Iris sphincter muscle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The iris sphincter muscle (pupillary sphincter, pupillary constrictor, circular muscle of iris, circular fibers) is a
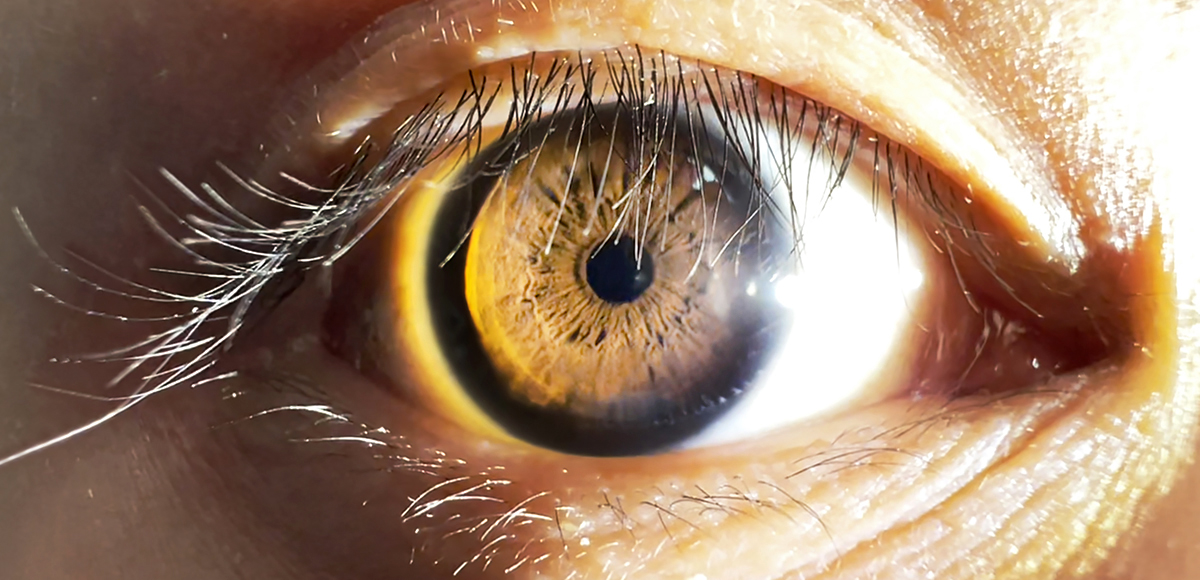 In humans, it functions to constrict the pupil in bright light (
In humans, it functions to constrict the pupil in bright light (
Overview of function at tedmontgomery.com
at mscd.edu * {{Authority control Human iris Muscular system
muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
in the part of the eye called the iris. It encircles the pupil of the iris, appropriate to its function as a constrictor of the pupil.
The ciliary muscle, pupillary sphincter muscle and pupillary dilator muscle sometimes are called intrinsic ocular muscles or intraocular muscles.
Comparative anatomy
This structure is found invertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s and in some cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
s.
General structure
All themyocyte
A muscle cell, also known as a myocyte, is a mature contractile Cell (biology), cell in the muscle of an animal. In humans and other vertebrates there are three types: skeletal muscle, skeletal, smooth muscle, smooth, and Cardiac muscle, cardiac ...
s are of the smooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
type.
Its dimensions are about 0.75 mm wide by 0.15 mm thick.
Mode of action
 In humans, it functions to constrict the pupil in bright light (
In humans, it functions to constrict the pupil in bright light (pupillary light reflex
The pupillary light reflex (PLR) or photopupillary reflex is a reflex that controls the diameter of the pupil, in response to the intensity ( luminance) of light that falls on the retinal ganglion cells of the retina in the back of the eye, t ...
) or during accommodation. In , the muscle cells themselves are photosensitive causing iris action without brain input.
Innervation
It is controlled byparasympathetic
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulat ...
postganglionic fibers releasing acetylcholine acting primarily on the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (M3) of iris sphincter muscle. Preganglionic fibers originate from the Edinger–Westphal nucleus, travel along the oculomotor nerve
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements o ...
(CN III), and make nicotinic cholinergic synapses on neurons in the ciliary ganglion. Those neurons' postganglionic parasympathetic fibers then enter the eye through the short ciliary nerves. The short ciliary nerves then run forward and pierce the sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber.
In the development of t ...
at the back of the eye, traveling between the sclera and the choroid to innervate the iris sphincter muscle.
See also
* Iris dilator muscle *Miosis
Miosis, or myosis (), is excessive constriction of the pupil.Farlex medical dictionary
citing: ...
citing: ...
References
External links
Overview of function at tedmontgomery.com
at mscd.edu * {{Authority control Human iris Muscular system