien. ''Mussolini in the First World War: the Journalist, the Soldier, the Fascist''. Oxford, England, UK; New York, New York, USA: Berg, 2005. Pp. 17. In 1918, Admiral Enrico Millo declared himself Italy's Governor of Dalmatia. Famous Italian nationalism, Italian nationalist Gabriele d'Annunzio supported the seizure of Dalmatia and proceeded to Zara in an Italian warship in December 1918.
Dalmatia was a strategic region during World War I that both Italy and Serbia intended to seize from Austria-Hungary. Italy joined the Triple Entente Allies of World War I, Allies in 1915 upon agreeing to the Treaty of London (1915) that guaranteed Italy the right to annex a large portion of Dalmatia in exchange for Italy's participation on the Allied side. From 5–6 November 1918, Italian forces were reported to have reached Vis (island), Lissa, Lastovo, Lagosta, Šibenik, Sebenico, and other localities on the Dalmatian coast. By the end of hostilities in November 1918, the Italian military had seized control of the entire portion of Dalmatia that had been guaranteed to Italy by the Treaty of London and by 17 November had seized Fiume as well.Paul O'Brien. ''Mussolini in the First World War: the Journalist, the Soldier, the Fascist''. Oxford, England, UK; New York, New York, USA: Berg, 2005. Pp. 17. In 1918, Admiral Enrico Millo declared himself Italy's Governor of Dalmatia. Famous Italian nationalism, Italian nationalist Gabriele d'Annunzio supported the seizure of Dalmatia and proceeded to Zara in an Italian warship in December 1918.
 The last city with a significant Italian presence in Dalmatia was the city of Zara (now called
The last city with a significant Italian presence in Dalmatia was the city of Zara (now called Zadar
Zadar ( , ), historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian, ; see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited city in Croatia. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar ...
). In the Austro-Hungarian census of 1910, the city of Zara had an Italian population of 9,318 (or 69.3% out of the total of 13,438 inhabitants). In 1921 the population grew to 17,075 inhabitants, of which 12,075 Italians (corresponding to 70,76%).
In 1941, during the Second World War, Yugoslavia was occupied by Italy and Germany. Dalmatia was divided between Italy, which constituted the Governorate of Dalmatia, and the Independent State of Croatia, which annexed Dubrovnik, Ragusa and Morlachia. After the Armistice of Cassibile, Italian surrender (8 September 1943) the Independent State of Croatia annexed the Governorate of Dalmatia, except for the territories that had been Italian before the start of the conflict, such as Zara. In 1943, Josip Broz Tito informed the Allies of World War II, Allies that Zara was a chief logistic centre for German forces in Yugoslavia. By overstating its importance, he persuaded them of its military significance. Italy surrendered in September 1943 and over the following year, specifically between 2 November 1943 and 31 October 1944, Allied Forces Bombing of Zadar in World War II, bombarded the town fifty-four times. Nearly 2,000 people were buried beneath rubble: 10–12,000 people escaped and took refuge in Trieste and slightly over 1,000 reached Apulia. Tito's partisans entered Zara on 31 October 1944 and 138 people were killed. With the Peace Treaty of 1947, Italians still living in Zara followed the Istrian exodus, Italian exodus from Dalmatia and only about 100 Dalmatian Italians now remain in the city.
Post-World War II

Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, Kvarner, most of the Julian March as well as the Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
n city of Zadar, Zara was annexed by Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia causing the Istrian-Dalmatian exodus, which led to the emigration of between 230,000 and 350,000 of local ethnic Italians ( Istrian Italians and Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians (; ) are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Historically, Italian language-speaking Dalmatians accounted for 12.5% of population in 1865, 5.8% in 18 ...
), the others being ethnic Slovenians, ethnic Croatians, and ethnic Istro-Romanians, choosing to maintain Italian citizenship.
The Istrian-Dalmatian exodus started in 1943 and ended completely only in 1960. According to the census organized in Croatia in 2001 and that organized in Slovenia in 2002, the Italians who remained in the former Yugoslavia amounted to 21,894 people (2,258 in Slovenia and 19,636 in Croatia).
