Inhalation Administration on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A route of administration in
A route of administration in
Citing: The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000
 Many drugs as tablets, capsules, or drops are taken orally. Administration methods directly into the stomach include those by
Many drugs as tablets, capsules, or drops are taken orally. Administration methods directly into the stomach include those by  The rectal route is an effective route of administration for many medications, especially those used at the
The rectal route is an effective route of administration for many medications, especially those used at the
 The parenteral route is any route that is not enteral ('' par-'' + ''enteral'').
Parenteral administration can be performed by injection, that is, using a needle (usually a
The parenteral route is any route that is not enteral ('' par-'' + ''enteral'').
Parenteral administration can be performed by injection, that is, using a needle (usually a  * Epicutaneous (application onto the skin). It can be used both for local effect as in allergy testing and typical
* Epicutaneous (application onto the skin). It can be used both for local effect as in allergy testing and typical  * Intraocular, into the eye, e.g., some medications for
* Intraocular, into the eye, e.g., some medications for

 Inhaled medications can be absorbed quickly and act both locally and systemically. Proper technique with
Inhaled medications can be absorbed quickly and act both locally and systemically. Proper technique with

 The term injection encompasses intravenous (IV),
The term injection encompasses intravenous (IV),
The 10th US-Japan Symposium on Drug Delivery Systems
* [https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/FormsSubmissionRequirements/ElectronicSubmissions/DataStandardsManualmonographs/ucm071666.htm FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Data Standards Manual: Dosage Form.]
A.S.P.E.N. American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Route Of Administration Drugs Pharmacokinetics Routes of administration
 A route of administration in
A route of administration in pharmacology
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemi ...
and toxicology
Toxicology is a scientific discipline, overlapping with biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and medicine, that involves the study of the adverse effects of chemical substances on living organisms and the practice of diagnosing and treating expos ...
is the way by which a drug
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhal ...
, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. Common examples include oral and intravenous administration. Routes can also be classified based on where the target of action is. Action may be topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of class ...
(local), enteral (system-wide effect, but delivered through the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
), or parenteral
A route of administration in pharmacology and toxicology is the way by which a drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance is applied. ...
(systemic action, but delivered by routes other than the GI tract). Route of administration and dosage form
Dosage forms (also called unit doses) are pharmaceutical drug products in the form in which they are marketed for use, with a specific mixture of active ingredients and inactive components ( excipients), in a particular configuration (such as a c ...
are aspects of drug delivery.
Classification
Routes of administration are usually classified by application location (or exposition). The route or course the active substance takes from application location to the location where it has its target effect is usually rather a matter ofpharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered ...
(concerning the processes of uptake, distribution, and elimination of drugs). Exceptions include the transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointme ...
or transmucosal routes, which are still commonly referred to as ''routes of administration''.
The location of the target effect of active substances are usually rather a matter of pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms ( ...
(concerning e.g. the physiological effects of drugs). An exception is topical administration
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
, which generally means that both the application location and the effect thereof is local.
Topical administration
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
is sometimes defined as both a local application location and local pharmacodynamic
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for ...
effect, and sometimes merely as a local application location regardless of location of the effects.thefreedictionary.com > topicalCiting: The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000
By application location
Enteral/gastrointestinal
through thegastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
is sometimes termed ''enteral or enteric administration'' (literally meaning 'through the intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
'). ''Enteral/enteric administration'' usually includes '' oral'' (through the mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on t ...
) and '' rectal'' (into the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the l ...
) administration, in the sense that these are taken up by the intestines. However, uptake of drugs administered orally may also occur already in the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
, and as such ''gastrointestinal'' (along the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
) may be a more fitting term for this route of administration. Furthermore, some application locations often classified as ''enteral'', such as sublingual
Sublingual ( abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
The sublingual glands receive their pr ...
(under the tongue) and sublabial or buccal (between the cheek and gums/gingiva
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue l ...
), are taken up in the proximal part of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
without reaching the intestines. Strictly enteral administration
Enteral administration is food or drug administration via the human gastrointestinal tract. This contrasts with parenteral nutrition or drug administration (Greek ''para'', "besides" + ''enteros''), which occurs from routes outside the GI tract, ...
