Influenzavirus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Orthomyxoviridae'' () is a family of
 The influenzavirus
The influenzavirus
 Viruses of the family ''Orthomyxoviridae'' contain six to eight segments of linear
Viruses of the family ''Orthomyxoviridae'' contain six to eight segments of linear
 Typically, influenza is transmitted from infected mammals through the air by coughs or sneezes, creating
Typically, influenza is transmitted from infected mammals through the air by coughs or sneezes, creating  Orthomyxoviridae viruses are one of two RNA viruses that replicate in the nucleus (the other being
Orthomyxoviridae viruses are one of two RNA viruses that replicate in the nucleus (the other being
 Influenza A viruses are further classified, based on the viral surface proteins
Influenza A viruses are further classified, based on the viral surface proteins
 Influenza B virus is almost exclusively a human pathogen, and is less common than influenza A. The only other animal known to be susceptible to influenza B infection is the
Influenza B virus is almost exclusively a human pathogen, and is less common than influenza A. The only other animal known to be susceptible to influenza B infection is the
 Vaccines and drugs are available for the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza virus infections. Vaccines are composed of either inactivated or live attenuated virions of the H1N1 and H3N2 human influenza A viruses, as well as those of influenza B viruses. Because the antigenicities of the wild viruses evolve, vaccines are reformulated annually by updating the seed strains.
More specifically, flu vaccines are made using the reassortment method, and this has been used for over 50 years. In this method, scientists inject eggs with both one noninfectious flu strain and also one infectious strain. The inert strain must be one that multiples very well in chicken eggs. Scientists pick an infectious strain that carries the desired HA and N receptors that the final product should prevent from infection. They choose these strains by picking the surface HA and NA versions circulating the most in the public, and the ones thought most likely to be prevalent in the upcoming flu season. The two strains—pathogenic and non pathogenic—then multiply and exchange DNA until an inert strain carries eight copies of the infectious strain’s two glycoprotein targets. Finally, of the newly created viruses, scientists pick six versions that multiplied the best in chicken eggs which also carry the necessary HA and NA genes. Ultimately, millions of eggs are injected with those noninfectious strains—which carry the desired proteins—so that the genes can be harvested and used for the vaccine product.
Another method of making the vaccine is by splicing genes from infectious strains and then creating copies in a lab, without the need for the tedious process of chicken egg culture. This method relies on using virus plasmids to excerpt the target genes.
When the antigenicities of the seed strains and wild viruses do not match, vaccines fail to protect the vaccines.
Drugs available for the treatment of influenza include
Vaccines and drugs are available for the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza virus infections. Vaccines are composed of either inactivated or live attenuated virions of the H1N1 and H3N2 human influenza A viruses, as well as those of influenza B viruses. Because the antigenicities of the wild viruses evolve, vaccines are reformulated annually by updating the seed strains.
More specifically, flu vaccines are made using the reassortment method, and this has been used for over 50 years. In this method, scientists inject eggs with both one noninfectious flu strain and also one infectious strain. The inert strain must be one that multiples very well in chicken eggs. Scientists pick an infectious strain that carries the desired HA and N receptors that the final product should prevent from infection. They choose these strains by picking the surface HA and NA versions circulating the most in the public, and the ones thought most likely to be prevalent in the upcoming flu season. The two strains—pathogenic and non pathogenic—then multiply and exchange DNA until an inert strain carries eight copies of the infectious strain’s two glycoprotein targets. Finally, of the newly created viruses, scientists pick six versions that multiplied the best in chicken eggs which also carry the necessary HA and NA genes. Ultimately, millions of eggs are injected with those noninfectious strains—which carry the desired proteins—so that the genes can be harvested and used for the vaccine product.
Another method of making the vaccine is by splicing genes from infectious strains and then creating copies in a lab, without the need for the tedious process of chicken egg culture. This method relies on using virus plasmids to excerpt the target genes.
When the antigenicities of the seed strains and wild viruses do not match, vaccines fail to protect the vaccines.
Drugs available for the treatment of influenza include
Health-EU Portal
EU work to prepare a global response to influenza.
Influenza Research Database
Database of influenza genomic sequences and related information.