After World War II, Italian irredentism disappeared along with the defeated Fascists and the Monarchy of the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy (, ) is a royal house (formally a dynasty) of Franco-Italian origin that was established in 1003 in the historical region of Savoy, which was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy and now lies mostly within southeastern F ...
. After the Treaty of Paris (1947) and the Treaty of Osimo (1975), all territorial claims were abandoned by the Italian Republic
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
(see Foreign relations of Italy
The foreign relations of the Italian Republic are the Italian government's external relations with the outside world. Located in Europe, Italy has been considered a major Western power since its unification in 1860. Its main allies are the NA ...
). The Italian irredentist movement thus vanished from Italian politics. Today, Italy, France, Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
, Greece, Croatia and Slovenia are all members of the European Union, while Montenegro and Albania are candidates for accession. The 1947 Constitution of Italy established five autonomous regions (Sardinia, Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Sicily, Aosta Valley and Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol), in recognition of their cultural and linguistic distinctiveness.
In the early 1990s, the breakup of Yugoslavia caused nationalistic sentiments to re-emerge in these areas; worthy of note in this regard are the demonstrations in Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
on 6 October 1991 "for a new Italian irredentism". These were promoted by the Italian Social Movement and inspired by rumours about negotiations for the passage through Trieste of the Yugoslav troops expelled from Slovenia during the Ten-Day War which saw the participation of thousands of people at the political rally in Piazza della Borsa followed by a long procession through the streets of the city, and on 8 November 1992, again in Trieste.
The same Italian Social Movement and National Alliance (Italy), National Alliance asked for the review of the peace treaties signed by Italy after World War II, especially with regard to Zone B of the former Free Territory of Trieste, given that the qualification of Slovenia and Croatia as heirs of Yugoslavia was not a given and that the division of Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
between Slovenia and Croatia contradicted the clauses of the peace treaties which guaranteed the unity of the surviving Italian component in Istria ( Istrian Italians), assigned to Yugoslavia after World War II, proposing the creation of an Istrian Euro-region also including the city of Rijeka. These claims, which also concerned Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
(including islands such as Pag, Ugljan, Vis, Lastovo, Hvar, Korčula and Mljet) and the coast with the cities of Zadar
Zadar ( , ), historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian, ; see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited city in Croatia. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar ...
, Šibenik
Šibenik (), historically known as Sebenico (), is a historic town in Croatia, located in central Dalmatia, where the river Krka (Croatia), Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea. Šibenik is one of the oldest Croatia, Croatian self-governing cities ...
, Trogir and Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, enter ...
, remained completely unheeded by all the Italian governments that followed one another in that period.
Italian populations of the claimed territories
Various points were brought forward as arguments in support of the irredentist theses of claim, such as the geographical belonging of those lands to the Italian peninsula or the presence of more or less numerous communities of Italians or Italian speakers. After World War I the situation of the claimed lands was as follows: * Italians and Italian speakers in theCounty of Nice
The County of Nice (; ; Niçard ) was a historical region of France and Italy located around the southeastern city of Nice and roughly equivalent to the modern arrondissement of Nice. It was part of the Savoyard state within the Holy Roman Emp ...
: around 4,000 (estimate);
* Italian speakers in Ticino
Ticino ( ), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts ...
and Grisons
The Grisons (; ) or Graubünden (),Names include:
* ;
*Romansh language, Romansh:
**
**
**
**
**
**;
* ;
* ;
* .
See also list of European regions with alternative names#G, other names. more formally the Canton of the Grisons or the Canton ...
(Switzerland): approximately 230,000;
* Italians and Italian speakers in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
: around 20,000;
* Italian speakers in Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
: approximately 200,000 estimated;
* Italian speakers in Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
: approximately 200,000 estimated.
Italian irredentism by region

Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
. The Republic of Venice, between the 9th century and 1797, extended its dominion to Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
, the islands of Kvarner and Dalmatia, when it was conquered by Napoleon. After the fall of Napoleon (1814) Istria, the islands of Kvarner and Dalmatia were annexed to the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
. Many Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians (; ) are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Historically, Italian language-speaking Dalmatians accounted for 12.5% of population in 1865, 5.8% in 18 ...
looked with sympathy towards the ''Risorgimento
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
'' movement that fought for the unification of Italy. The first events that involved the Dalmatian Italians in the unification of Italy were the revolutions of 1848
The revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the springtime of the peoples or the springtime of nations, were a series of revolutions throughout Europe over the course of more than one year, from 1848 to 1849. It remains the most widespre ...