(directly into the intestines) can be used for systemic administration, as well as local (sometimes termed topical
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of class ...
), such as in a contrast enema
An enema, also known as a clyster, is an injection of fluid into the lower bowel by way of the rectum.Cullingworth, ''A Manual of Nursing, Medical and Surgical'':155 The word enema can also refer to the liquid injected, as well as to a devic ...
, whereby contrast media are infused into the intestines for imaging. However, for the purposes of classification based on location of effects, the term enteral is reserved for substances with systemic effects.
 Many drugs as tablets, capsules, or drops are taken orally. Administration methods directly into the stomach include those by
Many drugs as tablets, capsules, or drops are taken orally. Administration methods directly into the stomach include those by gastric feeding tube
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is ...
or gastrostomy. Substances may also be placed into the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through t ...
s, as with a duodenal feeding tube and enteral nutrition. Enteric coated tablets are designed to dissolve in the intestine, not the stomach, because the drug present in the tablet causes irritation in the stomach.
 The rectal route is an effective route of administration for many medications, especially those used at the
The rectal route is an effective route of administration for many medications, especially those used at the end of life End-of-life may refer to:
* End-of-life (product), a term used with respect to terminating the sale or support of goods and services
* End-of-life care, medical care for patients with terminal illnesses or conditions that have become advanced, prog ...
. The walls of the rectum absorb many medications quickly and effectively. Medications delivered to the distal one-third of the rectum at least partially avoid the "first pass effect
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism whereby the concentration of a drug, specifically when administered orally, is greatly reduced before it reaches the system ...
" through the liver, which allows for greater bio-availability of many medications than that of the oral route. Rectal mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
is highly vascularized tissue that allows for rapid and effective absorption of medications. A suppository
A suppository is a dosage form used to deliver medications by insertion into a body orifice where it dissolves or melts to exert local or systemic effects. There are three types of suppositories, each to insert into a different sections: rectal ...
is a solid dosage form
Dosage forms (also called unit doses) are pharmaceutical drug products in the form in which they are marketed for use, with a specific mixture of active ingredients and inactive components ( excipients), in a particular configuration (such as a c ...
that fits for rectal administration
Rectal administration uses the rectum as a route of administration for medication and other fluids, which are absorbed by the rectum's blood vessels,The rectum has numerous blood vessels available to absorb drugs. and flow into the body's ci ...
. In hospice care, a specialized rectal catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Cat ...
, designed to provide comfortable and discreet administration of ongoing medications provides a practical way to deliver and retain liquid formulations in the distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
rectum, giving health practitioners a way to leverage the established benefits of rectal administration. The Murphy drip
A Murphy drip is a rectal infusion apparatus to administer the medical procedure of proctoclysis, also known as rectoclysis. During the procedure, an end of the Murphy drip is inserted into the rectum and large quantities of liquid are infused in ...
is an example of rectal infusion.
Parenteral
 The parenteral route is any route that is not enteral ('' par-'' + ''enteral'').
Parenteral administration can be performed by injection, that is, using a needle (usually a
The parenteral route is any route that is not enteral ('' par-'' + ''enteral'').
Parenteral administration can be performed by injection, that is, using a needle (usually a hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)), one of a category of medical tools which enter the skin, called sharps, is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. It is commonly used w ...
) and a syringe
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside o ...
, or by the insertion of an indwelling catheter.
Locations of application of parenteral administration include:
* Central nervous system:
:* Epidural
Epidural administration (from Ancient Greek ἐπί, , upon" + ''dura mater'') is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians an ...
(synonym: peridural) (injection or infusion into the epidural space
In anatomy, the epidural space is the potential space between the dura mater and vertebrae ( spine).
The anatomy term "epidural space" has its origin in the Ancient Greek language; , "on, upon" + dura mater also known as "epidural cavity", "ext ...
), e.g. epidural anesthesia.
:* Intracerebral (into the cerebrum) administration by direct injection into the brain. Used in experimental research of chemicals and as a treatment for malignancies of the brain. The intracerebral route can also interrupt the blood brain barrier from holding up against subsequent routes.