EU coordination on Pandemic (H1N1) 2009
3D Influenza-virus-related structures from the EM Data Bank (EMDB)
{{Authority control Virus families
negative-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, ...
RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virus characterized by a ribonucleic acid (RNA) based genome. The genome can be single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or double-stranded (Double-stranded RNA, dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include influenza, SARS, ...
es. It includes nine genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
: '' Alphainfluenzavirus'', '' Betainfluenzavirus'', '' Gammainfluenzavirus'', '' Deltainfluenzavirus'', ''Isavirus
Infectious salmon anemia (ISA) is a viral disease of Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') caused by Infectious salmon anemia virus. It affects fish farms in Canada, Norway, Scotland and Chile, causing severe losses to infected farms. ISA has bee ...
'', '' Mykissvirus'', ''Quaranjavirus
''Quaranjavirus'' is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. The genome is single-stranded, negative-sense segmented RNA, generally with six segments. The genus contains six species. Quar ...
'', '' Sardinovirus'', and ''Thogotovirus
''Thogotovirus'' is a genus of viral envelope, enveloped RNA viruses in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Their single-stranded, sense (molecular biology), negative-sense RNA genome has six or seven segments. Thogotoviruses are distinguishe ...
''. The first four genera contain viruses that cause influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
in bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s (see also avian influenza
Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus, which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Wild aquatic birds are the primary host of the influenza A viru ...
) and mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, including humans. Isaviruses infect salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
; the thogotoviruses are arbovirus
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is Transmission (medicine), transmitted by arthropod Vector (epidemiology), vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo ...
es, infecting vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s and invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s (such as tick
Ticks are parasitic arachnids of the order Ixodida. They are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, and species, but can become larger when engorged. Ticks a ...
s and mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mos ...
es). The Quaranjaviruses are also arbovirus
Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is Transmission (medicine), transmitted by arthropod Vector (epidemiology), vectors. The term ''arbovirus'' is a portmanteau word (''ar''thropod-''bo''rne ''virus''). ''Tibovirus'' (''ti''ck-''bo ...
es, infecting vertebrates (birds) and invertebrates (arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s).
The four genera of Influenza virus that infect vertebrates, which are identified by antigenic differences in their nucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins.
Structures
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating inte ...
and matrix protein
Viral matrix proteins are structural proteins linking the viral envelope with the virus core. They play a crucial role in virus assembly, and interact with the RNP complex as well as with the viral membrane. They are found in many enveloped viru ...
, are as follows:
* '' Alphainfluenzavirus'' infects humans, other mammals, and birds, and causes all flu pandemic
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
s
* '' Betainfluenzavirus'' infects humans and seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
* '' Gammainfluenzavirus'' infects humans and pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
s
* '' Deltainfluenzavirus'' infects pigs and cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
.
Structure
 The influenzavirus
The influenzavirus virion
A virion (plural, ''viria'' or ''virions'') is an inert virus particle capable of invading a Cell (biology), cell. Upon entering the cell, the virion disassembles and the genetic material from the virus takes control of the cell infrastructure, t ...
is pleomorphic; the viral envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. A viral envelope protein or E protein is a protein in the en ...
can occur in spherical and filamentous forms. In general, the virus's morphology is ellipsoidal with particles 100–120 nm in diameter, or filamentous with particles 80–100 nm in diameter and up to 20 μm long. There are approximately 500 distinct spike-like surface projections in the envelope each projecting 10–14 nm from the surface with varying surface densities. The major glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
(HA) spike is interposed irregularly by clusters of neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glycosidic linkag ...
(NA) spikes, with a ratio of HA to NA of about 10 to 1.
The viral envelope composed of a lipid bilayer
The lipid bilayer (or phospholipid bilayer) is a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules. These membranes form a continuous barrier around all cell (biology), cells. The cell membranes of almost all organisms and many viruses a ...
membrane in which the glycoprotein spikes are anchored encloses the nucleocapsids; nucleoproteins of different size classes with a loop at each end; the arrangement within the virion is uncertain. The ribonuclear proteins are filamentous and fall in the range of 50–130 nm long and 9–15 nm in diameter with helical symmetry.