, during which they took part in the constitution of the Republic of San Marco in Venice. The most notable Dalmatian Italians exponents who intervened were Niccolò Tommaseo
Niccolò Tommaseo (; 9 October 1802 – 1 May 1874) was a Dalmatian Italian linguist, journalist and essayist, the editor of a (''A Dictionary of the Italian Language'') in eight volumes (1861–74), of a dictionary of synonyms (1830) and other ...
and Federico Seismit-Doda.''Dizionario Enciclopedico Italiano'' (Vol. III, pag. 729-730), Roma, Ed. Istituto dell'Enciclopedia Italiana, founded by Giovanni Treccani, 1970 (In Italian)
* Italian irredentism in Istria was the political movement supporting the unification to Italy, during the 19th and 20th centuries, of the peninsula of Istria. It is considered closely related to the Italian irredentism in Trieste
Trieste ( , ; ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital and largest city of the Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special statute, autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as of the Province of Trieste, ...
and Fiume
Rijeka (;
Fiume ( �fjuːme in Italian and in Fiuman Venetian) is the principal seaport and the third-largest city in Croatia. It is located in Primorje-Gorski Kotar County on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and in 2021 had a po ...
, two cities bordering the peninsula. When Napoleon conquered the territory of Istria, he found that Istria was populated by Istrian Italians on the coast and in the main cities, but the interior was populated mainly by Croats and Slovenians: this multi-ethnic population in the same peninsula created a situation of antagonism between Slovenes, Croats and Italians, when started the first nationalism
Nationalism is an idea or movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, it presupposes the existence and tends to promote the interests of a particular nation, Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: Theory, I ...
s after Napoleon's fall. Since 1815 Istria was a part of the Austrian Empire, Austrian monarchy, and Croats
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
, Slovenians and Italians engaged in a nationalistic feud with each other. As a consequence, Istria has been a theater of a nationalistic ethnic struggle between them during the 19th and 20th centuries. Italian irredentism was actively followed by many Italians in Istria, like the Italian sailor and irredentist Nazario Sauro, native to Koper, Capodistria.
* Italian irredentism in Corsica was a cultural and historical movement promoted by Italians and by Corsican people, people from Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
who identified themselves as part of Italy rather than France, and promoted the Italian annexation of the island. Corsica was part of the Republic of Genoa for centuries until 1768, when the Republic ceded the island to France, one year before the birth of Napoleon Bonaparte in the capital city of Ajaccio. Under France, the use of Corsican language, Corsican (a regional tongue which is closely related to Italian language, Italian) has gradually declined in favour of the standard French language. Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as (). In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as () or (). 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, revolutionary and republican. H ...
called for the inclusion of the "Corsican Italians" within Italy when the city of Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
was annexed to the Kingdom of Italy, but Victor Emmanuel II
Victor Emmanuel II (; full name: ''Vittorio Emanuele Maria Alberto Eugenio Ferdinando Tommaso di Savoia''; 14 March 1820 – 9 January 1878) was King of Sardinia (also informally known as Piedmont–Sardinia) from 23 March 1849 until 17 March ...
did not agree to it. The course of Italian irredentism did not affect Corsica very much, and only during the Fascist rule of Benito Mussolini were the first organizations strongly promoting the unification of the island to the Kingdom of Italy founded. Italian was the official language of Corsica until 1859.
* Italian irredentism in Nice was the political movement supporting the annexation of the County of Nice
The County of Nice (; ; Niçard ) was a historical region of France and Italy located around the southeastern city of Nice and roughly equivalent to the modern arrondissement of Nice. It was part of the Savoyard state within the Holy Roman Emp ...
to the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
. According to some nationalism, Italian nationalists and Fascism, fascists like Ermanno Amicucci, Italian- and Ligurian (Romance language), Ligurian-speaking populations of the County of Nice (Italian: ) formed the majority of the county's population until the mid-19th century. However, French nationalists and linguists argue that both Occitan language, Occitan and Ligurian languages were spoken in the County of Nice. During the Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
, in 1860, the House of Savoy
The House of Savoy (, ) is a royal house (formally a dynasty) of Franco-Italian origin that was established in 1003 in the historical region of Savoy, which was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy and now lies mostly within southeastern F ...