:* Intracerebroventricular (into the cerebral ventricles) administration into the ventricular system of the brain. One use is as a last line of opioid treatment for terminal cancer patients with intractable cancer pain
Pain in cancer may arise from a tumor compressing or infiltrating nearby body parts; from treatments and diagnostic procedures; or from skin, nerve and other changes caused by a hormone imbalance or immune response. Most chronic (long-lasting) pai ...
.
 * Epicutaneous (application onto the skin). It can be used both for local effect as in allergy testing and typical
* Epicutaneous (application onto the skin). It can be used both for local effect as in allergy testing and typical local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, that is, local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. I ...
, as well as systemic effects when the active substance diffuses through skin in a transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointme ...
route.
*Sublingual and buccal medication administration is a way of giving someone medicine orally (by mouth). Sublingual administration
Sublingual (abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
The sublingual glands receive their primar ...
is when medication is placed under the tongue to be absorbed by the body. The word "sublingual" means "under the tongue." Buccal administration involves placement of the drug between the gums and the cheek. These medications can come in the form of tablets, films, or sprays. Many drugs are designed for sublingual administration, including cardiovascular drugs, steroids, barbiturates, opioid analgesics with poor gastrointestinal bioavailability, enzymes and, increasingly, vitamins and minerals.
* Extra-amniotic administration, between the endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional lay ...
and fetal membranes
The fetal membranes are the four extraembryonic membranes, associated with the developing embryo, and fetus in humans and other mammals.. They are the amnion, chorion, allantois, and yolk sac. The amnion and the chorion are the chorioamniotic m ...
.
* Nasal administration
Nasal administration, popularly known as snorting, is a route of administration in which drugs are insufflated through the nose. It can be a form of either topical administration or systemic administration, as the drugs thus locally delivered ...
(through the nose) can be used for topically acting substances, as well as for insufflation of e.g. decongestant
A decongestant, or nasal decongestant, is a type of pharmaceutical drug that is used to relieve nasal congestion in the upper respiratory tract. The active ingredient in most decongestants is either pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine (the latter ...
nasal sprays to be taken up along the respiratory tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
. Such substances are also called ''inhalational'', e.g. inhalational anesthetics.
* Intra-arterial (into an artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
), e.g. vasodilator
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstriction ...
drugs in the treatment of vasospasm
Vasospasm refers to a condition in which an arterial spasm leads to vasoconstriction. This can lead to tissue ischemia and tissue death (necrosis). Cerebral vasospasm may arise in the context of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Symptomatic vasospasm or ...
and thrombolytic drugs for treatment of embolism
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule (fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas ( gas embolism), amniotic fluid ( a ...
.
* Intra-articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two oth ...
, into a joint space. It is generally performed by joint injection. It is mainly used for symptomatic relief in osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the ...
.
* Intracardiac (into the heart), e.g. adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
during cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spon ...
(no longer commonly performed).
* Intracavernous injection
An intracavernous (or intracavernosal) injection is an injection into the base of the penis. This injection site is often used to administer medications to check for or treat erectile dysfunction in adult men (in, for example, a combined intra ...
, an injection into the base of the penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males d ...
.
* Intradermal, (into the skin itself) is used for skin testing
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
some allergens
An allergen is a type of antigen that produces an abnormally vigorous immune response in which the immune system fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless to the body. Such reactions are called allergies.
In technical t ...
, and also for mantoux test
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening for tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis dia ...
for tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in w ...
.
* Intralesional (into a skin lesion), is used for local skin lesions, e.g. acne medication.
* Intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have ...
(into a muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are Organ (biology), organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other ...
), e.g. many vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious or malignant disease. The safety and effectiveness of vaccines has been widely studied and verified. ...
s, antibiotics, and long-term psychoactive agents. Recreationally the colloquial term 'muscling' is used.
 * Intraocular, into the eye, e.g., some medications for
* Intraocular, into the eye, e.g., some medications for glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye re ...
or eye neoplasm
Eye neoplasms can affect all parts of the eye, and can be a benign tumor or a malignant tumor (cancer). Eye cancers can be primary (starts within the eye) or metastatic cancer (spread to the eye from another organ). The two most common cancers tha ...
s.
