intracellular digestion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Every organism requires energy to be active.Anderson, O. Roger (1 January 1970). "Intracellular Digestion". ''The American Biology Teacher''. 32 (8): 461–467. doi:10.2307/4443206. However, to obtain energy from its outside environment, cells must not only retrieve molecules from their surroundings but also break them down. This process is known as intracellular digestion. In its broadest sense, intracellular digestion is the breakdown of substances within the
Every organism requires energy to be active.Anderson, O. Roger (1 January 1970). "Intracellular Digestion". ''The American Biology Teacher''. 32 (8): 461–467. doi:10.2307/4443206. However, to obtain energy from its outside environment, cells must not only retrieve molecules from their surroundings but also break them down. This process is known as intracellular digestion. In its broadest sense, intracellular digestion is the breakdown of substances within the
"Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms"
''The Journal of Pathology''. 221 (1): 3–12. doi: 10.1002/path.2697.
"Autophagy: process and function"
''Genes & Development''. 21(22): 2861–2873. doi: 10.1101/gad.1599207.
 Every organism requires energy to be active.Anderson, O. Roger (1 January 1970). "Intracellular Digestion". ''The American Biology Teacher''. 32 (8): 461–467. doi:10.2307/4443206. However, to obtain energy from its outside environment, cells must not only retrieve molecules from their surroundings but also break them down. This process is known as intracellular digestion. In its broadest sense, intracellular digestion is the breakdown of substances within the
Every organism requires energy to be active.Anderson, O. Roger (1 January 1970). "Intracellular Digestion". ''The American Biology Teacher''. 32 (8): 461–467. doi:10.2307/4443206. However, to obtain energy from its outside environment, cells must not only retrieve molecules from their surroundings but also break them down. This process is known as intracellular digestion. In its broadest sense, intracellular digestion is the breakdown of substances within the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
of a cell. In detail, a phagocyte's duty is obtaining food particles and digesting it in a vacuole.Roberts, M. B. V. ''Biology: A Functional Approach''. Nelson Thornes. . For example, following phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs ph ...
, the ingested particle (or phagosome) fuses with a lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation cent ...
containing hydrolytic enzymes to form a phagolysosome; the pathogens or food particles within the phagosome are then digested by the lysosome's enzymes.
Intracellular digestion can also refer to the process in which animals that ''lack'' a digestive tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
bring food items into the cell for the purposes of digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food compounds into small water-soluble components so that they can be absorbed into the blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intestine into th ...
for nutritional needs. This kind of intracellular digestion occurs in many unicellular protozoans, in Pycnogonida, in some molluscs
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
, Cnidaria
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
and Porifera
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a Basal (phylogenetics) , basal clade and a sister taxon of the Eumetazoa , diploblasts. They are sessility (motility) , sessile ...
. There is another type of digestion, called extracellular digestion. In amphioxus
The lancelets ( ), also known as amphioxi (: amphioxus ), consist of 32 described species of somewhat fish-like benthic filter feeding chordates in the subphylum Cephalochordata, class Leptocardii, and family Branchiostomatidae.
Lancelets div ...
, digestion is both extracellular and intracellular.
Function
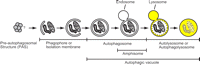
Intracellular digestion is divided into heterophagic digestion and autophagic digestion.Jamieson, G. A.; Robinson, D. M. ''Mammalian Cell Membranes: Volume 2: The Diversity of Membranes''. Elsevier. . These two types take place in the lysosome and they both have very specific functions. Heterophagic intracellular digestion has an important job which is to break down all molecules that are brought into a cell by endocytosis. The degraded molecules need to be delivered to the cytoplasm; however, this will not be possible if the molecules are not hydrolyzed in the lysosome. Autophagic intracellular digestion is processed in the cell, which means it digests the internal molecules.Autophagy
Generally,autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Greek language, Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-depe ...
includes three small branches, which are macroautophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated ...
, microautophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy.
Occurrence
Most organisms that use intracellular digestion belong to Kingdom Protista, such asamoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by ...
and paramecium
''Paramecium'' ( , , plural "paramecia" only when used as a Common name, vernacular name) is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, widespread in freshwater, brackish, and Ocean, marine environments. Paramecia are often abundant in stagna ...
.
Amoeba
Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by ...
uses pseudopodia
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and ...
to capture food for nutrition in a process called phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs ph ...
.
Paramecium
Paramecium
''Paramecium'' ( , , plural "paramecia" only when used as a Common name, vernacular name) is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular ciliates, widespread in freshwater, brackish, and Ocean, marine environments. Paramecia are often abundant in stagna ...
uses cilia in the oral groove to bring food into the mouth pore which goes to the gullet. At the end of the gullet, a food vacuole forms. Undigested food is carried to the anal pore.
Euglena
Euglena
''Euglena'' is a genus of Unicellular organism, single-celled, flagellate eukaryotes. It is the best-known and most widely studied member of the class Euglenoidea, a diverse group containing some 54 genera and at least 200 species. Species of '' ...
is photosynthetic but also engulfs and digests microorganisms.
References
* Roberts, M. B. V. ''Biology: A Functional Approach''. Nelson Thornes. . * Jamieson, G. A.; Robinson, D. M. ''Mammalian Cell Membranes: Volume 2: The Diversity of Membranes''. Elsevier. {{ISBN, 9781483162782. * Anderson, O. Roger (1 January 1970). "Intracellular Digestion". ''The American Biology Teacher''. 32 (8): 461–467. doi:10.2307/4443206. * Glick, Danielle; Barth, Sandra; Macleod, Kay F. (21 November 2016)"Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms"
''The Journal of Pathology''. 221 (1): 3–12. doi: 10.1002/path.2697.
ISSN
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit to uniquely identify a periodical publication (periodical), such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs a ...
0022-3417.
* Mizushima, Noboru (15 November 2007)"Autophagy: process and function"
''Genes & Development''. 21(22): 2861–2873. doi: 10.1101/gad.1599207.
ISSN
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit to uniquely identify a periodical publication (periodical), such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs a ...
0890-9369.
Cell biology
es:Digestión intracelular