Genome
 Viruses of the family ''Orthomyxoviridae'' contain six to eight segments of linear
Viruses of the family ''Orthomyxoviridae'' contain six to eight segments of linear negative-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, ...
single stranded RNA. They have a total genome length that is 10,000–14,600 nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s (nt). The influenza A genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
, for instance, has eight pieces of segmented negative-sense RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
(13.5 kilobases total).
The best-characterised of the influenzavirus proteins are hemagglutinin
The term hemagglutinin (alternatively spelt ''haemagglutinin'', from the Greek , 'blood' + Latin , 'glue') refers to any protein that can cause red blood cells (erythrocytes) to clump together (" agglutinate") ''in vitro''. They do this by bindin ...
and neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glycosidic linkag ...
, two large glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide (sugar) chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known a ...
s found on the outside of the viral particles. Hemagglutinin is a lectin
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar Moiety (chemistry), groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination (biology), agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates an ...
that mediates binding of the virus to target cells and entry of the viral genome into the target cell. In contrast, neuraminidase is an enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
involved in the release of progeny virus from infected cells, by cleaving sugars that bind the mature viral particles. The hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N) protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s are key targets for antibodies and antiviral drugs, and they are used to classify the different serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or Cell (biology), cells are classified together based on their shared reactivity ...
s of influenza A viruses, hence the ''H'' and ''N'' in ''H5N1''.
The genome sequence has terminal repeated sequences, and these are repeated at both ends (i.e., at both the 5’ end and the 3’ end). These terminal repeats at the 5′-end are 12–13 nucleotides long. Nucleotide sequences at the 3′-terminus are identical, are the same in genera of the same family, most on RNA (segments), or on all RNA species. Terminal repeats at the 3′-end are 9–11 nucleotides long. Encapsidated nucleic acid is solely genomic. Each virion may contain defective interfering copies. In Influenza A (specifically, in H1N1) PB1-F2 is produced from an alternative reading frame in PB1. The M and NS genes produce two genes each (4 genes total) via alternative splicing
Alternative splicing, alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative RNA splicing, splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to produce different splice variants. For example, some exons of a gene ma ...
.
Replication cycle
aerosols
An aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be generated from natural or human causes. The term ''aerosol'' commonly refers to the mixture of particulates in air, and not to t ...
containing the virus, and from infected birds through their droppings
Feces (also known as faeces or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the large intestine. Feces contain a relatively small amount of ...
. Influenza can also be transmitted by saliva
Saliva (commonly referred as spit or drool) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which ...
, nasal secretions, feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
and blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.
Blood is com ...
. Infections occur through contact with these bodily fluids or with contaminated surfaces. On certain surfaces (i.e, outside of a host), flu viruses can remain infectious for about one week at human body temperature, over 30 days at , and indefinitely at very low temperatures (such as in lakes in northeast Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states ...
). They can be inactivated easily by disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than ...
s and detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with Cleanliness, cleansing properties when in Concentration, dilute Solution (chemistry), solutions. There are a large variety of detergents. A common family is the alkylbenzene sulfonate ...
s.
The viruses interacts between its surface hemagglutinin
The term hemagglutinin (alternatively spelt ''haemagglutinin'', from the Greek , 'blood' + Latin , 'glue') refers to any protein that can cause red blood cells (erythrocytes) to clump together (" agglutinate") ''in vitro''. They do this by bindin ...
glycoprotein to bind to the host’s surface sialic acid
Sialic acids are a class of alpha-keto acid sugars with a nine-carbon backbone.
The term "sialic acid" () was first introduced by Swedish biochemist Gunnar Blix in 1952. The most common member of this group is ''N''-acetylneuraminic acid ...
sugars, specifically on the surfaces of epithelial cells
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
in the lung and throat (Stage 1 in infection figure). The cell imports the virus by endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which Chemical substance, substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a Vesicle (biology and chem ...
. In the acidic pH environment of the endosome
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of the endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membra ...