* Intraosseous infusion (into the bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
marrow) is, in effect, an indirect intravenous access because the bone marrow drains directly into the venous system. This route is occasionally used for drugs and fluids in emergency medicine and pediatrics when intravenous access is difficult.
* Intraperitoneal, (infusion or injection into the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesot ...
) e.g. peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis which uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte prob ...
.
* Intrathecal
Intrathecal administration is a route of administration for drugs via an injection into the spinal canal, or into the subarachnoid space so that it reaches the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and is useful in spinal anesthesia, chemotherapy, or pa ...
(into the spinal canal) is most commonly used for spinal anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), a ...
and chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothe ...
.
* Intrauterine.
* Intravaginal administration, in the vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hy ...
.
* Intravenous (into a vein
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenate ...
), e.g. many drugs, total parenteral nutrition.
* Intravesical infusion is into the urinary bladder.
* Intravitreal, through the eye.
* Subcutaneous (under the skin). This generally takes the form of subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion.
A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and epidermis, co ...
, e.g. with insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
. Skin popping is a slang term that includes subcutaneous injection, and is usually used in association with recreational drugs. In addition to injection, it is also possible to slowly infuse fluids subcutaneously in the form of hypodermoclysis.
* Transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointme ...
(diffusion through the intact skin for systemic rather than topical distribution), e.g. transdermal patch
A transdermal patch is a medicated adhesive patch that is placed on the skin to deliver a specific dose of medication through the skin and into the bloodstream. An advantage of a transdermal drug delivery route over other types of medicat ...
es such as fentanyl
Fentanyl, also spelled fentanil, is a very potent synthetic opioid used as a pain medication. Together with other drugs, fentanyl is used for anesthesia. It is also used illicitly as a recreational drug, sometimes mixed with heroin, cocaine ...
in pain therapy, nicotine patches for treatment of addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to engage in certain behaviors, one of which is the usage of a drug, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use oft ...
and nitroglycerine
Nitroglycerin (NG), (alternative spelling of nitroglycerine) also known as trinitroglycerin (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating g ...
for treatment of angina pectoris
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of obstr ...
.
* Perivascular administration Mural cells are the vascular smooth muscle cells (vSMCs), and pericytes, of the microcirculation. Both types are in close contact with the endothelial cells lining the capillaries, and are important for vascular development and stability. Mural cell ...
(perivascular medical devices and perivascular drug delivery systems are conceived for local application around a blood vessel during open vascular surgery).
* Transmucosal (diffusion through a mucous membrane), e.g. insufflation (snorting) of cocaine
Cocaine (from , from , ultimately from Quechua: ''kúka'') is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant mainly used recreationally for its euphoric effects. It is primarily obtained from the leaves of two Coca species native to South Am ...
, sublingual
Sublingual ( abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
The sublingual glands receive their pr ...
, i.e. under the tongue, sublabial, i.e. between the lips and gingiva
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue l ...
, nitroglycerine
Nitroglycerin (NG), (alternative spelling of nitroglycerine) also known as trinitroglycerin (TNG), nitro, glyceryl trinitrate (GTN), or 1,2,3-trinitroxypropane, is a dense, colorless, oily, explosive liquid most commonly produced by nitrating g ...
, vaginal suppositories.
Topical
The definition of the topical route of administration sometimes states that both the application location and thepharmacodynamic
Pharmacodynamics (PD) is the study of the biochemical and physiologic effects of drugs (especially pharmaceutical drugs). The effects can include those manifested within animals (including humans), microorganisms, or combinations of organisms (for ...
effect thereof is local.
In other cases, ''topical'' is defined as applied to a localized area of the body or to the surface of a body part regardless of the location of the effect. By this definition, topical administration
A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ...
also includes transdermal
Transdermal is a route of administration wherein active ingredients are delivered across the skin for systemic distribution. Examples include transdermal patches used for medicine delivery.
The drug is administered in the form of a patch or ointme ...
application, where the substance is administered onto the skin but is absorbed into the body to attain systemic distribution.