allowed the Second French Empire to annex Nice from the Kingdom of Sardinia in exchange for French support of its quest to unify Italy. Consequently, the Niçois were excluded from the Italian unification movement and the region has since become primarily French-speaking. The pro-Italian irredentist movement persisted throughout the period 1860–1914, despite the repression carried out since the annexation. The French government implemented a policy of Francization of society, language and culture. The toponyms of the communes of the ancient County have been francized, with the obligation to use French in Nice, as well as certain surnames (for example the Italian surname "Bianchi" was francized into "Leblanc", and the Italian surname "Del Ponte" was francized into "Dupont").
* Italian irredentism in Savoy was the political movement among Savoyards promoting annexation to the House of Savoy, Savoy dynasty's Kingdom of Italy. It was active from 1860 to World War II. During the Italian unification, in 1860, the House of Savoy allowed the Second French Empire to annex Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
from the Kingdom of Sardinia in exchange for French support of its quest to unify Italy. Italian irredentists were citizens of Savoy who considered themselves to have ties with the House of Savoy dynasty. Savoy was the original territory of the duke of Savoy that later became King of Italy. Since the Renaissance the area had ruled over Piedmont and had for regional capital the town of Chambéry.
* Italian irredentism in Malta is the movement that uses an irredentist argument to propose the incorporation of the Maltese islands into Italy, with reference to past support in Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
for Italian territorial claims on the islands. Although Malta had formally ceased to be part of the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily (; ; ) was a state that existed in Sicily and the southern Italian peninsula, Italian Peninsula as well as, for a time, in Kingdom of Africa, Northern Africa, from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was ...
only since 1814 following the Treaty of Paris (1814), Treaty of Paris, Italian irredentism in Malta was mainly significant during the Italian Fascism, Italian Fascist era. Until the end of the 18th century History of Malta, Malta's fortunes—political, economic, religious, cultural—were closely tied with History of Sicily, Sicily's. Successive waves of immigration from Sicily and Italy strengthened these ties and increased the demographic similarity. Italian was Malta's language of administration, law, contracts and public records, Culture of Malta, Malta's culture was similar to Culture of Italy, Italy's, Malta's nobility was originally composed of Italian families who had moved to Malta mainly in the 13th century and the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Malta, Maltese Catholic Church was suffragan of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Palermo, Archdiocese of Palermo. For many centuries and until 1936, Italian was the official language of Malta (see Maltese Italian).
* Italian irredentism in Switzerland was a political movement that promoted the unification to Italy of the Italian-speaking areas of Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
during the ''Risorgimento''. The current Italian Switzerland belonged to the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan (; ) was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti of Milan, Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277. At that time, ...
until the 16th century, when it became part of Switzerland. These territories have maintained their native Italian population speaking the Italian language and the Lombard language
The Lombard language (,Classical Milanese orthography, and . ,Ticino, Ticinese orthography. Modern Western orthography and Classical Cremish Orthography. or ,Eastern Lombard, Eastern unified orthography. depending on the orthography; pronuncia ...
, specifically the Ticinese dialect. In the early 19th century the ideals of unification in a single Nation of all the territories populated by Italian speaking people created the Italian irredentism. Italian irredentism in Switzerland was based on moderate ''Risorgimento'' ideals, and was promoted by Italian-Ticinese such as Adolfo Carmine.