, part of the hemagglutinin protein fuses the viral envelope with the vacuole's membrane, releasing: the viral RNA (vRNA) molecules, accessory proteins and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the self-replication, replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand Complementarity (molecular biology), compleme ...
into the host cell’s cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
(Stage 2). These proteins and vRNA form a complex that is transported into the host cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
, where the host’s own RNA-dependent RNA polymerase begins transcribing complementary positive-sense cRNA (Steps 3a and b). The cRNA is either exported into the cytoplasm and translated (step 4), or remains in the host nucleus. Newly synthesised viral proteins are either secreted through the Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic Cell (biology), cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it protein targeting, packages proteins ...
onto the host cell surface (in the case of neuraminidase and hemagglutinin, step 5b) or transported back into the host nucleus, where they bind vRNA and form new viral genome particles (step 5a). Other viral proteins have multiple actions in the host cell, including degrading cellular mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
and using those consequently-released nucleotide
Nucleotides are Organic compound, organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both o ...
s for vRNA synthesis, while also inhibiting translation of the host cell’s mRNAs.
A virion assembles from negative-sense vRNAs (that form the genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
s of newly created viruses), RNA-dependent RNA transcriptase and other viral proteins. Hemagglutinin and neuraminidase molecules cluster into a bulge in the host cell membrane. The vRNA and viral core
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
proteins leave the nucleus and enter this membrane protrusion (step 6). The mature virus buds off from the host cell in a sphere of host phospholipid membrane, acquiring hemagglutinin and neuraminidase with this membrane coat (step 7). As before, the viruses then adhere to the same host cell capsule through hemagglutinin; the mature viruses detach once their neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glycosidic linkag ...
has cleaved sialic acid residues from the host cell. After the release of new influenza virus, the host cell dies, and infection repeats in other host cells.
 Orthomyxoviridae viruses are one of two RNA viruses that replicate in the nucleus (the other being
Orthomyxoviridae viruses are one of two RNA viruses that replicate in the nucleus (the other being retroviridae
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. After invading a host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
). This is because the machinery of orthomyxo viruses cannot make their own mRNAs. They use cellular RNAs as primers for initiating the viral mRNA synthesis in a process known as cap snatching
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. The origin of the word "cap" comes from the Old French word "chapeau" which means "head co ...
. Once in the nucleus, the RNA Polymerase Protein PB2 finds a cellular pre-mRNA and binds to its 5′ capped end. Then RNA Polymerase PA cleaves off the cellular mRNA near the 5′ end and uses this capped fragment as a primer for transcribing the rest of the viral RNA genome in viral mRNA. This is due to the need of mRNA to have a 5′ cap in order to be recognized by the cell's ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
for translation.
Since RNA proofreading
Proofreading is a phase in the process of publishing where galley proofs are compared against the original manuscripts or graphic artworks, to identify transcription errors in the typesetting process. In the past, proofreaders would place corr ...
enzymes are absent, the RNA-dependent RNA transcriptase makes a single nucleotide insertion error roughly every 10 thousand nucleotides, which is the approximate length of the influenza vRNA. Hence, nearly every newly manufactured influenza virus will contain a mutation in its genome. The separation of the genome into eight separate segments of vRNA allows mixing (reassortment
Reassortment is the mixing of the genetic material of a species into new combinations in different individuals. The product of reassortment is called a reassortant. It is particularly used when two similar viruses that are infecting the same cell ...
) of the genes if more than one variety of influenza virus has infected the same cell (superinfection
A superinfection is a second infection superimposed on an earlier one, especially by a different microbial agent of exogenous or endogenous origin, that is resistant to the treatment being used against the first infection. Examples of this in bact ...
). The resulting alteration in the genome segments packaged into viral progeny confers new behavior, sometimes the ability to infect new host species or to overcome protective immunity of host populations to its old genome (in which case it is called an antigenic shift
Antigenic shift is the process by which two or more different strains of a virus, or strains of two or more different viruses, combine to form a new subtype having a mixture of the surface antigens of the two or more original strains. The term is ...
).
Classification
In aphylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical dat ...
-based taxonomy
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme o ...
, RNA viruses
''Orthornavirae'' is a kingdom of viruses that have genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA), including genes which encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The RdRp is used to transcribe the viral RNA genome into messenger RNA (mRNA) and t ...
include the subcategory negative-sense ssRNA virus
Negative-strand RNA viruses (−ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) ...