If defined strictly as having local effect, the topical route of administration can also include enteral administration
Enteral administration is food or drug administration via the human gastrointestinal tract. This contrasts with parenteral nutrition or drug administration (Greek ''para'', "besides" + ''enteros''), which occurs from routes outside the GI tract, ...
of medications that are poorly absorbable by the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
. One such medication is the antibiotic vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infection ...
, which cannot be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and is used orally only as a treatment for ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis.
Choice of routes
The reason for choice of routes of drug administration are governing by various factors: * Physical and chemical properties of the drug. The physical properties are solid, liquid and gas. The chemical properties are solubility, stability, pH, irritancy etc. * Site of desired action: the action may be localised and approachable or generalised and not approachable. * Rate of extent of absorption of the drug from different routes. * Effect of digestive juices and the first pass metabolism of drugs. * Condition of the patient. In acute situations, inemergency medicine
Emergency medicine is the medical speciality concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (often called “ER doctors” in the United States) continuously learn to care for un ...
and intensive care medicine
Intensive care medicine, also called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes pro ...
, drugs are most often given intravenously. This is the most reliable route, as in acutely ill patients the absorption of substances from the tissues and from the digestive tract can often be unpredictable due to altered blood flow or bowel motility.
Convenience
Enteral routes are generally the most convenient for the patient, as no punctures or sterile procedures are necessary. Enteral medications are therefore often preferred in the treatment of chronic disease. However, some drugs can not be used enterally because their absorption in the digestive tract is low or unpredictable. Transdermal administration is a comfortable alternative; there are, however, only a few drug preparations that are suitable for transdermal administration.Desired target effect
Identical drugs can produce different results depending on the route of administration. For example, some drugs are not significantly absorbed into the bloodstream from the gastrointestinal tract and their action after enteral administration is therefore different from that after parenteral administration. This can be illustrated by the action ofnaloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand names Narcan (4 mg) and Kloxxado (8 mg) among others, is a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. It is commonly used to counter decreased breathing in opioid overdose. Effects begin withi ...
(Narcan), an antagonist of opiate
An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term ''opioid'' is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain (including antagonist ...
s such as morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies ('' Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a pain medication, and is also commonly used recreationally, or to make other illicit opioids. Ther ...
. Naloxone counteracts opiate action in the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
when given intravenously and is therefore used in the treatment of opiate overdose. The same drug, when swallowed, acts exclusively on the bowels; it is here used to treat constipation under opiate pain therapy and does not affect the pain-reducing effect of the opiate.
Oral
The oral route is generally the most convenient and costs the least. However, some drugs can causegastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
irritation. For drugs that come in delayed release A delayed release or late release may refer to:
* Delayed release (film), the delayed release of a film to the public
* Delayed release (pharmacology), oral medicines that do not immediately disintegrate and release the active ingredient(s) into t ...
or time-release formulations, breaking the tablets or capsules can lead to more rapid delivery of the drug than intended. The oral route is limited to formulations containing small molecule
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs are ...
s only while biopharmaceuticals (usually proteins) would be digested in the stomach and thereby become ineffective. Biopharmaceuticals have to be given by injection or infusion. However, recent research (2018) found an organic ionic liquid
An ionic liquid (IL) is a salt in the liquid state. In some contexts, the term has been restricted to salts whose melting point is below a specific temperature, such as . While ordinary liquids such as water and gasoline are predominantly made of ...
suitable for oral insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
delivery (a biopharmaceutical) into the blood stream.
Oral administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are in ...
is often denoted "PO" from "per os", the Latin for "by mouth".
The bioavailability of oral administration is affected by the amount of drug that is absorbed across the intestinal epithelium
The intestinal epithelium is the single cell layer that form the luminal surface (lining) of both the small and large intestine (colon) of the gastrointestinal tract. Composed of simple columnar epithelial cells, it serves two main functio ...
and first-pass metabolism.
Local
By delivering drugs almost directly to the site of action, the risk of systemicside effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequence ...
is reduced.
Skin absorption (dermal absorption), for example, is to directly deliver drug to the skin and, hopefully, to the systemic circulation. However, skin irritation may result, and for some forms such as creams or lotions, the dosage is difficult to control. Upon contact with the skin, the drug penetrates into the dead stratum corneum
The stratum corneum (Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis. The human stratum corneum comprises several levels of flattened corneocytes that are divided into two layers: the ''stratum disjunctum'' and ''stratum compac ...
and can afterwards reach the viable epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
, the dermis, and the blood vessel
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from ...
s.