* Corfiot Italians#Corfiot Italians and the Risorgimento, Italian irredentism in Corfu was the political movement supporting the unification to Italy, during the 19th and 20th centuries, of the island of Corfu. Corfiot Italians are a population from the Greece, Greek island of Corfu (Kerkyra) with ethnic and linguistic ties to the Republic of Venice. Their name was specifically established by Niccolò Tommaseo during the Italian ''Risorgimento''. During the first half of the 20th century, Mussolini (whose fascist regime promoted the ideals of Italian irredentism) successfully used the Corfiot Italians as a pretext to occupy Corfu twice. The Italian ''Risorgimento'' was initially concentrated in the Italian peninsula with the surrounding continental areas (Istria, Dalmatia, Corsica, County of Nice, etc.) and did not reach Corfu and the Ionian islands. One of the main heroes of the Italian ''Risorgimento'', the poet Ugo Foscolo, was born in Zante from a noble Venetian family of the island, but only superficially promoted the possible unification of the Ionian islands to Italy. According to historian Ezio Gray, the small communities of Venetian-speaking people in Corfu were mostly assimilated after the island became part of Greece in 1864 and especially after all Italian schools were closed in 1870.Gray, Ezio. ''Le terre nostre ritornano... Malta, Corsica, Nizza'', p. 118. After World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, however, the Kingdom of Italy started to apply a policy of expansionism toward the Adriatic area and saw Corfu as the gate of this sea.
Political figures in Italian irredentism
* Guglielmo Oberdan * Cesare Battisti (politician), Cesare Battisti * Nazario Sauro * Carmelo Borg Pisani *Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as (). In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as () or (). 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, revolutionary and republican. H ...
* Gabriele D'Annunzio
* Simon Petru Cristofini, Petru Simone Cristofini
* Petru Giovacchini
* Maria Pasquinelli
Regions historically claimed by Italian irredentism
*Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; ; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian: ; ; ) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. Located at th ...
* Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
* Monaco
* Nice
Nice ( ; ) is a city in and the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative city limits, with a population of nearly one millionCorsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
* Savoy
Savoy (; ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps. Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south and west and to the Aosta Vall ...
* Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two ...
* Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands (Modern Greek: , ; Ancient Greek, Katharevousa: , ) are a archipelago, group of islands in the Ionian Sea, west of mainland Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese ("Seven Islands"; , ''Heptanēsa'' or , ''Heptanē ...
* Canton Ticino, parts of Valais, Canton Vallese and Italian Graubünden
* San Marino
* Coastal parts of Vlorë region and Vlorë
* Palagruža
See also
*Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy wa ...
* Istrian-Dalmatian exodus
* Istrian Italians
* Dalmatian Italians
Dalmatian Italians (; ) are the historical Italian national minority living in the region of Dalmatia, now part of Croatia and Montenegro.
Historically, Italian language-speaking Dalmatians accounted for 12.5% of population in 1865, 5.8% in 18 ...
* Niçard exodus
* Niçard Italians
Niçard Italians ( ) are Italians who have full or partial County of Nice, Nice heritage by birth or ethnicity.
History
Niçard Italians have roots in Nice and the County of Nice. They often speak the Ligurian language after Nice joined the Genoa ...
* Italian Empire
The Italian colonial empire (), also known as the Italian Empire (''Impero italiano'') between 1936 and 1941, was founded in Africa in the 19th century. It comprised the colonies, protectorates, concession (territory), concessions and depende ...
* Italian geographical region
* Italian Regency of Carnaro
* Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( ), also known as the Risorgimento (; ), was the 19th century political and social movement that in 1861 ended in the annexation of various states of the Italian peninsula and its outlying isles to the Kingdom of ...
References
Sources
* Bartoli, Matteo. ''Le parlate italiane della Venezia Giulia e della Dalmazia. Tipografia italo-orientale''. Grottaferrata. 1919. * Colonel von Haymerle, ''Italicae res'', Vienna, 1879 – the early history of irredentists. * Lovrovici, don Giovanni Eleuterio. ''Zara dai bombardamenti all'esodo (1943–1947)''. Tipografia Santa Lucia – Marino. Roma. 1974. * Petacco, Arrigo. ''A tragedy revealed: the story of Italians from Istria, Dalmatia, Venezia Giulia (1943–1953)''. University of Toronto Press. Toronto. 1998. * Večerina, Duško. ''Talijanski Iredentizam'' ("Italian Irredentism"). . Zagreb. 2001. * Vivante, Angelo. ''Irredentismo adriatico'' ("The Adriatic Irredentism"). 1984.External links
Unredeemed Italy (Google Books)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Italian Irredentism Italian irredentism, * History of Austria-Hungary History of Istria History of Dalmatia Political history of Malta Politics of World War II Politics of World War I National unifications, Italy de:Irredentismus#Italienischer Irredentismus