, which includes the order '' Articulavirales'', and the family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. The family contains the following genera:
* '' Alphainfluenzavirus''
* '' Betainfluenzavirus''
* '' Deltainfluenzavirus''
* '' Gammainfluenzavirus''
* ''Isavirus
Infectious salmon anemia (ISA) is a viral disease of Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') caused by Infectious salmon anemia virus. It affects fish farms in Canada, Norway, Scotland and Chile, causing severe losses to infected farms. ISA has bee ...
''
* '' Mykissvirus''
* ''Quaranjavirus
''Quaranjavirus'' is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. The genome is single-stranded, negative-sense segmented RNA, generally with six segments. The genus contains six species. Quar ...
''
* '' Sardinovirus''
* ''Thogotovirus
''Thogotovirus'' is a genus of viral envelope, enveloped RNA viruses in the virus family ''Orthomyxoviridae''. Their single-stranded, sense (molecular biology), negative-sense RNA genome has six or seven segments. Thogotoviruses are distinguishe ...
''
Influenza types
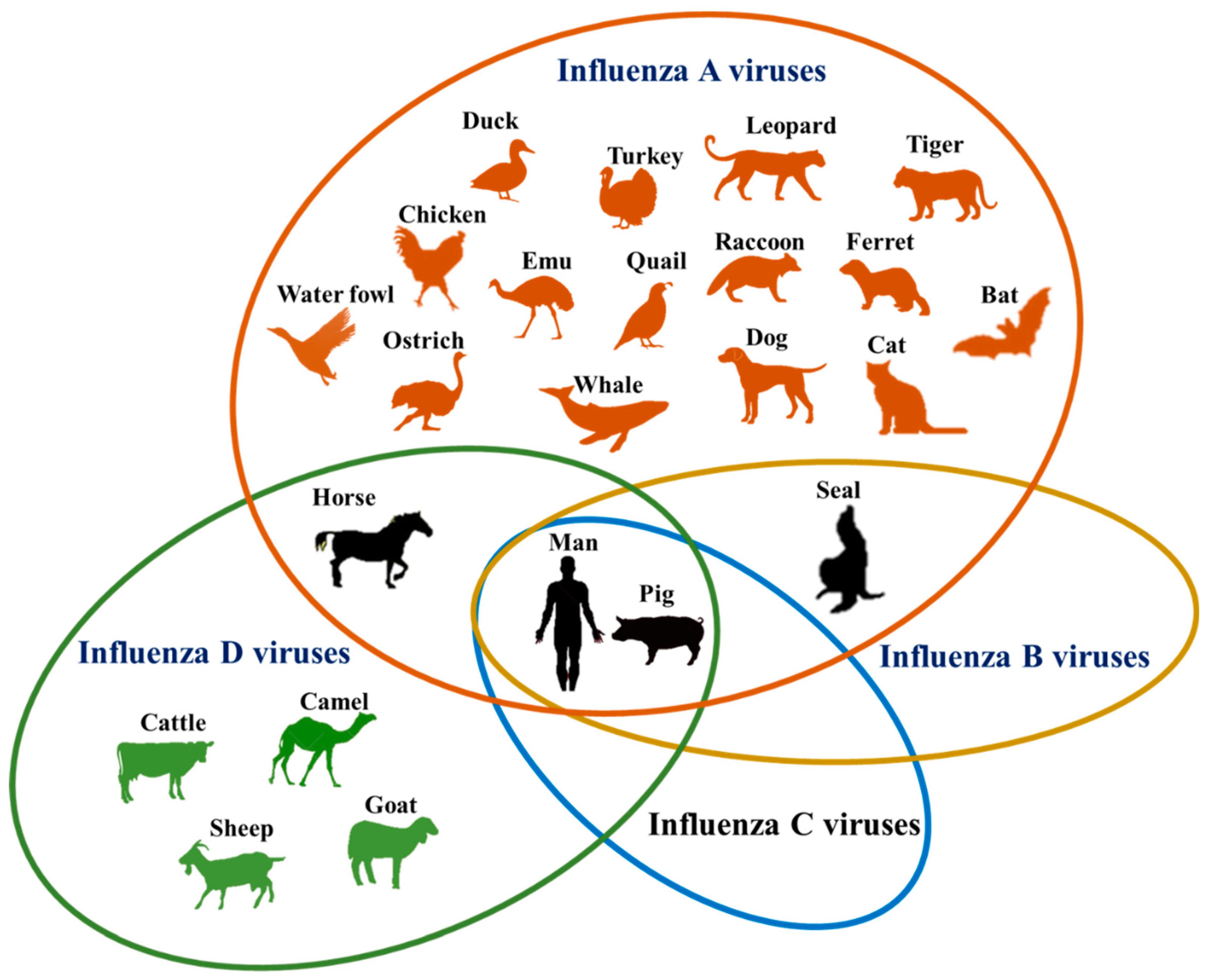
There are four genera of influenza virus, each containing only a single species, or type. Influenza A and C infect a variety of species (including humans), while influenza B almost exclusively infects humans, and influenza D infects cattle and pigs.Influenza A
hemagglutinin
The term hemagglutinin (alternatively spelt ''haemagglutinin'', from the Greek , 'blood' + Latin , 'glue') refers to any protein that can cause red blood cells (erythrocytes) to clump together (" agglutinate") ''in vitro''. They do this by bindin ...