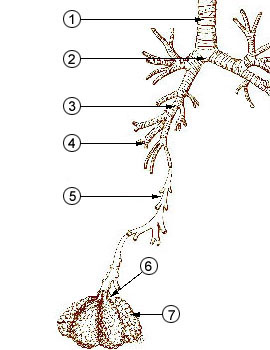
Mouth inhalation

 Inhaled medications can be absorbed quickly and act both locally and systemically. Proper technique with
Inhaled medications can be absorbed quickly and act both locally and systemically. Proper technique with inhaler
An inhaler (also known as a puffer, pump or allergy spray) is a medical device used for delivering medicines into the lungs through the work of a person's breathing. This allows medicines to be delivered to and absorbed in the lungs, which prov ...
devices is necessary to achieve the correct dose. Some medications can have an unpleasant taste or irritate the mouth.
In general, only 20–50% of the pulmonary-delivered dose rendered in powdery particles will be deposited in the lung upon mouth inhalation. The remainder of 50-70% undeposited aerosolized particles are cleared out of lung as soon as exhalation
Exhalation (or expiration) is the flow of the breath out of an organism. In animals, it is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways, to the external environment during breathing.
This happens due to elastic properties of the lungs, ...
.
An inhaled powdery particle that is >8 μm is structurally predisposed to depositing in the central and conducting airways (conducting zone
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa.
Air is breathed in through the nose to ...
) by inertial impaction.
An inhaled powdery particle that is between 3 and 8 μm in diameter tend to largely deposit in the transitional zone
Transition or transitional may refer to:
Mathematics, science, and technology Biology
* Transition (genetics), a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (A ↔ G) or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (C ↔ ...
s of the lung by sedimentation.
An inhaled powdery particle that is <3 μm in diameter is structurally predisposed to depositing primarily in the respiratory region
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
s of the peripheral lung via diffusion.
Particles that deposit in the upper and central airways are generally absorbed systemically to great extent because they are only partially removed by mucociliary clearance, which results in orally mediated absorption when the transported mucous is swallowed, and first pass metabolism or incomplete absorption through loss at the fecal route can sometimes reduce the bioavailability. This should in no way suggest to clinicians or researchers that inhaled particles are not a greater threat than swallowed particles, it merely signifies that a combination of both methods may occur with some particles, no matter the size of or lipo/hydrophilicity of the different particle surfaces.
Nasal inhalation
Inhalation by nose of a substance is almost identical to oral inhalation, except that some of the drug is absorbed intranasally instead of in the oral cavity before entering the airways. Both methods can result in varying levels of the substance to be deposited in their respective initial cavities, and the level of mucous in either of these cavities will reflect the amount of substance swallowed. The rate of inhalation will usually determine the amount of the substance which enters the lungs. Faster inhalation results in more rapid absorption because more substance finds the lungs. Substances in a form that resists absorption in the lung will likely resist absorption in the nasal passage, and the oral cavity, and are often even more resistant to absorption after they fail absorption in the former cavities and are swallowed.Parenteral
