ingested on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an
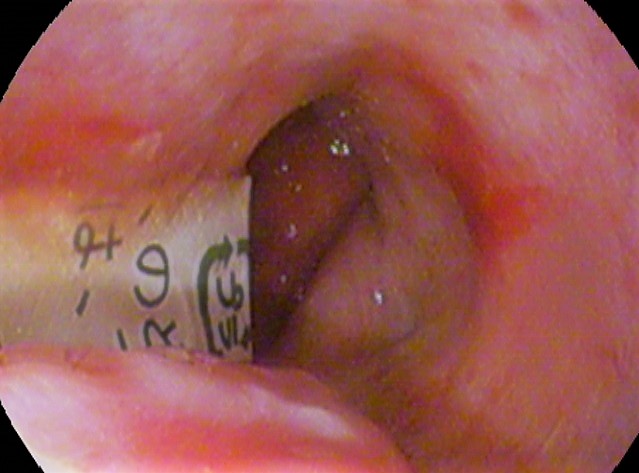 Disk batteries, also called button cells, are often mistakenly ingested, particularly by
Disk batteries, also called button cells, are often mistakenly ingested, particularly by
organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
. In animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also t ...
into the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
, such as through eating
Eating (also known as consuming) is the ingestion of food. In biology, this is typically done to provide a heterotrophic organism with energy and nutrients and to allow for growth. Animals and other heterotrophs must eat in order to survive – ...
or drinking
Drinking is the act of ingesting water or other liquids into the body through the mouth, proboscis, or elsewhere. Humans drink by swallowing, completed by peristalsis in the esophagus. The physiological processes of drinking vary widely among ...
. In single-celled organisms, ingestion takes place by absorbing a substance through the cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extr ...
.
Besides nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemistry, biochemical and physiology, physiological process by which an organism uses food and water to support its life. The intake of these substances provides organisms with nutrients (divided into Macronutrient, macro- ...
al items, substances that may be ingested include medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
(where ingestion is termed oral administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications.
Oral administ ...
), recreational drugs
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for enjoyment, amusement, or plea ...
, and substances considered inedible, such as foreign bodies
A foreign body (FB) is any object originating outside the body of an organism. In machinery, it can mean any unwanted intruding object.
Most references to foreign bodies involve propulsion through natural orifices into hollow organs.
Foreign b ...
or excrement
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
. Ingestion is a common route taken by pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
ic organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s and poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
s entering the body.
Ingestion can also refer to a mechanism picking up something and making it enter an internal hollow of that mechanism, e.g. "''a grille was fitted to prevent the pump from ingesting driftwood
Driftwood is a wood that has been washed onto a shore or beach of a sea, lake, or river by the action of winds, tides or waves. It is part of beach wrack.
In some waterfront areas, driftwood is a major nuisance. However, the driftwood provides ...
''".
Pathogens
Somepathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s are transmitted via ingestion, including virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es, bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
, and parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
s. Most commonly, this takes place via the faecal-oral route. An intermediate step is often involved, such as drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
contaminated by faeces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
or food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for Nutrient, nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or Fungus, fungal origin and contains essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, protein (nutrient), proteins, vitamins, ...
prepared by workers who fail to practice adequate hand-washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to the han ...
, and is more common in regions where untreated sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
is common. Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
s transmitted via the fecal-oral route include hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an infectious liver disease caused by Hepatitis A virus (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is ...
, polio
Poliomyelitis ( ), commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 75% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe ...
, and cholera
Cholera () is an infection of the small intestine by some Strain (biology), strains of the Bacteria, bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea last ...
.
Some pathogenic organisms are typically ingested by other routes.
* Larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
e of the parasite ''Trichinella
''Trichinella'' is the genus of parasitic roundworms of the phylum Nematoda that cause trichinosis (also known as trichinellosis). Members of this genus are often called trichinella or trichina worms. A characteristic of Nematoda is the one-way ...
'' encyst within muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s and are transmitted when a new host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
* Host Island, in the Wilhelm Archipelago, Antarctica
People
* ...
eats the infected flesh of a former host animal.
* The parasite '' Dracunculus'' is ingested in drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
, which is contaminated with larvae released as the parasite emerges from the host's skin.
* The bacterium ''Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' ...
'' most commonly infects humans via consumption of undercooked eggs.
Foreign objects
 Disk batteries, also called button cells, are often mistakenly ingested, particularly by
Disk batteries, also called button cells, are often mistakenly ingested, particularly by child
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
ren and the elderly
Old age is the range of ages for people nearing and surpassing life expectancy. People who are of old age are also referred to as: old people, elderly, elders, senior citizens, seniors or older adults. Old age is not a definite biological sta ...
. They may be mistaken for a medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
pill
Pill or The Pill may refer to:
Drugs
* Pill (pharmacy), referring to anything small for a specific dose of medicine
* "The Pill", a general nickname for the combined oral contraceptive pill
Film and television
* ''The Pill'' (film), a 2011 fil ...
because of their size and shape, or they may be swallowed after being held in the mouth while the battery is being changed. Battery ingestion can cause medical problems including blocked airway
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of conducting air to the alveoli for the purposes of gas exchange in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory ...
, vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, irritability
Irritability is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimul ...
, persistent drooling, and rash
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
(due to nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
metal allergy
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food al ...
).
Abnormal ingestion
Pica is an abnormal appetite for non- nutritive objects or for food items in a form not normally eaten, such asflour
Flour is a powder made by Mill (grinding), grinding raw grains, List of root vegetables, roots, beans, Nut (fruit), nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredie ...
. Coprophagia
Coprophagia ( ) or coprophagy ( ) is the consumption of feces. The word is derived from the Ancient Greek "feces" and "to eat". Coprophagy refers to many kinds of feces-eating, including eating feces of other species (heterospecifics), of o ...
is the consumption of feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
, an abnormal ingestive behavior common in some animals.
References
{{Ethology Digestive system Ethology Mouth