(HA or H) and neuraminidase
Exo-α-sialidase (, sialidase, neuraminidase; systematic name acetylneuraminyl hydrolase) is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
: Hydrolysis of α-(2→3)-, α-(2→6)-, α-(2→8)- glycosidic linkag ...
(NA or N). 18 HA subtypes (or serotypes) and 11 NA subtypes of influenza A virus have been isolated in nature. Among these, the HA subtype 1-16 and NA subtype 1-9 are found in wild waterfowl and shorebirds and the HA subtypes 17-18 and NA subtypes 10-11 have only been isolated from bats.
Further variation exists; thus, specific influenza strain isolates are identified by the ''Influenza virus nomenclature,'' specifying virus type, host species (if not human), geographical location where first isolated, laboratory reference, year of isolation, and HA and NA subtype.
Examples of the nomenclature are:
# - isolated from a human
# - isolated from a pig
The type A influenza viruses are the most virulent human pathogens among the three influenza types and cause the most severe disease. It is thought that all influenza A viruses causing outbreaks or pandemics originate from wild aquatic birds. All influenza A virus pandemics since the 1900s were caused by Avian influenza
Avian influenza, also known as avian flu or bird flu, is a disease caused by the influenza A virus, which primarily affects birds but can sometimes affect mammals including humans. Wild aquatic birds are the primary host of the influenza A viru ...
, through Reassortment
Reassortment is the mixing of the genetic material of a species into new combinations in different individuals. The product of reassortment is called a reassortant. It is particularly used when two similar viruses that are infecting the same cell ...
with other influenza strains, either those that affect humans (seasonal flu) or those affecting other animals (see 2009 swine flu pandemic
The 2009 swine flu pandemic, caused by the H1N1/swine flu/influenza virus and declared by the World Health Organization (WHO) from June 2009 to August 2010, was the third recent flu pandemic involving the H1N1 virus (the first being the 1918� ...
). The serotypes that have been confirmed in humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
, ordered by the number of confirmed human deaths, are:
* H1N1
Influenza A virus subtype H1N1 (A/H1N1) is a subtype of influenza A virus (IAV). Some human-adapted strains of H1N1 are endemic in humans and are one cause of seasonal influenza (flu). Other strains of H1N1 are endemic in pigs ( swine influen ...
caused "Spanish flu
The 1918–1920 flu pandemic, also known as the Great Influenza epidemic or by the common misnomer Spanish flu, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the H1N1 subtype of the influenza A virus. The earliest docum ...
" in 1918 and "Swine flu
Swine influenza is an infection caused by any of several types of swine influenza viruses. Swine influenza virus (SIV) or swine-origin influenza virus (S-OIV) refers to any strain of the influenza family of viruses that is endemic in pigs. As ...
" in 2009.
* H2N2
Influenza A virus subtype H2N2 (A/H2N2) is a subtype of '' Influenza A virus''. H2N2 has mutated into various strains including the " Asian flu" strain (now extinct in the wild), H3N2, and various strains found in birds. It is also suspected o ...
caused "Asian Flu".