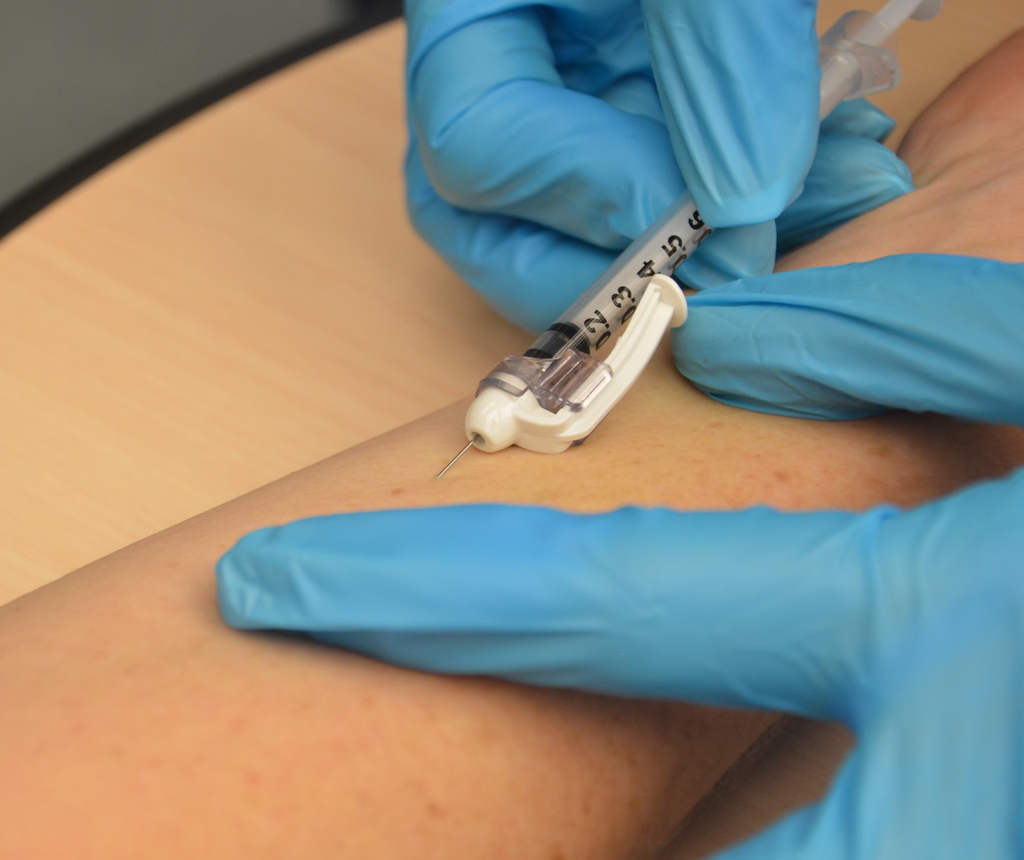
The term parenteral is from para-1 ‘beside’ + Greek enteron ‘intestine’ + -al. This name is due to the fact that it encompasses a route of administration that is not intestinal. However, in common English the term has mostly been used to describe the 4 most well-known routes of injection. The term injection encompasses intravenous (IV),
The term injection encompasses intravenous (IV), intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have ...
(IM), subcutaneous Subcutaneous may refer to:
* Subcutaneous injection
* Subcutaneous tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The ...
(SC) and intradermal (ID) administration.
Parenteral administration generally acts more rapidly than topical or enteral administration, with onset of action often occurring in 15–30 seconds for IV, 10–20 minutes for IM and 15–30 minutes for SC. They also have essentially 100% bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. ...
and can be used for drugs that are poorly absorbed or ineffective when they are given orally. Some medications, such as certain antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizophrenia but also in a range o ...
s, can be administered as long-acting intramuscular injections. The practice is often carried out through physical force in company of law-enforcement, and often against the will of the patient. However, all doses of long-acting antipsychotics injections are of at extreme risk to the health and well-being of the patient. Extreme ethical concerns should be considered. If the choice is made to use force, care should be taken to use only the smallest dose that is currently scientifically demonstrated to be efficacious for the specific drug. This is because, despite being injected, the drugs are designed with heavy esterifying molecular additions which can cause traces of the drugs to be found in circulation for up to one year. Ongoing IV infusions can be used to deliver continuous medication or fluids
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that continuously deforms (''flows'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear ...
.
Disadvantages of injections include potential pain or discomfort for the patient and the requirement of trained staff using aseptic technique
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms (such as pathogenic bacteria, viruses, pathogenic fungi, and parasites). There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgical. The modern day notion of asepsis is der ...
s for administration. However, in some cases, patients are taught to self-inject, such as SC injection of insulin in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. As the drug is delivered to the site of action extremely rapidly with IV injection, there is a risk of overdose
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended.
if the dose has been calculated incorrectly, and there is an increased risk of side effects if the drug is administered too rapidly.