* H3N2
Influenza A virus subtype H3N2 (A/H3N2) is a subtype of influenza A virus (IAV). Some human-adapted strains of A/H3N2 are endemic in humans and are one cause of seasonal influenza (flu). Other strains of H1N1 are endemic in pigs ( swine influen ...
caused "Hong Kong Flu
The Hong Kong flu, also known as the 1968 flu pandemic, was an influenza pandemic that occurred between 1968 and 1970 and which killed between one and four million people globally. It is among the deadliest pandemics in history, and was caus ...
".
* H5N1
Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 (A/H5N1) is a subtype of the influenza A virus, which causes the disease avian influenza (often referred to as "bird flu"). It is enzootic (maintained in the population) in many bird populations, and also panzoo ...
, "avian" or "bird flu".
* H7N7
Influenza A virus subtype H7N7 (A/H7N7) is a subtype of Influenza A virus, a genus of Orthomyxovirus, the viruses responsible for influenza. Highly pathogenic strains (HPAI) and low pathogenic strains (LPAI) exist. H7N7 can infect humans, bir ...
has unusual zoonotic potential.
* H1N2 infects pigs and humans.
* H9N2, H7N2
Influenza A virus subtype H7N2 (A/H7N2) is a subtype of the species Influenza A virus. This subtype is one of several sometimes called bird flu virus. H7N2 is considered a low pathogenicity avian influenza (LPAI) virus. With this in mind, H5 ...
, H7N3
Influenza A virus subtype H7N3 (A/H7N3) is a subtype of the species Influenza A virus (sometimes called bird flu virus).
In North America, the presence of H7N3 was confirmed at several poultry farms in British Columbia in February 2004; flocks ...
, H10N7
Influenza A virus subtype H10N7 (A/H10N7) is a subtype of the species Influenza A virus (sometimes called bird flu virus). H10N7 was first reported in humans in Egypt in 2004. It caused illness in two one-year-old infants, and residents of Ism ...
.
Influenza B
 Influenza B virus is almost exclusively a human pathogen, and is less common than influenza A. The only other animal known to be susceptible to influenza B infection is the
Influenza B virus is almost exclusively a human pathogen, and is less common than influenza A. The only other animal known to be susceptible to influenza B infection is the seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, also called "true seal"
** Fur seal
** Eared seal
* Seal ( ...
. This type of influenza mutates at a rate 2–3 times lower than type A and consequently is less genetically diverse, with only one influenza B serotype. As a result of this lack of antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
ic diversity, a degree of immunity to influenza B is usually acquired at an early age. However, influenza B mutates enough that lasting immunity is not possible. This reduced rate of antigenic change, combined with its limited host range (inhibiting cross species antigenic shift
Antigenic shift is the process by which two or more different strains of a virus, or strains of two or more different viruses, combine to form a new subtype having a mixture of the surface antigens of the two or more original strains. The term is ...
), ensures that pandemics of influenza B do not occur.
Influenza C
The influenza C virus infectshuman
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s and pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
s, and can cause severe illness and local epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
s. However, influenza C is less common than the other types and usually causes mild disease in children.
Influenza D
This is a genus that was classified in 2016, the members of which were first isolated in 2011. This genus appears to be most closely related to Influenza C, from which it diverged several hundred years ago. There are at least two extant strains of this genus. The main hosts appear to be cattle, but the virus has been known to infect pigs as well.Viability and disinfection
Mammalian influenza viruses tend to be labile, but they can survive several hours in a host’s mucus. Avian influenza virus can survive for 100 days in distilled water at room temperature and for 200 days at . The avian virus is inactivated more quickly in manure but can survive for up to two weeks in feces on cages. Avian influenza viruses can survive indefinitely when frozen. Influenza viruses are susceptible to bleach, 70% ethanol, aldehydes, oxidizing agents and quaternary ammonium compounds. They are inactivated by heat at for minimum of 60 minutes, as well as by low pH <2.Vaccination and prophylaxis
 Vaccines and drugs are available for the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza virus infections. Vaccines are composed of either inactivated or live attenuated virions of the H1N1 and H3N2 human influenza A viruses, as well as those of influenza B viruses. Because the antigenicities of the wild viruses evolve, vaccines are reformulated annually by updating the seed strains.