Intranasal
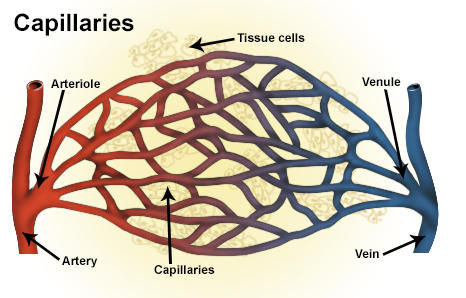
Drug administration via the nasal cavity yields rapid drug absorption and therapeutic effects. This is because drug absorption through the nasal passages doesn't go through the gut before enteringcapillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
situated at tissue cell
Tissue may refer to:
Biology
* Tissue (biology), an ensemble of similar (or dissimilar in structure but same in origin) cells that together carry out a specific function
* ''Triphosa haesitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue moth") found in ...
s and then systemic circulation and such absorption route allows transport of drugs into the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
via the pathways of olfactory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, i ...
and trigeminal nerve
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (literal translation, lit. ''triplet'' nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for Sense, sensation in the face and motor functions ...
.
Intranasal absorption features low lipophilicity, enzymatic degradation within the nasal cavity, large molecular size, and rapid mucociliary clearance from the nasal passages, which explains the low risk of systemic exposure of the administered drug absorbed via intranasal.

Sublingual
Sublingual administration
Sublingual (abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
The sublingual glands receive their primar ...
is fulfilled by placing the drug between the tongue and the lower surface of the mouth. The sublingual mucosa
Sublingual (abbreviated SL), from the Latin for "under the tongue", refers to the pharmacological route of administration by which substances diffuse into the blood through tissues under the tongue.
The sublingual glands receive their prima ...
is highly permeable and thereby provides access to the underlying expansive network composed of capillaries, leading to rapid drug absorption.
Buccal
Buccally administered medication is achieved by placing the drug betweengums
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue l ...
and the inner lining of the cheek
The cheeks ( la, buccae) constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. "Buccal" means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the insi ...
. In comparison with sublingual tissue, buccal tissue is less permeable resulting in slower absorption.
Sublabial administration
Sublabial administrationResearch
Neural drug delivery is the next step beyond the basic addition ofgrowth factors
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and occasionally cellular differentiation. Usually it is a secreted protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for re ...
to nerve guidance conduits. Drug delivery systems allow the rate of growth factor release to be regulated over time, which is critical for creating an environment more closely representative of in vivo development environments.Lavik, E. and R. Langer, Tissue engineering; current state and perspectives. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology, 2004. 65: p. 1-8
See also
*ADME
ADME is an abbreviation in pharmacokinetics and pharmacology for " absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion", and describes the disposition of a pharmaceutical compound within an organism. The four criteria all influence the drug l ...
* Catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Cat ...
* Dosage form
Dosage forms (also called unit doses) are pharmaceutical drug products in the form in which they are marketed for use, with a specific mixture of active ingredients and inactive components ( excipients), in a particular configuration (such as a c ...
* Drug injection
Drug injection is a method of introducing a drug into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body (usually intravenously, but also at an intramuscular or Subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous l ...
* Ear instillation
* Hypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)), one of a category of medical tools which enter the skin, called sharps, is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. It is commonly used w ...
* Intravenous marijuana syndrome
Intravenous marijuana syndrome is a distinct short-term clinical syndrome related to the intravenous injection of boiled cannabis broth, which had been filtered through a cotton cloth. The syndrome has at least 25 known cases in the English languag ...
* List of medical inhalants
* Nanomedicine
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology. Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials and biological devices, to nanoelectronic biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotec ...
* Absorption (pharmacology)
Absorption is the journey of a drug travelling from the site of administration to the site of action.
The drug travels by some route of administration ( oral, topical-dermal, etc.) in a chosen dosage form (e.g., tablets, capsules, or in sol ...
References
External links
The 10th US-Japan Symposium on Drug Delivery Systems
* [https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/FormsSubmissionRequirements/ElectronicSubmissions/DataStandardsManualmonographs/ucm071666.htm FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Data Standards Manual: Dosage Form.]
A.S.P.E.N. American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Route Of Administration Drugs Pharmacokinetics Routes of administration