More specifically, flu vaccines are made using the reassortment method, and this has been used for over 50 years. In this method, scientists inject eggs with both one noninfectious flu strain and also one infectious strain. The inert strain must be one that multiples very well in chicken eggs. Scientists pick an infectious strain that carries the desired HA and N receptors that the final product should prevent from infection. They choose these strains by picking the surface HA and NA versions circulating the most in the public, and the ones thought most likely to be prevalent in the upcoming flu season. The two strains—pathogenic and non pathogenic—then multiply and exchange DNA until an inert strain carries eight copies of the infectious strain’s two glycoprotein targets. Finally, of the newly created viruses, scientists pick six versions that multiplied the best in chicken eggs which also carry the necessary HA and NA genes. Ultimately, millions of eggs are injected with those noninfectious strains—which carry the desired proteins—so that the genes can be harvested and used for the vaccine product.
Another method of making the vaccine is by splicing genes from infectious strains and then creating copies in a lab, without the need for the tedious process of chicken egg culture. This method relies on using virus plasmids to excerpt the target genes.
When the antigenicities of the seed strains and wild viruses do not match, vaccines fail to protect the vaccines.
Drugs available for the treatment of influenza include
Vaccines and drugs are available for the prophylaxis and treatment of influenza virus infections. Vaccines are composed of either inactivated or live attenuated virions of the H1N1 and H3N2 human influenza A viruses, as well as those of influenza B viruses. Because the antigenicities of the wild viruses evolve, vaccines are reformulated annually by updating the seed strains.
More specifically, flu vaccines are made using the reassortment method, and this has been used for over 50 years. In this method, scientists inject eggs with both one noninfectious flu strain and also one infectious strain. The inert strain must be one that multiples very well in chicken eggs. Scientists pick an infectious strain that carries the desired HA and N receptors that the final product should prevent from infection. They choose these strains by picking the surface HA and NA versions circulating the most in the public, and the ones thought most likely to be prevalent in the upcoming flu season. The two strains—pathogenic and non pathogenic—then multiply and exchange DNA until an inert strain carries eight copies of the infectious strain’s two glycoprotein targets. Finally, of the newly created viruses, scientists pick six versions that multiplied the best in chicken eggs which also carry the necessary HA and NA genes. Ultimately, millions of eggs are injected with those noninfectious strains—which carry the desired proteins—so that the genes can be harvested and used for the vaccine product.
Another method of making the vaccine is by splicing genes from infectious strains and then creating copies in a lab, without the need for the tedious process of chicken egg culture. This method relies on using virus plasmids to excerpt the target genes.
When the antigenicities of the seed strains and wild viruses do not match, vaccines fail to protect the vaccines.
Drugs available for the treatment of influenza include Amantadine
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended because ...
and Rimantadine
Rimantadine (INN, sold under the trade name Flumadine) is an orally administered antiviral drug used to treat, and in rare cases prevent, influenzavirus A infection. When taken within one to two days of developing symptoms, rimantadine can short ...
, which inhibit the uncoating of virions by interfering with M2 proton channel, and Oseltamivir
Oseltamivir, sold under the brand name Tamiflu among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat and prevent influenza A and influenza B, viruses that cause the flu. Many medical organizations recommend it in people who have complicati ...
(marketed under the brand name Tamiflu
Oseltamivir, sold under the brand name Tamiflu among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat and prevent influenza A and influenza B, viruses that cause the flu. Many medical organizations recommend it in people who have complicati ...
), Zanamivir
Zanamivir, sold under the brand name Relenza among others, is an anti-viral medication used to treat and prevent influenza caused by influenza A and influenza B viruses. It is a neuraminidase inhibitor and was developed by the Australian biot ...
, and Peramivir, which inhibit the release of virions from infected cells by interfering with NA. However, escape mutants are often generated for the former drug and less frequently for the latter drug.
See also
*Influenza-like illness
Influenza-like illness (ILI), also known as flu-like syndrome or flu-like symptoms, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms. These include fever, shivering, chills, malaise, dry cough, loss ...
References
Further reading
*External links
Health-EU Portal
EU work to prepare a global response to influenza.
Influenza Research Database
Database of influenza genomic sequences and related information.
EU coordination on Pandemic (H1N1) 2009
3D Influenza-virus-related structures from the EM Data Bank (EMDB)
{{Authority control Virus families